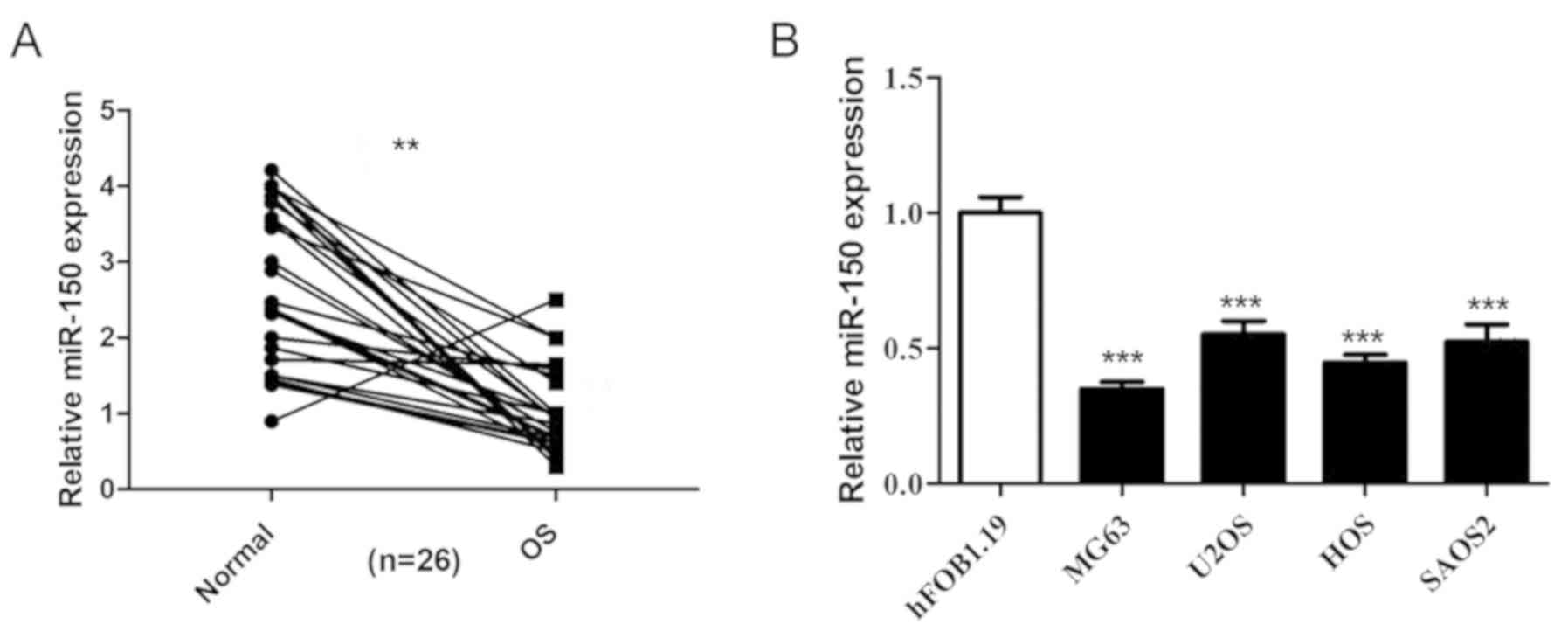
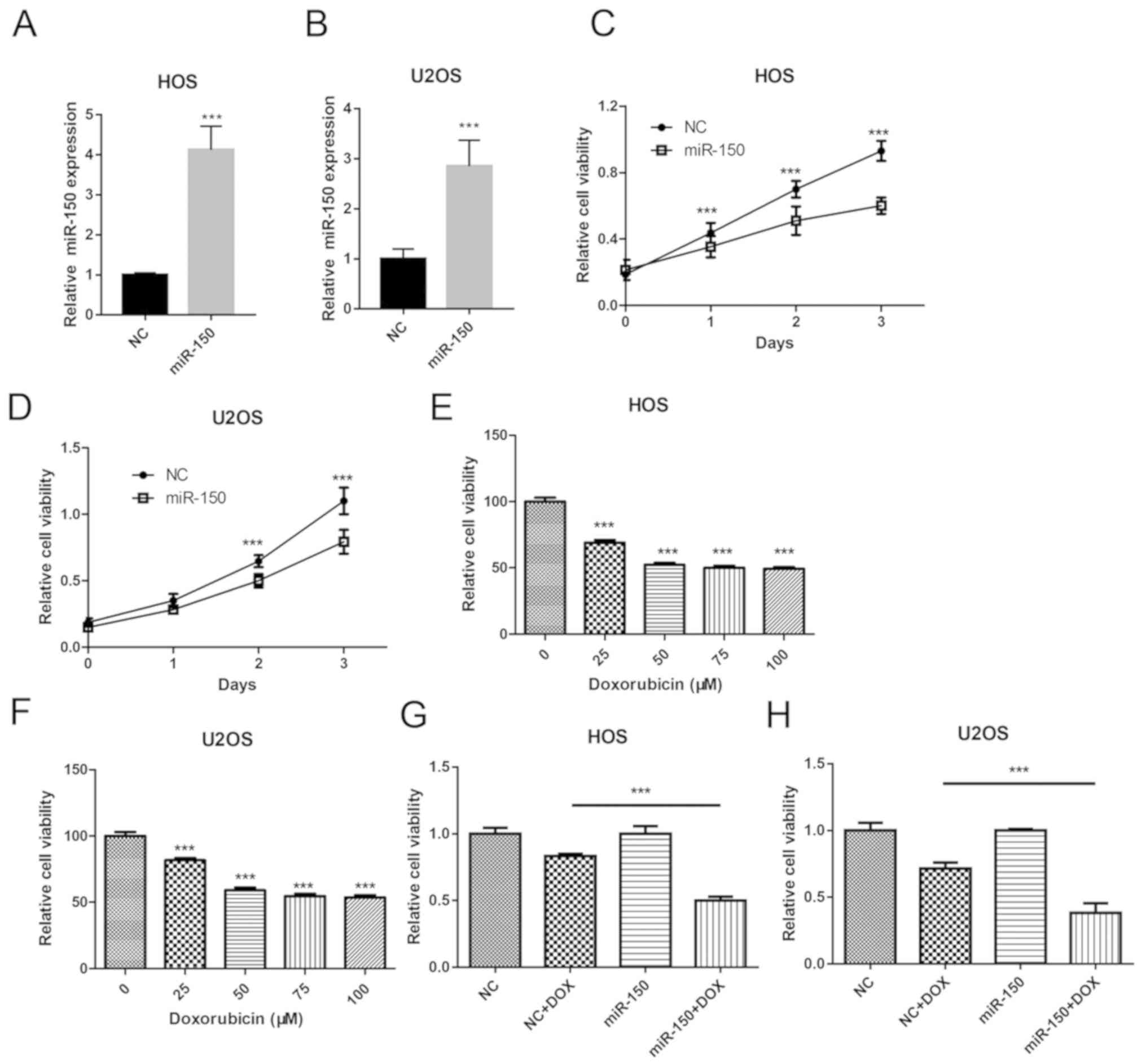
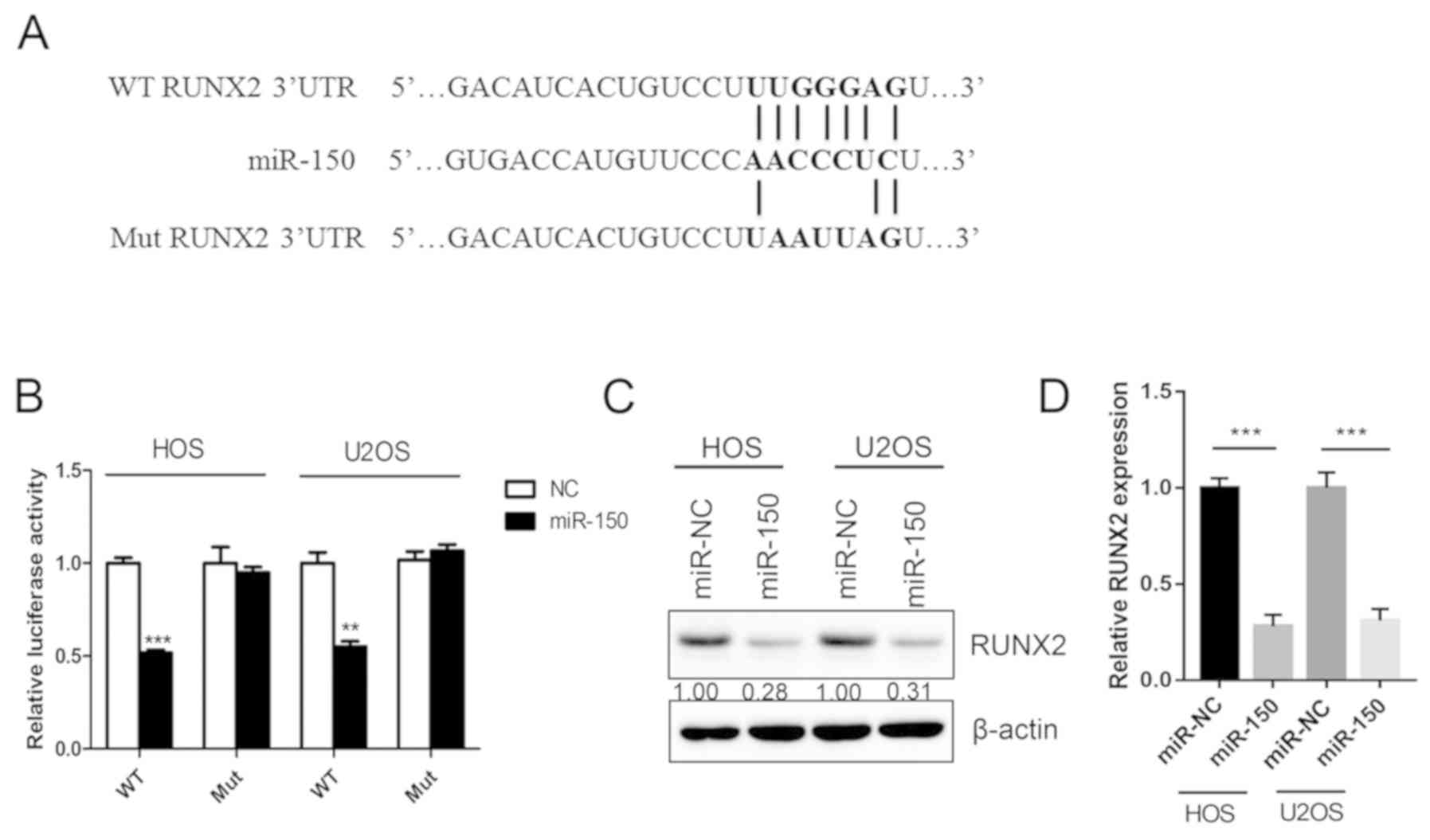
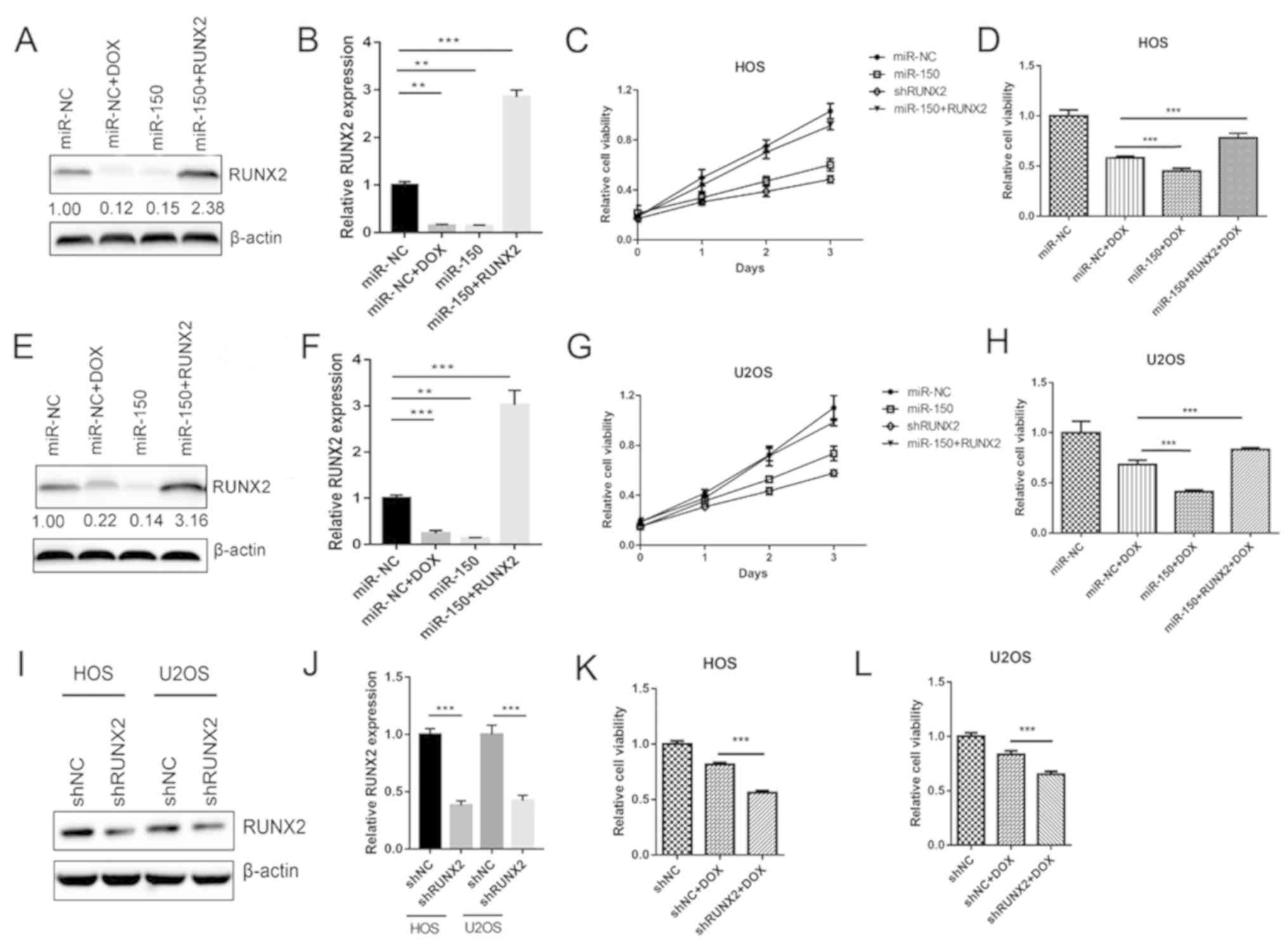
|
1
|
Mousa SA, Gallati C, Simone T, Dier E,
Yalcin M, Dyskin E, Thangirala S, Hanko C and Rebbaa A: Dual
targeting of the antagonistic pathways mediated by Sirt1 and TXNIP
as a putative approach to enhance the efficacy of anti-aging
interventions. Aging (Albany NY). 1:412–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bielack SS, Marina N, Ferrari S, Helman
LJ, Smeland S, Whelan JS and Reaman GH: Osteosarcoma: The same old
drugs or more? J Clin Oncol. 26:3102–3105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Longhi A, Errani C, De Paolis M, Mercuri M
and Bacci G: Primary bone osteosarcoma in the pediatric age: State
