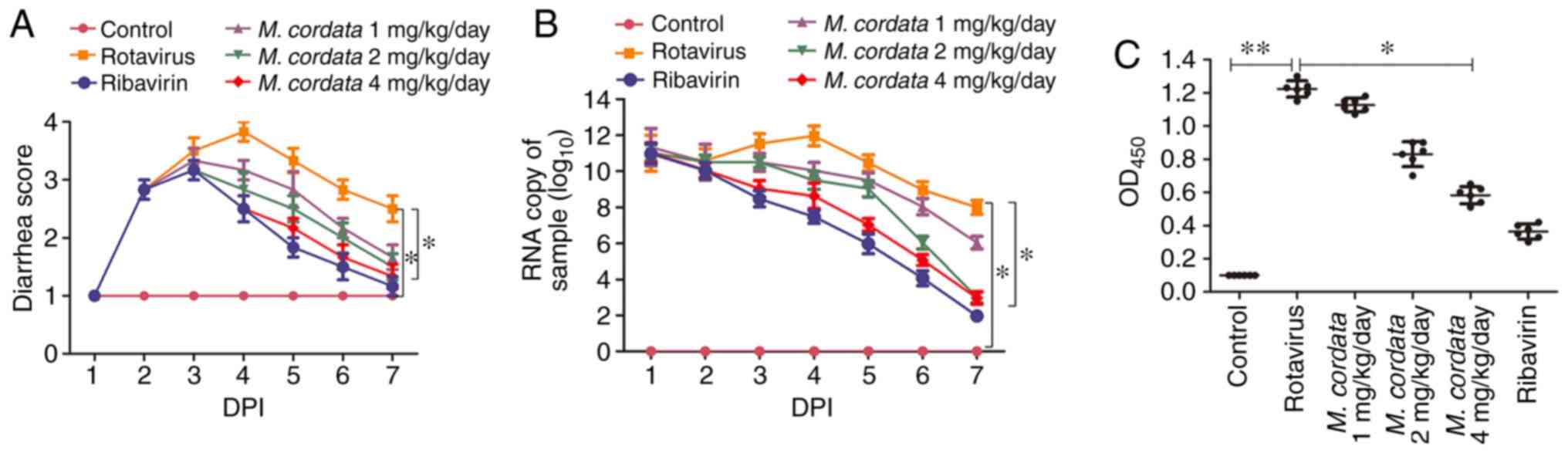
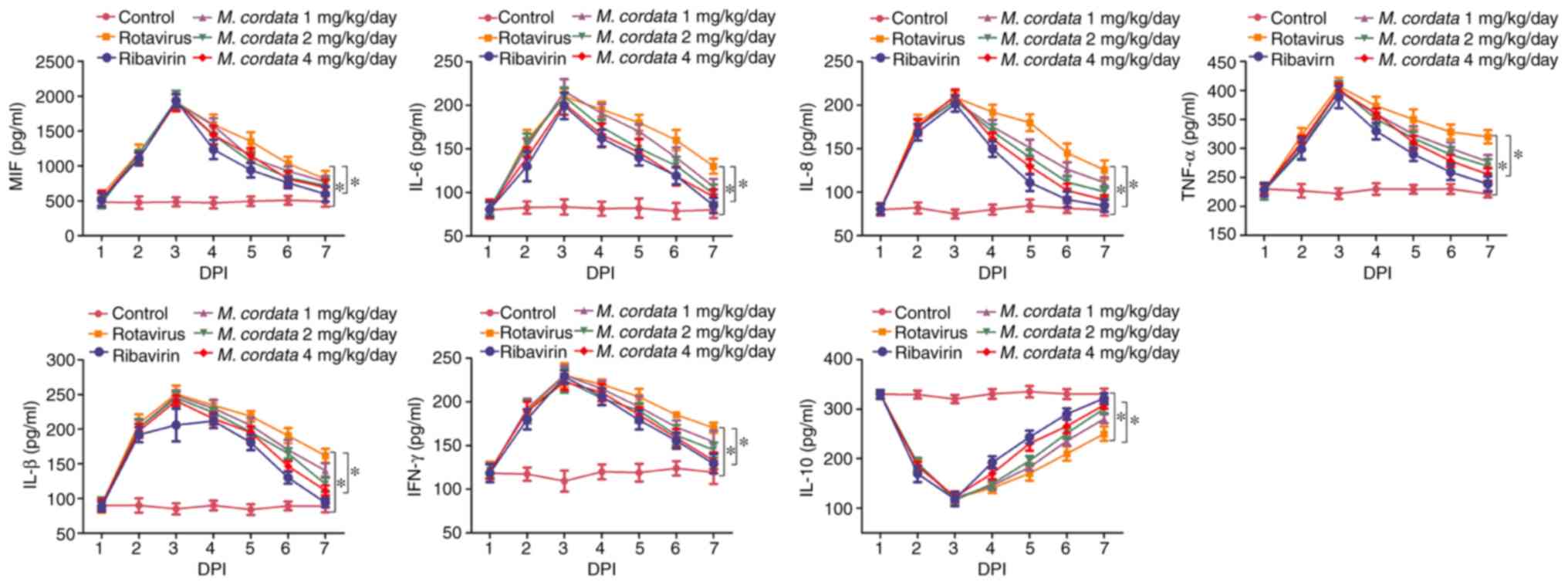
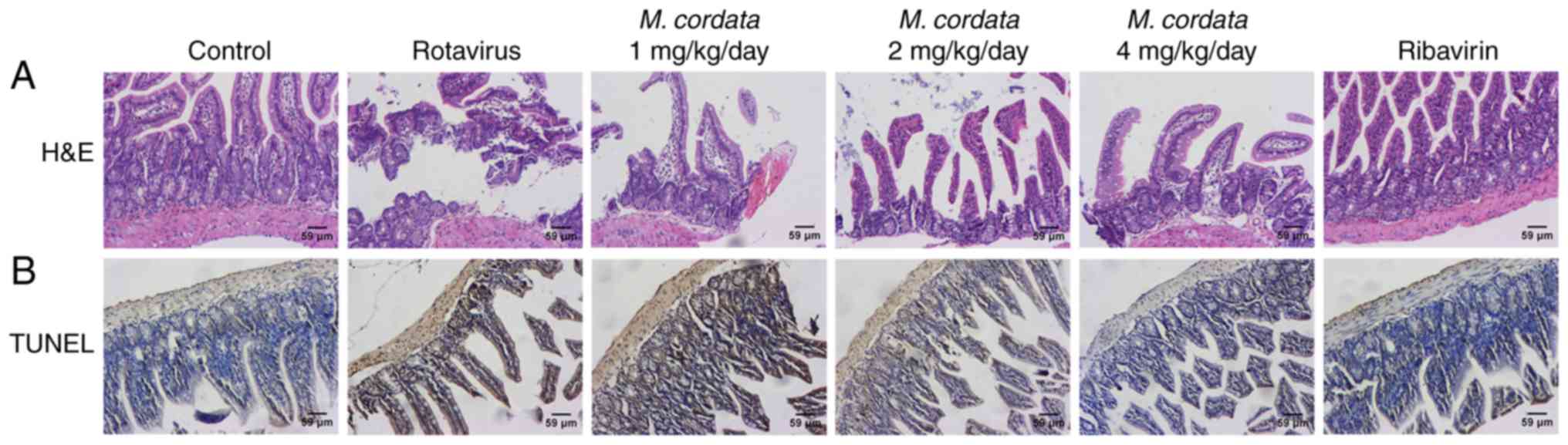
