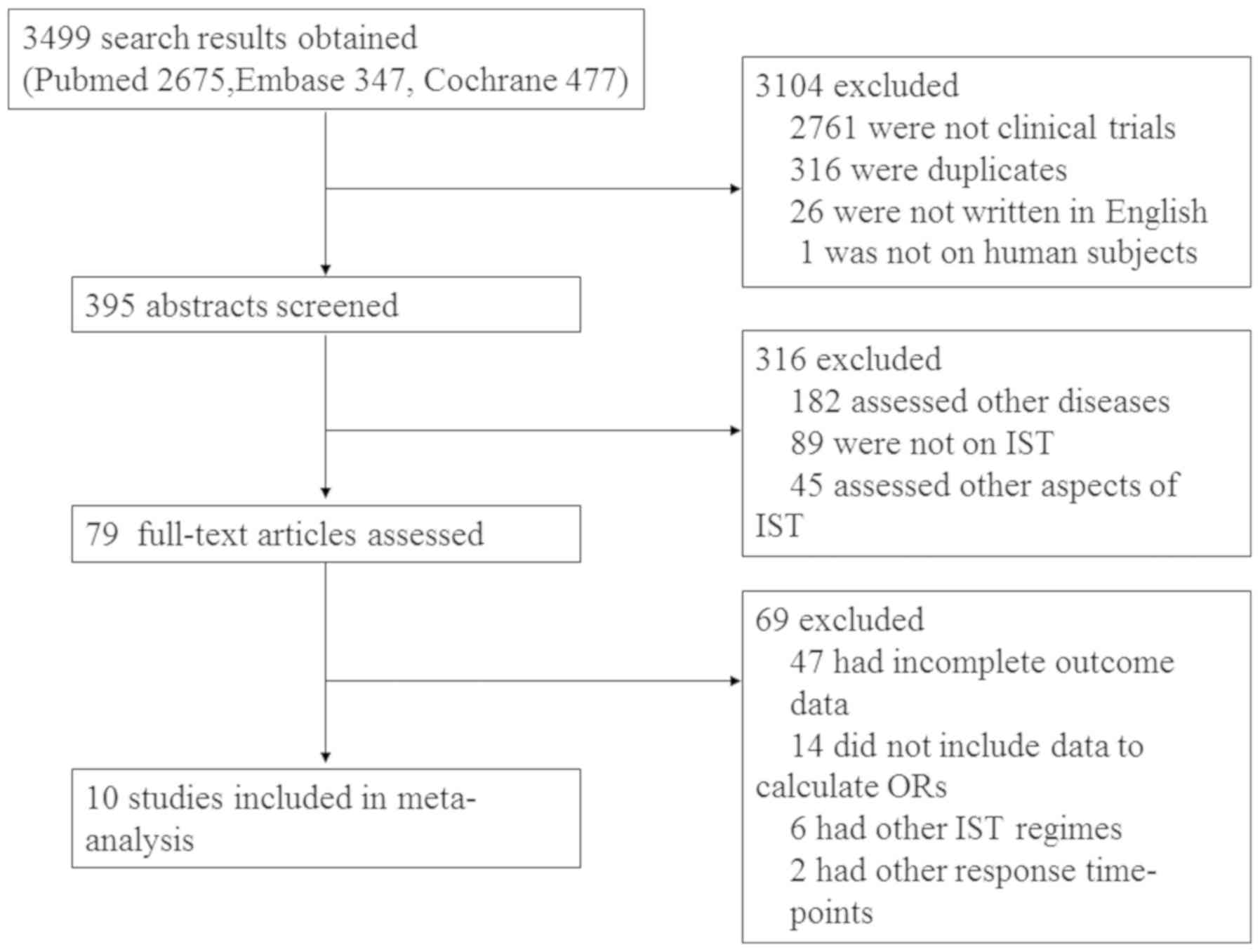
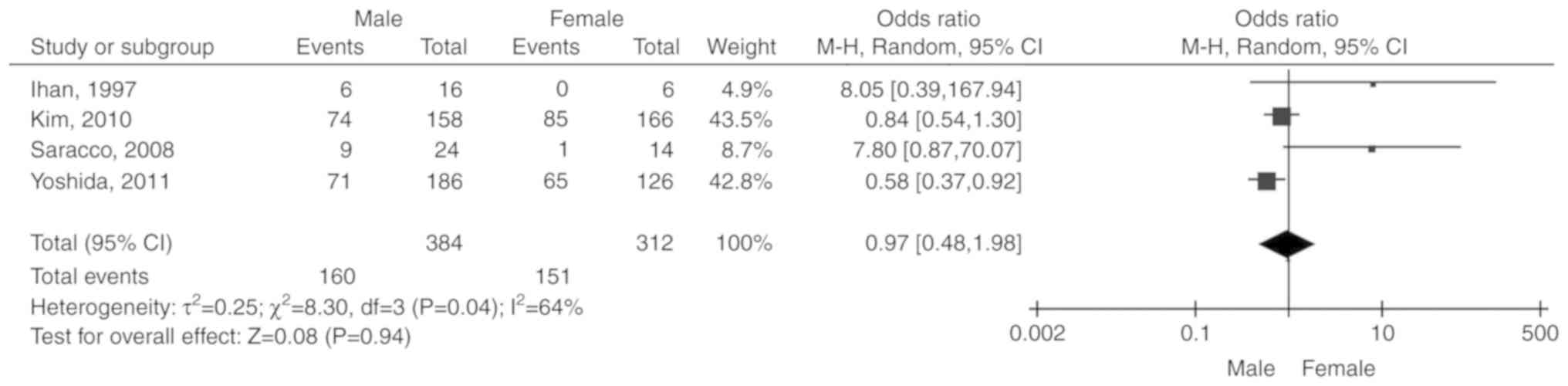
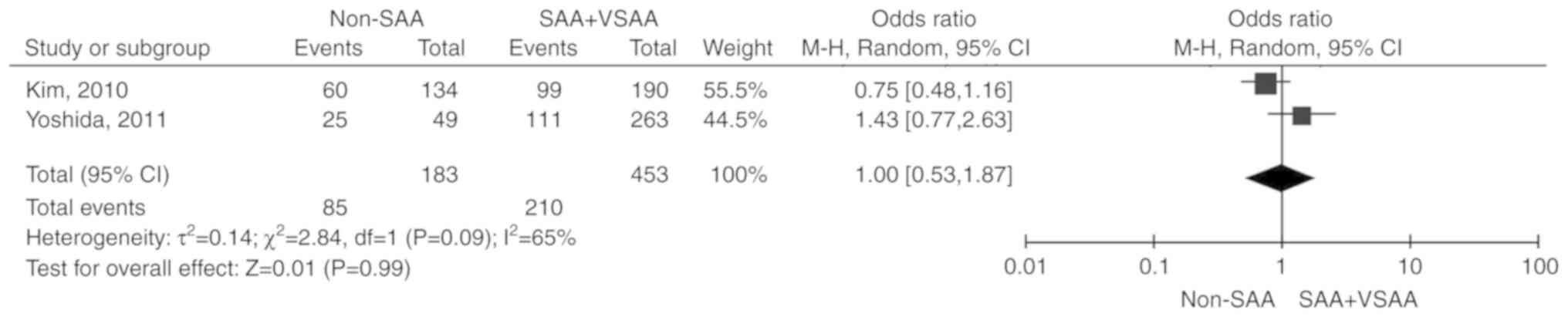
