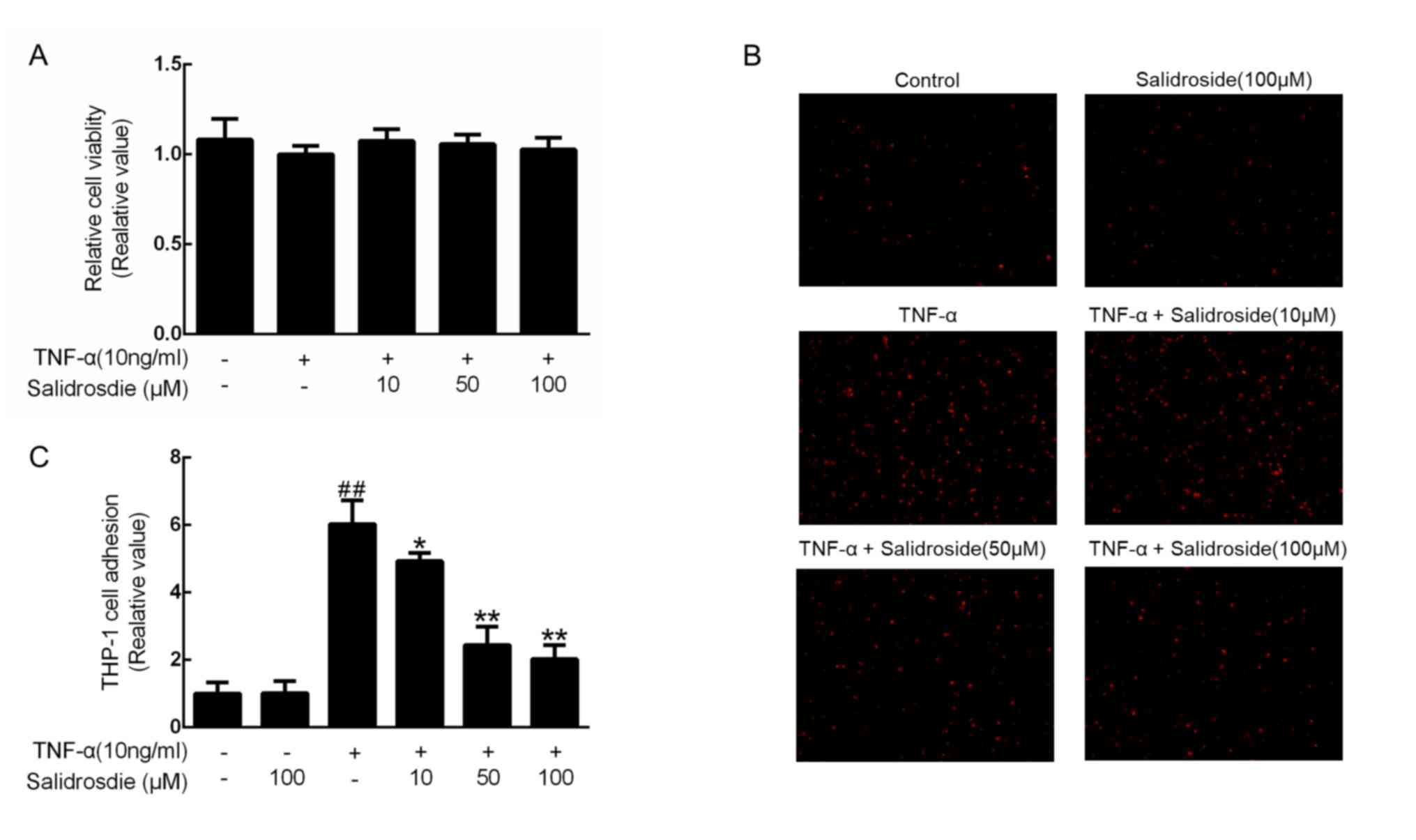
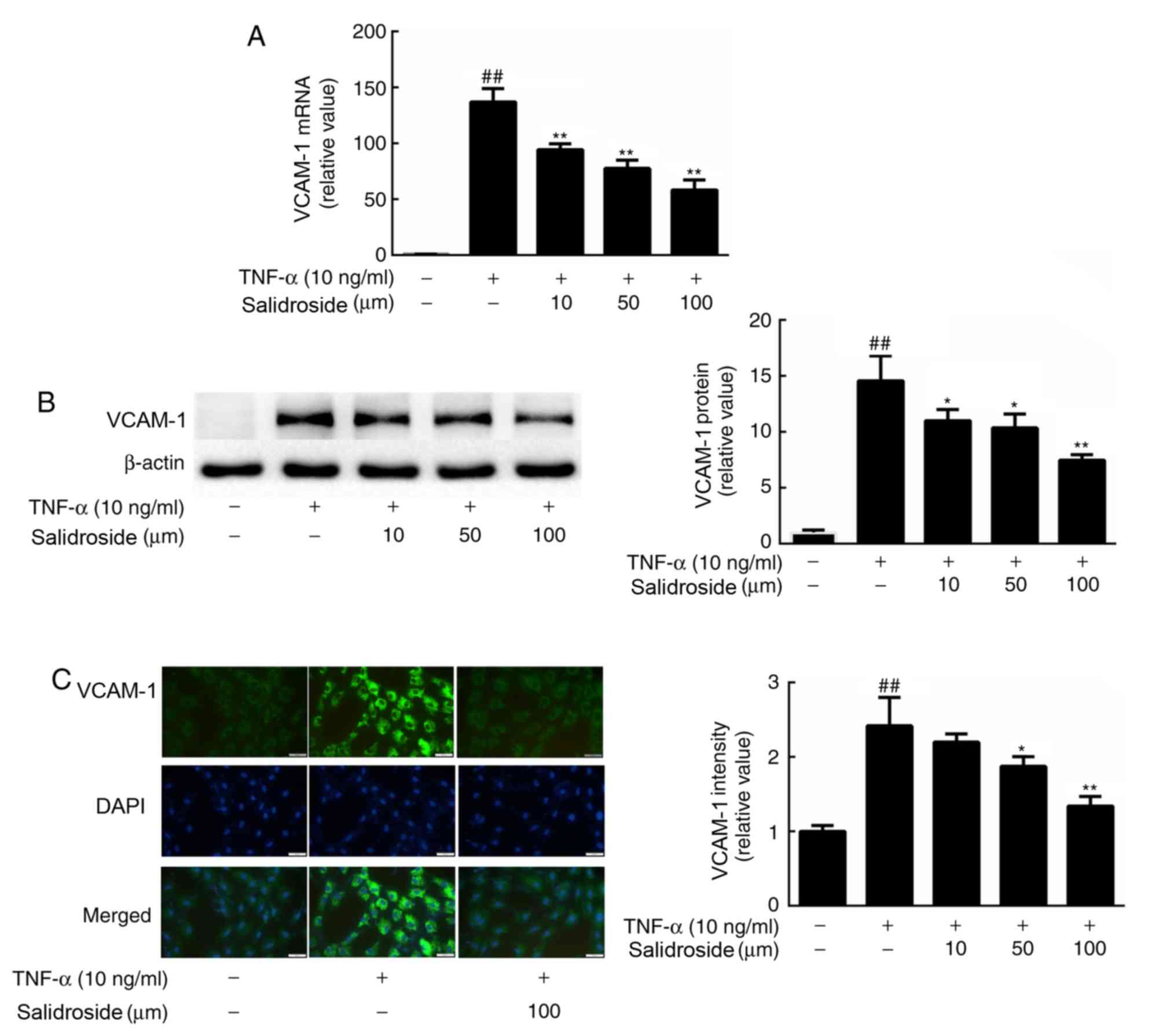
|
1
|
Pober JS and Sessa WC: Evolving functions
of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:803–815.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu S, Xu H, Peng J, Wang C, Jin Y, Liu K,
Sun H and Qin J: Potent anti-inflammatory effect of dioscin
mediated by suppression of TNF-α-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1and EL
expression via the NF-κB pathway. Biochimie. 110:62–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang W, Huang M, Ouyang H, Peng J and
Liang J: Oridonin inhibits vascular inflammation by blocking NF-κB
and MAPK activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 826:133–139. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Park Y, Wu J, Chen Xp, Lee S,
Yang J, Dellsperger KC and Zhang C: Role of TNF-alpha in vascular
dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:219–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cook-Mills JM, Marchese ME and
Abdala-Valencia H: Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression and
signaling during disease: Regulation by reactive oxygen species and
antioxidants. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:1607–1638. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Collins T, Read MA, Neish AS, Whitley MZ,
Thanos D and Maniatis T: Transcriptional regulation of endothelial
cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible
enhancers. FASEB J. 9:899–909. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan LL and Dai M: Paeonol from Paeonia
suffruticosa prevents TNF-alpha-induced monocytic cell adhesion to
rat aortic endothelial cells by suppression of VCAM-1 expression.
Phytomedicine. 16:1027–1032. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee CW, Lin WN, Lin CC, Luo SF, Wang JS,
Pouyssegur J and Yang CM: Transcriptional regulation of VCAM-1
expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human tracheal smooth
muscle cells: Involvement of MAPKs, NF-kappaB, p300, and histone
acetylation. J Cell Physiol. 207:174–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng T, Bian F, Chen L, Wang Q and Jin S:
beneficial effects of rhodiola and salidroside in diabetes:
Potential role of AMP-activated protein kinase. Mol Diagn Ther.
