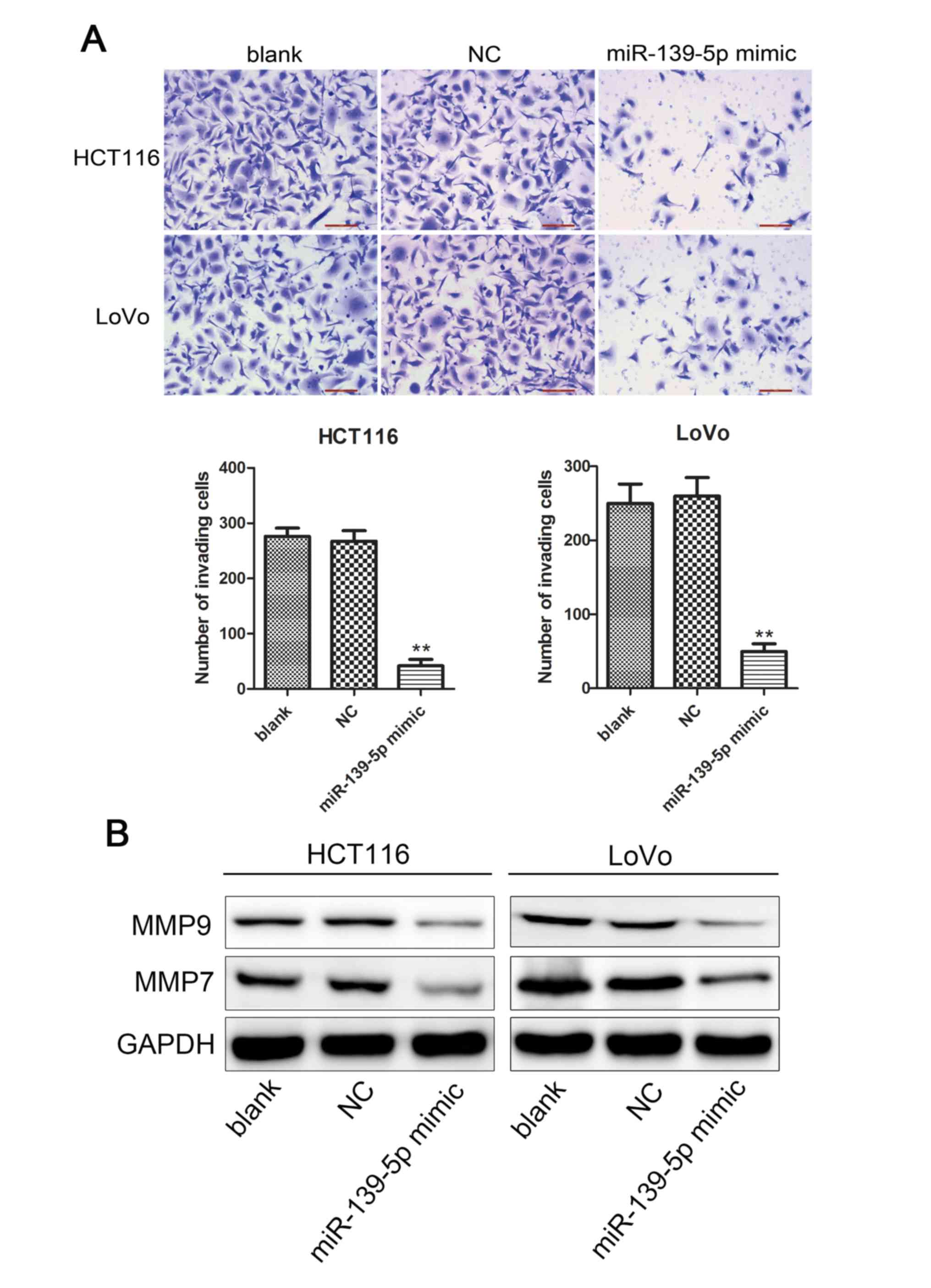
|
1
|
Schreuders EH, Ruco A, Rabeneck L, Schoen
RE, Sung JJ, Young GP and Kuipers EJ: Colorectal cancer screening:
A global overview of existing programmes. Gut. 64:1637–1649. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Payne JK: State of the science: Stress,
inflammation, and cancer. Oncol Nurs Forum. 41:533–540. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rhodes JM and Campbell BJ: Inflammation
and colorectal cancer: IBD-associated and sporadic cancer compared.