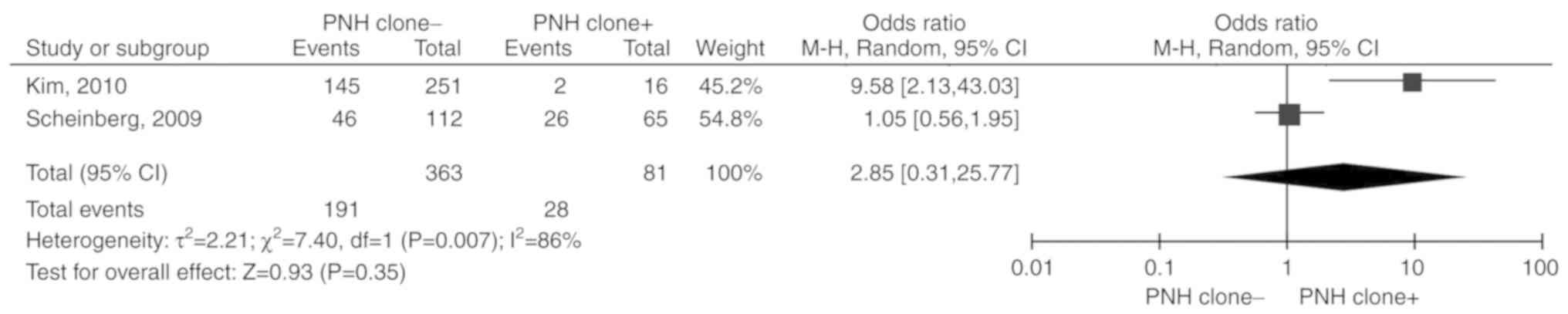
|
1
|
Kaushansky KWW: Williams hematology. New
York: McGraw-Hill Medical xxiii: pp.2439, 2010.