23:489–498. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao G, Shi A, Fan Z and Du Y: Salidroside
inhibits the growth of human breast cancer in vitro and
in vivo. Oncol Rep. 33:2553–2560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen L, Liu P, Feng X and Ma C:
Salidroside suppressing LPS-induced myocardial injury by inhibiting
ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Mol
Med. 21:3178–3189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guan S, Feng H, Song B, Guo W, Xiong Y,
Huang G, Zhong W, Huo M, Chen N, Lu J and Deng X: Salidroside
attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine responses and
improves survival in murine endotoxemia. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:2194–2199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Han X, Fu M, Wang J, Song Y, Liu
Y, Zhang J, Zhou J and Ge J: Qiliqiangxin attenuates
hypoxia-induced injury in primary rat cardiac microvascular
endothelial cells via promoting HIF-1α-dependent glycolysis. J Cell
Mol Med. 22:2791–2803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JF Jr and
Vita JA: The clinical implications of endothelial dysfunction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 42:1149–1160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Amodio G, Moltedo O, Faraonio R and
Remondelli P: Targeting the Endoplasmic Reticulum Unfolded Protein
Response to Counteract the Oxidative Stress-Induced endothelial
dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018:49462892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gareus R, Kotsaki E, Xanthoulea S, van der
Made I, Gijbels MJ, Kardakaris R, Polykratis A, Kollias G, de
Winther MP and Pasparakis M: Endothelial cell-specific NF-kappaB
inhibition protects mice from atherosclerosis. Cell Metab.
8:372–383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2045–2051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Robinson A: Dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera)
for multiple sclerosis. Nurse Pract. 39:10–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian Y, Jain S, Kelemen SE and Autieri MV:
AIF-1 expression regulates endothelial cell activation, signal
transduction, and vasculogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
296:C256–C266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cybulsky MI, Iiyama K, Li H, Zhu S, Chen
M, Iiyama M, Davis V, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Connelly PW and Milstone
DS: A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 107:1255–1262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dansky HM, Barlow CB, Lominska C, Sikes
JL, Kao C, Weinsaft J, Cybulsky MI and Smith JD: Adhesion of
monocytes to arterial endothelium and initiation of atherosclerosis
are critically dependent on vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 gene
dosage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:1662–1667. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kirii H, Niwa T, Yamada Y, Wada H, Saito
K, Iwakura Y, Asano M, Moriwaki H and Seishima M: Lack of
interleukin-1beta decreases the severity of atherosclerosis in
ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:656–660.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Atreya R and Neurath MF: Involvement of
IL-6 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease and colon
cancer. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 28:187–196. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gu L, Okada Y, Clinton SK, Gerard C,
Sukhova GK, Libby P and Rollins BJ: Absence of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 reduces atherosclerosis in low density
lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Mol Cell. 2:275–281. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pober JS: Endothelial activation:
Intracellular signaling pathways. Arthritis Res. 4 (Suppl
3):S109–S116. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Csiszar A, Wang M, Lakatta EG and Ungvari
Z: Inflammation and endothelial dysfunction during aging: role of
NF-kappaB. J Appl Physiol (1985). 105:1333–1341. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Z, Connell MC and MacEwan DJ:
TNFR1-induced NF-kappaB, but not ERK, p38MAPK or JNK activation,
mediates TNF-induced ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression on endothelial
cells. Cell Signal. 19:1238–1248. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wei G, Zhang X, Su Z and Li X: Glatiramer
acetate (GA) prevents TNF-α-induced monocyte adhesion to primary
endothelial cells through interfering with the NF-κB pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:101–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Tang Y, Ma B, Wang Z, Jiang J, Hou
S, Wang S, Zhang J, Deng M, Duan Z, et al: The peptide lycosin-I
attenuates TNF-α-induced inflammation in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells via IκB/NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm Res.
67:455–466. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Collins T and Cybulsky MI: NF-kappaB:
Pivotal mediator or innocent bystander in atherogenesis? J Clin
Invest. 107:255–264. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen YH, Lin SJ, Ku HH, Shiao MS, Lin FY,
Chen JW and Chen YL: Salvianolic acid B attenuates VCAM-1 and
ICAM-1 expression in TNF-alpha-treated human aortic endothelial
cells. J Cell Biochem. 82:512–521. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim KH, Lee EN, Park JK, Lee JR, Kim JH,
Choi HJ, Kim BS, Lee HW, Lee KS and Yoon S: Curcumin attenuates
TNF-α-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1,
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and proinflammatory cytokines in
human endometriotic stromal cells. Phytother Res. 26:1037–1047.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu H, Li Z, Zhu X, Lin R and Chen L:
Salidroside reduces cell mobility via NF-κ B and MAPK signaling in
LPS-induced BV2 microglial cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2014:3838212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|