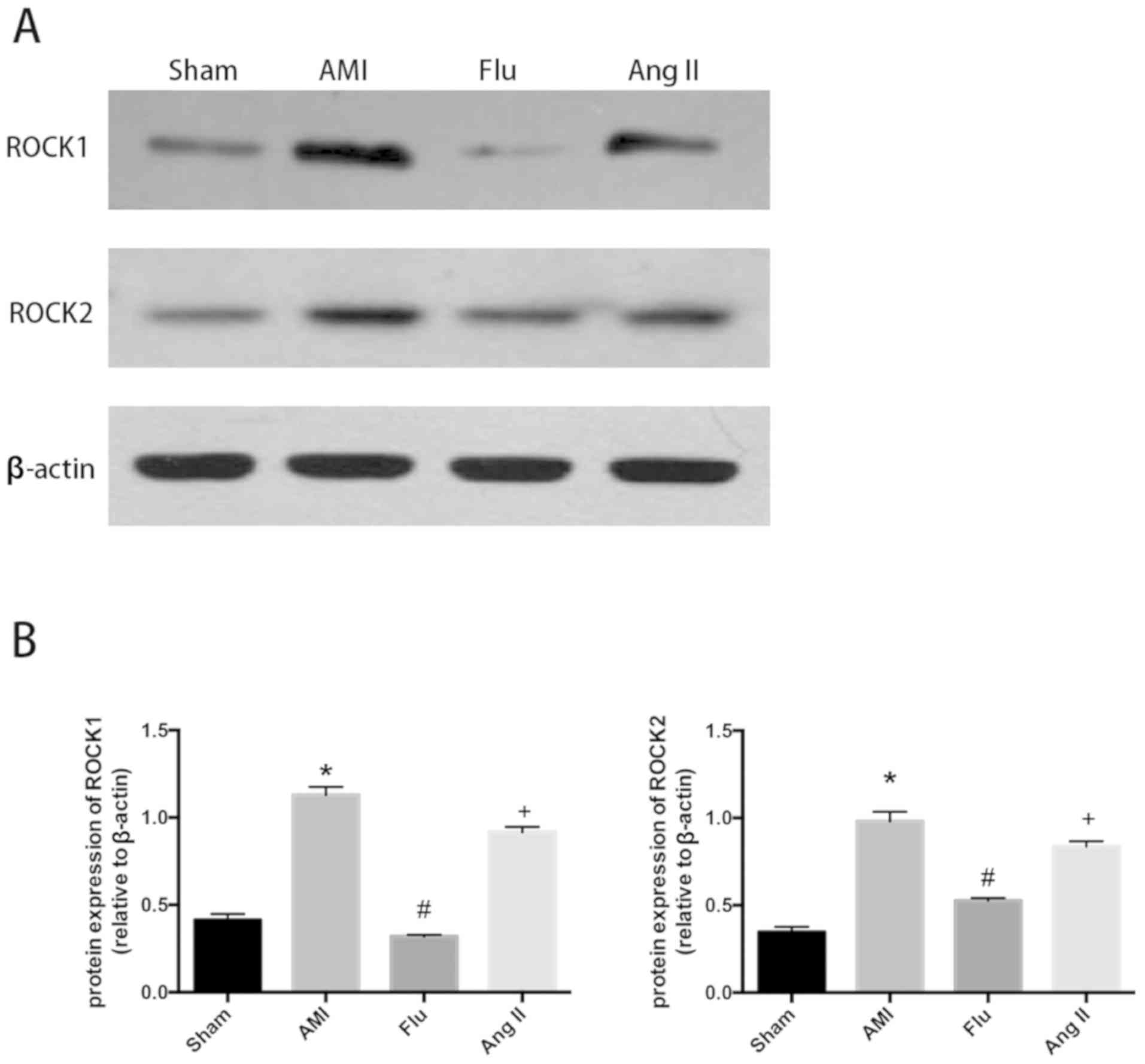
|
1
|
Shiny KS, Kumar SH, Farvin KH, Anandan R
and Devadasan K: Protective effect of taurine on myocardial
antioxidant status in isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in
rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 57:1313–1317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carson DA and Ribeiro JM: Apoptosis and
disease. Lancet. 341:1251–1254. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wyllie AH, Kerr JF and Currie AR: Cell
death: The significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 68:251–306.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yi J and An Y: Circulating miR-379 as a
potential novel biomarker for diagnosis of acute myocardial
infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:540–546. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baldi A, Abbate A, Bussani R, Patti G,
Melfi R, Angelini A, Dobrina A, Rossiello R, Silvestri F, Baldi F,
et al: Apoptosis and post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:165–174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slee EA, Harte MT, Kluck RM, Wolf BB,
Casiano CA, Newmeyer DD, Wang HG, Reed JC, Nicholson DW, Alnemri
ES, et al: Ordering the cytochrome c-initiated caspase cascade:
Hierarchical activation of caspases-2, −3, −6, −7, −8, and −10 in a
caspase-9-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 144:281–292. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sam F, Sawyer DB, Chang DL, Eberli FR,
Ngoy S, Jain M, Amin J, Apstein CS and Colucci WS: Progressive left
ventricular remodeling and apoptosis late after myocardial
infarction in mouse heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H422–H428. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu J, Guo Z, Wang LL and Zhang RL:
Degeneration of sensory afferent nerves enhances pulmonary
inflammatory alterations in acute myocardial infarction in rats.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 21:149–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burridge K and Wennerberg K: Rho and Rac
take center stage. Cell. 116:167–179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Etienne-Manneville S and Hall A: Rho
GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 420:629–635. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shimokawa H: Rho-kinase as a novel
therapeutic target in treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 39:319–327. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamakawa T, Tanaka S, Kamei J, Kadonosono
K and Okuda K: Pitavastatin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by inactivating extracellular signal-regulated
kinases 1/2. J Atheroscler Thromb. 10:37–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiesbauer F, Kaun C, Zorn G, Maurer G,
Huber K and Wojta J: HMG CoA reductase inhibitors affect the
fibrinolytic system of human vascular cells in vitro: A comparative
study using different statins. Br J Pharmacol. 135:284–292. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kitano K, Usui S, Ootsuji H, Takashima S,
Kobayashi D, Murai H, Furusho H, Nomura A, Kaneko S and Takamura M:
Rho-kinase activation in leukocytes plays a pivotal role in
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 9:e922422014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang CC, Wang SS, Hsieh HG, Lee WS,
Chuang CL, Lin HC, Lee FY, Lee SD and Huang HC: Rosuvastatin
improves hepatopulmonary syndrome through inhibition of
inflammatory angiogenesis of lung. Clin Sci (Lond). 129:449–460.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Zhang H, Chai F, Liu X and Berk M:
The effects of escitalopram on myocardial apoptosis and the
expression of Bax and Bcl-2 during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
