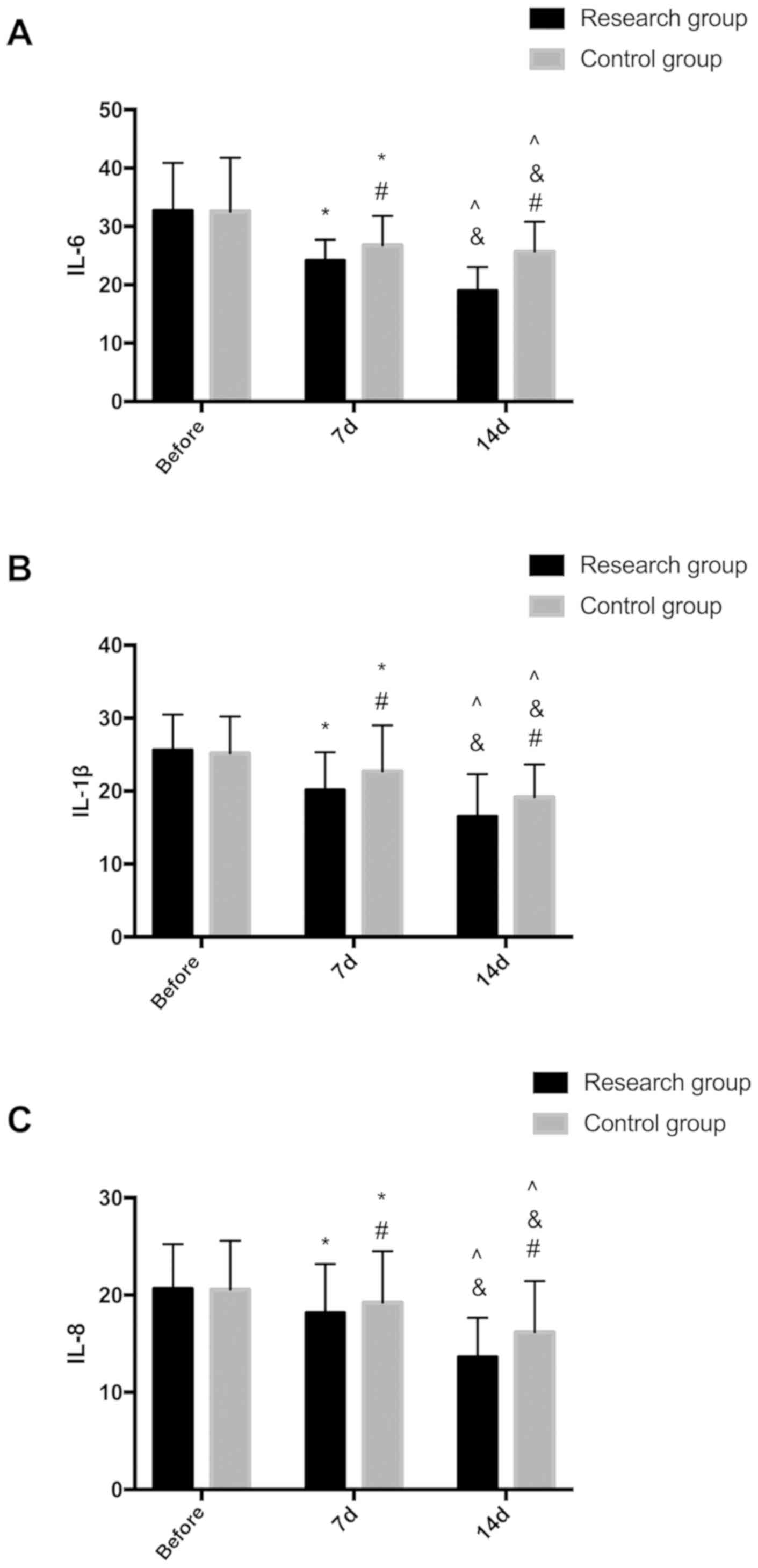
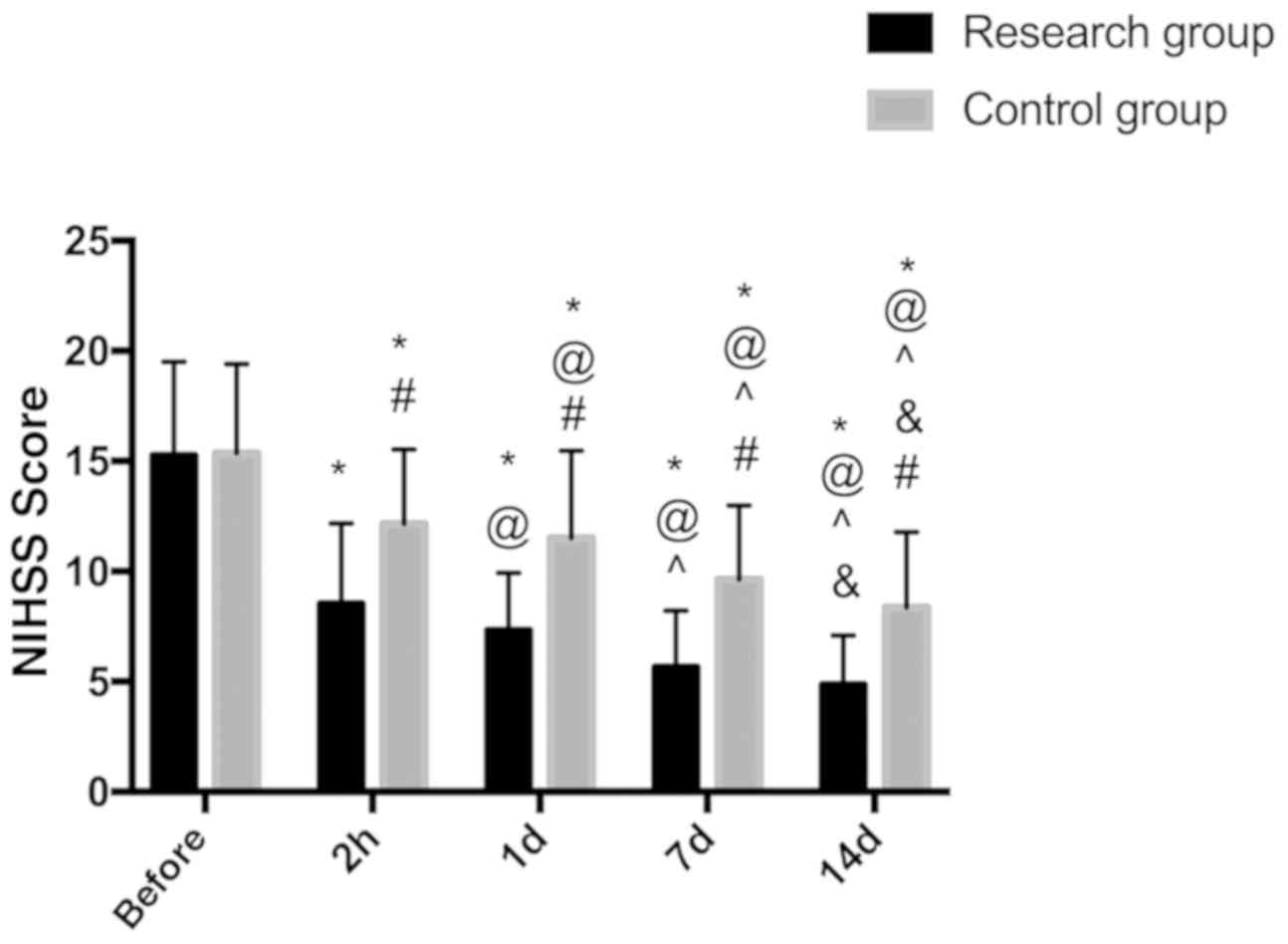
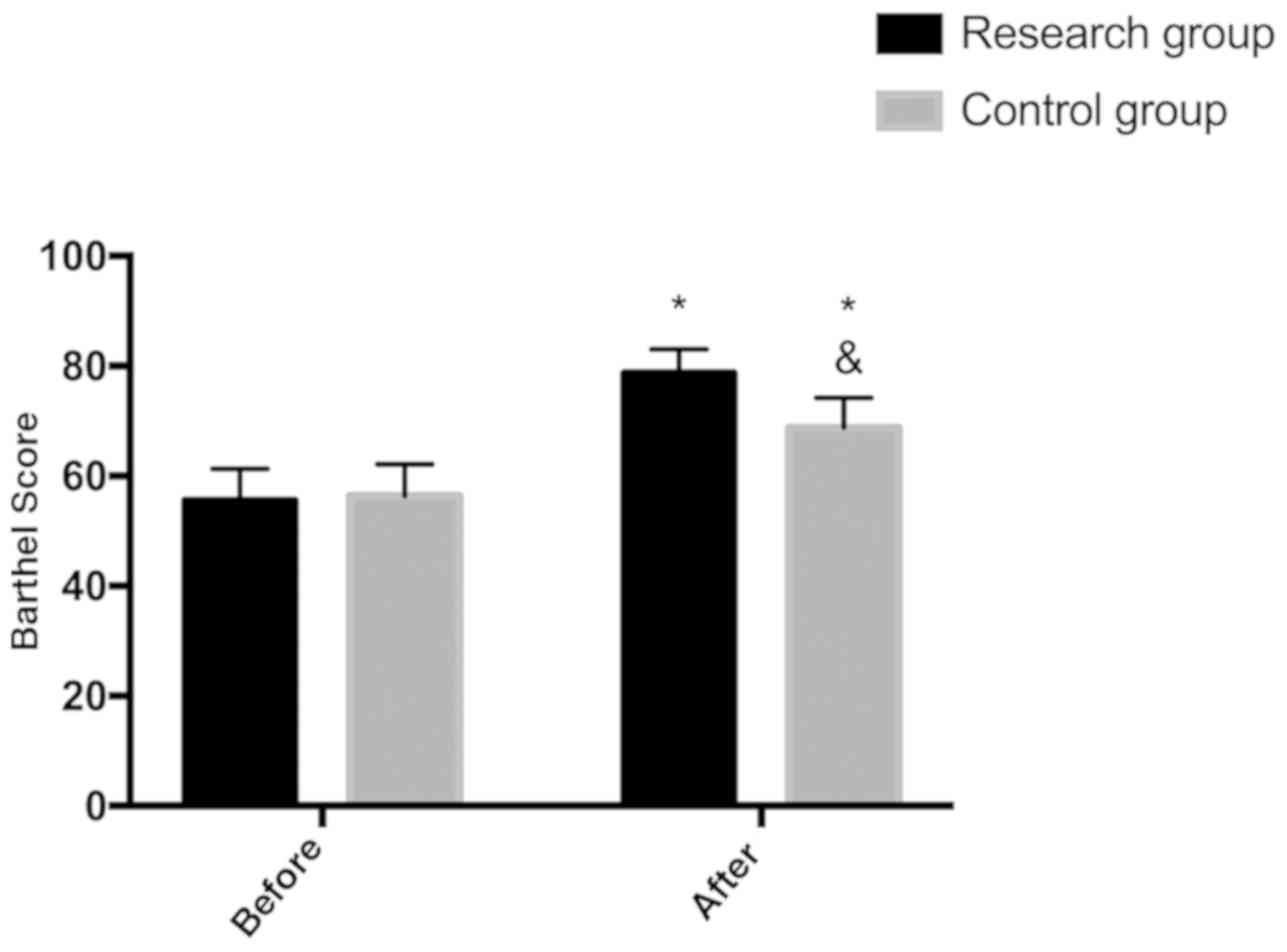
|
1
|
Horie N, Tateishi Y, Morikawa M, Morofuji
Y, Hayashi K, Izumo T, Tsujino A, Nagata I and Matsuo T: Acute
stroke with major intracranial vessel occlusion: characteristics of
cardioembolism and atherosclerosis-related in situ
stenosis/occlusion. J Clin Neurosci. 32:24–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park MG, Yoon CH, Baik SK and Park KP:
Susceptibility vessel sign for intra-arterial thrombus in acute
posterior cerebral artery infarction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
24:1229–1234. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jayaraman MV, Hussain MS, Abruzzo T,
Albani B, Albuquerque FC, Alexander MJ, Ansari SA, Arthur AS,
Baxter B, Bulsara KR, et al: Embolectomy for stroke with emergent
large vessel occlusion (ELVO): Report of the Standards and
Guidelines Committee of the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery.
J Neurointerv Surg. 7:316–321. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferrer I and Vidal N: Neuropathology of
cerebrovascular diseases. Handb Clin Neurol. 145:79–114. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vedantham S, Piazza G, Sista AK and
Goldenberg NA: Guidance for the use of thrombolytic therapy for the
treatment of venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis.
41:68–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lindekleiv H, Berge E, Bruins Slot KM and
Wardlaw JM: Percutaneous vascular interventions versus intravenous
thrombolytic treatment for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. Oct 26–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1002/14651858.CD009292.pub2. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tian Q, Zhu G and Dong S: Clinical
efficacy of neurointerventional catheter thrombolysis for cerebral
infarction. J Clin Nurs Res. Nov 30–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
doi: 10.26689/jcnr.v3i6.867.
|
|
8
|
Lei X, Zheng H, Wang Y and Liu C:
Observation of the clinical effect of interventional therapy of
acute cerebral infarction with digital subtraction angiography.
