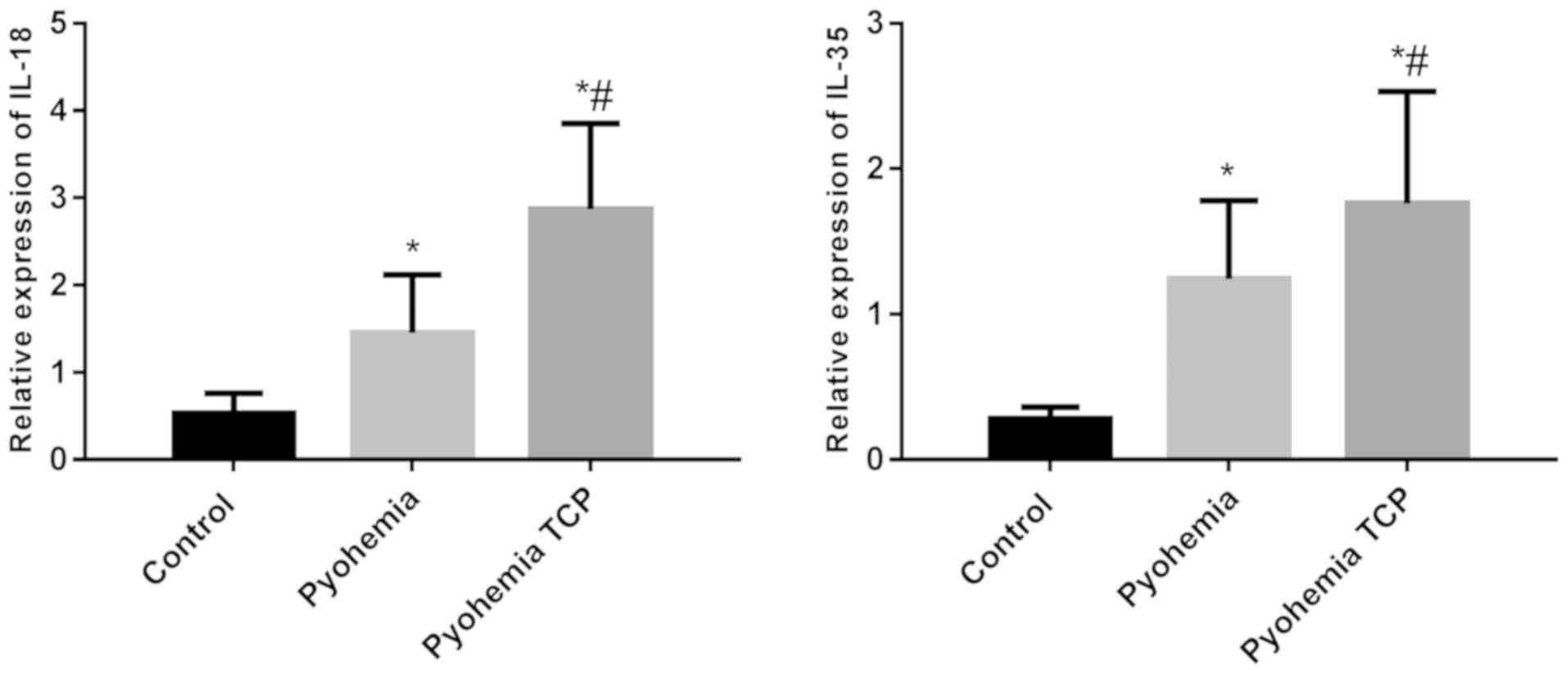
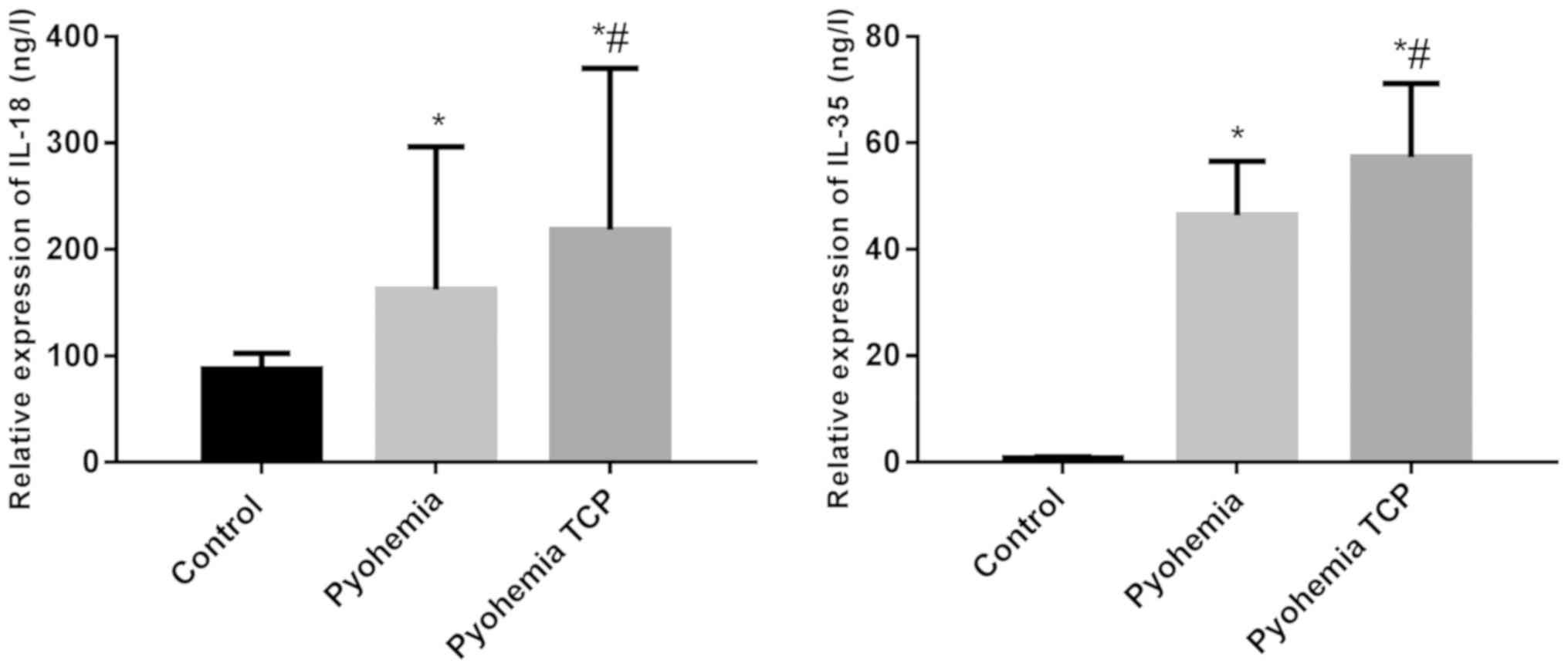
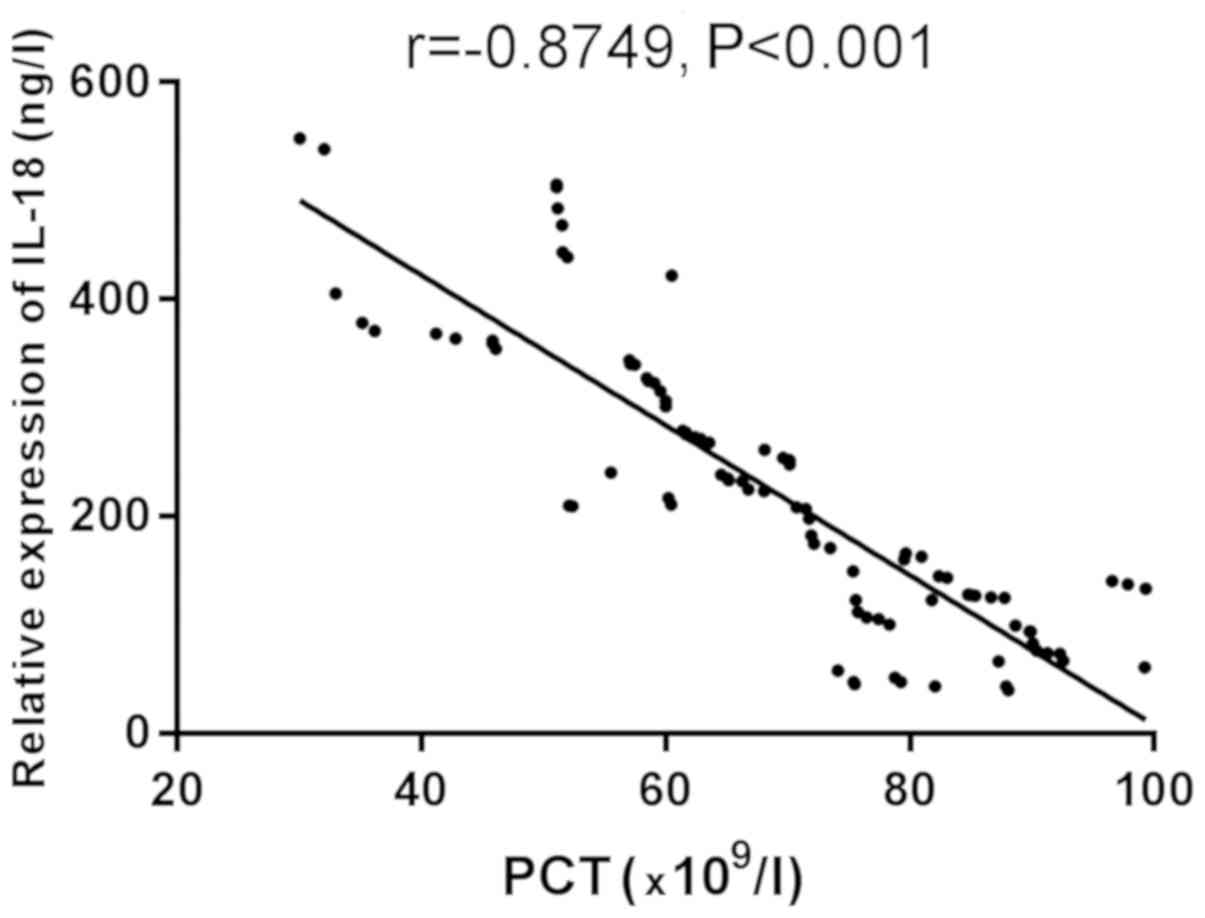
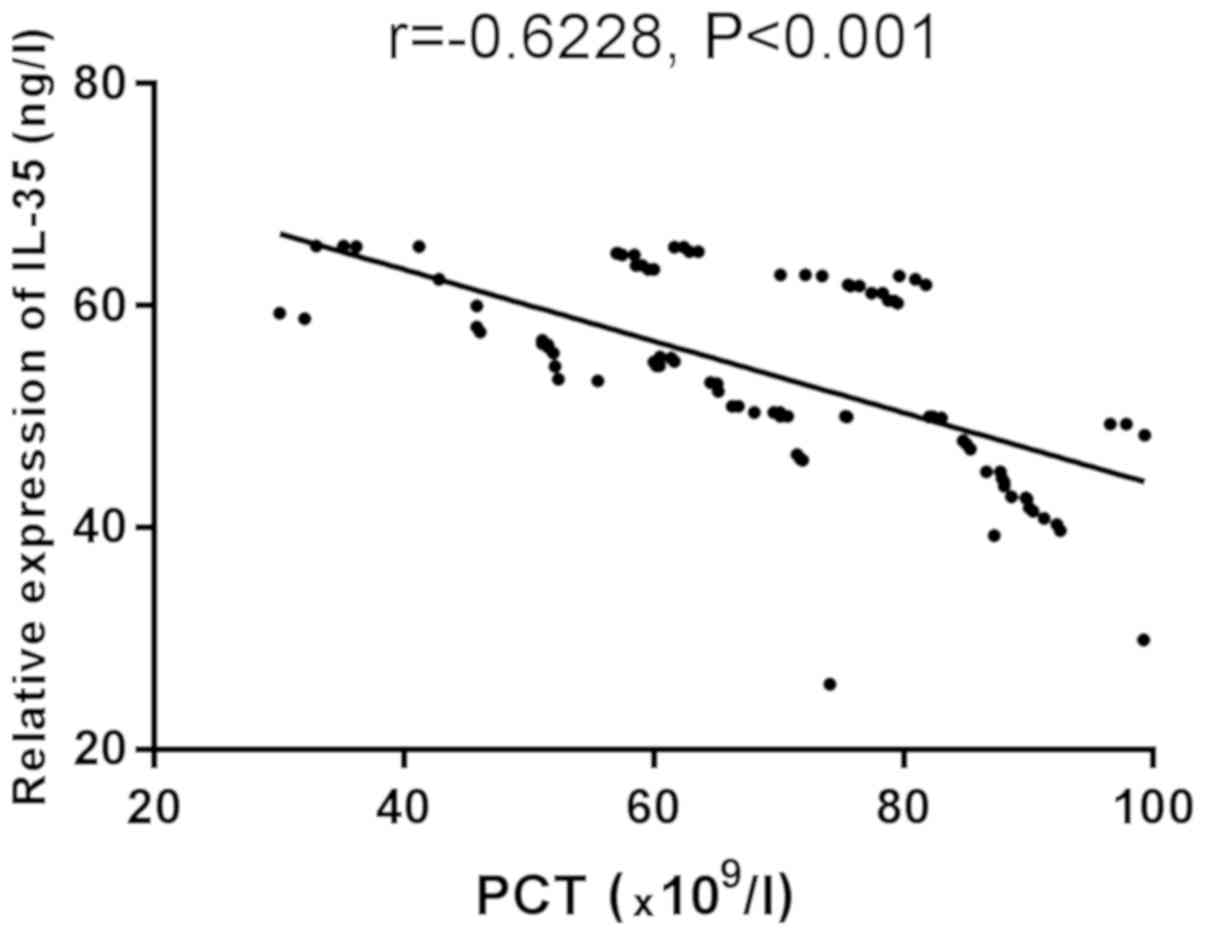
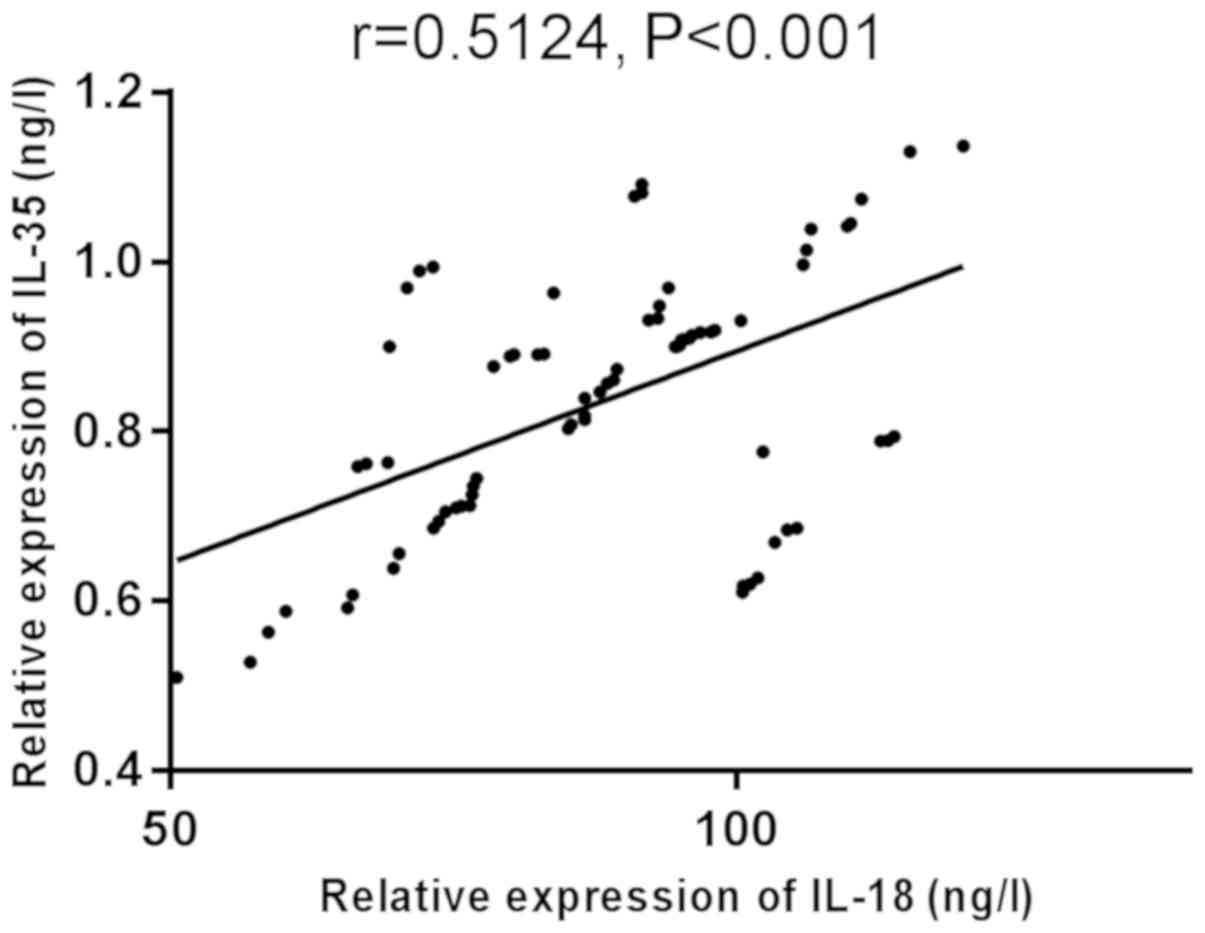
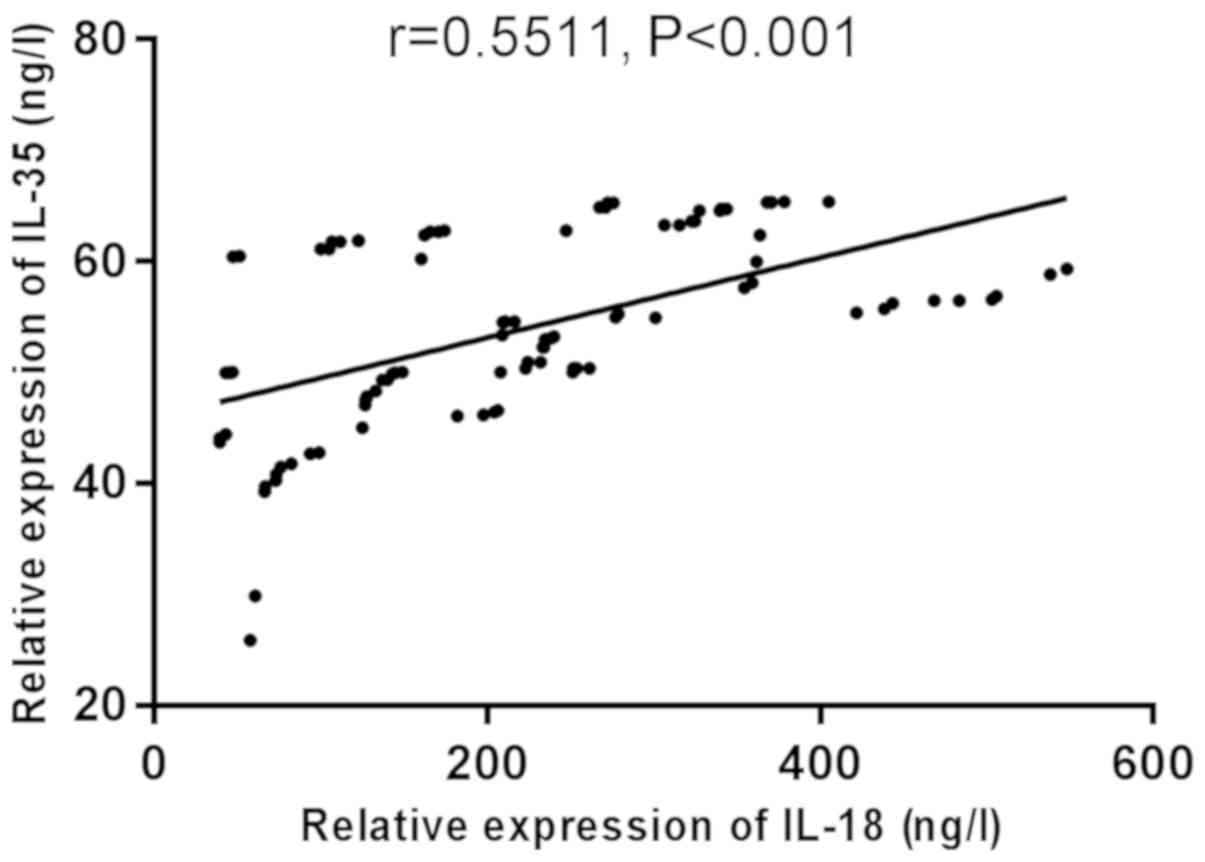
|
1
|
Dewitte A, Lepreux S, Villeneuve J,
Rigothier C, Combe C, Ouattara A and Ripoche J: Blood platelets and
sepsis pathophysiology: A new therapeutic prospect in critically
[corrected] ill patients? Ann Intensive Care. 7:1152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K;
