|
1
|
Boehncke WH and Schön MP: Psoriasis.
Lancet. 386:983–994. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dowlatshahi EA, van der Voort EAM, Arends
LR and Nijsten T: Markers of systemic inflammation in psoriasis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 169:266–282.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parisi R, Symmons DPM, Griffiths CEM and
Ashcroft DM; Identification and Management of Psoriasis and
Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team, : Global epidemiology
of psoriasis: A systematic review of incidence and prevalence. J
Invest Dermatol. 133:377–385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cohen AD, Dreiher J, Shapiro Y, Vidavsky
L, Vardy DA, Davidovici B and Meyerovitch J: Psoriasis and
diabetes: A population-based cross-sectional study. J Eur Acad
Dermatol Venereol. 22:585–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armstrong AW, Harskamp CT and Armstrong
EJ: The association between psoriasis and obesity: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr Diabetes.
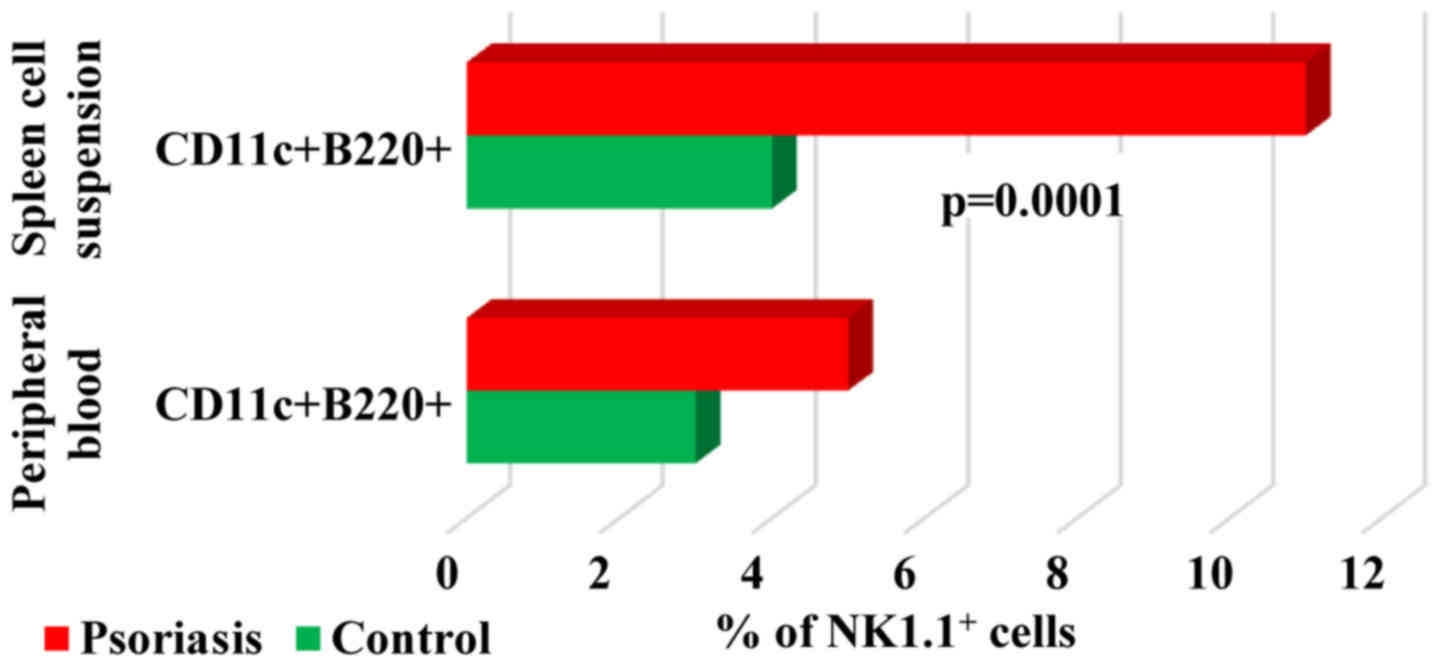
2:e542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shah K, Mellars L, Changolkar A and
Feldman SR: Real-world burden of comorbidities in US patients with
psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 77:287–292.e4. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kölliker Frers RA, Bisoendial RJ, Montoya
SF, Kerzkerg E, Castilla R, Tak PP, Milei J and Capani F: Psoriasis
and cardiovascular risk: Immune-mediated crosstalk between
metabolic, vascular and autoimmune inflammation. IJC Metab Endocr.
