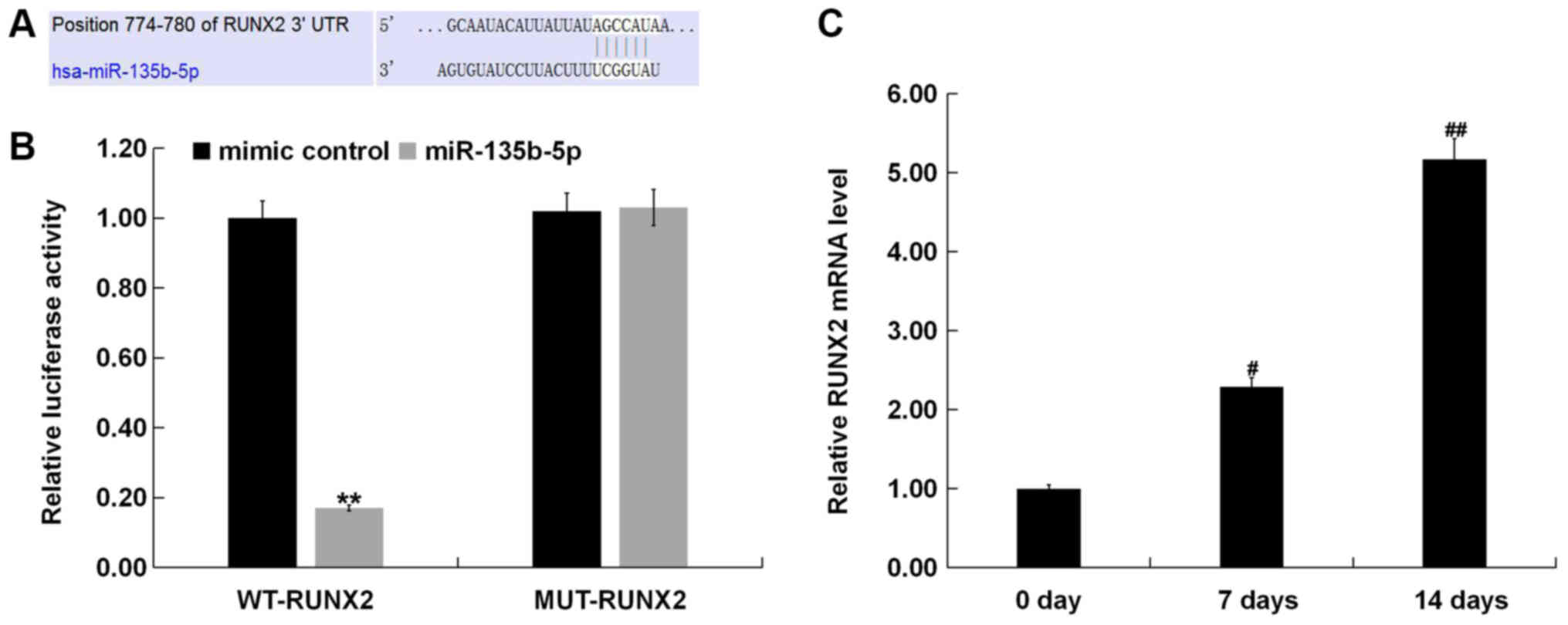
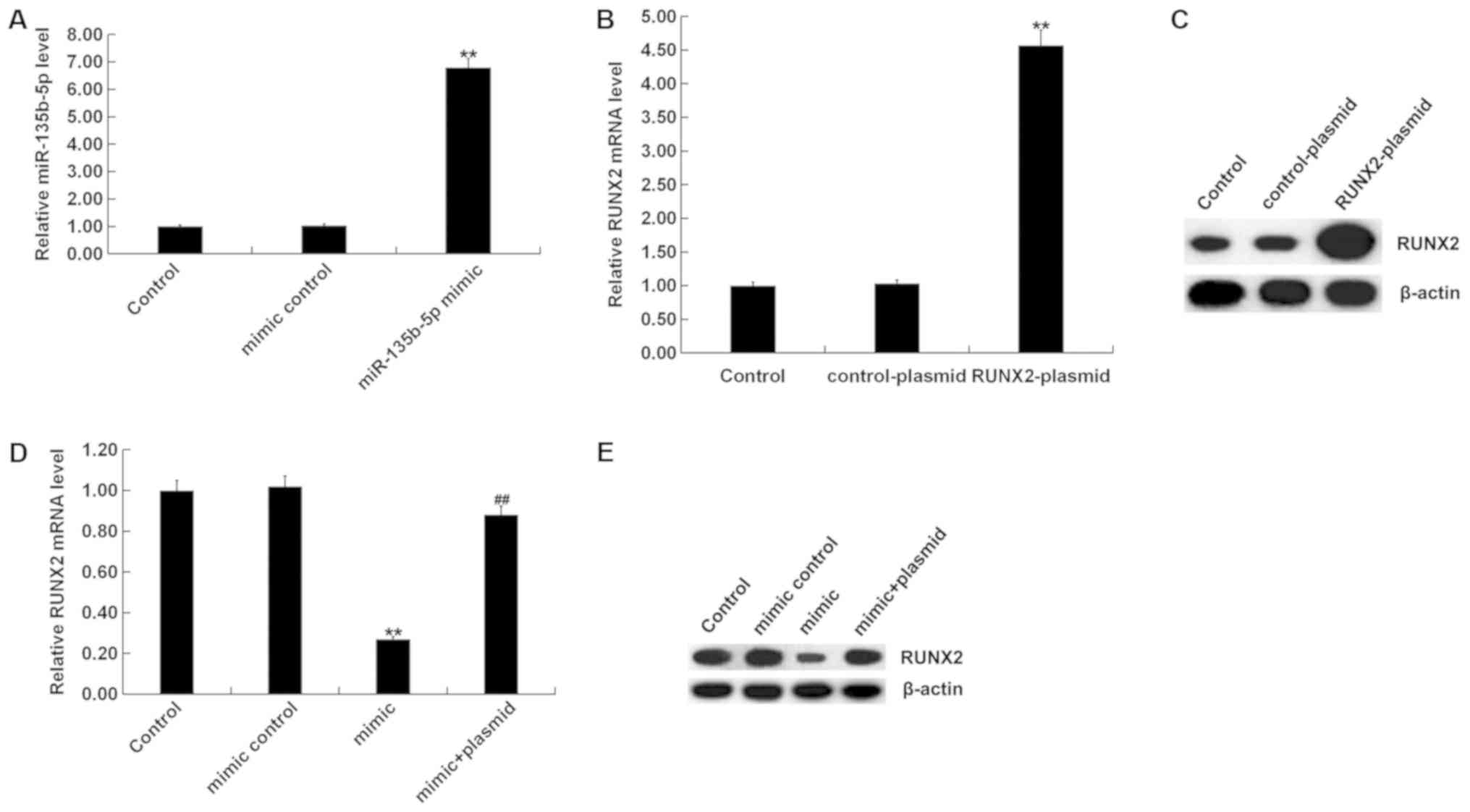
|
1
|
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki
EM, Tanner B, Randall S and Lindsay R: Erratum to: Clinician's
guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.
26:2045–2047. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sotorník I: Osteoporosis-epidemiology and
pathogenesis. Vnitr Lek. 62 (Suppl 6):S84–S87. 2016.(In Czech).
|
|
3
|
Body JJ, Bergmann P, Boonen S, Boutsen Y,
Devogelaer JP, Goemaere S, Kaufman JM, Rozenberg S and Reginster
JY: Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of
postmenopausal osteoporosis: A consensus document by the Belgian
Bone Club. Osteoporos Int. 21:1657–1680. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen P, Li Z and Hu Y: Prevalence of
osteoporosis in China: A meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC
Public Health. 16:10392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Svedbom A, Hernlund E, Ivergård M,
Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jönsson B and Kanis
JA; EU Review Panel of IOF, : Osteoporosis in the European Union: A
compendium of country-specifc reports. Arch Osteoporos. 8:1372013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ge DW, Wang WW, Chen HT, Yang L and Cao
XJ: Functions of microRNAs in osteoporosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:4784–4789. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dadra A, Aggarwal S, Kumar P, Kumar V,
Dibar DP and Bhadada SK: High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency
and osteoporosis in patients with fragility fractures of hip: A
pilot study. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 10:1097–1100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leutner M, Matzhold C, Bellach L,
Deischinger C, Harreiter J, Thurner S, Klimek P and Kautzky-Willer
A: Diagnosis of osteoporosis in statin-treated patients is
dose-dependent. Ann Rheum Dis. 78:1706–1711. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Loh FE, Stuart B, Sturpe D, Davidoff A,
Onukwugha E and Hochberg M: Osteoporosis medication use: A
comparison of elderly females living in long-term care facilities
versus community Dwellers. Sr Care Pharm. 34:109–126.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–97. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Darnet S, Moreira FC, Hamoy IG, Burbano R,
Khayat A, Cruz A, Magalhães L, Silva A, Santos S, Demachki S, et
al: High-throughput sequencing of miRNAs reveals a tissue signature
in gastric cancer and suggests novel potential biomarkers.
