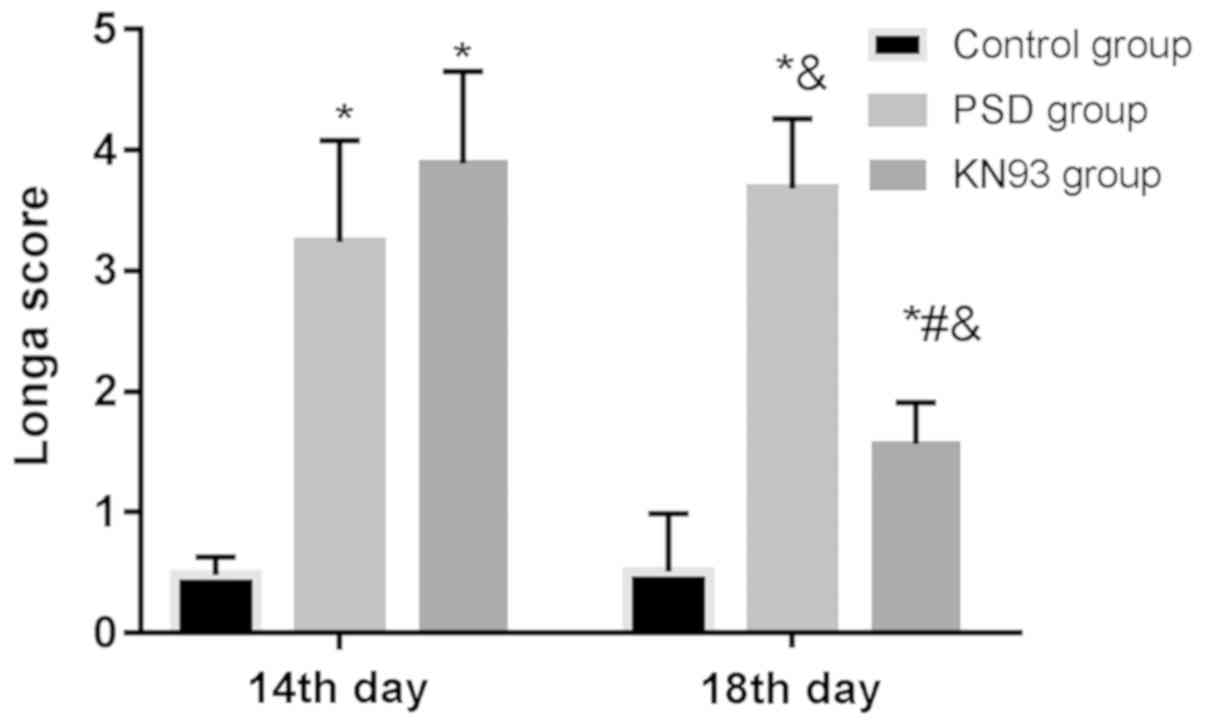
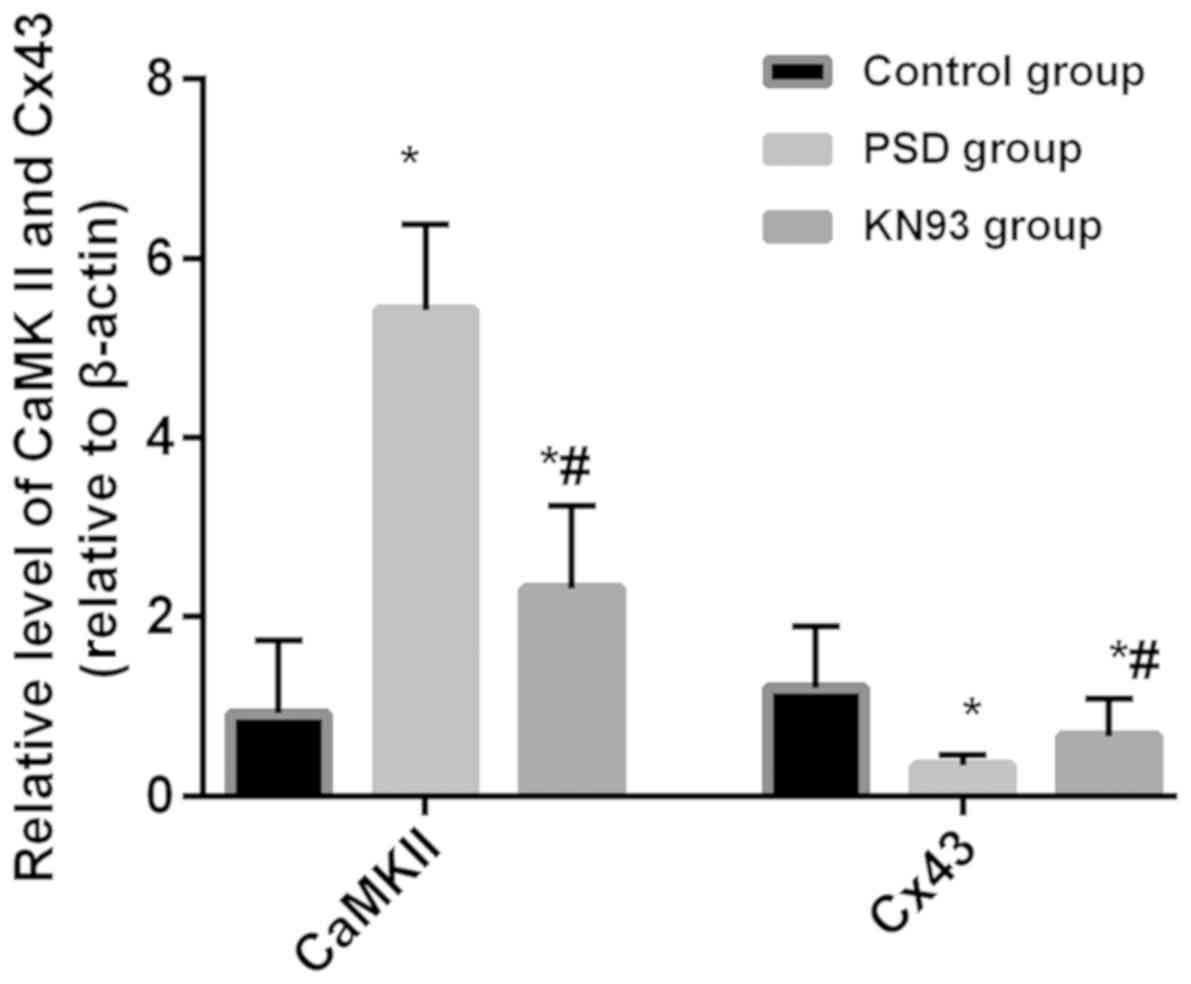
|
1
|
Wei C, Gao J, Chen L, Zhang F, Ma X, Zhang
N, Zhang W, Xue R, Luo L and Hao J: Factors associated with
post-stroke depression and emotional incontinence: Lesion location
and coping styles. Int J Neurosci. 126:623–629. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Valiengo L, Casati R, Bolognini N, Lotufo
PA, Benseñor IM, Goulart AC and Brunoni AR: Transcranial direct
current stimulation for the treatment of post-stroke depression in
aphasic patients: A case series. Neurocase. 22:225–228. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Quaranta D, Marra C and Gainotti G:
Post-stroke depression: Main phenomenological clusters and their
relationships with clinical measures. Behav Neurol. 25:303–310.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shen L, Piao L and Piao H: Clinical
significance of SEP and plasma 5-HT in post stroke depression. J
Apo Nerv Dis. 12:1122–1125. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Andersen G, Vestergaard K,
Ingemann-Nielsen M and Lauritzen L: Risk factors for post-stroke
depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 92:193–198. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cunha MP, Budni J, Pazini FL, Oliveira Á,
Rosa JM, Lopes MW, Leal RB and Rodrigues AL: Involvement of PKA,
PKC, CAMK-II and MEK1/2 in the acute antidepressant-like effect of
creatine in mice. Pharmacol Rep. 66:653–659. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coultrap SJ and Bayer KU: CaMKII
regulation in information processing and storage. Trends Neurosci.