6:43–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Møller AH, Erntoft S, Vinding GR and Jemec
GB: A systematic literature review to compare quality of life in
psoriasis with other chronic diseases using EQ-5D-derived utility
values. Patient Relat Outcome Meas. 6:167–177. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Caruntu C, Boda D, Dumitrascu G,
Constantin C and Neagu M: Proteomics focusing on immune markers in
psoriatic arthritis. Biomarkers Med. 9:513–528. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wolf P, Weger W, Patra V,
Gruber-Wackernagel A and Byrne SN: Desired response to phototherapy
vs photoaggravation in psoriasis: What makes the difference? Exp
Dermatol. 25:937–944. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dalkilic E, Bulbul Baskan E, Alkis N,
Gullulu M, Yavuz M, Dilek K, Ersoy A and Yurtkuran M: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy-induced psoriasis in
Turkey: Analysis of 514 patients. Mod Rheumatol. 22:738–742. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tatu AL and Nwabudike LC:
Metoprolol-associated onset of psoriatic arthropathy. Am J Ther.
24:e370–e371. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moriwaki Y, Takada K, Tsuji S, Kawashima K
and Misawa H: Transcriptional regulation of SLURP2, a
psoriasis-associated gene, is under control of IL-22 in the skin: A
special reference to the nested gene LYNX1. Int Immunopharmacol.
29:71–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wheatley R, Brooks J, Stumpf B and Boh E:
Obesity, diet, and inflammation in psoriasis. J Psoriasis Psoriatic
Arthritis. 2:97–101. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Farkas A and Kemény L: Alcohol, liver,
systemic inflammation and skin: A focus on patients with psoriasis.
Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 26:119–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fry L and Baker BS: Triggering psoriasis:
The role of infections and medications. Clin Dermatol. 25:606–615.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeng J, Luo S, Huang Y and Lu Q: Critical
role of environmental factors in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J
Dermatol. 44:863–872. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mrowietz U and Reich K: Psoriasis - new
insights into pathogenesis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int.
106:11–18, quiz 19. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carrascosa JM, Jacobs I, Petersel D and
Strohal R: Biosimilar drugs for psoriasis: Principles, present, and
near future. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 8:173–194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Niculet E, Neculia GV, Tatu AL and Buzia
OD: Curcumin-extraction, physical and chemical analysis, formulas
and control. basic methods for further research. Mater Plast.
55:672–675. 2018.
|
|
21
|
Nwabudike LC and Tatu AL: Using
complementary and alternative medicine for the treatment of
psoriasis. A step in the right direction. JAMA Dermatol. Mar
13–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karczewski J, Dobrowolska A,
Rychlewska-Hańczewska A and Adamski Z: New insights into the role
of T cells in pathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Autoimmunity. 49:435–450. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Surcel M, Huica R, Constantin C, Ursaciuc
C and Neagu M: Biomarkers insights in psoriasis - Regulatory
cytokines. Curr Biomark. 7:3–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mahil SK, Capon F and Barker JN: Update on
psoriasis immunopathogenesis and targeted immunotherapy. Semin
Immunopathol. 38:11–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caligiuri MA: Human natural killer cells.
Blood. 112:461–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dunphy SE, Sweeney CM, Kelly G, Tobin AM,
Kirby B and Gardiner CM: Natural killer cells from psoriasis
vulgaris patients have reduced levels of cytotoxicity associated
degranulation and cytokine production. Clin Immunol. 177:43–49.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
von Bubnoff D, Andrès E, Hentges F, Bieber
T, Michel T and Zimmer J: Natural killer cells in atopic and
autoimmune diseases of the skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125:60–68.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takahashi H, Amagai M, Tanikawa A, Suzuki
S, Ikeda Y, Nishikawa T, Kawakami Y and Kuwana M: T helper type
2-biased natural killer cell phenotype in patients with pemphigus
vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 127:324–330. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zakka LR, Fradkov E, Keskin DB, Tabansky
I, Stern JNH and Ahmed AR: The role of natural killer cells in
autoimmune blistering diseases. Autoimmunity. 45:44–54. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bocheńska K, Smolińska E, Moskot M,
Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka J and Gabig-Cimińska M: Models in the research
process of psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E25142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Banerjee S and Kaunelis D: Imiquimod for
the treatment of genital warts: A review of clinical effectiveness
and cost-effectivenessCADTH Rapid Response Report: Summary with
critical appraisal. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in
Health; Ottawa, ON: 2017
|
|
32
|
Bhatta AK, Wang P, Keyal U, Zhao Z, Ji J,
Zhu L, Wang X and Zhang G: Therapeutic effect of Imiquimod enhanced
ALA-PDT on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Photodiagnosis
Photodyn Ther. 23:273–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Banerjee S and Kaunelis D: Imiquimod for
the treatment of actinic keratosis: A review of clinical
effectiveness and cost-effectivenessCADTH Rapid Response Report:
Summary with critical appraisal. Canadian Agency for Drugs and
Technologies in Health; Ottawa, ON: 2017
|
|
34
|
Surcel M, Huică R-I, Munteanu AN, Isvoranu
G, Pîrvu IR, Ciotaru D, Constantin C, Bratu O, Căruntu C, Neagu M,
et al: Phenotypic changes of lymphocyte populations in psoriasiform
dermatitis animal model. Exp Ther Med. 17:1030–1038.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals8th.
