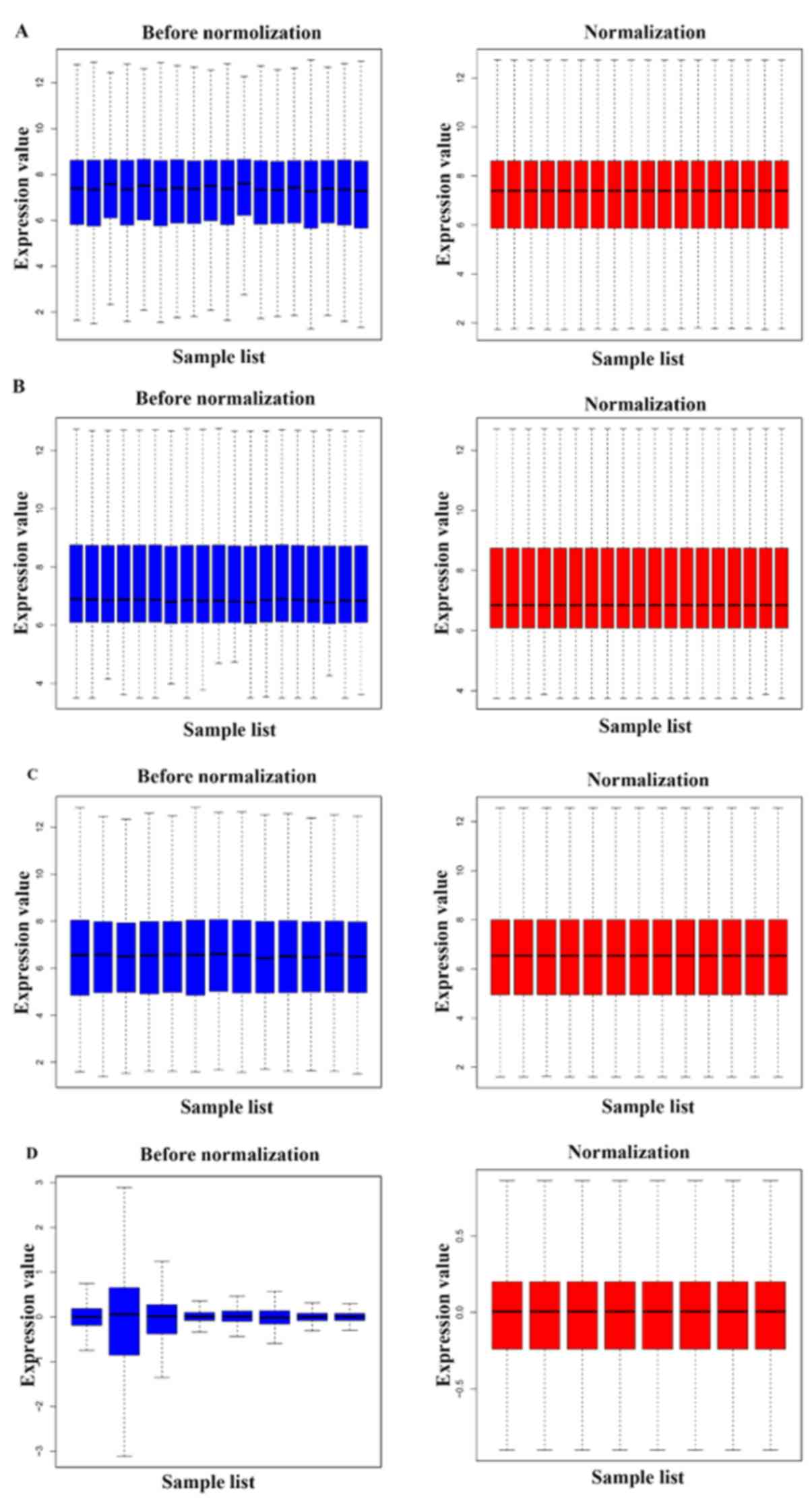
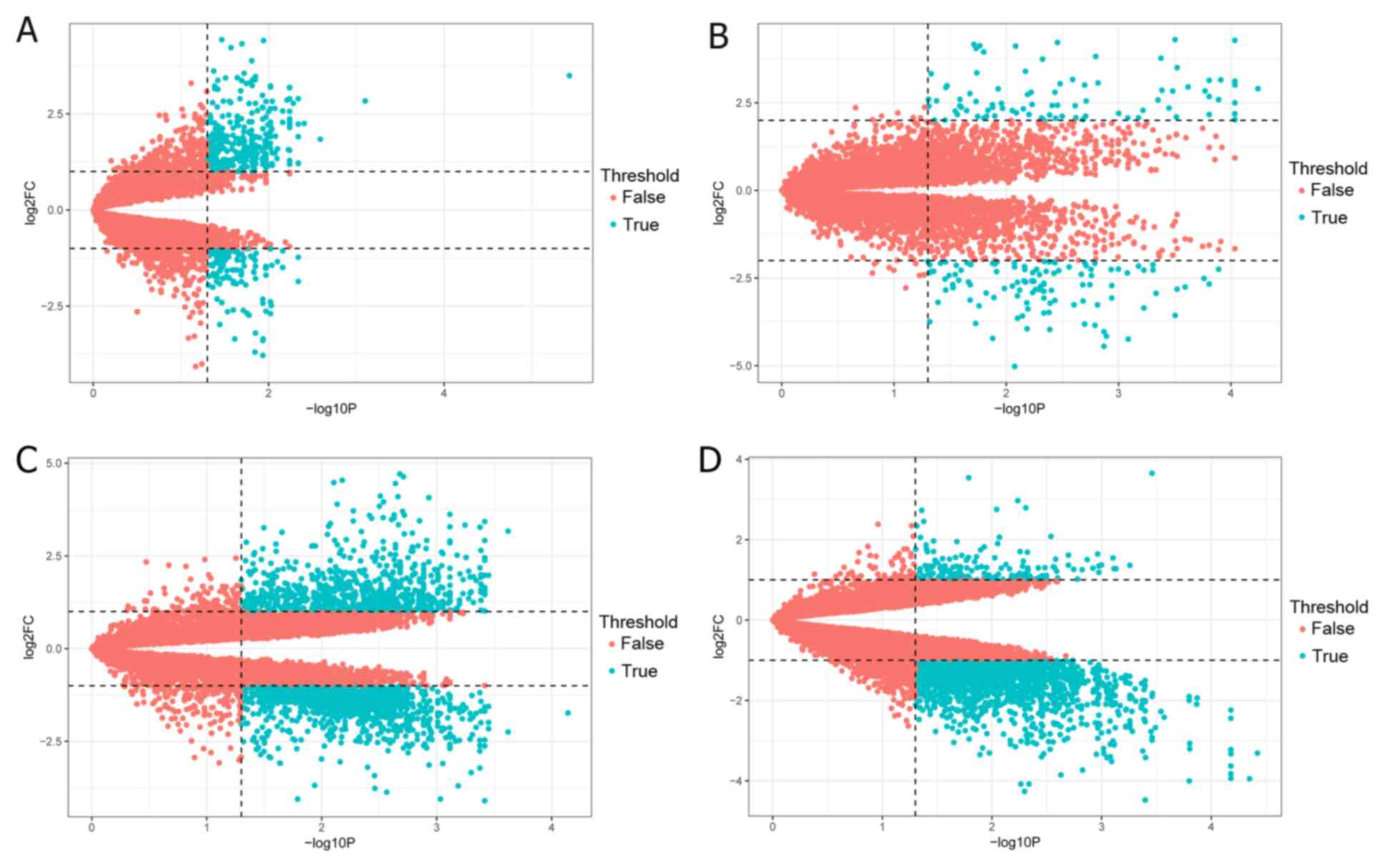
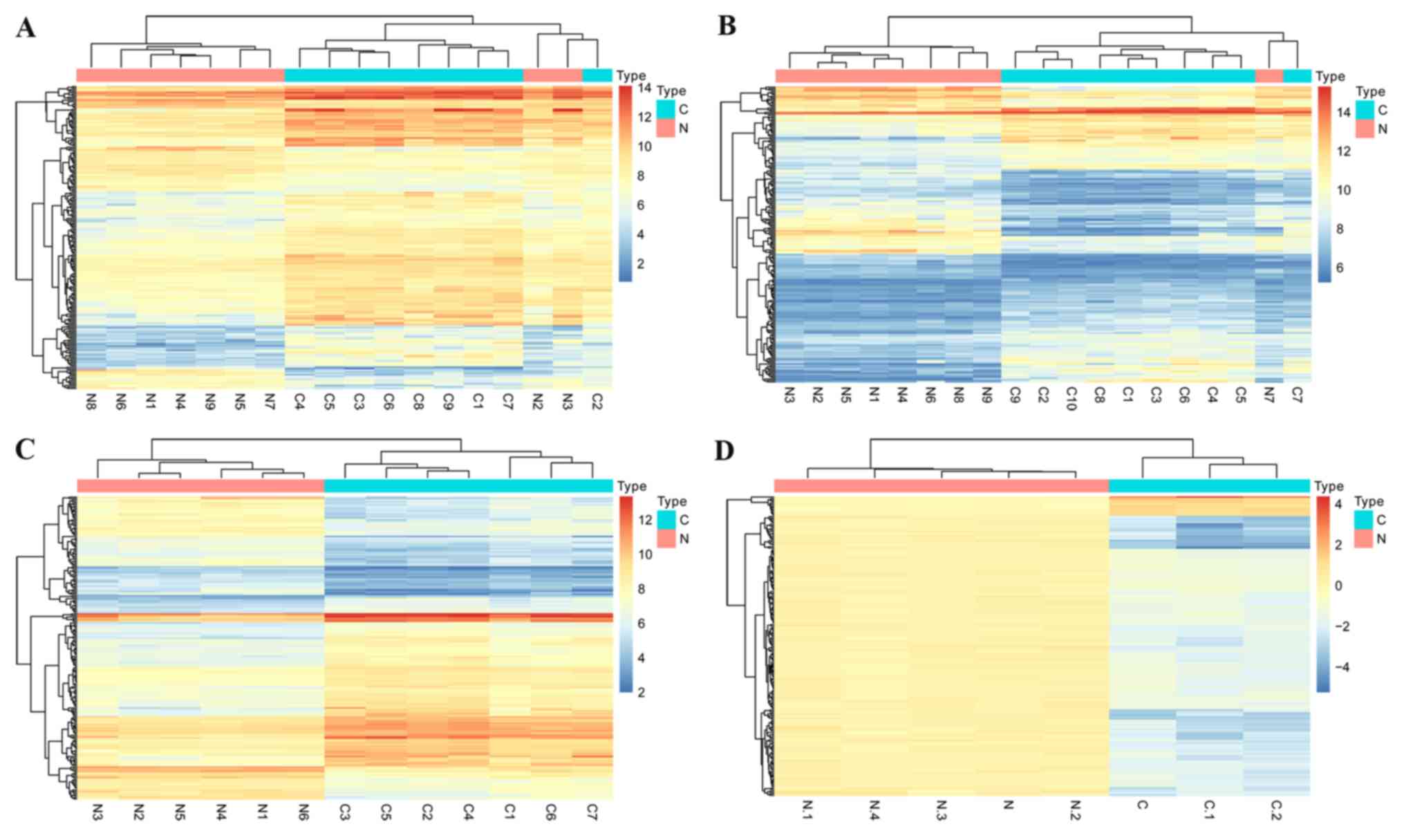
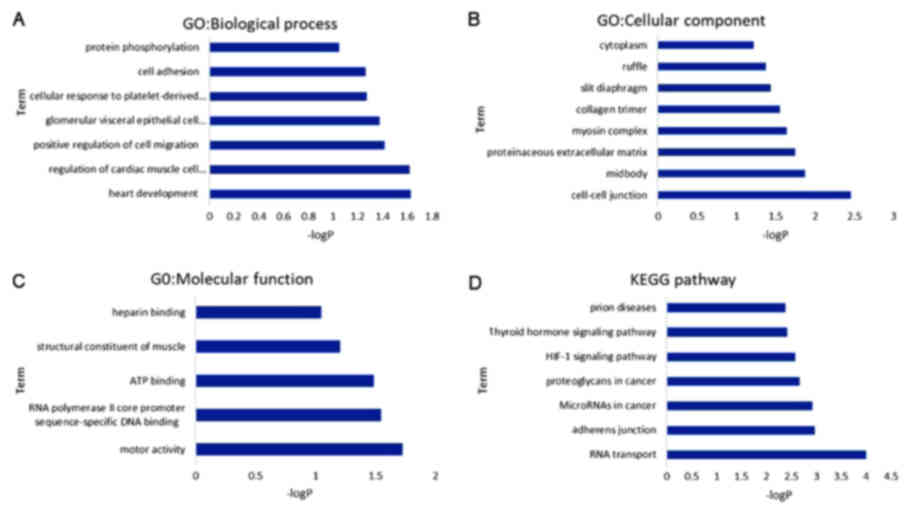
|
1
|
Jenkins S, Olive DL and Haney AF:
Endometriosis: Pathogenetic implications of the anatomic
distribution. Obstet Gynecol. 67:335–338. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krawczyk N, Banys-Paluchowski M, Schmidt
D, Ulrich U and Fehm T: Endometriosis-associated malignancy.
Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 76:176–181. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laganà AS, La Rosa VL, Rapisarda AMC,
Valenti G, Sapia F, Chiofalo B, Rossetti D, Ban Frangež H, Vrtačnik
Bokal E and Vitale SG: Anxiety and depression in patients with
endometriosis: Impact and management challenges. Int J Womens
Health. 9:323–330. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fuldeore MJ and Soliman AM: Prevalence and
symptomatic burden of diagnosed endometriosis in the United States:
National estimates from a cross-sectional survey of 59,411 women.
Gynecol Obstet Invest. 82:453–461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu F, Lv X, Yu H, Xu P, Ma R and Zou K:
In search of key genes associated with endometriosis using
bioinformatics approach. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
194:119–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kobayashi H, Imanaka S, Nakamura H and
Tsuji A: Understanding the role of epigenomic, genomic and genetic
alterations in the development of endometriosis (review). Mol Med
Rep. 9:1483–1505. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sha G, Wu D, Zhang L, Chen X, Lei M, Sun
H, Lin S and Lang J: Differentially expressed genes in human
endometrial endothelial cells derived from eutopic endometrium of
patients with endometriosis compared with those from patients
without endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 22:3159–3169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang X, Zhu S, Li L, Zhang L, Xian S, Wang
Y and Cheng Y: Identification of differentially expressed genes and
signaling pathways in ovarian cancer by integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 11:1457–1474. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Huang Q and Li C:
Integrated bioinformatics analysis reveals key candidate genes and
pathways in breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 17:8091–8100.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ni M, Liu X, Wu J, Zhang D, Tian J, Wang
T, Liu S, Meng Z, Wang K, Duan X, et al: Identification of
candidate biomarkers correlated with the pathogenesis and prognosis
of non-small cell lung cancer via integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Front Genet. 9:4692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hull ML, Escareno CR, Godsland JM, Doig
JR, Johnson CM, Phillips SC, Smith SK, Tavaré S, Print CG and
Charnock-Jones DS: Endometrial-peritoneal interactions during
endometriotic lesion establishment. Am J Pathol. 173:700–715. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hawkins SM, Creighton CJ, Han DY, Zariff
A, Anderson ML, Gunaratne PH and Matzuk MM: Functional microRNA
involved in endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol. 25:821–832. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Crispi S, Piccolo MT, D'Avino A, Donizetti
A, Viceconte R, Spyrou M, Calogero RA, Baldi A and Signorile PG:
Transcriptional profiling of endometriosis tissues identifies genes
related to organogenesis defects. J Cell Physiol. 228:1927–1934.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Herndon CN, Aghajanova L, Balayan S,
Erikson D, Barragan F, Goldfien G, Vo KC, Hawkins S and Giudice LC:
Global transcriptome abnormalities of the eutopic endometrium from
women with adenomyosis. Reprod Sci. 23:1289–1303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kolde R, Laur S, Adler P and Vilo J:
Robust rank aggregation for gene list integration and
meta-analysis. Bioinformatics. 28:573–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiong DD, Dang YW, Lin P, Wen DY, He RQ,
Luo DZ, Feng ZB and Chen G: A circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network
identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy
strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 16:2202018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao X, Chen Y, Chen M, Wang S, Wen X and
Zhang S: Identification of key candidate genes and biological
pathways in bladder cancer. PeerJ. 6:e60362018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rogers PA, D'Hooghe TM, Fazleabas A,
Gargett CE, Giudice LC, Montgomery GW, Rombauts L, Salamonsen LA
and Zondervan KT: Priorities for endometriosis research:
Recommendations from an international consensus workshop. Reprod
Sci. 16:335–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Simoens S, Dunselman G, Dirksen C,
Hummelshoj L, Bokor A, Brandes I, Brodszky V, Canis M, Colombo GL,
DeLeire T, et al: The burden of endometriosis: Costs and quality of
life of women with endometriosis and treated in referral centres.
