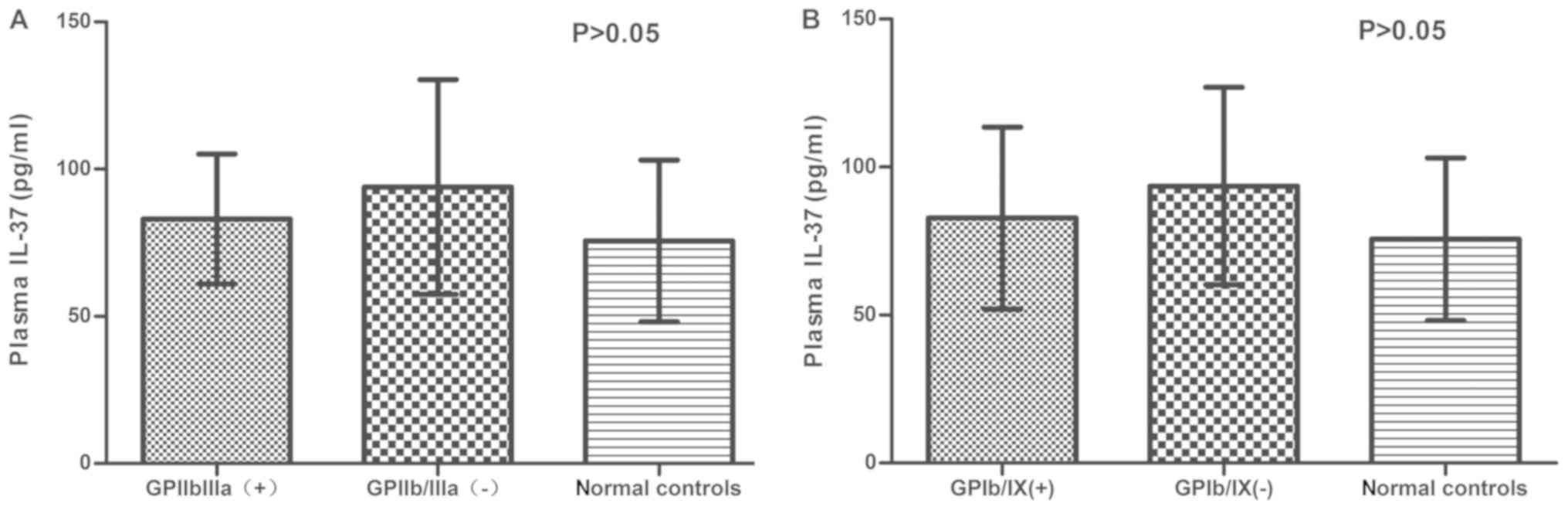
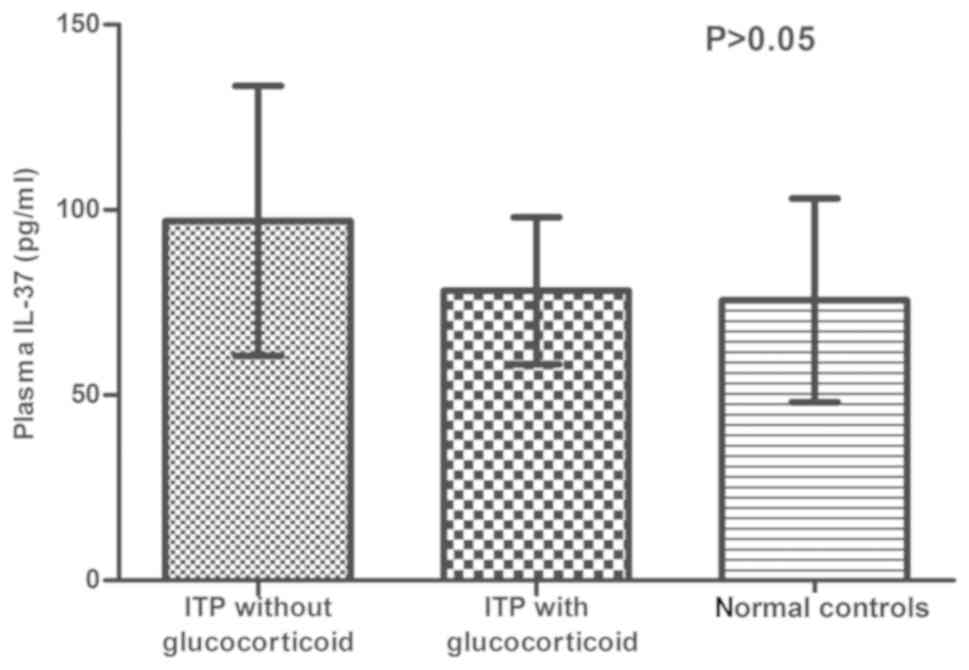
|
1
|
Stasi R, Evangelista ML, Stipa E,
Buccisano F, Venditti A and Amadori S: Idiopathic thrombocytopenic
purpura: Current concepts in pathophysiology and management. Thromb
Haemost. 99:4–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Panitsas FP, Theodoropoulou M, Kouraklis
A, Karakantza M, Theodorou GL, Zoumbos NC, Maniatis A and Mouzaki
A: Adult chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is the
manifestation of a type-1 polarized immune response. Blood.