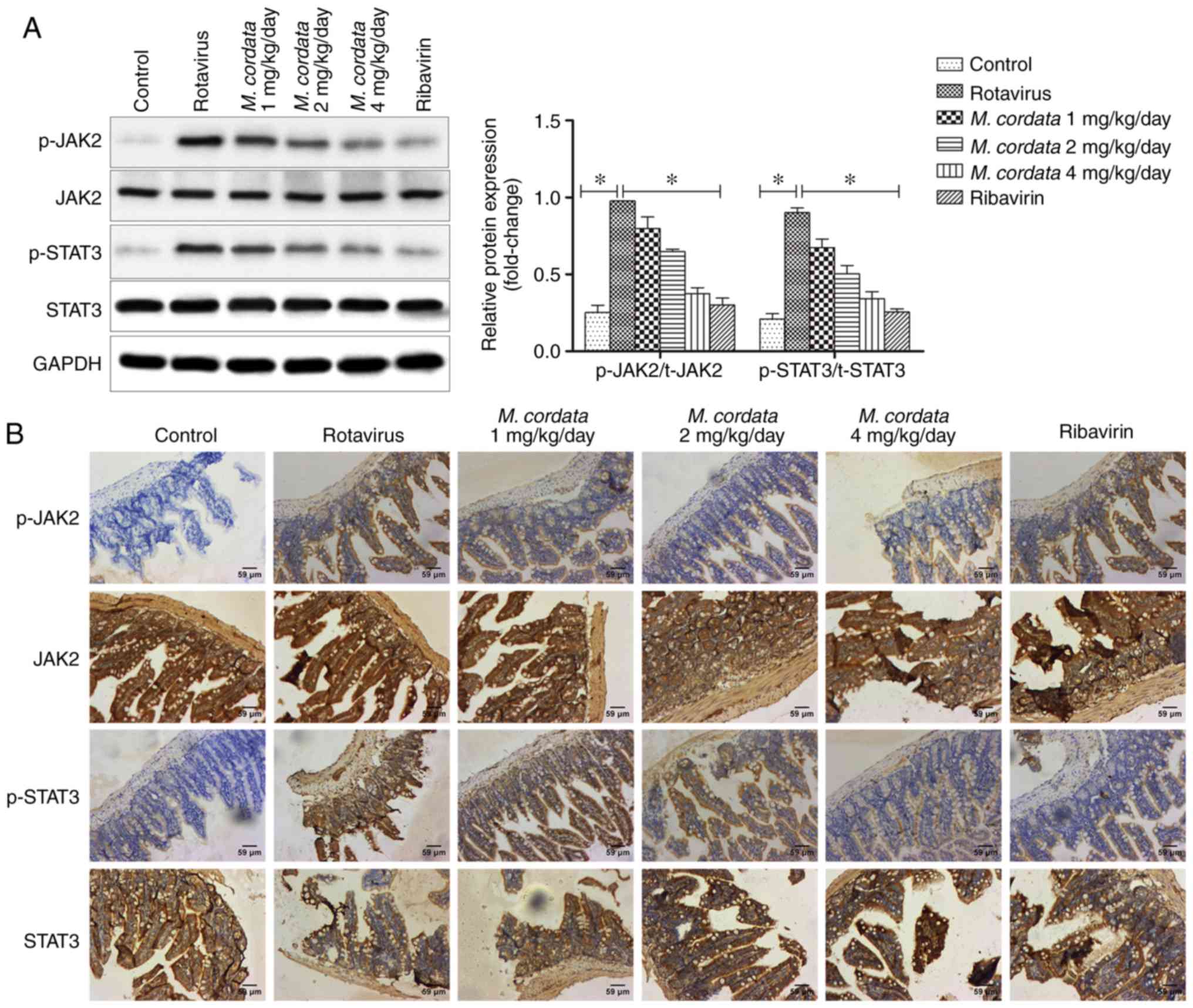
|
1
|
Boshuizen JA, Reimerink JH, Korteland-van
Male AM, van Ham VJ, Koopmans MP, Büller HA, Dekker J and Einerhand
AW: Changes in small intestinal homeostasis, morphology, and gene
expression during rotavirus infection of infant mice. J Virol.