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists, : Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Larkin CM, Santos-Martinez MJ, Ryan T and
Radomski MW: Sepsis-associated thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res.
141:11–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yaguchi A, Lobo FL, Vincent JL and Pradier
O: Platelet function in sepsis. J Thromb Haemost. 2:2096–2102.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vandijck DM, Blot SI, De Waele JJ, Hoste
EA, Vandewoude KH and Decruyenaere JM: Thrombocytopenia and outcome
in critically ill patients with bloodstream infection. Heart Lung.
39:21–26. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu R, Lin F, Bao C, Huang H, Ji C, Wang S,
Jin L, Sun L, Li K, Zhang Z, et al: Complement 5a receptor-mediated
neutrophil dysfunction is associated with a poor outcome in sepsis.
Cell Mol Immunol. 13:103–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li MF, Li XL, Fan KL, Yu YY, Gong J, Geng
SY, Liang YF, Huang L, Qiu JH, Tian XH, et al: Platelet
desialylation is a novel mechanism and a therapeutic target in
thrombocytopenia during sepsis: An open-label, multicenter,
randomized controlled trial. J Hematol Oncol. 10:1042017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeaman MR and Bayer AS: Staphylococcus
aureus, platelets, and the heart. Curr Infect Dis Rep.
2:281–298. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Claushuis TA, van Vught LA, Scicluna BP,
Wiewel MA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Hoogendijk AJ, Ong DS, Cremer OL,
Horn J, Franitza M, et al Molecular Diagnosis and Risk
Stratification of Sepsis Consortium, : Thrombocytopenia is
associated with a dysregulated host response in critically ill
sepsis patients. Blood. 127:3062–3072. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwak A, Lee Y, Kim H and Kim S:
Intracellular interleukin (IL)-1 family cytokine processing enzyme.
Arch Pharm Res. 39:1556–1564. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eidt MV, Nunes FB, Pedrazza L, Caeran G,
Pellegrin G, Melo DA, Possuelo L, Jost RT, Dias HB, Donadio MV, et
al: Biochemical and inflammatory aspects in patients with severe
sepsis and septic shock: The predictive role of IL-18 in mortality.
Clin Chim Acta. 453:100–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okuhara Y, Yokoe S, Iwasaku T, Eguchi A,
Nishimura K, Li W, Oboshi M, Naito Y, Mano T, Asahi M, et al:
Interleukin-18 gene deletion protects against sepsis-induced
cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting PP2A activity. Int J Cardiol.
