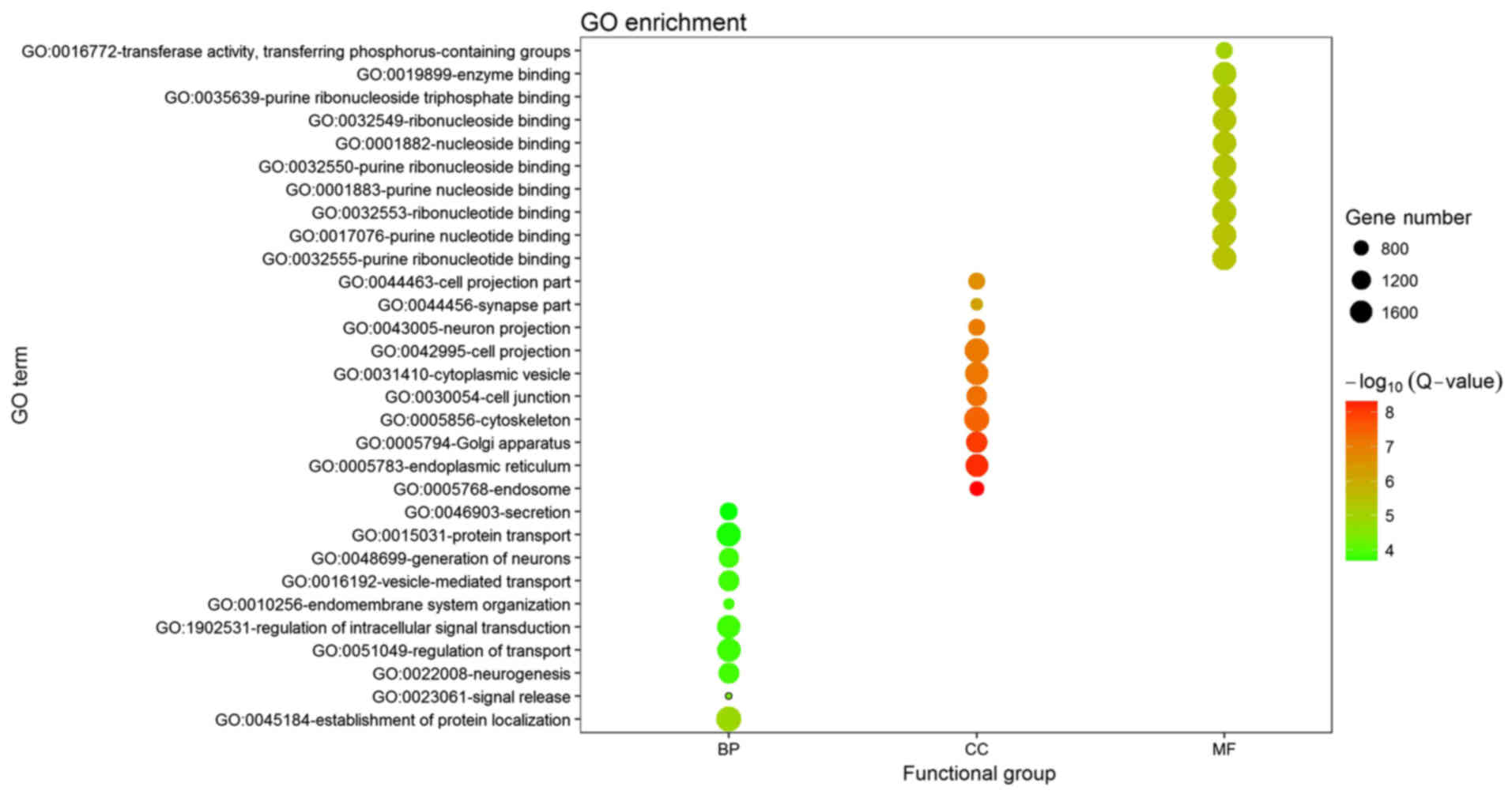
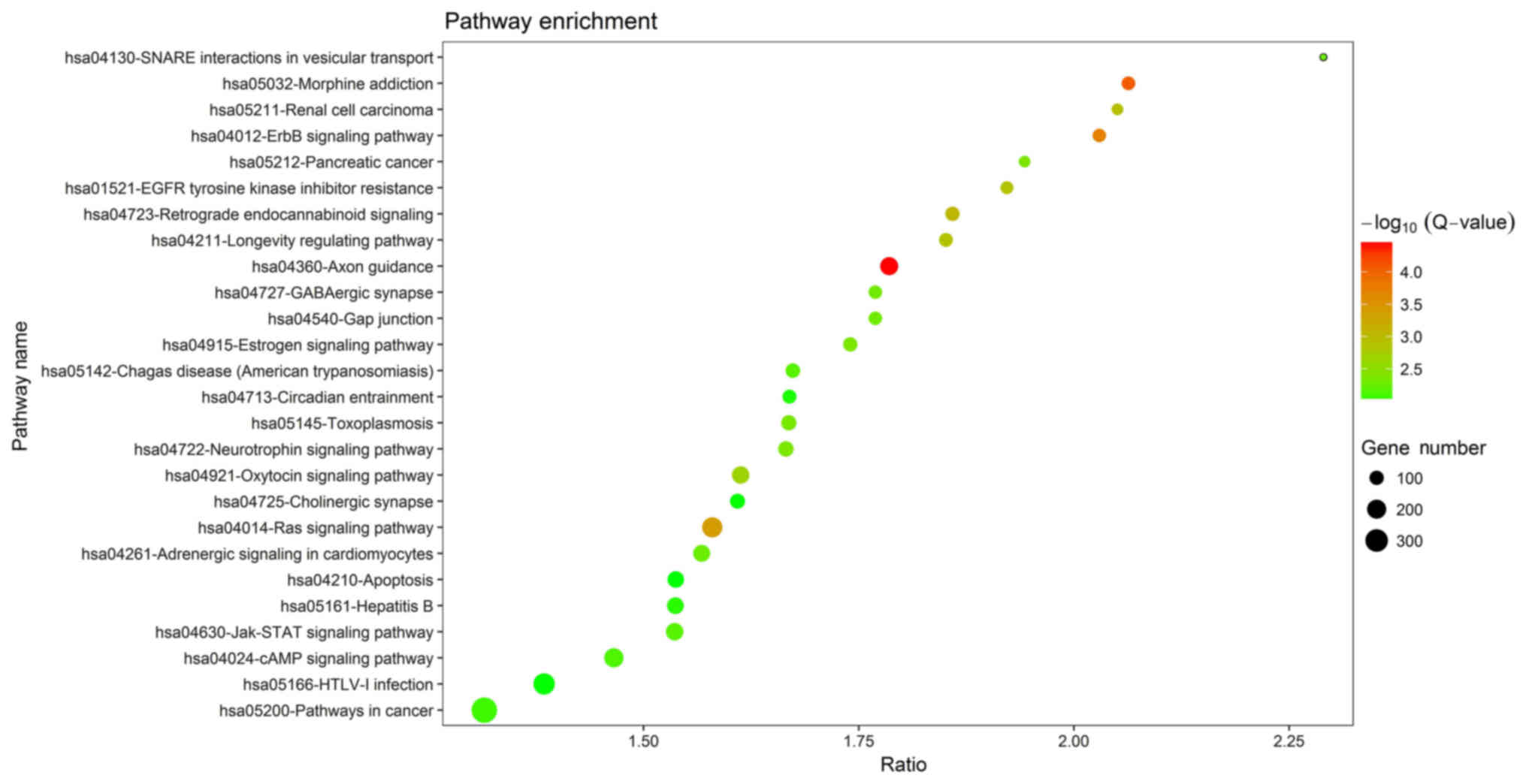
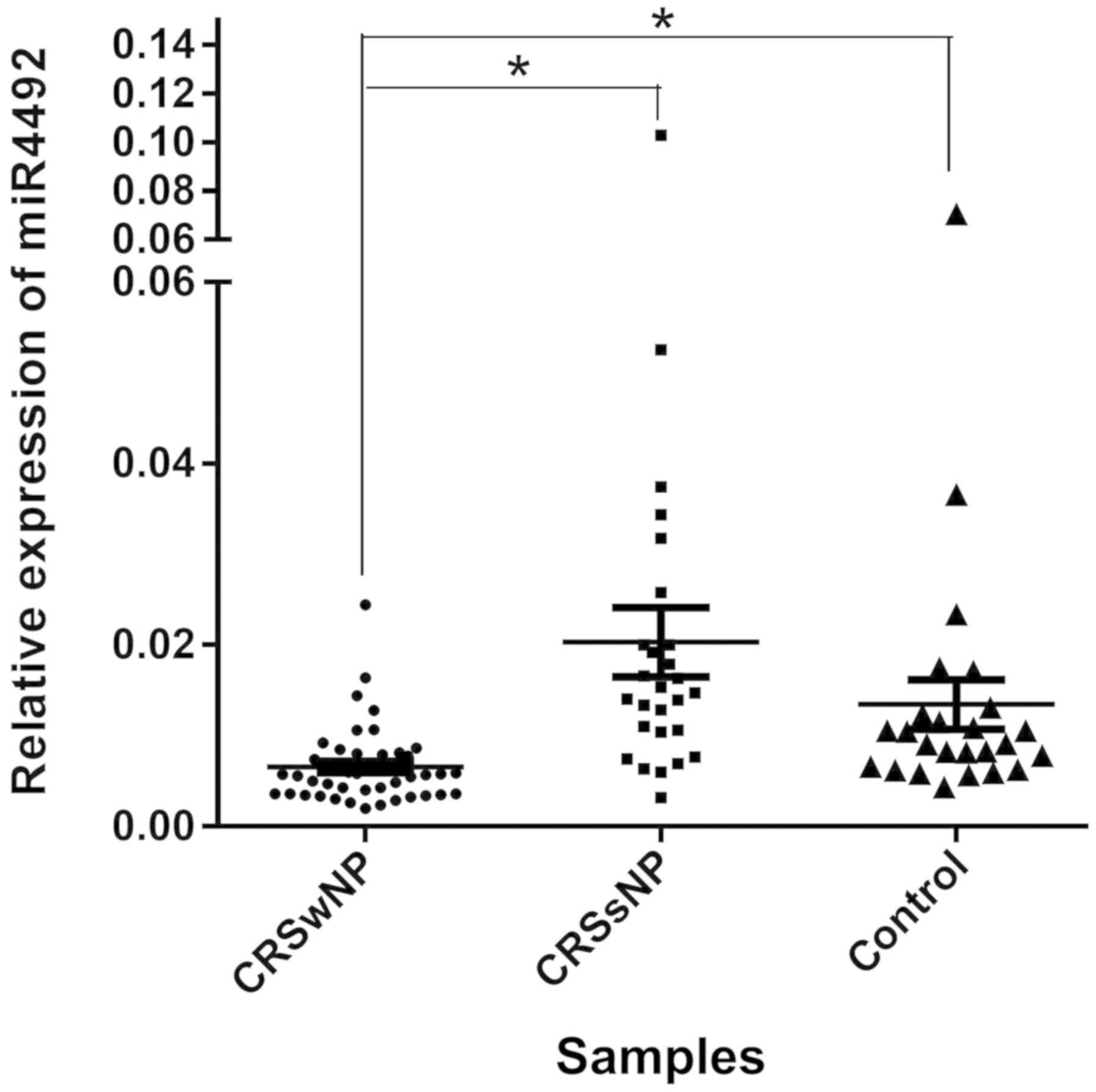
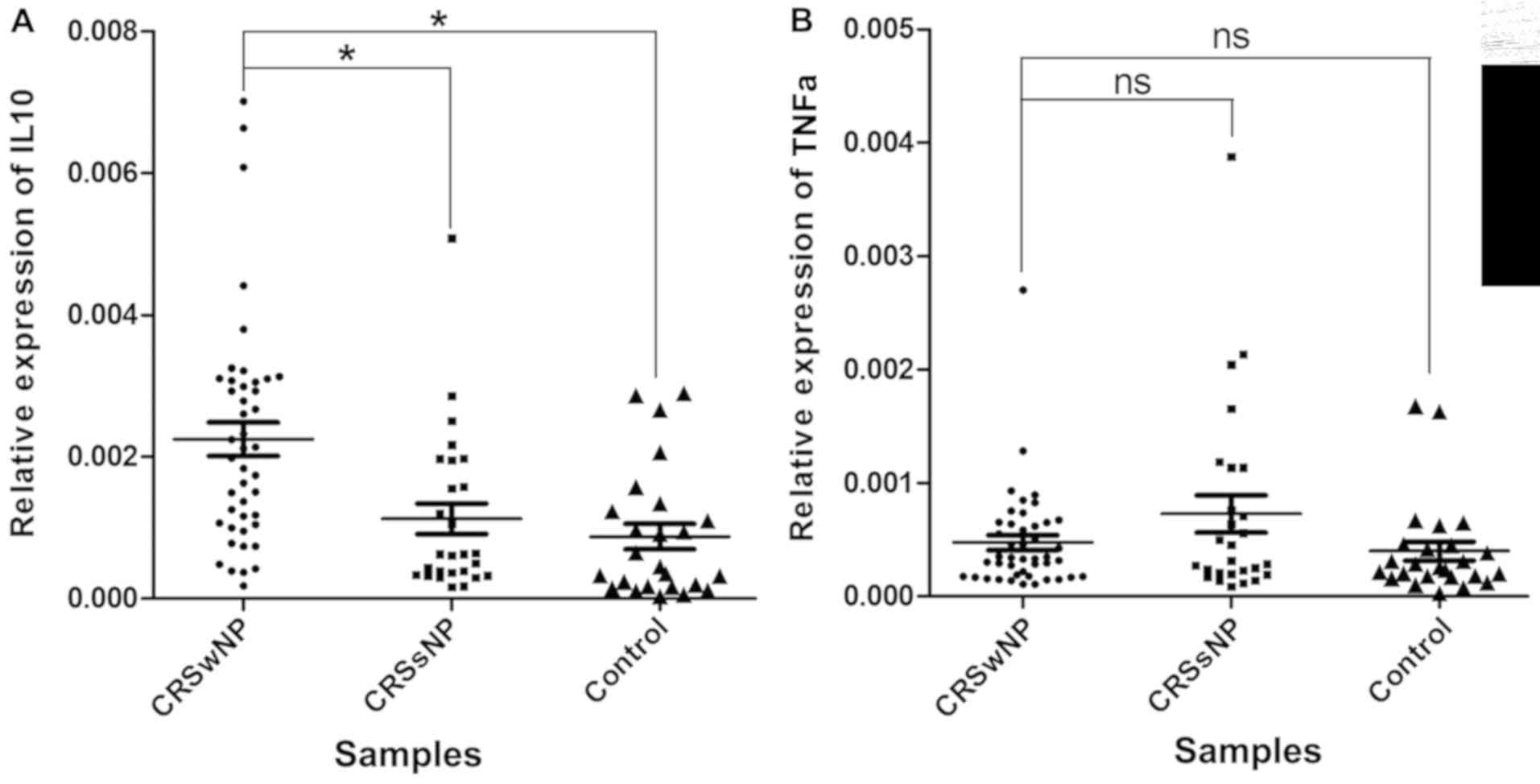
|
1
|
DeConde AS and Soler ZM: Chronic
rhinosinusitis: Epidemiology and burden of disease. Am J Rhinol
Allergy. 30:134–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hoffmans R, Schermer T, van der Linde K,
Bor H, van Boven K, van Weel C and Fokkens W: Rhinosinusitis in
morbidity registrations in dutch general practice: A retro-spective
case-control study. BMC Fam Pract. 16:1202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meltzer EO, Hamilos DL, Hadley JA, Lanza
DC, Marple BF, Nicklas RA, Bachert C, Baraniuk J, Baroody FM,