|
|
2
|
Townsley DM, Dumitriu B and Young NS: Bone
marrow failure and the telomeropathies. Blood. 124:2775–2783.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Marsh JC: Results of immunosuppression in
aplastic anaemia. Acta Haematol. 103:26–32. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Risitano AM: Immunosuppressive therapies
in the management of immune-mediated marrow failures in adults:
Where we stand and where we are going. Br J Haematol. 152:127–140.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Scheinberg P: Aplastic anemia: Therapeutic
updates in immunosuppression and transplantation. Hematology Am Soc
Hematol Educ Program. 2012:292–300. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Scheinberg P and Young NS: How I treat
acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 120:1185–1196. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Marsh JC, Ball SE, Cavenagh J, Darbyshire
P, Dokal I, Gordon-Smith EC, Keidan J, Laurie A, Martin A, Mercieca
J, et al: Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aplastic
anaemia. Br J Haematol. 147:43–70. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bacigalupo A, Broccia G, Corda G, Arcese
W, Carotenuto M, Gallamini A, Locatelli F, Mori PG, Saracco P,
Todeschini G, et al: Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporin, and
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired
severe aplastic anemia (SAA): A pilot study of the EBMT SAA Working
Party. Blood. 85:1348–1353. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Margulis AV, Pladevall M, Riera-Guardia N,
Varas-Lorenzo C, Hazell L, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M and
Perez-Gutthann S: Quality assessment of observational studies in a
drug-safety systematic review, comparison of two tools: The
Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and the RTI item bank. Clin Epidemiol.
6:359–368. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
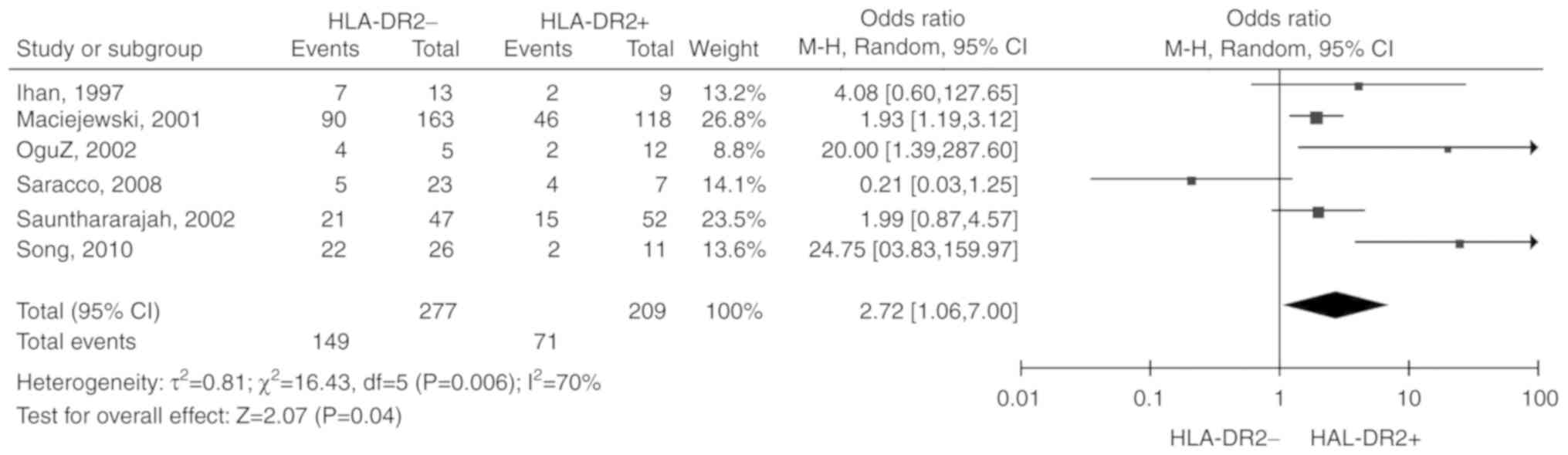
Ihan O, Beksaç M, Arslan O, Ozcan M, Koç
H, Akan H, Gürman G, Konuk N and Uysal A: HLA DR2: A predictive
marker in response to cyclosporine therapy in aplastic anemia. Int