243:396–403. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li M, Eckl J, Geiger C, Schendel DJ and
Pohla H: A novel and effective method to generate human
porcine-specific regulatory T cells with high expression of IL-10,
TGF-β1 and IL-35. Sci Rep. 7:39742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao P, Su Z, Lv X and Zhang J:
Interleukin-35 in asthma and its potential as an effective
therapeutic agent. Mediators Inflamm. 2017:59318652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sha X, Meng S, Li X, Xi H, Maddaloni M,
Pascual DW, Shan H, Jiang X, Wang H and Yang XF: Interleukin-35
inhibits endothelial cell activation by suppressing MAPK-AP-1
pathway. J Biol Chem. 290:19307–19318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E,
Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL and Ramsay G;
SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS, : 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS
International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit Care Med.
31:1250–1256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vardas K, Apostolou K, Briassouli E,
Goukos D, Psarra K, Botoula E, Tsagarakis S, Magira E, Routsi C,
Nanas S, et al: Early response roles for prolactin cortisol and
circulating and cellular levels of heat shock proteins 72 and 90α
in severe sepsis and SIRS. BioMed Res Int. 2014:8035612014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang G, Wang XM, Meng JX, Luan CL, Chen
JF, Wu YQ, Zhang XN and He ZY: Efficacy of recombinant human
thrombopoietin and recombinant human interleukin 11 for treatment
of chemotherapy induced thrombocytopenia in acute myeloid leukaemia
patients. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 26:234–238. 2018.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Semple JW and Freedman J: Platelets and
innate immunity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:499–511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yeaman MR: Platelets in defense against
bacterial pathogens. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:525–544. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan Y, Jiang W, Liu L, Wang X, Ding C,
Tian Z and Zhou R: Dopamine controls systemic inflammation through
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell. 160:62–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cui YL, Wang B, Gao HM, Xing YH, Li J, Li
HJ, Lin Z and Wang YQ: Interleukin-18 and miR-130a in severe sepsis
patients with thrombocytopenia. Patient Prefer Adherence.
10:313–319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vignali DA and Kuchroo VK: IL-12 family
cytokines: Immunological playmakers. Nat Immunol. 13:722–728. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kochetkova I, Golden S, Holderness K,
Callis G and Pascual DW: IL-35 stimulation of CD39+ regulatory T
cells confers protection against collagen II-induced arthritis via
the production of IL-10. J Immunol. 184:7144–7153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Du WX, He Y, Jiang HY, Ai Q and Yu JL:
Interleukin 35: A novel candidate biomarker to diagnose early onset
sepsis in neonates. Clin Chim Acta. 462:90–95. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oberholzer A, Steckholzer U, Kurimoto M,
Trentz O and Ertel W: Interleukin-18 plasma levels are increased in
patients with sepsis compared to severely injured patients. Shock.
16:411–414. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun RQ and Zhang SL: The value of serum
interleukin-18 and 10 in the evaluation of severity and prognosis
in the early stage of sepsis. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 23:299–301. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Emmanuilidis K, Weighardt H, Matevossian
E, Heidecke CD, Ulm K, Bartels H, Siewert JR and Holzmann B:
Differential regulation of systemic IL-18 and IL-12 release during
postoperative sepsis: High serum IL-18 as an early predictive
indicator of lethal outcome. Shock. 18:301–305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lally KP, Cruz E and Xue H: The role of
anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10 in protecting
murine neonates from Escherichia coli sepsis. J Pediatr
Surg. 35:852–855. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao HQ, Li WM, Lu ZQ, Sheng ZY and Yao
YM: The growing spectrum of anti-inflammatory interleukins and
their potential roles in the development of sepsis. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 35:242–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shaheen IA, Botros SKA and Morgan DS:
Detection of expression of IL-18 and its binding protein in
Egyptian pediatric immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Platelets.
25:193–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao J, Xu F, Lin S, Tao X, Xiang Y, Lai X
and Zhang L: IL-35 is elevated in clinical and experimental sepsis
and mediates inflammation. Clin Immunol. 161:89–95. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|