Bioinform Biol Insights. 9 (Suppl 1):S1–S8. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Tseng CW, Lin CC, Chen CN, Huang HC and
Juan HF: Integrative network analysis reveals active microRNAs and
their functions in gastric cancer. BMC Syst Biol. 5:992011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cui H, Wang L, Gong P, Zhao C, Zhang S,
Zhang K, Zhou R, Zhao Z and Fan H: Deregulation between miR-29b/c
and DNMT3A is associated with epigenetic silencing of the CDH1
gene, affecting cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01239262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He Y, Wang J, Wang J, Yung VY, Hsu E, Li
A, Kang Q, Ma J, Han Q, Jin P, et al: MicroRNA-135b regulates
apoptosis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by targeting
large tumor suppressor kinase 2. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1382–1395.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Imam JS, Plyler JR, Bansal H, Prajapati S,
Bansal S, Rebeles J, Chen HI, Chang YF, Panneerdoss S, Zoghi B, et
al: Genomic loss of tumor suppressor miRNA-204 promotes cancer cell
migration and invasion by activating AKT/mTOR/Rac1 signaling and
actin reorganization. PLoS One. 7:e523972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Valeri N, Braconi C, Gasparini P, Murgia
C, Lampis A, Paulus-Hock V, Hart JR, Ueno L, Grivennikov SI, Lovat
F, et al: MicroRNA-135b promotes cancer progression by acting as a
downstream effector of oncogenic pathways in colon cancer. Cancer
Cell. 25:469–483. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Xu D, Bao C, Zhang Y, Chen D, Zhao
F, Ding J, Liang L, Wang Q, Liu L, et al: MicroRNA-135b, a HSF1
target, promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating RECK
and EVI5 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2421–2433.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Y, Hu J, Sun W, Li S, Deng S and Li M:
MiR-29c inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of pancreatic
cancer by targeting ITGB1. Onco Targets Ther. 9:99–109.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhao M, Wu C, Zhang P, Tang
L, Zhang H, Chen X, Yang Y and Liu G: miRNA-29c suppresses lung
cancer cell adhesion to extracellular matrix and metastasis by
targeting integrin β1 and matrix metalloproteinase2 (MMP2). PLoS
One. 8:e701922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seeliger C, Karpinski K, Haug AT, Vester
H, Schmitt A, Bauer JS and van Griensven M: Five freely circulating
miRNAs and bone tissue miRNAs are associated with osteoporotic
fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 29:1718–1728. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Q, Li Y and Zhang Y, Ma L, Lin L,
Meng J, Jiang L, Wang L, Zhou P and Zhang Y: LncRNA MEG3 inhibited
osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
from postmenopausal osteoporosis by targeting miR-133a-3p. Biomed
Pharmacother. 89:1178–1186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li H, Xie H, Liu W, Hu R, Huang B, Tan YF,
Xu K, Sheng ZF, Zhou HD, Wu XP and Luo XH: A novel microRNA
targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and
contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest.
19:3666–3677. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li CJ, Cheng P, Liang MK, Chen YS, Lu Q,
Wang JY, Xia ZY, Zhou HD, Cao X, Xie H, et al: MicroRNA-188
regulates age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte
differentiation. J Clin Invest. 125:1509–1522. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Guo B, Li Q, Peng J, Yang Z, Wang
A, Li D, Hou Z, Lv K, Kan G, et al: miR-214 targets ATF4 to inhibit
bone formation. Nat Med. 19:93–100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng F, Wang F and Xu Z: MicroRNA-98-5p
prevents bone regeneration by targeting high mobility group AT-Hook
2. Exp Ther Med. 18:2660–2666. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zou W, Greenblatt MB, Brady N, Lotinun S,
Zhai B, de Rivera H, Singh A, Sun J, Gygi SP, Baron R, et al: The
microtubule-associated protein DCAMKL1 regulates osteoblast
function via repression of Runx2. J Exp Med. 210:1793–1806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu B, Xue F, Zhang C and Li G: Ginkgolide
B promotes osteoblast differentiation via activation of canonical
Wnt signalling and alleviates osteoporosis through a bone anabolic
way. J Cell Mol Med. 23:5782–5793. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao W, Zhang WL, Yang B, Sun J and Yang
MW: NIPA2 regulates osteoblast function via its effect on apoptosis
pathways in type 2 diabetes osteoporosis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 513:883–890. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yuan M, Wang Y and Qin YX: SPIO-Au
core-shell nanoparticles for promoting osteogenic differentiation
of MC3T3-E1 cells: Concentration-dependence study. J Biomed Mater
Res A. 105:3350–3359. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhai F, Song N, Ma J, Gong W, Tian H, Li
X, Jiang C and Wang H: FGF18 inhibits MC3T3-E1 cell osteogenic
differentiation via the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
16:4127–4132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Xu F, Pei HX, Zhu X, Lin X, Song
CY, Liang QH, Liao EY and Yuan LQ: Vaspin regulates the osteogenic
differentiation of MC3T3-E1 through the PI3K-Akt/miR-34c loop. Sci
Rep. 6:255782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schuiling KD, Robinia K and Nye R:
Osteoporosis update. J Midwifery Womens Health. 56:615–627. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tucker KL: Dietary intake and bone status
with aging. Curr Pharm Des. 9:2687–2704. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Caillet P: Consensus development
conference: Diagnosis, prophylaxis, and treatment of osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis International. 295:914–915. 1987.