Hum Reprod. 27:1292–1299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mehasseb MK, Panchal R, Taylor AH, Brown
L, Bell SC and Habiba M: Estrogen and progesterone receptor isoform
distribution through the menstrual cycle in uteri with and without
adenomyosis. Fertil Steril. 95:2228–2235, 2235 e1. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aghajanova L, Velarde MC and Giudice LC:
Altered gene expression profiling in endometrium: Evidence for
progesterone resistance. Semin Reprod Med. 28:51–58. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kobayashi H: Invasive capacity of
heterotopic endometrium. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 50 (Suppl
1):S26–S32. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Saare M, Krigul KL, Laisk-Podar T,
Ponandai-Srinivasan S, Rahmioglu N, Lalit Kumar PG, Zondervan K,
Salumets A and Peters M: DNA methylation alterations-potential
cause of endometriosis pathogenesis or a reflection of tissue
heterogeneity? Biol Reprod. 99:273–282. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng T and Yang J: Differential
expression of EWI-2 in endometriosis, its functional role and
underlying molecular mechanisms. J Obstet Gynaecol Res.
43:1180–1188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rai P and Shivaji S: The role of DJ-1 in
the pathogenesis of endometriosis. PLoS One. 6:e180742011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grund S and Grümmer R: Direct cell-cell
interactions in the endometrium and in endometrial pathophysiology.
Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E22272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan XY, Li X, Weng ZP and Wang B: Altered
expression of claudin-3 and claudin-4 in ectopic endometrium of
women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 91:1692–1699. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sohler F, Sommer A, Wachter DL, Agaimy A,
Fischer OM, Renner SP, Burghaus S, Fasching PA, Beckmann MW,
Fuhrmann U, et al: Tissue remodeling and nonendometrium-like
menstrual cycling are hallmarks of peritoneal endometriosis
lesions. Reprod Sci. 20:85–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shaco-Levy R, Sharabi S, Benharroch D,
Piura B and Sion-Vardy N: Matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9,
E-cadherin, and beta-catenin expression in endometriosis, low-grade
endometrial carcinoma and non-neoplastic eutopic endometrium. Eur J
Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 139:226–232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhan L, Wang W, Zhang Y, Song E, Fan Y and
Wei B: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha: A promising therapeutic
target in endometriosis. Biochimie. 123:130–137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang F, Liu XL, Wang W, Dong HL, Xia YF,
Ruan LP and Liu LP: Expression of MMIF, HIF-1α and VEGF in serum
and endometrial tissues of patients with endometriosis. Curr Med
Sci. 38:499–504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiong W, Zhang L, Xiong Y, Liu H and Liu
Y: Hypoxia promotes invasion of endometrial stromal cells via
hypoxia-inducible factor 1α upregulation-mediated β-catenin
activation in endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 23:531–541. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Becker CM, Rohwer N, Funakoshi T, Cramer
T, Bernhardt W, Birsner A, Folkman J and D'Amato RJ:
2-methoxyestradiol inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1{alpha} and
suppresses growth of lesions in a mouse model of endometriosis. Am
J Pathol. 172:534–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|