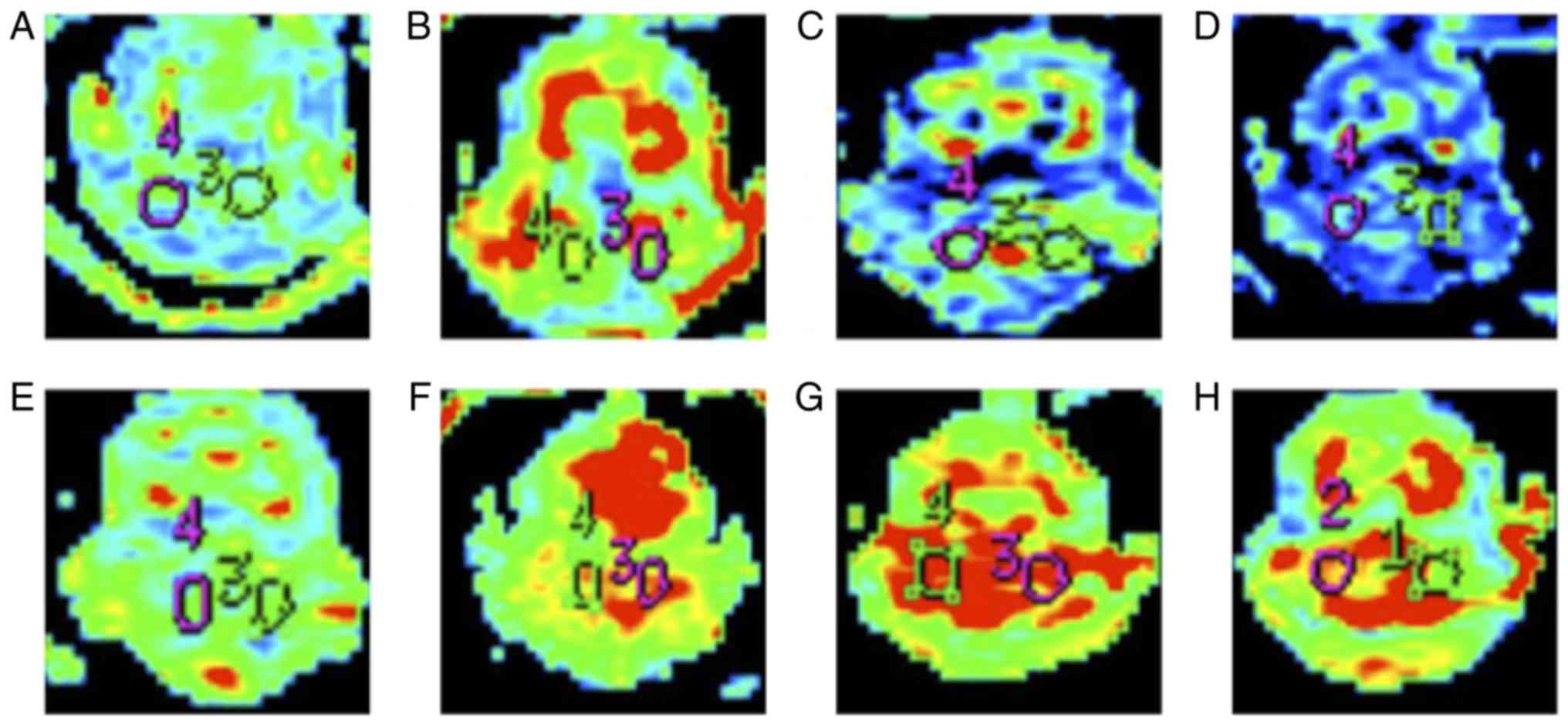
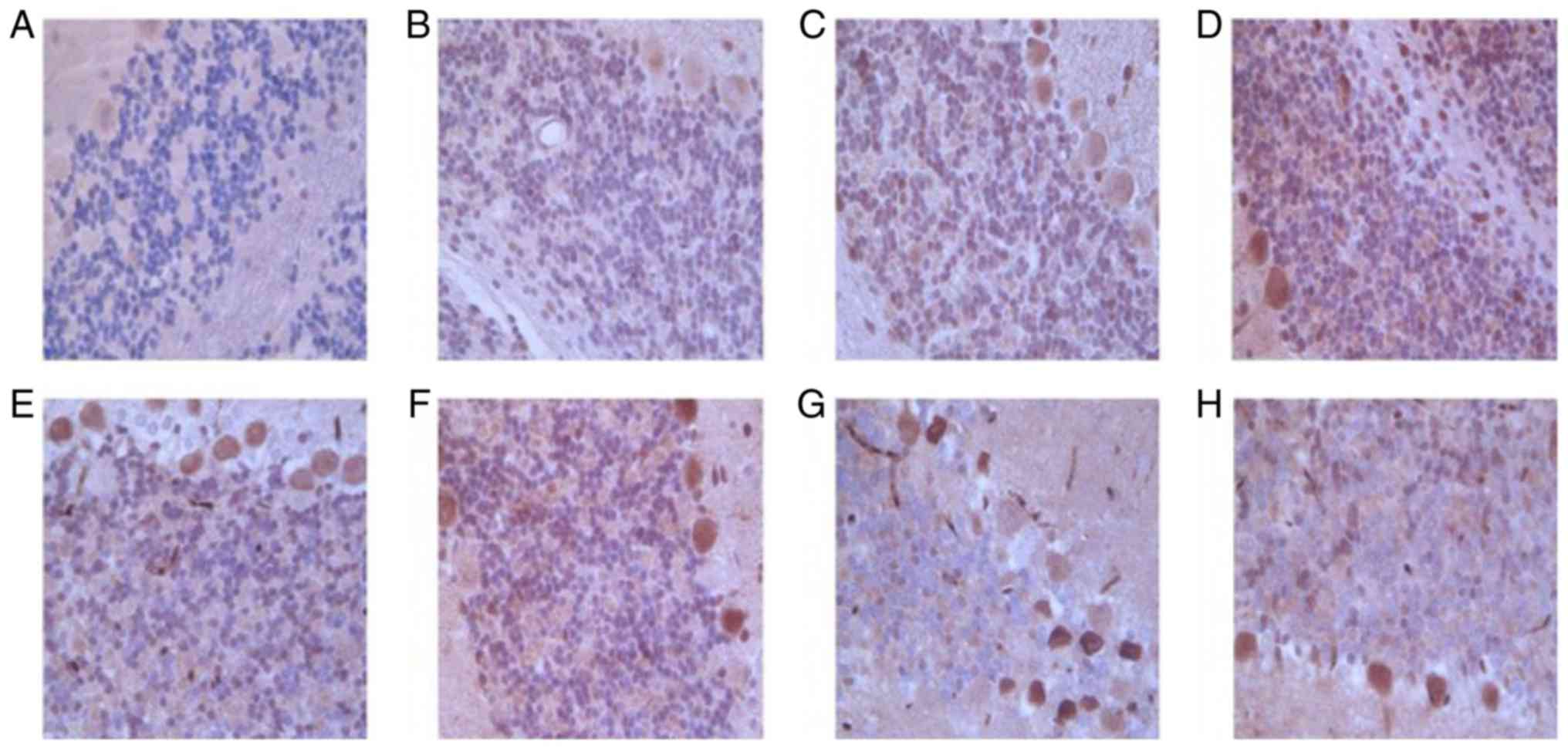
|
1
|
Mendis S: Stroke disability and
rehabilitation of stroke: World Health Organization perspective.
Int J Stroke. 8:3–4. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Savitz SI and Caplan LR: Vertebrobasilar
disease. N Engl J Med. 352:2618–2626. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gupta R, Joshi S, Mittal A, Luthra I,
Mittal P and Verma V: Magnetic resonance imaging depiction of
acquired Dyke-Davidoff-Masson syndrome with crossed
cerebro-cerebellar diaschisis: Report of two cases. J Pediatr
Neurosci. 10:294–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang KM, Sohn CH, Kim BS, Kim YI, Choi SH,
Yun TJ, Kim JH, Park SW, Cheon GJ and Han MH: Correlation of
asymmetry indices measured by arterial Spin-Labeling MR Imaging and
SPECT in patients with crossed cerebellar diaschisis. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 36:1662–1668. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Komaba Y, Mishina M, Utsumi K, Katayama Y,
Kobayashi S and Mori O: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in patients
with cortical infarction: Logistic regression analysis to control
for confounding effects. Stroke. 35:472–476. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim J, Lee SK, Lee JD, Kim YW and Kim DI:
Decreased fractional anisotropy of middle cerebellar peduncle in
crossed cerebellar diaschisis: Diffusion-tensor
imaging-positron-emission tomography correlation study. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 26:2224–2228. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dani KA, Santosh C, Brennan D, Hadley DM
and Muir KW: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: Insights into oxygen
challenge MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 32:2114–2117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baron JC, Bousser MG, Comar D and
Castaigne P: ‘Crossed cerebellar diaschisis’ in human
supratentorial brain infarction. Trans Am Neurol Assoc.
