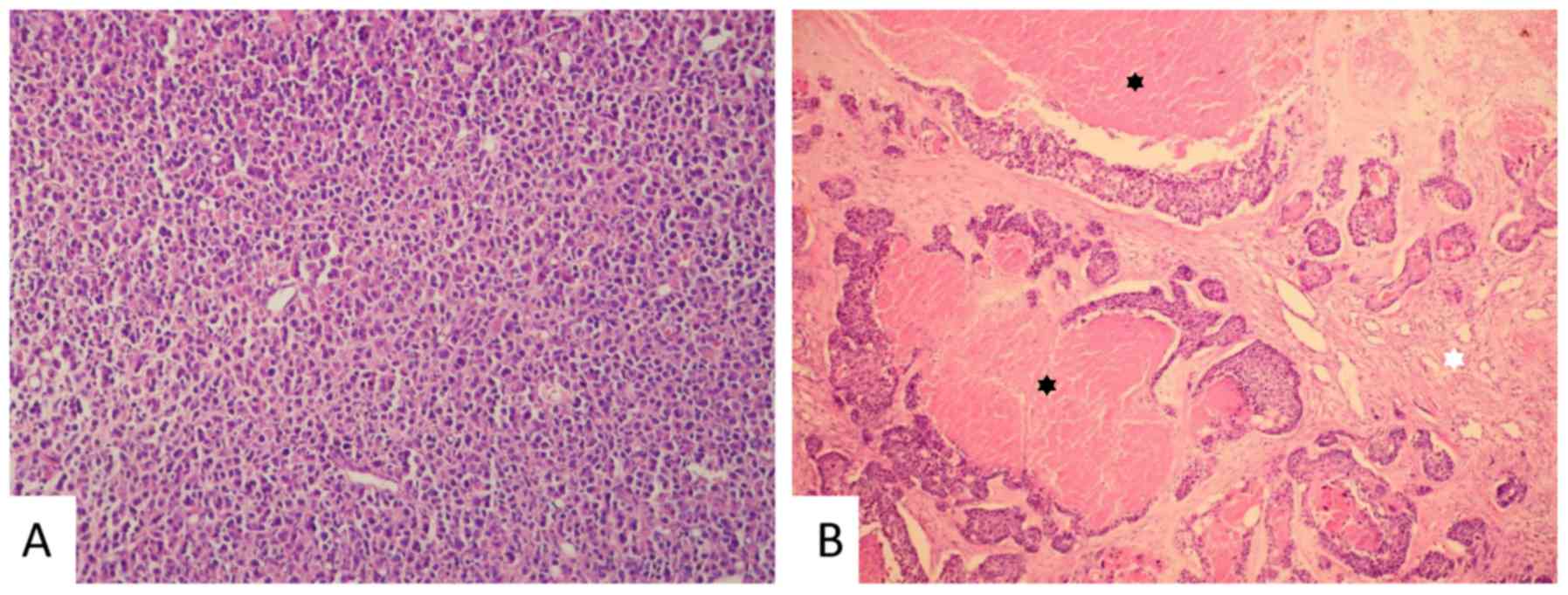
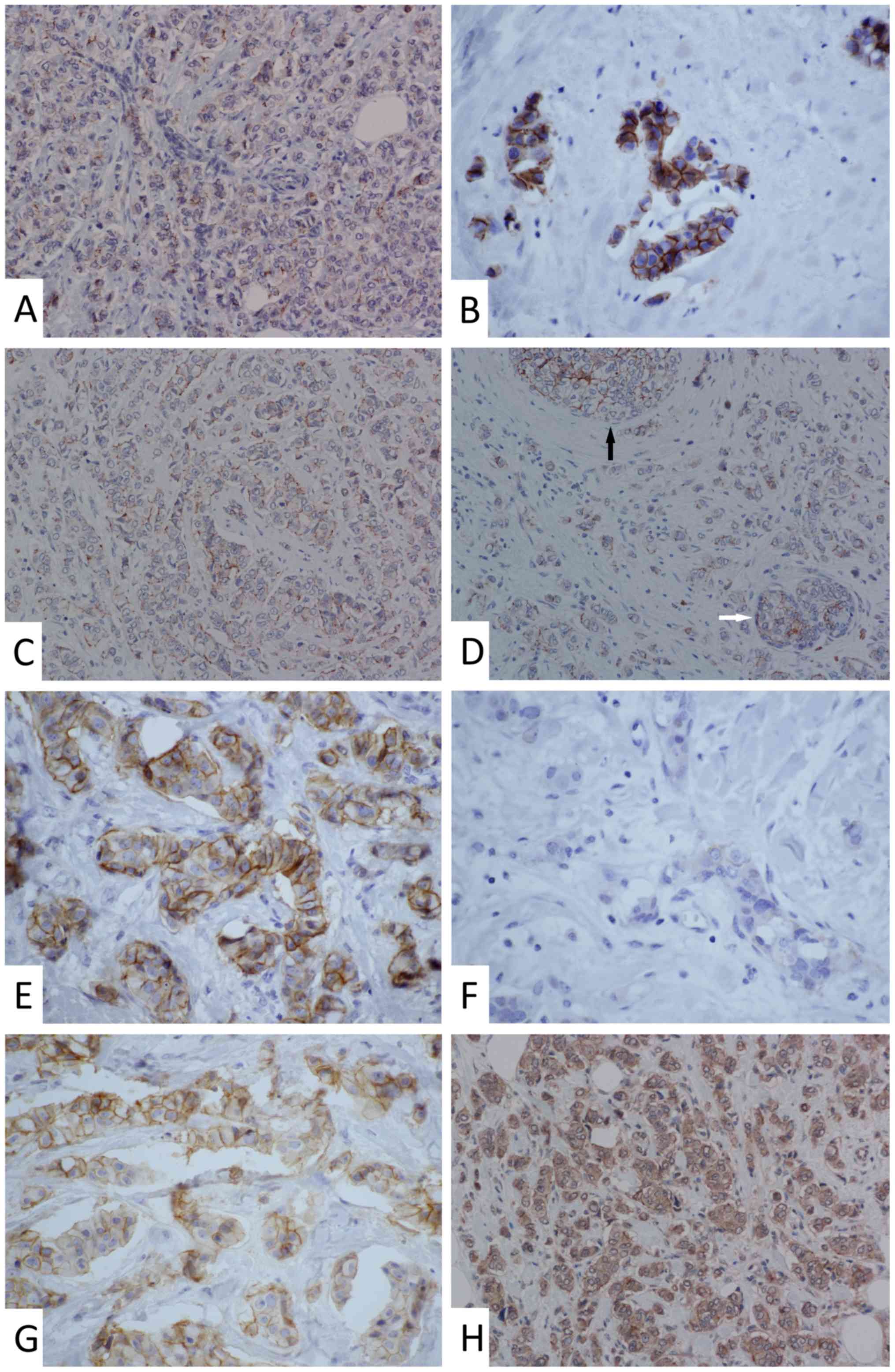
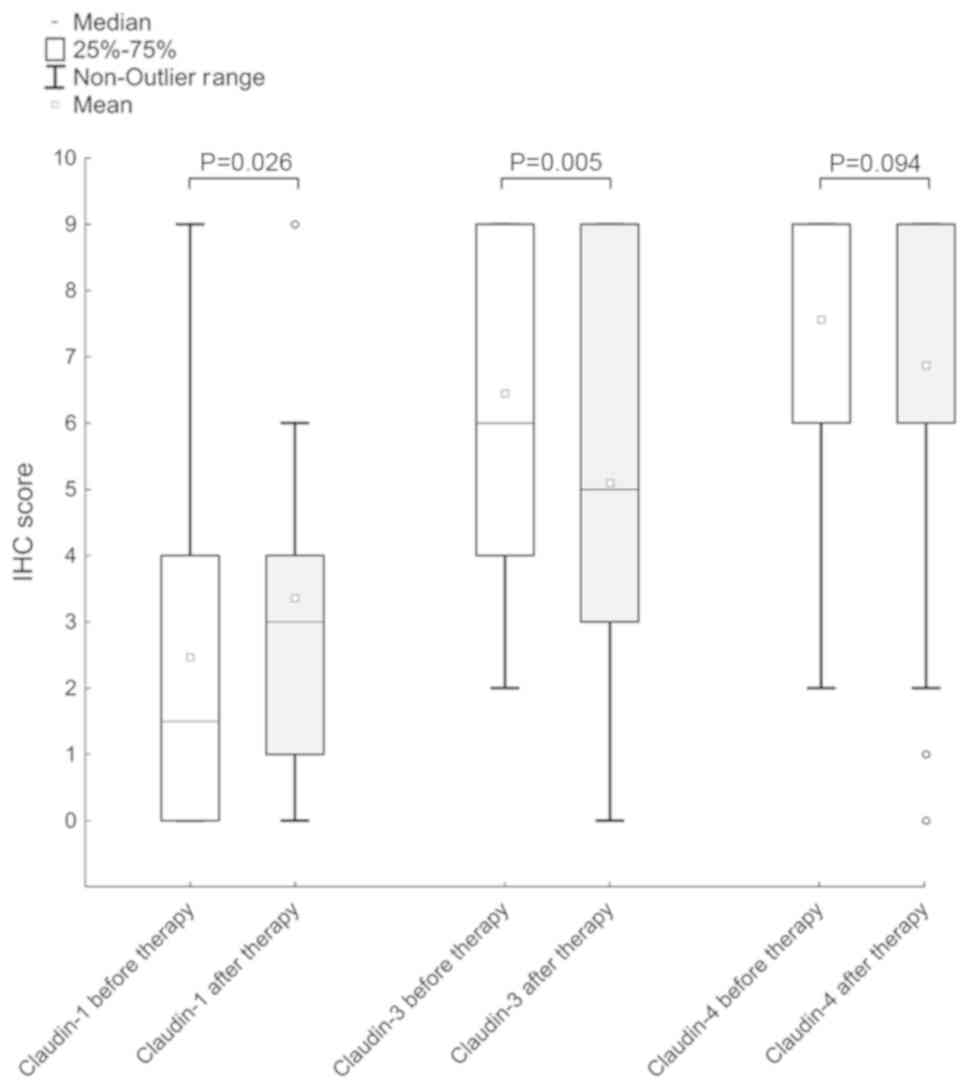
|
1
|
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH
and van de Vijver MJ: WHO classification of tumours of the
breastFourth. IARC; Lyon: 2012
|
|
2
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumour subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Myal Y, Leygue E and Blanchard AA: Claudin
1 in breast tumorigenesis: Revelation of a possible novel ‘claudin
high’ subset of breast cancers. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:9568972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ellis IO, Carder P, Hales S, Lee A, Pinder
S, Rakha E and Stephenson T: Pathology reporting of breast disease
in surgical excision speciemens incorporating tha dataset for
histological reporting of breast cancer. Royal College of
Pathologists. 2016.
|
|
7
|
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka
H, Tada Y, Saito K, Tamura A, Igarashi M, Endo T, Takeuchi K and
Tsukita S: Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family.
FEBS Lett. 585:606–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kulka J and Tökés AM: Claudin expression
in breast tumours. Hum Pathol. 36:859–860. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding L, Lu Z, Lu Q and Chen YH: The
claudin family of proteins in human malignancy: A clinical
perspective. Cancer Manag Res. 5:367–375. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turksen K and Troy TC: Junctions gone bad:
Claudins and loss of the barrier in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1816:73–79. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh AB, Sharma A and Dhawan P: Claudin
family of proteins and cancer: An overview. J Oncol.