103:2645–2647. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Ma D, Zhu X, Qu X, Ji C and Hou
M: Elevated profile of Th17, Th1 and Tc1 cells in patients with
immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica. 94:1326–1329. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu B, Zhao H, Poon MC, Han Z, Gu D, Xu M,
Jia H, Yang R and Han ZC: Abnormality of CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T
cell in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol.
78:139–143. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu J, Heck S, Patel V, Levan J, Yu Y,
Bussel JB and Yazdanbakhsh K: Defective circulating CD25 regulatory
T cells in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
Blood. 112:1325–1328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao C, Li X, Zhang F, Wang L, Peng J and
Hou M: Increased cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity
predominant in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
without platelet autoantibodies. Haematologica. 93:1428–1430. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer
BE, Bufler P and Dinarello CA: IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of
innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 11:1014–1022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo Y, Cai X, Liu S, Wang S, Nold-Petry
CA, Nold MF, Bufler P, Norris D, Dinarello CA and Fujita M:
Suppression of antigen-specific adaptive immunity by IL-37 via
induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:15178–15183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dinarallo CA and Bufler P: Interleukin-37.
Semin Immunol. 25:466–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bufler P, Gamboni-Robertson F, Azam T, Kim
SH and Dinarello CA: Interleukin-1 homologues IL-1F7b and IL-18
contain functional mRNA instability elements within the coding
region responsive to lipopolysaccharide. Biochem J. 381:503–510.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao W, Kumar S, Lotze MT, Hanning C,
Robbins PD and Gambotto A: Innate immunity mediated by the cytokine
IL-1 homologue 4 (IL-1H4/IL-1F7) induces IL-12-dependent adaptive
and profound antitumor immunity. J Immunol. 170:107–113. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McNamee EN, Masterson JC, Jedlicka P,
McManus M, Grenz A, Collins CB, Nold MF, Nold-Petry C, Bufler P,
Dinarello CA and Rivera-Nieves J: Interleukin 37 expression
protects mice from colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:16711–16716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sakai N, Van Sweringen HL, Belizaire RM,
Quillin RC, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Burns JM, Tevar AD, Edwards MJ
and Lentsch AB: Interleukin-37 reduces liver inflammatory injury
via effects on hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:1609–1616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ballak DB, van Diepen JA, Moschen AR,
Jansen HJ, Hijmans A, Groenhof GJ, Leenders F, Bufler P,
Boekschoten MV, Müller M, et al: IL-37 protects against
obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Commun.
5:47112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coll-Miro M, Francos-Quijorna I,
Santos-Nogueira E, Torres-Espin A, Bufler P, Dinarello CA and
López-Vales R: Beneficial effects of IL-37 after spinal cord injury
in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:1411–1416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li S, Neff CP, Barber K, Hong J, Luo Y,
Azam T, Palmer BE, Fujita M, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, et al:
Extracellular forms of IL-37 inhibit innate inflammation in vitro
and in vivo but require the IL-1 family decoy receptor IL-1R8. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:2497–2502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lunding L, Webering S, Vock C, Schröder A,
Raedler D, Schaub B, Fehrenbach H and Wegmann M: IL-37 requires
IL-18Rα and SIGIRR/IL-1R8 to diminish allergic airway inflammation
in mice. Allergy. 70:366–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Zhang J, Tao J and Lu T: Elevated
serum levels of Interleukin-37 are associated with inflammatory
cytokines and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. APMIS.