Benninger MS, et al: Rhinosinusitis: Establishing definitions for
clinical research and patient care. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 114((6
Suppl)): S155–S212. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Benninger MS, Ferguson BJ, Hadley JA,
Hamilos DL, Jacobs M, Kennedy DW, Lanza DC, Marple BF, Osguthorpe
JD, Stankiewicz JA, et al: Adult chronic rhinosinusitis:
Definitions, diagnosis, epidemiology, and pathophysiology.
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 129((3 Suppl)): S1–S32. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Banerji A, Piccirillo JF, Thawley SE,
Levitt RG, Schechtman KB, Kramper MA and Hamilos DL: Chronic
rhinosinusitis patients with polyps or polypoid mucosa have a
greater burden of illness. Am J Rhinol. 21:19–26. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koskinen A, Numminen J, Markkola A,
Karjalainen J, Karstila T, Seppälä M, Julkunen A, Lemmetyinen R,
Pekkanen J, Rautiainen M, et al: Diagnostic accuracy of symptoms,
endoscopy, and imaging signs of chronic rhinosinusitis without
nasal polyps compared to allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy.
32:121–131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dietz de Loos DA, Hopkins C and Fokkens
WJ: Symptoms in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal
polyps. Laryngoscope. 123:57–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Avdeeva K and Fokkens W: Precision
medicine in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Curr Allergy
Asthma Rep. 18:252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C,
Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P, et
al: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps
2012. Rhinol. Suppl 23:3 p preceding table of contents. 1–298.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C,
Alobid I, Baroody F, Cohen N, Cervin A, Douglas R, Gevaert P, et
al: EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal
polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology.