105:459–461. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patay Z, Parra C, Hawk H, George A, Li Y,
Scoggins M, Broniscer A and Ogg RJ: Quantitative longitudinal
evaluation of diaschisis-related cerebellar perfusion and diffusion
parameters in patients with supratentorial hemispheric high-grade
gliomas after surgery. Cerebellum. 13:580–587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takasawa M, Hashikawa K, Ohtsuki T,
Imaizumi M, Oku N, Kitagawa K, Hori M and Matsumoto M: Transient
crossed cerebellar diaschisis following thalamic hemorrhage. J
Neuroimaging. 11:438–440. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Strother MK, Buckingham C, Faraco CC,
Arteaga DF, Lu P, Xu Y and Donahue MJ: Crossed cerebellar
diaschisis after stroke identified noninvasively with cerebral
blood flow-weighted arterial spin labeling MRI. Eur J Radiol.
85:136–142. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y, Karonen JO, Nuutinen J, Vanninen E,
Kuikka JT and Vanninen RL: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute
ischemic stroke: A study with serial SPECT and MRI. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 27:1724–1732. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peled S and Yeshurun Y: Superresolution in
MRI: Application to human white matter fiber tract visualization by
diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med. 45:29–35. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoon B, Kim JS, Lee KS, Kim BS, Chung SR
and Kim YI: Early pathological changes in the cerebellum of
patients with pure cerebellar syndrome demonstrated by
diffusion-tensor imaging. Eur Neurol. 56:166–171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hata K, Fujitani M, Yasuda Y, Doya H,
Saito T, Yamagishi S, Mueller BK and Yamashita T: RGMa inhibition
promotes axonal growth and recovery after spinal cord injury. J
Cell Biol. 173:47–58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsunaga E, Nakamura H and Chédotal A:
Repulsive guidance molecule plays multiple roles in neuronal
differentiation and axon guidance. J Neurosci. 26:6082–6088. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schwab JM, Conrad S, Monnier PP, Julien S,
Mueller BK and Schluesener HJ: Spinal cord injury-induced lesional
expression of the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM). Eur J
Neurosci. 21:1569–1576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Key B and Lah GJ: Repulsive guidance
molecule A (RGMa) A molecule for all seasons. Cell Adh Migr.
6:85–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Severyn CJ, Shinde U and Rotwein P:
Molecular biology, genetics and biochemistry of the repulsive
guidance molecule family. Biochem J. 422:393–403. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Cheng JL, Ran YC, Zhang Y, Yang L
and Lin YN: Expression of RGMb in brain tissue of MCAO rats and its
relationship with axonal regeneration. J Neurol Sci. 383:79–86.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Zhang R, Xing X, Guo J, Xie F,
Zhang G and Qin X: Repulsive guidance molecule asuppresses
angiogenesis after ischemia/reperfusion injury of middle cerebral
artery occlusion in rats. Neurosci Lett. 662:318–323. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng G, Chen X, Xu B, Zhang J, Lv X, Li
J, Li F, Hu S, Zhang T and Li Y: Plasticity of language pathways in
patients with low-grade glioma: A diffusion tensor imaging study.
Neural Regen Res. 8:647–654. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kwon YH, Jang SH and Yeo SS: Age-related
changes of lateral ventricular width and periventricular white
matter in the human brain: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Neural
Regen Res. 9:986–989. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng X, Wang Q, Hou J, Zhang X, Wang E, Li
Q, Zeng Q, Wang Q, Li C and Ma X: Diffusion tensor imaging of
normal-appearing white matter in unilateral cerebral arterial
occlusive disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 38:650–654. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Wan S and Zhang X:
Geniculocalcarine tract disintegration after ischemic stroke: A
diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
34:1890–1894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA,
Pappata S, Molko N and Chabriat H: Diffusion tensor imaging:
Concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging. 13:534–546. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao J, Chang W and Liu Y: Clinical
application of diffusion tensor imaging in acute stroke. Clin Med
China. 30:1166–1168. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Erbetta A, Mandelli M, Savoiardo M,
Grisoli M, Bizzi A, Soliveri P, Chiapparini L, Prioni S, Bruzzone
MG and Girotti F: Diffusion tensor imaging shows different
topographic involvement of the thalamus in progressive supranuclear
palsy and corticobasal degeneration. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
30:1482–1487. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karampinos DC, Van AT, Olivero WC,
Georgiadis JG and Sutton BP: High-resolution diffusion tensor
imaging of the human pons with a reduced field-of-view, multishot,
variable-density, spiral acquisition at 3 T. Magn Reson Med.