|
|
36
|
Wade SW, Strader C, Fitzpatrick LA,
Anthony MS and O'Malley CD: Estimating prevalence of osteoporosis:
Examples from industrialized countries. Arch Osteoporos. 9:1822014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Raisz LG: Pathogenesis of osteoporosis:
Concepts, conflicts, and prospects. J Clin Invest. 115:3318–3325.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Marie PJ and Kassem M: Osteoblasts in
osteoporosis: Past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur J
Endocrinol. 165:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ruiz-Gaspà S, Blanch-Rubió J,
Ciria-Recasens M, Monfort J, Tío L, Garcia-Giralt N, Nogués X,
Monllau JC, Carbonell-Abelló J and Pérez-Edo L: Reduced
proliferation and osteocalcin expression in osteoblasts of male
idiopathic osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int. 86:220–226. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kerschan-Schindl K: Prevention and
rehabilitation of osteoporosis. Wien Med Wochenschr. 166:22–27.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Moreira LD, Oliveira ML, Lirani-Galvão AP,
Marin-Mio RV, Santos RN and Lazaretti-Castro M: Physical exercise
and osteoporosis: Effects of different types of exercises on bone
and physical function of postmenopausal women. Arq Bras Endocrinol
Metabol. 58:514–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lian JB, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ, Stein
JL, Hassan MQ, Gaur T and Zhang Y: MicroRNA control of bone
formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:212–227. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Valenti MT, Dalle Carbonare L and Mottes
M: Role of microRNAs in progenitor cell commitment and osteogenic
differentiation in health and disease (Review). Int J Mol Med.
41:2441–2449. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li ZW, Zhu YR, Zhou XZ, Zhuo BB and Wang
XD: microRNA-135b expression silences Ppm1e to provoke AMPK
activation and inhibit osteoblastoma cell proliferation.
Oncotarget. 8:26424–26433. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li P, Fan JB, Gao Y, Zhang M, Zhang L,
Yang N and Zhao X: miR-135b-5p inhibits LPS-induced TNFα production
via silencing AMPK phosphatase Ppm1e. Oncotarget. 7:77978–77986.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han X, Saiyin H, Zhao J, Fang Y, Rong Y,
Shi C, Lou W and Kuang T: Overexpression of miR-135b-5p promotes
unfavorable clinical characteristics and poor prognosis via the
repression of SFRP4 in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
8:62195–62207. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stein GS, Lian JB, van Wijnen AJ, Stein
JL, Montecino M, Javed A, Zaidi SK, Young DW, Choi JY and Pockwinse
SM: Runx2 control of organization, assembly and activity of the
regulatory machinery for skeletal gene expression. Oncogene.
23:4315–4329. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiao ZS, Hjelmeland AB and Quarles LD:
Selective deficiency of the ‘bone-related’ Runx2-II unexpectedly
preserves osteoblast-mediated skeletogenesis. J Biol Chem.
279:20307–20313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang S, Wei D, Wang D, Phimphilai M,
Krebsbach PH and Franceschi RT: In vitro and in vivo synergistic
interactions between the Runx2/Cbfa1 transcription factor and bone
morphogenetic protein-2 in stimulating osteoblast differentiation.
J Bone Miner Res. 18:705–715. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Komori T: Regulation of osteoblast
differentiation by Runx2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 658:43–9. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jia F, Zhang Z and Zhang X:
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in
osteosarcoma cells by targeting RUNX2/CDK4 and inhibition of MAPK
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:6420–6430. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li N, Wang WB, Bao H, Shi Q, Jiang ZL, Qi
YX and Han Y: MicroRNA-129-1-3p regulates cyclic stretch-induced
endothelial progenitor cell differentiation by targeting Runx2. J
Cell Biochem. 120:5256–5267. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|