123:1025–1031. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xia L, Shen H and Lu J: Elevated serum and
synovial fluid levels of interleukin-37 in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis: Attenuated the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Cytokine. 76:553–557. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia T, Zheng XF, Qian BH, Fang H, Wang JJ,
Zhang LL, Pang YF, Zhang J, Wei XQ, Xia ZF and Zhao DB: Plasma
interleukin-37 is elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:
Its correlation with disease activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-related
cytokines. Dis Markers. 2015:7950432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao PW, Jiang WG, Wang L, Jiang ZY, Shan
YX and Jiang YF: Plasma levels of IL-37 and correlation with TNF-α,
IL-17A, and disease activity during DMARD treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis. PLoS One. 9:e953462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ye L, Ji L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Hu D, Li Y, Yu
T, Chen B, Zhang J, Ding L, et al: IL-37 inhibits the production of
inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Its correlation with
disease activity. J Transl Med. 12:692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song L, Qiu F, Fan Y, Ding F, Liu H, Shu
Q, Liu W and Li X: Glucocorticoid regulates interleukin-37 in
systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 33:111–117. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Farrokhi M, Rezaei A, Amani-Beni A,
Etemadifar M, Kouchaki E and Zahedi A: Increased serum level of
IL-37 in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica.
Acta Neurol Belg. 115:609–614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Imaeda H, Takahashi K, Fujimoto T, Kasumi
E, Ban H, Bamba S, Sonoda H, Shimizu T, Fujiyama Y and Andoh A:
Epithelial expression of interleukin-37b in inflammatory bowel
disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 172:410–416. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen B, Huang K, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang J,
Zhang J, Fan X, Liu X, Li L, Sun J, et al: Interleukin-37 is
increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with
disease activity. J Transl Med. 13:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Yu T, Chen B, Zhang J, Huang
K and Huang Z: Increased expression of IL-37 in patients with
Graves' disease and its contribution to suppression of
proinflammatory cytokines production in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. PLoS One. 9:e1071832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
British Committee for Standards in
Haematology General Haematology Task Force, . Guidelines for the
investigation and management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
in adults, children and in pregnancy. Br J Haematol. 120:574–596.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou M, Peng J, Shi Y, Zhang C, Qin P, Zhao
C, Ji X, Wang X and Zhang M: Mycophenolatemofetil (MMF) for the
treatment of steroid-resistant idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Eur J Haematol. 70:353–357. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu WD, Zhao Y and Liu Y: Insights into
IL-37, the role in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev.
14:1170–1175. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bouali E, Kaabachi W, Hamzaoui A and
Hamzaoui K: Interleukin-37 expression is decreased in Behçet's
disease and is associated with inflammation. Immunol Lett.
167:87–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Charrad R, Berraïes A, Hamdi B, Ammar J,
Hamzaoui K and Hamzaoui A: Anti-inflammatory activity of IL-37 in
asthmatic children: Correlation with inflammatory cytokines TNF-α,
IL-β, IL-6 and IL-17A. Immunobiology. 221:182–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ye Z, Wang C, Tang J, Zhou Y, Bai L, Liu
Y, Kijlstra A and Yang P: Decreased interleukin-37 expression in
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease and upregulation following
immunosuppressive treatment. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 35:265–272.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu W, Deng L, Chen Y, Sun C, Wang J, Zhou
L, Li H and Luo R: Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-37b in children
with allergic rhinitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:7468462014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sharma S, Kulk N, Nold MF, Gräf R, Kim SH,
Reinhardt D, Dinarello CA and Bufler P: The IL-1 family member 7b
translocates to the nucleus and down-regulates proinflammatory
cytokines. J Immunol. 180:5477–5482. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|