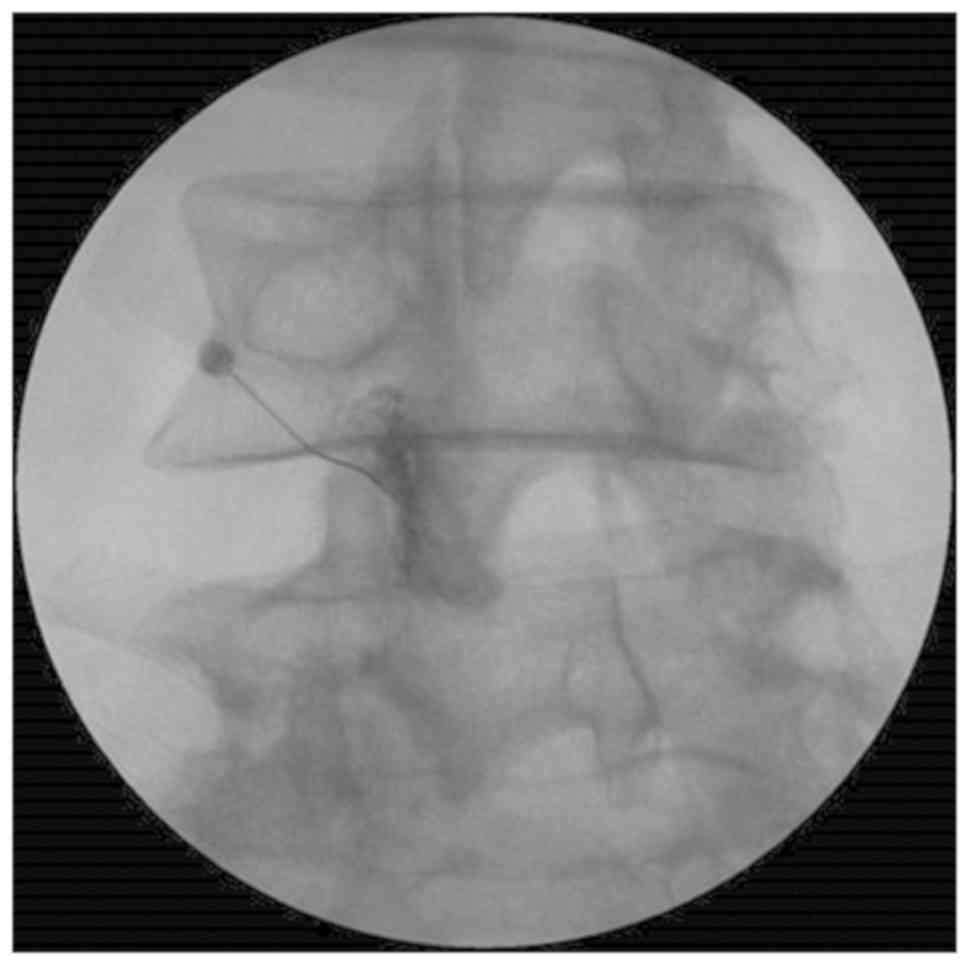
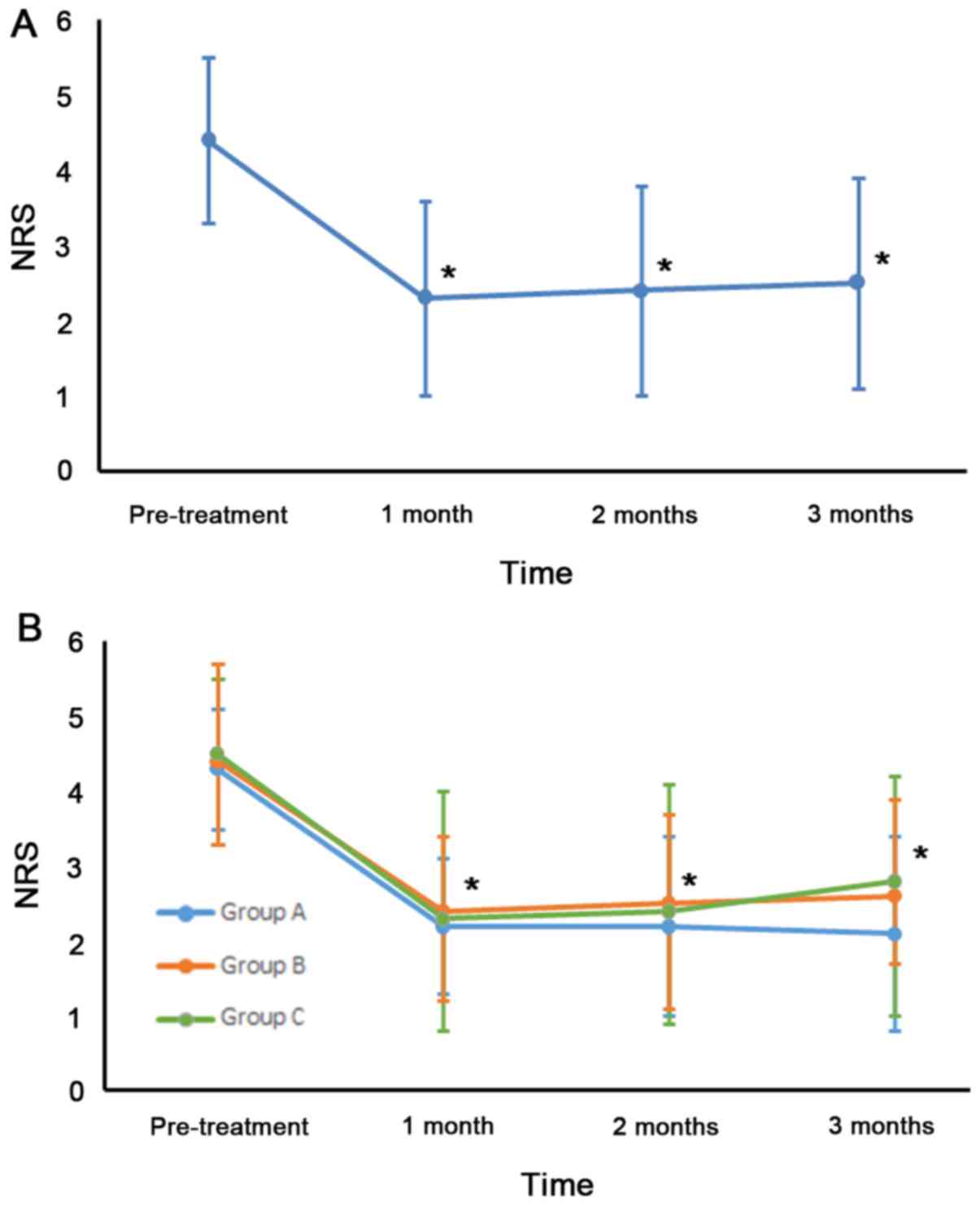
|
1
|
Vekaria R, Bhatt R, Ellard DR, Henschke N,
Underwood M and Sandhu H: Intra-articular facet joint injections
for low back pain: A systemic review. Eur Spine J. 25:1266–1281.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Perolat R, Kastler A, Nicot B, Pellat JM,
Tahon F, Attye A, Heck O, Boubagra K, Grand S and Krainik A: Facet
joint syndrome: From diagnosis to interventional management.
Insights Imaging. 9:773–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, Fortin
J, Kine G and Bogduk N: Clinical features of patients with pain
stemming from the lumbar zygapophysial joints. Is the lumbar facet
syndrome a clinical entity? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 19:1132–1137.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bogduk N: The anatomical basis for spinal
pain syndromes. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 18:603–605.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ashton IK, Ashton BA, Gibson SJ, Polak JM,
Jaffray DC and Eisenstein SM: Morphological basis for back pain:
The demonstration of nerve fibers and neuropeptides in the lumbar
facet joint capsule but not in ligamentum flavum. J Orthop Res.
10:72–78. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuslich SD, Ulstrom CL and Michael CJ: The
tissue origin of low back pain and sciatica: A report of pain
response to tissue stimulation during operations on the lumbar
spine using local anesthesia. Orthop Clin North Am. 22:181–187.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Manchikanti L, Boswell MV, Singh V,
Pampati V, Damron KS and Beyer CD: Prevalence of facet joint from
in chronic spinal pain of cervical, thoracic, and lumbar regions.
BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 5:152004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Marks R: Distribution of pain provoked
from lumbar facet joints and related structures during diagnostic
spinal infiltration. Pain. 39:37–40. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eubanks JD, Lee MJ, Cassinelli E and Ahn
NU: Prevalence of lumbar facet arthrosis and its relationship to
age, sex, and race: An anatomic study of cadaveric specimens. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 32:2058–2062. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gellhorn AC, Katz JN and Suri P:
Osteoarthritis of the spine: The facet joints. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
9:216–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lawrence RC: Estimates of the prevalence
of arthritis and selected musculoskeletal disordersin the United
States. Arthritis Rheum. 16:427–441. 1989.
|
|
12
|
Kang YM, Choi WS and Pickar JG:
Electrophysiologic evidence for an intersegmental reflex pathway
between lumbar paraspinal tissues. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
27:E56–E63. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cavanaugh JM, Ozaktay AC, Yamashita T,
Avramov A, Getchell TV and King AI: Mechanisms of low back pain: A
neurophysiologic and neuroanatomic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
166–180. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cohen SP, Huang JH and Brummett C: Facet
joint pain-advances in patient selection and treatment. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 9:101–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bellamy N, Campbell J, Robinson V, Gee T,
Bourne R and Wells G: Intraarticular corticosteroid for treatment
of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
19:CD0053282006.
|
|
16
|
Buchbinder R, Green S and Youd JM:
Corticosteroid injections for shoulder pain. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev. CD0040162003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Machado E, Bonotto D and Cunali PA:
Intra-articular injections with corticosteroids and sodium
hyaluronate for treating temporomandibular joint disorders: A
systemic review. Dental Press J Orthod. 18:128–133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carette S, Marcoux S, Truchon R, Grondin
C, Gagnon J, Allard Y and Latulippe M: A controlled trial of
corticosteroid injections into facet joints for chronic low back
pain. N Engl J Med. 325:1002–1007. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schulte TL, Pietilä TA, Heidenreich J,
Brock M and Stendel R: Injection therapy of lumbar facet syndrome:
A prospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 148:1165–1172. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manchikanti L, Manchikanti KN, Manchukonda
R, Cash KA, Damron KS, Pampati V and McManus CD: Evaluation of
lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in the management of chronic low
back pain: A preliminary report of a randomized, double-blind
controlled trial: Clinical trial NCT00355914. Pain Physician.
10:425–440. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Farrar JT, Young JP Jr, LaMoreaux L, Werth
JL and Poole RM: Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain
intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale.
Pain. 94:149–158. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maataoui A, Voql TJ, Middendorp M,
Kafchitsas K and Khan MF: Association between facet joint
osteoarthritis and the Oswestry Disability Index. World J Radiol.
6:881–885. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Groen GJ, Baljet B and Drukker J: Nerves
and nerve plexuses of the human vertebral column. Am J Anat.
188:282–296. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen C, Lu Y, Kallakuri S, Patwardhan A
and Cavanaugh JM: Distribution of A-delta and C-fiber receptors in
the cervical facet joint capsule and their response to stretch. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 88:1807–1816. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee DG, Ahn SH and Lee J: Comparative
effectiveness of pulsed radiofrequency and transforaminal steroid
injection for radicular pain due to disc herniation: A prospective
randomized trial. J Korean Med Sci. 31:1324–1330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Olmarker K, Byröd G, Cornefjord M,
Nordborg C and Rydevik B: Effects of methylprednisolone on nucleus
pulposus-induced nerve root injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
19:1803–1808. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee DG, Cho YW, Cho KH and Chang MC:
Management of refractory sciatic neuropathic pain using
ultrasound-guided pulsed radiofrequency. J Back Musculoskelet
Rehabil. 30:1141–1145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Barnes PJ: Anti-inflammatory actions of
glucocorticoids: Molecular mechanisms. Clin Sci (Lond). 94:557–572.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suri P, Hunter DJ, Rainville J, Guermazi A
and Katz JN: Presence and extent of severe facet joint
osteoarthritis are associated with back pain in older adults.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1199–1206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawu AA, Olawepo A and Salami AO: Facet
joints infiltration: A viable alternative treatment to
physiotherapy in patients with low back pain due to facet joint
arthropathy. Niger J Clin Pract. 14:219–222. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Celik B, Er U, Simsek S, Altug T and
Bavbek M: Effectiveness of lumbar zygapophysial joint blockage for
low back pain. Turk Neurosurg. 21:467–470. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ribeiro LH, Furtado RN, Konai MS, Andero
AB, Rosenfeld A and Natour J: Effect of facet joint injection
versus systemic steroids in low back pain: A randomized controlled
trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:1995–2002. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Do KH, Ahn SH, Cho YW and Chang MC:
Comparison of intra-articular lumbar facet joint pulsed
radiofrequency and intra-articular lumbar facet joint
corticosteroid injection for management of lumbar facet joint pain:
A randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e65242017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|