Chin J Primary Med Pharm. 24:3152–3155. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Rao ACA, Shah SA, Sim BW, Yun ST, Jain NS,
Kalani Y and Francis IC: Neuroradiological endovascular
intervention for diplopia in a case of aneurysmal aberrant
regeneration of the third nerve. Cureus. 9:e13402017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xianxian Z, Chengsong Y, Qiang M, Fei W,
Lin S, Huiyan D and Zili G: The efficiency analysis of thrombolytic
rt-PA combined with intravascular interventional therapy in
patients with acute basilar artery occlusion. Int J Biol Sci.
13:57–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taslakian B, Sebaaly MG and Al-Kutoubi A:
Patient evaluation and preparation in vascular and interventional
radiology: What every interventional radiologist should know (part
2: patient preparation and medications). Cardiovasc Intervent
Radiol. 39:489–499. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mine B, Tancredi I, Aljishi A, Alghamdi F,
Beltran M, Herchuelz M and Lubicz B: Follow-up of intracranial
aneurysms treated by a WEB flow disrupter: A comparative study of
DSA and contrast-enhanced MR angiography. J Neurointerv Surg.
8:615–620. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Papafaklis MI, Bourantas CV, Yonetsu T,
Vergallo R, Kotsia A, Nakatani S, Lakkas LS, Athanasiou LS, Naka
KK, Fotiadis DI, et al: Anatomically correct three-dimensional
coronary artery reconstruction using frequency domain optical
coherence tomographic and angiographic data: Head-to-head
comparison with intravascular ultrasound for endothelial shear
stress assessment in humans. EuroIntervention. 11:407–415. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Athanasiou L, Rigas G, Sakellarios AI,
Exarchos TP, Siogkas PK, Bourantas CV, Garcia-Garcia HM, Lemos PA,
Falcao BA, Michalis LK, et al: Three-dimensional reconstruction of
coronary arteries and plaque morphology using CT angiography -
comparison and registration with IVUS. BMC Med Imaging. 16:92016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jeyaseelan RD, Vargo MM and Chae J:
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) as an early
predictor of poststroke dysphagia. PM R. 7:593–598. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Albers GW, Lansberg MG, Kemp S, Tsai JP,
Lavori P, Christensen S, Mlynash M, Kim S, Hamilton S, Yeatts SD,
et al: A multicenter randomized controlled trial of endovascular
therapy following imaging evaluation for ischemic stroke (DEFUSE
3). Int J Stroke. 12:896–905. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prodinger B, O'Connor RJ, Stucki G and
Tennant A: Establishing score equivalence of the Functional
Independence Measure motor scale and the Barthel Index, utilising
the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and
Health and Rasch measurement theory. J Rehabil Med. 49:416–422.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Buschmann EE, Hillmeister P, Bondke
Persson A, Liebeskind DS, Schlich L, Kamenzky R, Busjahn A,
Buschmann IR, Bramlage P, Hetzel A, et al: Short-term external
counterpulsation augments cerebral blood flow and tissue
oxygenation in chronic cerebrovascular occlusive disease. Eur J
Neurol. 25:1326–1332. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nerva JD and Levitt MR: Medical and
surgical treatment of cerebrovascular occlusive disease. Principles
Neurol Surg. Content Repository Only. 241–253. e3:2018.
|
|
20
|
Pulicherla KK and Verma MK: Targeting
therapeutics across the blood brain barrier (BBB), prerequisite
towards thrombolytic therapy for cerebrovascular disorders - an
overview and advancements. AAPS PharmSciTech. 16:223–233. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tocci G and Presta V: Increased arterial
stiffness and haemorrhagic transformation in ischaemic stroke after
thrombolysis: A new marker of risk for cerebrovascular events and
complications. Int J Cardiol. 243:471–472. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suzuki K, Ikeda S, Ueda K, Nakamura T,
Okabe M, Kadomura T, Baba R and Colbeth RE: Development of
angiography system with cone-beam reconstruction using large-area
flat-panel detector. Proc SPIE. 5368:488–498. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ishida F, Kawaguchi K, Mizuno M, Hoshino
T, Murao K and Taki W: The accuracy and usefulness of 3D-DSA and
3D-CT angiography for cerebral aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol. 7
(Suppl 1):181–186. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muruet W, Rudd A, Wolfe CDA and Douiri A:
Long-term survival after intravenous thrombolysis for ischemic
stroke: A propensity score-matched cohort with up to 10-year
follow-up. Stroke. 49:607–613. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|