J Hematol. 66:291–295. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Maciejewski JP, Follmann D, Nakamura R,
Saunthararajah Y, Rivera CE, Simonis T, Brown KE, Barrett JA and
Young NS: Increased frequency of HLA-DR2 in patients with
paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and the PNH/aplastic anemia
syndrome. Blood. 98:3513–3519. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Saunthararajah Y, Nakamura R, Nam JM,
Robyn J, Loberiza F, Maciejewski JP, Simonis T, Molldrem J, Young
NS and Barrett AJ: HLA-DR15 (DR2) is overrepresented in
myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia and predicts a
response to immunosuppression in myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood.
100:1570–1574. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oguz FS, Yalman N, Diler AS, Oguz R, Anak
S and Dorak MT: HLA-DRB1*15 and pediatric aplastic
anemia. Haematologica. 87:772–774. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
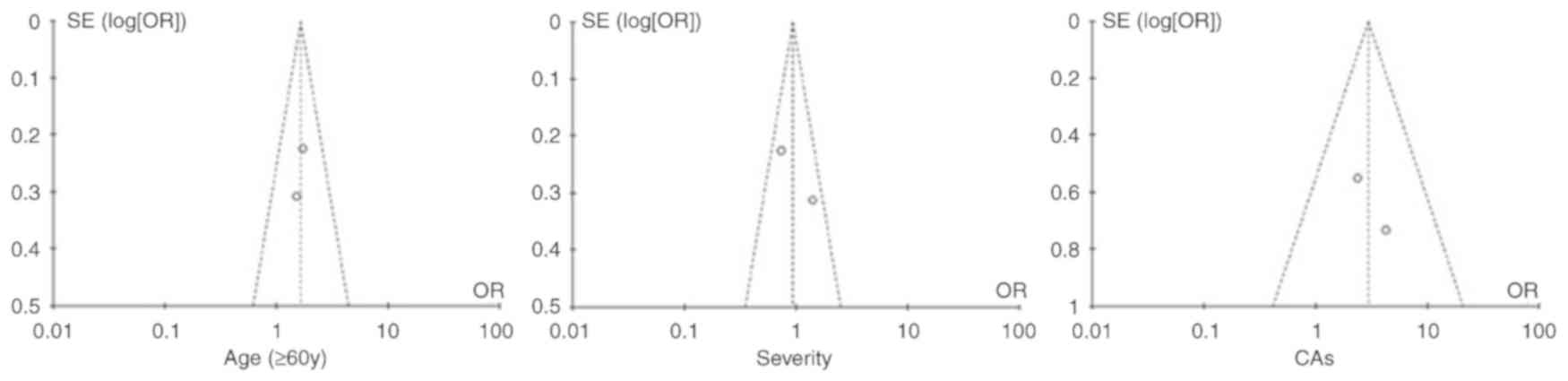
Gupta V, Brooker C, Tooze JA, Yi QL, Sage
D, Turner D, Kangasabapathy P and Marsh JC: Clinical relevance of
cytogenetic abnormalities at diagnosis of acquired aplastic anaemia
in adults. Br J Haematol. 134:95–99. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Saracco P, Quarello P, Iori AP, Zecca M,
Longoni D, Svahn J, Varotto S, Del Vecchio GC, Dufour C, Ramenghi
U, et al: Cyclosporin A response and dependence in children with
acquired aplastic anaemia: A multicentre retrospective study with
long-term observation follow-up. Br J Haematol. 140:197–205.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Scheinberg P, Wu CO, Nunez O and Young NS:
Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy and survival in
severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 144:206–216.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim SY, Lee JW, Lee SE, Cho BS, Kim M, Eom
KS, Kim YJ, Kim HJ, Lee S, Min CK, et al: The characteristics and
clinical outcome of adult patients with aplastic anemia and
abnormal cytogenetics at diagnosis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer.