2010:5419572010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwon MJ: Emerging roles of claudins in
human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:18148–18180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herschkowitz JI, Simin K, Weigman VJ,
Mikaelian I, Usary J, Hu Z, Rasmussen KE, Jones LP, Assefnia S,
Chandrasekharan S, et al: Identification of conserved gene
expression features between murine mammary carcinoma models and
human breast tumors. Genome Biol. 8:R762007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Buchholz TA, Hunt KK, Whitman GJ, Sahin AA
and Hortobagyi GN: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast carcinoma:
Multidisciplinary considerations of benefits and risks. Cancer.
98:1150–1160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prat A and Perou CM: Deconstructing the
molecular portraits of breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 5:5–23. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saeki R, Kondoh M, Kakutani H, Tsunoda S,
Mochizuki Y, Hamakubo T, Tsutsumi Y, Horiguchi Y and Yagi K: A
novel tumour-targeted therapy using a claudin-4-targeting molecule.
Mol Pharmacol. 76:918–926. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Walther W, Petkov S, Kuvardina ON, Aumann
J, Kobelt D, Fichtner I, Lemm M, Piontek J, Blasig IE, Stein U and
Schlag PM: Novel Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin suicide gene
therapy for selective treatment of claudin-3- and −4-overexpressing
tumors. Gene Ther. 19:494–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morin PJ: Claudin proteins in human
cancer: Promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer
Res. 65:9603–9606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh AB and Dhawan P: Claudins and
cancer: Fall of the soldiers entrusted to protect the gate and keep
the barrier intact. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 42:58–65. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Osanai M, Takasawa A, Murata M and Sawada
N: Claudins in cancer: Bench to bedside. Pflugers Arch. 469:55–67.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin X, Shang X, Manorek G and Howell SB:
Regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by claudin-3
and claudin-4. PLoS One. 8:e674962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF, Norton L
and Aaronson SA: Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast
cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J
Cell Biol. 148:779–790. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nieman MT, Prudoff RS, Johnson KR and
Wheelock MJ: N-cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer
cells regardless of their E-cadherin expression. J Cell Biol.
147:631–644. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rai H and Ahmed J: N-cadherin: A marker of
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumour progression.
Internet J Oncol. 10:1–8. 2014.
|
|
26
|
Zhou B, Moodie A, Blanchard AA, Leygue E
and Myal Y: Claudin 1 in breast cancer: New insights. J Clin Med.
4:1960–1976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baccelli I and Trumpp A: The evolving
concept of cancer and metastasis stem cells. J Cell Biol.
198:281–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chevallier B, Roche H, Olivier JP, Chollet
P and Hurteloup P: Inflammatory breast cancer. Pilot study of
intensive induction chemotherapy (FEC-HD) results in a high
histologic response rate. Am J Clin Oncol. 16:223–228. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lechpammer M, Resnick MB, Sabo E,
Yakirevich E, Greaves WO, Sciandra KT, Tavares R, Noble LC,
DeLellis RA and Wang LJ: The diagnostic and prognostic utility of
claudin expression in renal cell neoplasms. Mod Pathol.
21:1320–1329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu S, Singh K, Mangray S, Tavares R, Noble
L, Resnick MB and Yakirevich E: Claudin expression in high-grade
invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: Correlation with the
molecular subtype. Mod Pathol. 26:485–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dias K, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Hallett RM, Wu Y,
Hassell J, Pond GR, Levine M, Whelan T and Bane AL: Claudin-low
breast cancer; Clinical & pathological characteristics. PLoS
One. 12:e01686692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gerhard R, Ricardo S, Albergaria A, Gomes
M, Silva AR, Logullo ÂF, Cameselle-Teijeiro JF, Paredes J and
Schmitt F: Immunohistochemical features of claudin-low intrinsic
subtype in metaplastic breast carcinomas. Breast. 21:354–360. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kowalski PJ, Rubin MA and Kleer CG:
E-cadherin expression in primary carcinomas of the breast and its
distant metastases. Breast Cancer Res. 5:R217–R222. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dewis R and Gribbin J: Breast cancer:
Diagnosis and treatment: An assessment of needNational
Collaborating Centre for Cancer (UK); Cardiff, UK: 2009
|
|
35
|
Ordóñez NG: Value of claudin-4
immunostaining in the diagnosis of mesothelioma. Am J Clin Pathol.