in a model of rats with depression. BMC Psychiatry. 14:3492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen TL, Zhu GL, He XL, Wang JA, Wang Y
and Qi GA: Short-term pretreatment with atorvastatin attenuates
left ventricular dysfunction, reduces infarct size and apoptosis in
acute myocardial infarction rats. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:4799–4808.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malick M, Gilbert K, Barry M, Godbout R
and Rousseau G: Desvenlafaxine reduces apoptosis in amygdala after
myocardial infarction. Brain Res Bull. 109:158–163. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Q: Lentivirus mediated interference of
Caspase-3 expression ameliorates the heart function on rats with
acute myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:1852–1858. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumphune S, Surinkaew S, Chattipakorn SC
and Chattipakorn N: Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation protects
cardiac mitochondria from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharm Biol.
53:1831–1841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Motloch LJ, Hu J and Akar FG: The
mitochondrial translocator protein and arrhythmogenesis in ischemic
heart disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015:2341042015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Wang H, Yang YJ, Dong QT, Wang
TJ, Qian HY, Li N, Wang XM and Jin C: Atorvastatin treatment
improves the effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on
acute myocardial infarction: The role of the RhoA/ROCK/ERK pathway.
Int J Cardiol. 176:670–679. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Loirand G, Guérin P and Pacaud P: Rho
kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Circ Res.
98:322–334. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi J and Wei L: Rho kinases in
cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology: The effect of
fasudil. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 62:341–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hung CN, Huang HP, Wang CJ, Liu KL and Lii
CK: Sulforaphane inhibits TNF-α-induced adhesion molecule
expression through the Rho A/ROCK/NF-κB signaling pathway. J Med
Food. 17:1095–1102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bao W, Hu E, Tao L, Boyce R, Mirabile R,
Thudium DT, Ma XL, Willette RN and Yue TL: Inhibition of Rho-kinase
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc
Res. 61:548–558. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shimokawa H and Takeshita A: Rho-kinase is
an important therapeutic target in cardiovascular medicine.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:1767–1775. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Higashi M, Shimokawa H, Hattori T, Hiroki
J, Mukai Y, Morikawa K, Ichiki T, Takahashi S and Takeshita A:
Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase suppresses angiotensin
II-induced cardiovascular hypertrophy in rats in vivo: Effect on
endothelial NAD(P)H oxidase system. Circ Res. 93:767–775. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Petrache I, Crow MT, Neuss M and Garcia
JG: Central involvement of Rho family GTPases in TNF-alpha-mediated
bovine pulmonary endothelial cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 306:244–249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Del Re DP, Miyamoto S and Brown JH:
RhoA/Rho kinase up-regulate Bax to activate a mitochondrial death
pathway and induce cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
282:8069–8078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang J, Xie M, Shah VR, Schneider MD,
Entman ML, Wei L and Schwartz RJ: Activation of Rho-associated
coiled-coil protein kinase 1 (ROCK-1) by caspase-3 cleavage plays
an essential role in cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:14495–14500. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|