49:844–850. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Song EY, Kang HJ, Shin HY, Ahn HS, Kim I,
Yoon SS, Park S, Kim BK and Park MH: Association of human leukocyte
antigen class II alleles with response to immunosuppressive therapy
in Korean aplastic anemia patients. Hum Immunol. 71:88–92.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yoshida N, Yagasaki H, Hama A, Takahashi
Y, Kosaka Y, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, Kaneko T, Tsuchida M, Ohara A, et
al: Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy in childhood
aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 96:771–774. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marsh JC and Kulasekararaj AG: Management
of the refractory aplastic anemia patient: What are the options?
Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2013:87–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Reddy V, Khan S, Wingard JR and Mehta P:
Treatment results in aplastic anemia trials need to be analyzed
separately for pediatric and adult populations. Blood.
94:1833–1834. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shin SH and Lee JW: The optimal
immunosuppressive therapy for aplastic anemia. Int J Hematol.
97:564–572. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Locasciulli A, Oneto R, Bacigalupo A,
Socié G, Korthof E, Bekassy A, Schrezenmeier H, Passweg J and
Führer M: Severe Aplastic Anemia Working Party of the European
Blood and MarrowTransplant Group: Outcome of patients with acquired
aplastic anemia given first line bone marrow transplantation or
immunosuppressive treatment in the last decade: A report from the
European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT).
Haematologica. 92:11–18. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vadasz Z, Haj T, Kessel A and Toubi E:
Age-related autoimmunity. BMC Med. 11(94)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Andro M, Le Squere P, Estivin S and
Gentric A: Anaemia and cognitive performances in the elderly: A
systematic review. Eur J Neurol. 20:1234–1240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
den Elzen WP and Gussekloo J: Anaemia in
older persons. Neth J Med. 69:260–267. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Young NS: Pathophysiologic mechanisms in
acquired aplastic anemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
72–77. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Young NS, Calado RT and Scheinberg P:
Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic
anemia. Blood. 108:2509–2519. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nepom GT: Class II antigens and disease
susceptibility. Annu Rev Med. 46:17–25. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Haegert DG and Marrosu MG: Genetic
susceptibility to multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 36 (Suppl
2):S204–S210. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Peces R, Urra JM and de la Torre M:
Influence of HLA-DR phenotype on tumor necrosis factor-alpha
production in renal-transplant recipients. Nephron. 71:180–183.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bendtzen K, Morling N, Fomsgaard A,
Svenson M, Jakobsen B, Odum N and Svejgaard A: Association between
HLA-DR2 and production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and
interleukin 1 by mononuclear cells activated by lipopolysaccharide.