139:611–619. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szabó I, Kiss A, Schaff Z and Sobel G:
Claudins as diagnostic and prognostic markers in gynecological
cancer. Histol Histopathol. 24:1607–1615. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Worsley CM, Mayne ES and Veale RB: Clone
war: The evolution of therapeutic resistance in cancer. Evol Med
Public Health. 2016:180–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun D, Dalin S, Hemann MT, Lauffenburger
DA and Zhao B: Differential selective pressure alters rate of drug
resistance acquisition in heterogeneous tumor populations. Sci Rep.
6:361982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Asogan AB, Hong GS and Arni Prabhakaran
SK: Concordance between core needle biopsy and surgical specimen
for oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 status in breast cancer. Singapore Med J.
58:145–149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dekker TJ, Smit VT, Hooijer GK, Van de
Vijver MJ, Mesker WE, Tollenaar RA, Nortier JW and Kroep JR:
Reliability of core needle biopsy for determining ER and HER2
status in breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 24:931–937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
You K, Park S, Ryu JM, Kim I, Lee SK, Yu
J, Kim SW, Nam SJ and Lee JE: Comparison of core needle biopsy and
surgical specimens in determining intrinsic biological subtypes of
breast cancer with immunohistochemistry. J Breast Cancer.
20:297–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kinsella MD, Nassar A, Siddiqui MT and
Cohen C: Estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and
HER2 expression pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy in primary
breast carcinoma: A single institutional experience. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 5:530–536. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yin HF, Wang YH, Qin XQ, Zhang H, Li T, Ye
JM and Liu YH: Effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on histologic
grade and expression of biological markers in breast cancer.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 31:858–862. 2009.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
van de Ven S, Smit VT, Dekker TJ, Nortier
JW and Kroep JR: Discordances in ER, PR and HER2 receptors after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev.
37:422–430. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoshida A, Hayashi N, Suzuki K, Takimoto
M, Nakamura S and Yamauchi H: Change in HER2 status after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy and the prognostic impact in patients with
primary breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 116:1021–1028. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li P, Liu T, Wang Y, Shao S, Zhang W, Lv
Y, Yi J and Wang Z: Influence of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on
HER2/neu status in invasive breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer.
13:53–60. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cabrera-Galeana P, Muñoz-Montaño W,
Lara-Medina F, Alvarado-Miranda A, Pérez-Sánchez V,
Villarreal-Garza C, Quintero RM, Porras-Reyes F, Bargallo-Rocha E,
Del Carmen I, et al: Ki67 Changes identify worse outcomes in
residual breast cancer tumors after neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Oncologist. 23:670–678. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Moazed V, Jafari E, Kalantari Khandani B,
Nemati A, Roozdar A and Ben Razavi SA: Prognostic significance of
reduction in Ki67 index after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients
with breast cancer in kerman between 2009 And 2014. Iran J Pathol.
13:71–77. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dede DS, Gumuskaya B, Guler G, Onat D,
Altundag K and Ozisik Y: Evaluation of changes in biologic markers
ER, PR, HER 2 and Ki-67 index in breast cancer with administration
of neoadjuvant dose dense doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide followed by
paclitaxel chemotherapy. J BUON. 18:366–371. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee HC, Ko H, Seol H, Noh DY, Han W, Kim
TY, Im SA and Park IA: Expression of immunohistochemical markers
before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast carcinoma, and
their use as predictors of response. J Breast Cancer. 16:395–403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou X, Zhang J, Yun H, Shi R, Wang Y,
Wang W, Lagercrantz SB and Mu K: Alterations of biomarker profiles
after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: Tumor
heterogeneity should be taken into consideration. Oncotarget.