of the art. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:423–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gorlick R and Khanna C: Osteosarcoma. J
Bone Mineral Res. 25:683–691. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bacci G, Briccoli A, Rocca M, Ferrari S,
Donati D, Longhi A, Bertoni F, Bacchini P, Giacomini S, Forni C, et
al: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the extremities
with metastases at presentation: Recent experience at the Rizzoli
Institute in 57 patients treated with cisplatin, doxorubicin, and a
high dose of methotrexate and ifosfamide. Ann Oncol. 14:1126–1134.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rainusso N, Wang LL and Yustein JT: The
adolescent and young adult with cancer: State of the art e bone
tumors. Curr Oncol Rep. 15:296–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang T, Ji F, Dai Z, Xie Y and Yuan D:
Increased expression of microRNA-191 as a potential serum biomarker
for diagnosis and prognosis in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Biomark.
15:543–550. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Muoio DM: TXNIP links redox circuitry to
glucose control. Cell Metab. 5:412–414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Forrester MT, Seth D, Hausladen A, Eyler
CE, Foster MW, Matsumoto A, Benhar M, Marshall HE and Stamler JS:
Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) is a feedback regulator of
S-nitrosylation. J Biol Chem. 284:36160–36166. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dreyer F and Baur A: Biogenesis and
functions of exosomes and extracellular vesicles. Methods Mol Biol.
1448:201–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q and
Yin Y: Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show
significantly different biological patterns: From functions to
targets. PLoS One. 5(pii): e130672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jones KB, Salah Z, Del Mare S, Galasso M,
Gaudio E, Nuovo GJ, Lovat F, LeBlanc K, Palatini J, Randall RL, et
al: miRNA signatures associate with pathogenesis and progression of
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:1865–1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li CH, Yu TB, Qiu HW, Zhao X, Zhou CL and
Qi C: miR-150 is downregulated in osteosarcoma and suppresses cell
proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting ROCK1. Oncol
Lett. 13:2191–2197. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Quan X, Chen D, Li M, Chen X and Huang M:
MicroRNA-150-5p and SRC kinase signaling inhibitor 1 involvement in
the pathological development of gastric cancer. Exp Ther Med.
