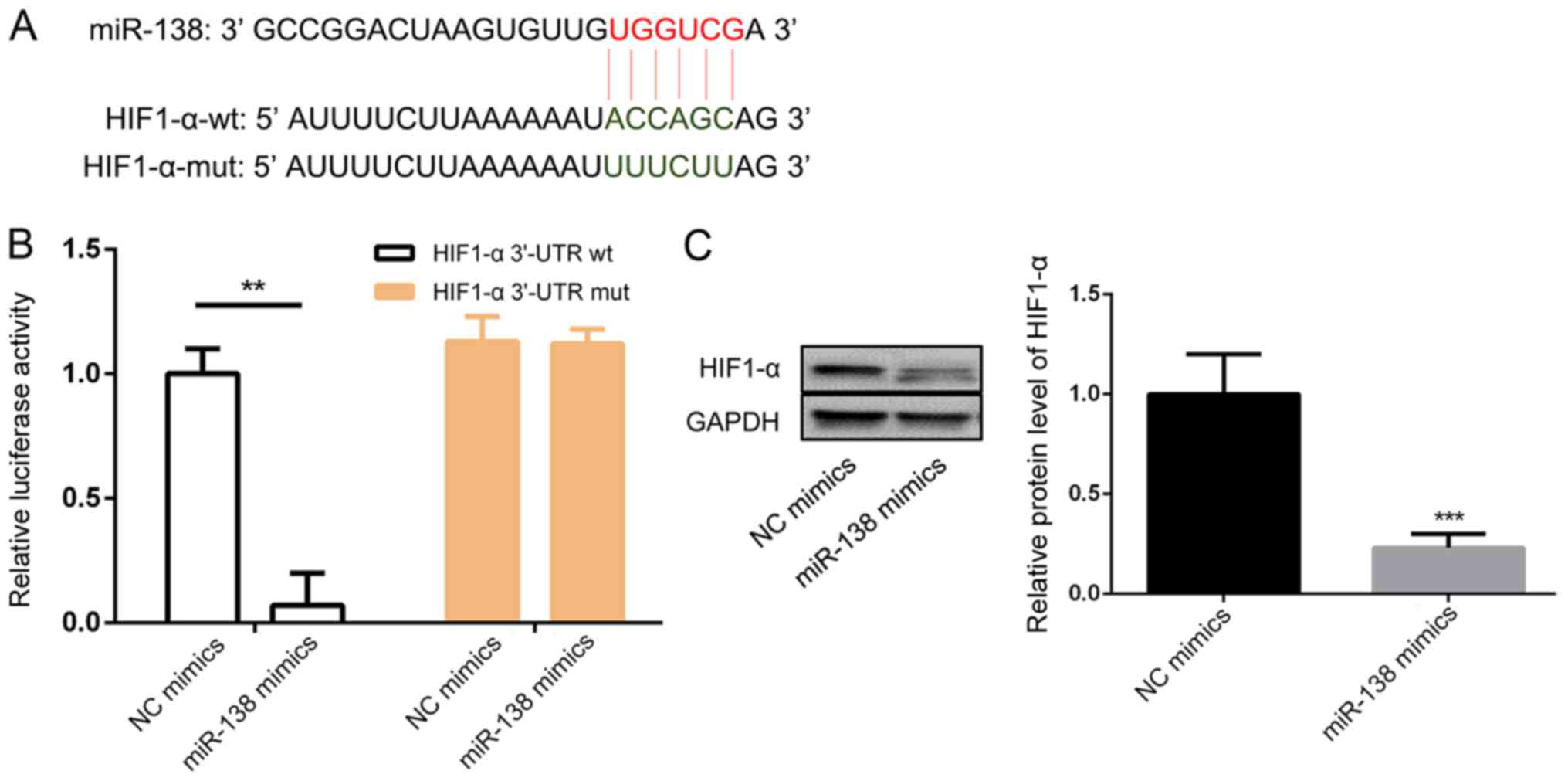
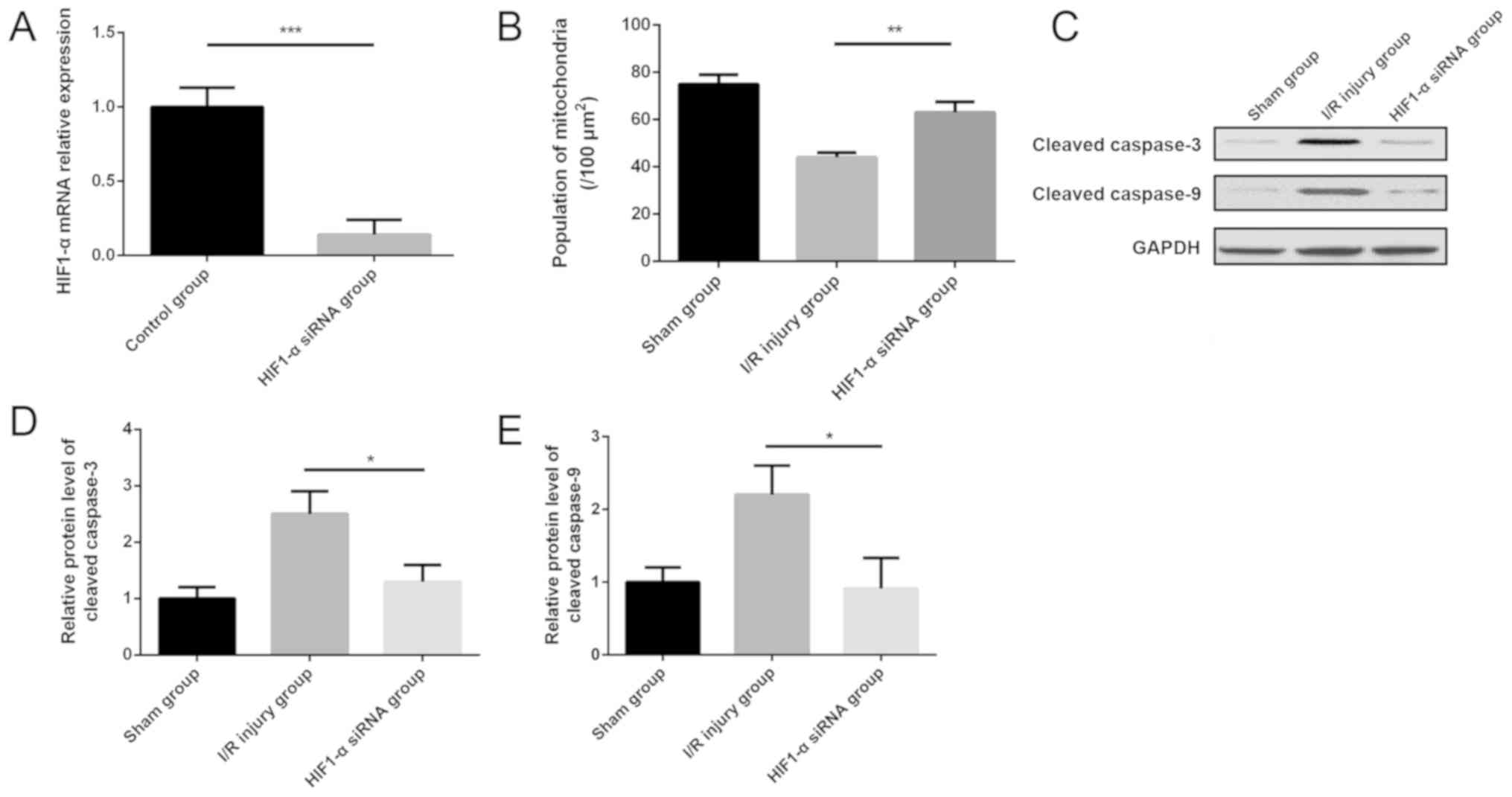
|
1
|
Nichols M, Townsend N, Scarborough P and
Rayner M: Cardiovascular disease in europe 2014: Epidemiological
update. Eur Heart J. 35:2950–2959. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cuevas P, Carceller F and Gimenez-Gallego
G: Fibroblast growth factors in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury and ischemic preconditioning. J Cell Mol Med. 5:132–142.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Song CL, Liu B, Wang JP, Zhang BL, Zhang
JC, Zhao LY, Shi YF, Li YX, Wang G, Diao HY, et al: Anti-apoptotic
effect of microRNA-30b in early phase of rat myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury model. J Cell Biochem. 116:2610–2619.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jennings RB and Reimer KA: The cell
biology of acute myocardial ischemia. Annu Rev Med. 42:225–246.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mu F, Duan J, Bian H, Yin Y, Zhu Y, Wei G,
Guan Y, Wang Y, Guo C, Wen A, et al: Cardioprotective effects and
mechanism of radix salviae miltiorrhizae and lignum dalbergiae
odoriferae on rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med
Rep. 16:1759–1770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. New Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prompunt E, Sanit J, Barrere-Lemaire S,
Nargeot J, Noordali H, Madhani M and Kumphune S: The
cardioprotective effects of secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor
against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med.
15:5231–5242. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Liu M, Sun R, Zeng Y, Chen S and
Zhang P: Protective approaches against myocardial ischemia
reperfusion injury. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 12. Exp
Ther Med. 12:3823–3829. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi Z, Zhou H, Lu L, Li X, Fu Z, Liu J,
Kang Y, Wei Z, Pan B, Liu L, et al: The roles of microRNAs in
spinal cord injury. Int J Neurosci. 127:1104–1115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen C, Zhou Y, Wang J, Yan Y, Peng L and
Qiu W: Dysregulated microRNA involvement in multiple sclerosis by
induction of T helper 17 cell differentiation. Front Immunol.