62:1007–1016. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lao Y, Kang Y, Collignon O, Brun C,
Kheibai SB, Alary F, Gee J, Nelson MD, Lepore F and Lepore N: A
study of brain white matter plasticity in early blinds using
tract-based spatial statistics and tract statistical analysis.
Neuroreport. 26:1151–1154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brillault J, Lam TI, Rutkowsky JM,
Foroutan S and O'Donnell ME: Hypoxia effects on cell volume and ion
uptake of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 294:C88–C96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang GY, Chen SF, Kinouchi H, Chan PH and
Weinstein PR: Edema, cation content, and ATPase activity after
middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke. 23:1331–1336.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sorensen AG, Wu O, Copen WA, Davis TL,
Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ, Reese TG, Rosen BR, Wedeen VJ and
Weisskoff RM: Human acute cerebral ischemia: Detection of changes
in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging. Radiology.
212:785–792. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Foong J, Maier M, Clark CA, Barker GJ,
Miller DH and Ron MA: Neuropathological abnormalities of the corpus
callosum in schizophrenia: A diffusion tensor imaging study. J
Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 68:242–244. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ito H, Takahashi K, Hatazawa J, Kim SG and
Kanno I: Changes in human regional cerebral blood flow and cerebral
blood volume during visual stimulation measured by positron
emission tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 21:608–612. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Devor A, Ulbert I, Dunn AK, Narayanan SN,
Jones SR, Andermann ML, Boas DA and Dale AM: Coupling of the
cortical hemodynamic response to cortical and thalamic neuronal
activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:3822–3827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ishihara M, Kumita S, Mizumura S and
Kumazaki T: Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: The role of motor and
premotor areas in functional connections. J Neuroimaging. 9:30–33.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jeon YW, Kim SH, Lee JY, Whang K, Kim MS,
Kim YJ and Lee MS: Dynamic CT perfusion imaging for the detection
of crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute ischemic stroke. Korean J
Radiol. 13:12–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SE and Lee MC: Cerebellar
vasoreactivity in stroke patients with crossed cerebellar
diaschisis assessRed by acetazolamide and 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT. J Nucl
Med. 41:416–420. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Matsunaga E, Tauszig-Delamasure S, Monnier
PP, Mueller BK, Strittmatter SM, Mehlen P and Chédotal A: RGM and
its receptor neogenin regulate neuronal survival. Nat Cell Biol.
6:749–755. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tian C and Liu J: Repulsive guidance
molecules (RGMs) and neogenin in bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)
signaling. Mol Reprod Dev. 80:700–717. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang T, Wu X, Yin C, Klebe D, Zhang JH and
Qin X: CRMP-2 is involved in axon growth inhibition induced by RGMa
in vitro and in vivo. Mol Neurobiol. 47:903–913. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brinks H, Conrad S, Vogt J, Oldecamp J,
Sierra A, Deitinghoff L, Bechmann I, Alvarez-Bolado G, Heimrich B,
Monnier PP, et al: The repulsive guidance molecule RGMa is involved
in the formation of afferent connections in the dentate gyrus. J
Neurosci. 24:3862–3869. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Metzger M, Conrad S, Skutella T and Just
L: RGMa inhibits neurite outgrowth of neuronal progenitors from
murine enteric nervous system via the neogenin receptor in vitro. J
Neurochem. 103:2665–2678. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tassew NG, Charish J, Seidah NG and
Monnier PP: SKI-1 and Furin generate multiple RGMa fragments that
regulate axonal growth. Dev Cell. 22:391–402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tao T, Xu G, Si Chen C, Feng J, Kong Y and
Qin X: Minocycline promotes axonal regeneration through suppression
of RGMa in rat MCAO/reperfusion model. Synapse. 67:189–198. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Feng J, Wang T, Li Q, Wu X and Qin X: RNA
interference against repulsive guidance molecule A improves axon
sprout and neural function recovery of rats after MCAO/reperfusion.
Exp Neurol. 238:235–242. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nimsky C, Ganslandt O, Hastreiter P, Wang
R, Benner T, Sorensen AG and Fahlbusch R: Intraoperative
diffusion-tensor MR imaging: Shifting of white matter tracts during
neurosurgical procedures-initial experience. Radiology.
234:218–225. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|