50:1–12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vishnoi A and Rani S: MiRNA biogenesis and
regulation of diseases: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 1509:1–10.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ni WJ and Leng XM: miRNA-dependent
activation of mRNA translation. Microrna. 5:83–86. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beilharz TH, Humphreys DT and Preiss T:
miRNA effects on mRNA closed-loop formation during translation
initiation. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 50:99–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fleshner M and Crane CR: Exosomes, DAMPs
and miRNA: Features of stress physiology and immune homeostasis.
Trends Immunol. 38:768–776. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Foley NH and O'Neill LA: miR-107: A
toll-like receptor-regulated miRNA dysregulated in obesity and type
II diabetes. J Leukoc Biol. 92:521–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou M, Li W, Xie Z, Ai J, Sun B and Tan G:
Effects of anticholinergic agent on miRNA profiles and
transcriptomes in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Mol Med Rep.
16:6558–6569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Solberg OD, Ostrin EJ, Love MI, Peng JC,
Bhakta NR, Hou L, Nguyen C, Solon M, Nguyen C, Barczak AJ, et al:
Airway epithelial miRNA expression is altered in asthma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 186:965–974. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu F, Qin HB, Xu B, Zhou H and Zhao DY:
Profiling of miRNAs in pediatric asthma: Upregulation of miRNA-221
and miRNA-485-3p. Mol Med Rep. 6:1178–1182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:D68–D73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kalvari I, Argasinska J, Quinones-Olvera
N, Nawrocki EP, Rivas E, Eddy SR, Bateman A, Finn RD and Petrov AI:
Rfam 13.0: Shifting to a genome-centric resource for non-coding RNA
families. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D335–D342. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dweep H, Gretz N and Sticht C: miRWalk
database for miRNA-target interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1182:289–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium, . Expansion
of the gene ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids
Res. 45:D331–D338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lal D, Scianna JM and Stankiewicz JA:
Efficacy of targeted medical therapy in chronic rhinosinusitis, and
predictors of failure. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 23:396–400. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia G, Bao L, Gao W, Liu S, Ji K and Li J:
Differentially expressed miRNA in inflammatory mucosa of chronic
rhinosinusitis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 15:2132–2139. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma Z, Shen Y, Zeng Q, Liu J, Yang L, Fu R
and Hu G: MiR-150-5p regulates EGR2 to promote the development of
chronic rhinosinusitis via the DC-Th axis. Int Immunopharmacol.
54:188–197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li FM and Zheng JF: Application and
progress of miRNA in chronic rhinosinusitis. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan
Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 30:1656–1658. 2016.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ma ZX, Tan X, Shen Y, Ke X, Yang YC, He
XB, Wang ZH, Dai YB, Hong SL and Hu GH: MicroRNA expression profile
of mature dendritic cell in chronic rhinosinusitis. Inflamm Res.
64:885–893. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang XH, Zhang YN, Li HB, Hu CY, Wang N,
Cao PP, Liao B, Lu X, Cui YH and Liu Z: Overexpression of miR-125b,
a novel regulator of innate immunity, in eosinophilic chronic
rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
185:140–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Izumchenko E, Chang X, Michailidi C,
Kagohara L, Ravi R, Paz K, Brait M, Hoque MO, Ling S, Bedi A and
Sidransky D: The TGFβ-miR200-MIG6 pathway orchestrates the
EMT-associated kinase switch that induces resistance to EGFR
inhibitors. Cancer Res. 74:3995–4005. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zidar N, Boštjančič E, Jerala M, Kojc N,
Drobne D, Štabuc B and Glavač D: Down-regulation of microRNAs of
the miR-200 family and up-regulation of Snail and Slug in
inflammatory bowel diseases-hallmark of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Mol Med. 20:1813–1820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Levänen B, Bhakta NR, Torregrosa Paredes
P, Barbeau R, Hiltbrunner S, Pollack JL, Sköld CM, Svartengren M,
Grunewald J, Gabrielsson S, et al: Altered microRNA profiles in
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid exosomes in asthmatic patients. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 131:894–903. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu CW, Cao X, Berger CK, Foote PH, Mahoney
DW, Simonson JA, Anderson BW, Yab TC, Taylor WR, Boardman LA, et
al: Novel approach to fecal occult blood testing by assay of
erythrocyte-specific microRNA markers. Dig Dis Sci. 62:1985–1994.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Panganiban RP, Wang Y, Howrylak J,
Chinchilli VM, Craig TJ, August A and Ishmael FT: Circulating
microRNAs as biomarkers in patients with allergic rhinitis and
asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 137:1423–1432. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Zhang XH, Callejas-Diaz B and
Mullol J: MicroRNA in united airway diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
17:E7162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xun M, Ma CF, Du QL, Ji YH and Xu JR:
Differential expression of miRNAs in enterovirus 71-infected cells.