9:12562018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Chen L, Yang J, Ding J, Li S, Wu
H, Zhang J, Fan Z, Dong W and Li X: MicroRNA-22 targeting CBP
protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through
anti-apoptosis in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 41:555–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang SB, Liu TJ, Pu GH, Li BY, Gao XZ and
Han XL: MicroRNA-374 exerts protective effects by inhibiting SP1
through activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat models of myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion after sevoflurane preconditioning. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 46:1455–1470. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu ZD, Ye JY, Niu H, Ma YM, Fu XM, Xia ZH
and Zhang X: Effects of microRNA-292-5p on myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury through the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha/-gamma signaling pathway.
Gene Ther. 25:234–248. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang LH, Li J, Gu JP, Qu MX, Yu J and
Wang ZY: Butorphanol attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury through inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mice.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1819–1824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu Y, Leng Y, Meng Q, Xue R, Zhao B, Zhan
L and Xia Z: Suppression of excessive histone deacetylases activity
in diabetic hearts attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury via mitochondria apoptosis pathway. J Diabetes Res.
2017:82080652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Yue X, Wu H, Huang
S, Chen J, Tomsky K, Xie H, Khella CA, et al: Parkin targets
HIF-1alpha for ubiquitination and degradation to inhibit breast
tumor progression. Nat Commun. 8:18232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Semenza GL, Shimoda LA and Prabhakar NR:
Regulation of gene expression by HIF-1. Novartis Found Symp.
272:2–8. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Semenza GL, Jiang BH, Leung SW, Passantino
R, Concordet JP, Maire P and Giallongo A: Hypoxia response elements
in the aldolase A, enolase 1, and lactate dehydrogenase A gene
promoters contain essential binding sites for hypoxia-inducible
factor 1. J Biol Chem. 271:32529–32537. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JX and Stinnett A: Ang-1 gene therapy
inhibits hypoxia- inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha)-prolyl-4-hydroxylase-2, stabilizes HIF-1alpha
expression, and normalizes immature vasculature in db/db mice.
Diabetes. 57:3335–3343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xue W, Cai L, Tan Y, Thistlethwaite P,
Kang YJ, Li X and Feng W: Cardiac-specific overexpression of
HIF-1{alpha} prevents deterioration of glycolytic pathway and
cardiac remodeling in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Am J
Pathol. 177:97–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, Doeller
JE, Kraus DW, Tao L, Jiao X, Scalia R, Kiss L, Szabo C, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15560–15565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gupta S and Knowlton AA: HSP60, Bax,
apoptosis and the heart. J Cell Mol Med. 9:51–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frank S, Gaume B, Bergmann-Leitner ES,
Leitner WW, Robert EG, Catez F, Smith CL and Youle RJ: The role of
dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in
apoptosis. Dev Cell. 1:515–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Perrelli MG, Pagliaro P and Penna C:
Ischemia/reperfusion injury and cardioprotective mechanisms: Role
of mitochondria and reactive oxygen species. World J Cardiol.
3:186–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang W, Li Y and Wang P: Long non-coding
RNA-ROR aggravates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 51:e65552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Arora M, Kaul D and Sharma YP: Human
coronary heart disease: Importance of blood cellular miR-2909
RNomics. Mol Cell Biochem. 392:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Venardos KM, Zatta AJ, Marshall T, Ritchie
R and Kaye DM: Reduced L-arginine transport contributes to the
pathogenesis of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cell
Biochem. 108:156–168. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheng J, Wu Q, Lv R, Huang L, Xu B, Wang
X, Chen A and He F: MicroRNA-449a inhibition protects H9C2 cells
against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury by targeting the
notch-1 signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:2587–2600.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Konstantinidis K, Whelan RS and Kitsis RN:
Mechanisms of cell death in heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1552–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Geng YJ: Molecular mechanisms for
cardiovascular stem cell apoptosis and growth in the hearts with
atherosclerotic coronary disease and ischemic heart failure. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 1010:687–697. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Basheer WA, Fu Y, Shimura D, Xiao S,
Agvanian S, Hernandez DM, Hitzeman TC, Hong T and Shaw RM: Stress
response protein GJA1-20k promotes mitochondrial biogenesis,
metabolic quiescence, and cardioprotection against
ischemia/reperfusion injury. JCI Insight. 3:2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kadenbach B, Ramzan R, Moosdorf R and Vogt
S: The role of mitochondrial membrane potential in ischemic heart
failure. Mitochondrion. 11:700–706. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Solaini G, Sgarbi G, Lenaz G and Baracca
A: Evaluating mitochondrial membrane potential in cells. Biosci
Rep. 27:11–21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Muzaffar S and Chattoo BB:
Apoptosis-inducing factor (Aif1) mediates anacardic acid-induced
apoptosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Apoptosis. 22:463–474. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang X, Chen J, Graham SH, Du L, Kochanek
PM, Draviam R, Guo F, Nathaniel PD, Szabó C, Watkins SC and Clark
RS: Intranuclear localization of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)
and large scale DNA fragmentation after traumatic brain injury in
rats and in neuronal cultures exposed to peroxynitrite. J
Neurochem. 82:181–191. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL,
Cho SK, Li CY, Sasaki T, Elia AJ, Cheng HY, Ravagnan L, et al:
Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in
programmed cell death. Nature. 410:549–554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|