Scand J Immunol. 28:599–606. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Maciejewski JP, Risitano A, Sloand EM,
Nunez O and Young NS: Distinct clinical outcomes for cytogenetic
abnormalities evolving from aplastic anemia. Blood. 99:3129–3135.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ohga S, Ohara A, Hibi S, Kojima S, Bessho
F, Tsuchiya S, Ohshima Y, Yoshida N, Kashii Y, Nishimura S, et al:
Treatment responses of childhood aplastic anaemia with chromosomal
aberrations at diagnosis. Br J Haematol. 118:313–319.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mikhailova N, Sessarego M, Fugazza G,
Caimo A, De Filippi S, van Lint MT, Bregante S, Valeriani A,
Mordini N, Lamparelli T, et al: Cytogenetic abnormalities in
patients with severe aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 81:418–422.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kearns WG, Sutton JF, Maciejewski JP,
Young NS and Liu JM: Genomic instability in bone marrow failure
syndromes. Am J Hematol. 76:220–224. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Keung YK, Pettenati MJ, Cruz JM, Powell
BL, Woodruff RD and Buss DH: Bone marrow cytogenetic abnormalities
of aplastic anemia. Am J Hematol. 66:167–171. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Piaggio G, Podestà M, Pitto A, Sessarego
M, Figari O, Fugazza G, Benvenuto F, Bruno B, Van Lint MT, Truini
M, et al: Coexistence of normal and clonal haemopoiesis in aplastic
anaemia patients treated with immunosuppressive therapy. Br J
Haematol. 107:505–511. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Geary CG, Harrison CJ, Philpott NJ, Hows
JM, Gordon-Smith EC and Marsh JC: Abnormal cytogenetic clones in
patients with aplastic anaemia: Response to immunosuppressive
therapy. Br J Haematol. 104:271–274. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Appelbaum FR, Barrall J, Storb R, Ramberg
R, Doney K, Sale GE and Thomas ED: Clonal cytogenetic abnormalities
in patients with otherwise typical aplastic anemia. Exp Hematol.
15:1134–1139. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Afable MG II, Tiu RV and Maciejewski JP:
Clonal evolution in aplastic anemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 2011:90–95. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sloand EM, Kim S, Fuhrer M, Risitano AM,
Nakamura R, Maciejewski JP, Barrett AJ and Young NS: Fas-mediated
apoptosis is important in regulating cell replication and death in
trisomy 8 hematopoietic cells but not in cells with other
cytogenetic abnormalities. Blood. 100:4427–4432. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Chen G, Zeng W, Miyazato A, Billings E,
Maciejewski JP, Kajigaya S, Sloand EM and Young NS: Distinctive
gene expression profiles of CD34 cells from patients with
myelodysplastic syndrome characterized by specific chromosomal
abnormalities. Blood. 104:4210–4218. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kojima S, Ohara A, Tsuchida M, Kudoh T,
Hanada R, Okimoto Y, Kaneko T, Takano T, Ikuta K and Tsukimoto I:
Japan Childhood Aplastic Anemia Study Group: Risk factors for
evolution of acquired aplastic anemia into myelodysplastic syndrome
and acute myeloid leukemia after immunosuppressive therapy in
children. Blood. 100:786–790. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sloand EM, Yong AS, Ramkissoon S, Solomou
E, Bruno TC, Kim S, Fuhrer M, Kajigaya S, Barrett AJ and Young NS:
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor preferentially stimulates
proliferation of monosomy 7 cells bearing the isoform IV receptor.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:14483–14488. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mohamed AN, Varterasian ML, Dobin SM,
McConnell TS, Wolman SR, Rankin C, Willman CL, Head DR and Slovak
ML: Trisomy 6 as a primary karyotypic aberration in hematologic
disorders. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 106:152–155. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Argiropoulos B, Clifford B, Crocker S,
Sinclair-Bourque E, McCready E, McGowan-Jordan J, Johnston DL and
Padmore R: HLA-DR(negative), CD34(negative) hypergranular acute
myeloid leukemia with trisomy 6 and del(5)(q22q33): Case report and
review of the literature. J Pediat Hematol Oncol. 33:e289–e295.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Boddu PC and Kadia TM: Molecular
pathogenesis of acquired aplastic anemia. Eur J Haematol.
102:103–110. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shallis RM, Ahmad R and Zeidan AM:
Aplastic anemia: Etiology, molecular pathogenesis, and emerging
concepts. Eur J Haematol. 101:711–720. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wang L and Liu H: Pathogenesis of aplastic
anemia. Hematology. 24:559–566. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|