Trends Mol Med. 8:10–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Inflammatory bowel disease and cancer
risk. Arch Dis Child. 103:272017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galvan-Roman JM, Curbelo J and Aspa J:
Inflammatory status and prognosis of locally advanced non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 9:2782–2785. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mayberry JF, Ballantyne KC, Hardcastle JD,
Mangham C and Pye G: Epidemiological study of asymptomatic
inflammatory bowel disease: The identification of cases during a
screening programme for colorectal cancer. Gut. 30:481–483. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bissell MJ, Radisky DC, Rizki A, Weaver VM
and Petersen OW: The organizing principle: Microenvironmental
influences in the normal and malignant breast. Differentiation.
70:537–546. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-kappaB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bonizzi G and Karin M: The two NF-kappaB
activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity.
Trends Immunol. 25:280–288. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen Z, Zhou R, Liu C, Wang Y, Zhan W,
Shao Z, Liu J, Zhang F, Xu L, Zhou X, et al: MicroRNA-105 is
involved in TNF-α-related tumor microenvironment enhanced
colorectal cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 8:32132017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baranwal S, Rawat SG and Gupta P: miR-301,
pleiotropic microRNA in regulation of inflammatory bowel disease
and colitis-associated cancer. Front Immunol. 9:5222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anfossi S, Giordano A, Gao H, Cohen EN,
Tin S, Wu Q, Garza RJ, Debeb BG, Alvarez RH, Valero V, et al: High
serum miR-19a levels are associated with inflammatory breast cancer
and are predictive of favorable clinical outcome in patients with
metastatic HER2+ inflammatory breast cancer. PLoS One.
9:e831132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen K, Mao R, Ma L, Li Y, Qiu Y, Cui D,
Le V, Yin P, Ni L and Liu J: Post-transcriptional regulation of the
tumor suppressor miR-139-5p and a network of miR-139-5p-mediated
mRNA interactions in colorectal cancer. FEBS J. 281:3609–3624.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z,
Quan C, Zhou L, Hu Y, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: MiR-139-5p inhibits
migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR
and NOTCH1. Protein Cell. 5:851–861. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Liang X, Wang Y, Meng X, Xu Y, Cai
S, Wang Z, Liu J and Cai G: miR-139-5p inhibits the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances the chemotherapeutic
sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating BCL2. Sci
Rep. 6:271572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zou F, Mao R, Yang L, Lin S, Lei K, Zheng
Y, Ding Y, Zhang P, Cai G, Liang X and Liu J: Targeted deletion of
miR-139-5p activates MAPK, NF-κB and STAT3 signaling and promotes
intestinal inflammation and colorectal cancer. FEBS J.
283:1438–1452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Takada Y, Khuri FR and Aggarwal BB:
Protein farnesyltransferase inhibitor (SCH 66336) abolishes
NF-kappaB activation induced by various carcinogens and
inflammatory stimuli leading to suppression of NF-kappaB-regulated
gene expression and up-regulation of apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
279:26287–26299. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuo YC, Lin WC, Chiang IT, Chang YF, Chen
CW, Su SH, Chen CL and Hwang JJ: Sorafenib sensitizes human
colorectal carcinoma to radiation via suppression of NF-κB
expression in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:12–20.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Dong Y, Zhu N, Tsoi H, Zhao Z, Wu
CW, Wang K, Zheng S, Ng SS, Chan FK, et al: microRNA-139-5p exerts
tumor suppressor function by targeting NOTCH1 in colorectal cancer.
Mol Cancer. 13:1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu H, Yin Y, Hu Y, Feng Y, Bian Z, Yao S,
Li M, You Q and Huang Z: miR-139-5p sensitizes colorectal cancer
cells to 5-fluorouracil by targeting NOTCH-1. Pathol Res Pract.