National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
36
|
van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JSA,
Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, Cornelissen F, Mus AM, Florencia E, Prens
EP, et al: Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in
mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol.
182:5836–5845. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Blasius AL, Barchet W, Cella M and Colonna
M: Development and function of murine B220+CD11c+NK1.1+ cells
identify them as a subset of NK cells. J Exp Med. 204:2561–2568.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Isvoranu G, Surcel M, Huică R-I, Munteanu
AN, Pîrvu IR, Ciotaru D, Constantin C, Bratu O, Neagu M and
Ursaciuc C: Natural killer cell monitoring in cutaneous melanoma -
new dynamic biomarker. Oncol Lett. 17:4197–4206. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abel AM, Yang C, Thakar MS and Malarkannan
S: Natural killer cells: Development, maturation, and clinical
utilization. Front Immunol. 9:18692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huntington ND, Tabarias H, Fairfax K,
Brady J, Hayakawa Y, Degli-Esposti MA, Smyth MJ, Tarlinton DM and
Nutt SL: NK cell maturation and peripheral homeostasis is
associated with KLRG1 up-regulation. J Immunol. 178:4764–4770.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim J, Lee J, Gonzalez J, Fuentes-Duculan
J, Garcet S and Krueger JG: Proportion of CD4+CD49b+LAG-3+ Type 1
regulatory T cells in the blood of psoriasis patients inversely
correlates with psoriasis area and severity index. J Invest
Dermatol. 138:2669–2672. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chiossone L, Chaix J, Fuseri N, Roth C,
Vivier E and Walzer T: Maturation of mouse NK cells is a 4-stage
developmental program. Blood. 113:5488–5496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hadad U, Thauland TJ, Martinez OM, Butte
MJ, Porgador A and Krams SM: NKp46 clusters at the immune synapse
and regulates NK cell polarization. Front Immunol. 6:4952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pessino A, Sivori S, Bottino C, Malaspina
A, Morelli L, Moretta L, Biassoni R and Moretta A: Molecular
cloning of NKp46: A novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily
involved in triggering of natural cytotoxicity. J Exp Med.
188:953–960. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dunphy S and Gardiner CM: NK cells and
psoriasis. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:2483172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang LL, Chu DT, Dokun AO and Yokoyama WM:
Inducible expression of the gp49B inhibitory receptor on NK cells.
J Immunol. 164:5215–5220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nandi D, Gross JA and Allison JP:
CD28-mediated costimulation is necessary for optimal proliferation
of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 152:3361–3369. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Georgescu SR, Tampa M, Caruntu C, Sarbu
MI, Mitran CI, Mitran MI, Matei C, Constantin C and Neagu M:
Advances in understanding the immunological pathways in psoriasis.
Int J Mol Sci. 20:E7392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Solberg SM, Sandvik LF, Eidsheim M,
Jonsson R, Bryceson YT and Appel S: Serum cytokine measurements and
biological therapy of psoriasis - Prospects for personalized
treatment? Scand J Immunol. 88:e127252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guarene M, Pasi A, Bolcato V, Cananzi R,
Piccolo A, Sbarsi I, Klersy C, Cacciatore R and Brazzelli V: The
presence of HLA-A Bw4-80I KIR ligands could predict
‘Difficult-to-Treat’ psoriasis and poor response to Etanercept. Mol
Diagn Ther. 22:471–474. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Batani A, Brănișteanu DE, Ilie MA, Boda D,
Ianosi S, Ianosi G and Caruntu C: Assessment of dermal papillary
and microvascular parameters in psoriasis vulgaris using in
vivo reflectance confocal microscopy. Exp Ther Med.
15:1241–1246. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Căruntu C, Boda D, Căruntu A, Rotaru M,
Baderca F and Zurac S: In vivo imaging techniques for psoriatic
lesions. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 55 (Suppl):1191–1196.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Negrei C, Căruntu C, Ginghină O, Burcea
Dragomiroiu GTA, Toderescu CD and Boda D: Qualitative and
quantitative determination of methotrexate polyglutamates in
erythrocytes by high performance liquid chromatography. Rev Chim
Buchar. 66:607–610. 2015.
|