18:2667–2674. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin M, Shi C, Yang C, Liu J and Huang G:
Upregulated circRNA ARHGAP10 predicts an unfavorable prognosis in
NSCLC through regulation of the miR-150-5p/GLUT-1 axis. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 18:219–231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Xu X, Pan B, Zeng K, Xu M, Liu X,
He B, Pan Y, Sun H and Wang S: miR-150-5p suppresses tumor
progression by targeting VEGFA in colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany
NY). 10:3421–3437. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JH, Choi YS, Park JH, Kim H, Lee I,
Won YB, Yun BH, Park JH, Seo SK, Lee BS and Cho S: miR-150-5p may
contribute to pathogenesis of human leiomyoma via regulation of the
Akt/p27Kip1 pathway in vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 20(pii): E26842019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sadikovic B, Thorner P, Chilton-Macneill
S, Martin JW, Cervigne NK, Squire J and Zielenska M: Expression
analysis of genes associated with human osteosarcoma tumors shows
correlation of RUNX2 overexpression with poor response to
chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 10:2022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Villadsen SB, Bramsen JB, Ostenfeld MS,
Wiklund ED, Fristrup N, Gao S, Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Borre M,
Ørntoft TF, et al: The miR-143/-145 cluster regulates plasminogen
activator inhibitor-1 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 106:366–374.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, Kawakami K,
Enokida H, Yoshino H, Nohata N, Fuse M, Seki N and Nakagawa M:
SWAP70, actin-binding protein, function as an oncogene targeting
tumor-suppressive miR-145 in prostate cancer. Prostate.
71:1559–1567. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takagi T, Iio A, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T,
Tanigawa N and Akao Y: Decreased expression of microRNA-143 and
−145 in human gastric cancers. Oncology. 77:12–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang M, Lin L, Cai H, Tang J and Zhou Z:
MicroRNA-145 downregulation associates with advanced tumor
progression and poor prognosis in patients suffering osteosarcoma.
Onco Targets Ther. 6:833–838. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watanabe A, Tagawa H, Yamashita J, Teshima
K, Nara M, Iwamoto K, Kume M, Kameoka Y, Takahashi N, Nakagawa T,
et al: The role of microRNA-150 as a tumor suppressor in malignant
lymphoma. Leukemia. 25:1324–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Aireti A, Aihaiti A and Li K:
Expression of microRNA-150 and its Target Gene IGF2BP1 in human
osteosarcoma and their clinical implications. Pathol Oncol Res.
25:527–533. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Chen L, Wang W, Meng FB, Zhao RT and
Chen Y: MicroRNA-150 inhibits cell invasion and migration and is
downregulated in human osteosarcoma. Cytogenet Genome Res.
146:124–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghali O, Chauveau C, Hardouin P, Broux O
and Devedjian JC: TNF-alpha's effects on proliferation and
apoptosis in human mesenchymal stem cells depend on RUNX2
expression. J Bone Miner Res. 25:1616–1626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Olfa G, Christophe C, Philippe L, Romain
S, Khaled H, Pierre H, Odile B and Jean-Christophe D: RUNX2
regulates the effects of TNFalpha on proliferation and apoptosis in
SaOs-2 cells. Bone. 46:901–910. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nathan SS, Pereira BP, Zhou YF, Gupta A,
Dombrowski C, Soong R, Pho RW, Stein GS, Salto-Tellez M, Cool SM
and van Wijnen AJ: Elevated expression of Runx2 as a key parameter
in the etiology of osteosarcoma. Mol Biol Rep. 36:153–158. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pereira BP, Zhou Y, Gupta A, Leong DT,
Aung KZ, Ling L, Pho RW, Galindo M, Salto-Tellez M, Stein GS, et
al: Runx2, p53, and pRB status as diagnostic parameters for
deregulation of osteoblast growth and differentiation in a new
pre-chemotherapeutic osteosarcoma cell line (OS1). J Cell Physiol.
221:778–788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee DH, Qi J, Bradner JE, Said JW, Doan
NB, Forscher C, Yang H and Koeffler HP: Synergistic effect of JQ1
and rapamycin for treatment of human osteosarcoma. Int J Cancer.
136:2055–2064. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|