212:643–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh RD, Haridas N, Patel JB, Shah FD,
Shukla SN, Shah PM and Patel PS: Matrix metalloproteinases and
their inhibitors: Correlation with invasion and metastasis in oral
cancer. Indian J Clin Biochem. 25:250–259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu JY, Pang ZJ and Yu YH: Regulation of
trophoblast invasion: The role of matrix metalloproteinases. Rev
Obstet Gynecol. 5:e137–e143. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shawki S, Ashburn J, Signs SA and Huang E:
Colon cancer: Inflammation-associated cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am.
27:269–287. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mantovani A: The inflammation-cancer
connection. FEBS J. 285:638–640. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Markopoulos GS, Roupakia E, Tokamani M,
Alabasi G, Sandaltzopoulos R, Marcu KB and Kolettas E: Roles of
NF-κB signaling in the regulation of miRNAs impacting on
inflammation in cancer. Biomedicines. 6:2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2:2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Olaru AV, Selaru FM, Mori Y, Vazquez C,
David S, Paun B, Cheng Y, Jin Z, Yang J, Agarwal R, et al: Dynamic
changes in the expression of MicroRNA-31 during inflammatory bowel
disease-associated neoplastic transformation. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
17:221–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen K, Liang Q, Xu K, Cui D, Jiang L, Yin
P, Lu Y, Li Q and Liu J: MiR-139 inhibits invasion and metastasis
of colorectal cancer by targeting the type I insulin-like growth
factor receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:320–330. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang KH, Miller N, Kheirelseid EA,
Lemetre C, Ball GR, Smith MJ, Regan M, McAnena OJ and Kerin MJ:
MicroRNA signature analysis in colorectal cancer: Identification of
expression profiles in stage II tumors associated with aggressive
disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 26:1415–1422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Li C, Jiang Y, Wan Y, Zhou S and
Cheng W: Tumor-suppressor role of miR-139-5p in endometrial cancer.
Cancer Cell Int. 18:512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hua S, Lei L, Deng L, Weng X, Liu C, Qi X,
Wang S, Zhang D, Zou X, Cao C, et al: miR-139-5p inhibits aerobic
glycolysis, cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in
hepatocellular carcinoma via a reciprocal regulatory interaction
with ETS1. Oncogene. 37:1624–1636. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Krowiorz K, Ruschmann J, Lai C, Ngom M,
Maetzig T, Martins V, Scheffold A, Schneider E, Pochert N, Miller
C, et al: MiR-139-5p is a potent tumor suppressor in adult acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 6:e5082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shi YK and Guo YH: MiR-139-5p suppresses
osteosarcoma cell growth and invasion through regulating DNMT1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:459–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maoa R, Zou F, Yang L, Lin S, Li Y, Ma M,
Yin P, Liang X and Liu J: The loss of MiR-139-5p promotes
colitis-associated tumorigenesis by mediating PI3K/AKT/Wnt
signaling. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 69:153–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu R, Yang M, Meng Y, Liao J, Sheng J, Pu
Y, Yin L and Kim SJ: Tumor-suppressive function of miR-139-5p in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e770682013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maletzki C and Emmrich J: Inflammation and
immunity in the tumor environment. Dig Dis. 28:574–578. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L and Zhang X:
NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer.
Cell Mol Immunol. 6:327–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Geng R, Tan X, Wu J, Pan Z, Yi M, Shi W,
Liu R, Yao C, Wang G, Lin J, et al: RNF183 promotes proliferation
and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via activation of
NF-κB-IL-8 axis. Cell Death Dis. 8:e29942017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang G, Chen C, Yang R, Cao X, Lai S, Luo
X, Feng Y, Xia X, Gong J and Hu J: p55PIK-PI3K stimulates
angiogenesis in colorectal cancer cell by activating NF-κB pathway.
Angiogenesis. 16:561–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu XB, Liu Y, Wang GH, Xu X, Cai Y, Wang
HY, Li YQ, Meng HF, Dai F and Jin JD: Mesenchymal stem cells
promote colorectal cancer progression through AMPK/mTOR-mediated
NF-κB activation. Sci Rep. 6:214202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu YX, Ju HQ, Wang F, Chen LZ, Wu QN,
Sheng H, Mo HY, Pan ZZ, Xie D, Kang TB, et al: Inhibition of the
NF-κB pathway by nafamostat mesilate suppresses colorectal cancer
growth and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 380:87–97. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|