Virol J. 12:562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Egaña-Gorroño L, Guardo AC, Bargalló ME,
Planet E, Vilaplana E, Escribà T, Pérez I, Gatell JM, García F,
Arnedo M, et al: MicroRNA profile in CD8+ T-Lymphocytes from
HIV-infected individuals: Relationship with antiviral immune
response and disease progression. PLoS One. 11:e01552452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ahn SH, Ahn JH, Ryu DR, Lee J, Cho MS and
Choi YH: Effect of Necrosis on the miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in
CRT-MG human astroglioma cells. Cancer Res Treat. 50:382–397. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao ZG, Chen QJ, Shao M, Qian YZ, Zhang
LF, Zhang YB and Xiong QX: Preliminary identification of key
miRNAs, signaling pathways, and genes associated with
hirschsprung's disease by analysis of tissue microRNA expression
profiles. World J Pediatr. 13:489–495. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boo L, Ho WY, Ali NM, Yeap SK, Ky H, Chan
KG, Yin WF, Satharasinghe DA, Liew WC, Tan SW, et al: MiRNA
transcriptome profiling of spheroid-enriched cells with cancer stem
cell properties in human breast MCF-7 cell line. Int J Biol Sci.
12:427–445. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei CH, Phan L, Feltz J, Maiti R, Hefferon
T and Lu Z: tmVar 2.0: Integrating genomic variant information from
literature with dbSNP and clinvar for precision medicine.
Bioinformatics. 34:80–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng KJ, Xu YY, Zhou ML, Zhou SH and Wang
SQ: Role of local allergic inflammation and staphylococcus aureus
enterotoxins in Chinese patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with
nasal polyps. J Laryngol otol. 131:707–713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mattes J, Collison A, Plank M, Phipps S
and Foster PS: Antagonism of microRNA-126 suppresses the effector
function of TH2 cells and the development of allergic airways
disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:18704–18709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang XH, Zhang YN and Liu Z: MicroRNA in
chronic rhinosinusitis and allergic rhinitis. Curr Allergy Asthma
Rep. 14:4152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu CC, Xia M, Zhang YJ, Jin P, Zhao L,
Zhang J, Li T, Zhou XM, Tu YY, Kong F, et al: Micro124-mediated AHR
expression regulates the inflammatory response of chronic
rhinosinusitis (CRS) with nasal polyps. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
500:141–151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Nishimura M, Mizuta I, Mizuta E, Yamasaki
S, Ohta M, Kaji R and Kuno S: Tumor necrosis factor gene
polymorphisms in patients with sporadic Parkinson's disease.
Neurosci Lett. 311:1–4. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lindenau JD, Altmann V, Schumacher-Schuh
AF, Rieder CR and Hutz MH: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
polymorphisms are associated with Parkinson's disease age at onset.
Neurosci Lett. 658:133–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mocellin S, Marincola F, Rossi CR, Nitti D
and Lise M: The multifaceted relationship between IL-10 and
adaptive immunity: Putting together the pieces of a puzzle.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:61–76. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Iyer SS and Cheng G: Role of interleukin
10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune
disease. Crit Rev Immunol. 32:23–63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xu J, Han R, Kim DW, Mo JH, Jin Y, Rha KS
and Kim YM: Role of interleukin-10 on nasal polypogenesis in
patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. PLoS One.
11:e01610132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li LG, Ma T and YR C: MiR-200A-3P and
miR4492 involved in regulation of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal
polyps. Int J Genet. 41:108–114. 2018.
|
|
53
|
Luo XQ, Shao JB, Xie RD, Zeng L, Li XX,
Qiu SQ, Geng XR, Yang LT, Li LJ, Liu DB, et al: Micro RNA-19a
interferes with IL-10 expression in peripheral dendritic cells of
patients with nasal polyposis. Oncotarget. 8:48915–48921.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|