35:607–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Isobe T and Okuyama T: The amino-acid
sequence of S-100 protein (PAP I-b protein) and its relation to the
calcium-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem. 89:379–388. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang X, Chu H, Tang Y and Dong Q: The role
of connexin43 in hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolysis in
vivo and in vitro. Neuroscience. 329:54–65. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Najjar S, Pearlman DM, Mackenzie TA,
Hernandez F Jr and Brown JR: Role of glial activation and BBB
disruption in the pathophysiology of depression. Neurol Psychiatry
Brain Res. 22:17–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Major S, Friedman A and Dreier JP:
Recurrent spreading depression (SD) causes early opening of the
blood-brain barrier (BBB). J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 25 (Suppl
1):S2602005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li X, Rao F, Deng CY, Wei W, Liu FZ, Yang
H, Wang ZY, Kuang SJ, Chen XY, Xue YM, et al: Involvement of ERK1/2
in Cx43 depression induced by macrophage migration inhibitory
factor in atrial myocytes. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 44:771–778.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu Y, Zhang SS, Xiao S, Basheer WA, Baum
R, Epifantseva I, Hong T and Shaw RM: Cx43 isoform GJA1-20k
promotes microtubule dependent mitochondrial transport. Front
Physiol. 8:9052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu X, Balesar R, Lu J, Farajnia S, Zhu Q,
Huang M, Bao AM and Swaab DF: Erratum to: Increased glutamic acid
decarboxylase expression in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic
nucleus in depression. Brain Struct Funct. 222:38632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Overstreet DH: Modeling depression in
animal models. Methods Mol Biol. 829:125–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative geneexpression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
No authors listed, . Correction to:
In-hospital risk prediction for post-stroke depression: Development
and validation of the post-stroke depression prediction scale.
Stroke. 48:e1512017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Swartz RH, Bayley M, Lanctôt KL, Murray
BJ, Cayley ML, Lien K, Sicard MN, Thorpe KE, Dowlatshahi D, Mandzia
JL, et al: Post-stroke depression, obstructive sleep apnea, and
cognitive impairment: Rationale for, and barriers to, routine
screening. Int J Stroke. 11:509–518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li W, Ling S, Yang Y, Hu Z, Davies H and
Fang M: Systematic hypothesis for post-stroke depression caused
inflammation and neurotransmission and resultant on possible
treatments. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 35:104–109. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Freitas-Andrade M, She J, Bechberger J,
Naus CC and Sin WC: Acute connexin43 temporal and spatial
expression in response to ischemic stroke. J Cell Commun Signal.
12:193–204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Z, Fei P, Mu J, Wang H, Li W and
Song J: Decreased expression of neuronal Per-Arnt-Sim domain
protein 4 gene in the hippocampus of a post-stroke depression rat
model. Exp Ther Med. 7:1045–1049. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Zhao M and Sui RB: Cerebellar
fastigial nucleus electrical stimulation alleviates depressive-like
behaviors in post-stroke depression rat model and potential
mechanisms. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1403–1412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu C, Zhang J and Chen Y: Study on the
behavioral changes of a post-stroke depression rat model. Exp Ther
Med. 10:159–163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kozoriz MG, Bechberger JF, Bechberger GR,
Suen MW, Moreno AP, Maass K, Willecke K and Naus CC: The connexin43
C-terminal region mediates neuroprotection during stroke. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 69:196–206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Margrie TW, Rostas JA and Sah P:
Presynaptic long-term depression at a central glutamatergic
synapse: A role for CaMKII. Nat Neurosci. 1:378–383. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feigin VL, Krishnamurthi RV, Parmar P,
Norrving B, Mensah GA, Bennett DA, Barker-Collo S, Moran AE, Sacco
RL, Truelsen T, et al GBD 2013 Writing Group; GBD 2013 stroke panel
experts group, : Update on the global burden of ischemic and
hemorrhagic stroke in 1990–2013: The GBD 2013 Study.
Neuroepidemiology. 45:161–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sacco RL, Adams R, Albers G, Alberts MJ,
Benavente O, Furie K, Goldstein LB, Gorelick P, Halperin J,
Harbaugh R, et al American Heart Association; American Stroke
Association Council on Stroke; Council on Cardiovascular Radiology
and Intervention; American Academy of Neurology, : Guidelines for
prevention of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke or transient
ischemic attack: A statement for healthcare professionals from the
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Council on
Stroke: Co-sponsored by the Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and
Intervention: The American Academy of Neurology affirms the value
of this guideline. Stroke. 37:577–617. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|