6:36894–36902. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yoshioka T, Hosoda M, Yamamoto M, Taguchi
K, Hatanaka KC, Takakuwa E, Hatanaka Y, Matsuno Y and Yamashita H:
Prognostic significance of pathologic complete response and Ki67
expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer. 22:185–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Adams AL, Eltoum I, Krontiras H, Wang W
and Chhieng DC: The effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on
histologic grade, hormone receptor status, and HER2/neu status in
breast carcinoma. Breast J. 14:141–146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey
BE, McShane LM and Dowsett M: HER2 testing in breast cancer:
American society of clinical oncology/college of American
pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update summary. J
Oncol Pract. 14:437–441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Davila E and Amazon K: The clinical
importance of the heterogeneity of HER2 neu. Case Rep Oncol.
3:268–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Deane NG, No Y, Shiou
SR, Schmidt C, Neff J, Washington MK and Beauchamp RD: Claudin-1
regulates cellular transformation and metastatic behavior in colon
cancer. J Clin Invest. 115:1765–1776. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Fortier AM, Asselin E and Cadrin M:
Keratin 8 and 18 loss in epithelial cancer cells increases
collective cell migration and cisplatin sensitivity through
claudin1 up-regulation. J Biol Chem. 288:11555–11571. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Li M, Balch C, Montgomery JS, Jeong M,
Chung JH, Yan P, Huang TH, Kim S and Nephew KP: Integrated analysis
of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals specific signaling
pathways associated with platinum resistance in ovarian cancer. BMC
Med Genomics. 2:342009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Blanchard AA, Ma X, Dueck KJ, Penner C,
Cooper SC, Mulhall D, Murphy LC, Leygue E and Myal Y: Claudin 1
expression in basal-like breast cancer is related to patient age.
BMC Cancer. 13:2682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Blanchard AA, Skliris GP, Watson PH,
Murphy LC, Penner C, Tomes L, Young TL, Leygue E and Myal Y:
Claudins 1, 3, and 4 protein expression in ER negative breast
cancer correlates with markers of the basal phenotype. Virchows
Arch. 454:647–656. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Qian X, Anzovino A, Kim S, Suyama K, Yao
J, Hulit J, Agiostratidou G, Chandiramani N, McDaid HM, Nagi C, et
al: N-cadherin/FGFR promotes metastasis through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem/progenitor cell-like
properties. Oncogene. 33:3411–3421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
ElMoneim HM and Zaghloul NM: Expression of
E-cadherin, N-cadherin and snail and their correlation with
clinicopathological variants: An immunohistochemical study of 132
invasive ductal breast carcinomas in Egypt. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
66:1765–1771. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shang X, Lin X, Manorek G and Howell SB:
Claudin-3 and claudin-4 regulate sensitivity to cisplatin by
controlling expression of the copper and cisplatin influx
transporter CTR1. Mol Pharmacol. 83:85–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Kulka J, Szász AM, Németh Z, Madaras L,
Schaff Z, Molnár IA and Tokés AM: Expression of tight junction
protein claudin-4 in basal-like breast carcinomas. Pathol Oncol
Res. 15:59–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Soini Y: Claudins 2, 3, 4, and 5 in
Paget's disease and breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 35:1531–1536.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sabatier R, Finetti P, Guille A, Adelaide
J, Chaffanet M, Viens P, Birnbaum D and Bertucci F: Claudin-low
breast cancers: Clinical, pathological, molecular and prognostic
characterization. Mol Cancer. 13:2282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Singhai R, Patil VW, Jaiswal SR, Patil SD,
Tayade MB and Patil AV: E-Cadherin as a diagnostic biomarker in
breast cancer. N Am J Med Sci. 3:227–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang W, Wang L, Mizokami A, Shi J, Zou C,
Dai J, Keller ET, Lu Y and Zhang J: Down-regulation of E-cadherin
enhances prostate cancer chemoresistance via Notch signaling. Chin
J Cancer. 36:352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Nakamura T, Kato Y, Fuji H, Horiuchi T,
Chiba Y and Tanaka K: E-cadherin-dependent intercellular adhesion
enhances chemoresistance. Int J Mol Med. 12:693–700.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|