77:13005–13016. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Steele
AD, Duque J and Parashar UD: WHO-coordinated Global Rotavirus
Surveillance Network: 2008 estimate of worldwide
rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years
before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination
programs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis.
12:136–141. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pesavento JB, Crawford SE, Estes MK and
Prasad BV: Rotavirus proteins: Structure and assembly. Curr Top
Microbiol Immunol. 309:189–219. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kawahara T, Tomono T, Hamauzu Y, Tanaka K
and Yasui H: Inhibitory effect of a hot-water extract of leaves of
Japanese big-leaf magnolia (magnolia obovata) on rotavirus-induced
diarrhea in mouse pups. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014(365831)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Anderson EJ: Rotavirus vaccines: Viral
shedding and risk of transmission. Lancet Infect Dis. 8:642–649.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lepage P and Vergison A: Prevention of
childhood rotavirus disease through the use of Rotarix and RotaTeq
vaccines. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 7:1881–1892. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu M, Lin YL, Chen XR, Liao CC and Poo
WK: In vitro assessment of Macleaya cordata crude extract
bioactivity and anticancer properties in normal and cancerous human
lung cells. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 65:775–787. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin L, Liu YC, Huang JL, Liu XB, Qing ZX,
Zeng JG and Liu ZY: Medicinal plants of the genus Macleaya
(Macleaya cordata, Macleaya microcarpa): A review of their
phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. Phytother Res.
32:19–48. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ke W, Lin X, Yu Z, Sun Q and Zhang Q:
Molluscicidal activity and physiological toxicity of Macleaya
cordata alkaloids components on snail oncomelania hupensis. Pestic
Biochem Physiol. 143:111–115. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Arnold M, Patton JT and McDonald SM:
Culturing, storage, and quantification of rotaviruses. Curr Protoc
Microbiol. 15(Unit 15C 3)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tian Z, Shen Z, He H, Zhang J, Li J and Wu
Y: Antiviral effects of cyclosporin a in neonatal mice with
rotavirus-induced diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 60:11–17.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shen Z, He H, Wu Y and Li J: Cyclosporin a
inhibits rotavirus replication and restores interferon-beta
signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
8(e71815)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu G, Guan G, Fang J, Martínez Y, Chen S,
Bin P, Duraipandiyan V, Gong T, Tossou MC, Al-Dhabi NA and Yin Y:
Macleaya cordata extract decreased diarrhea score and enhanced
intestinal barrier function in growing piglets. Biomed Res Int.
2016(1069585)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dung TT, Phat VV, Nga TV, My PV, Duy PT,
Campbell JI, Thuy CT, Hoang NV, Van Minh P, Le Phuc H, et al: The
validation and utility of a quantitative one-step multiplex RT
real-time PCR targeting rotavirus A and norovirus. J Virol Methods.
187:138–143. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Alfajaro MM, Kim HJ, Park JG, Ryu EH, Kim
JY, Jeong YJ, Kim DS, Hosmillo M, Son KY, Lee JH, et al:
Anti-rotaviral effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis extract in piglets
with rotavirus diarrhea. Virol J. 9(310)2012.
|
|
17
|
Ciarlet M, Conner ME, Finegold MJ and
Estes MK: Group A rotavirus infection and age-dependent diarrheal
disease in rats: A new animal model to study the pathophysiology of
rotavirus infection. J Virol. 76:41–57. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guerin-Danan C, Meslin JC, Lambre F,
Charpilienne A, Serezat M, Bouley C, Cohen J and Andrieux C:
Development of a heterologous model in germfree suckling rats for
studies of rotavirus diarrhea. J Virol. 72:9298–9302.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ward RL: Possible mechanisms of protection
elicited by candidate rotavirus vaccines as determined with the
adult mouse model. Viral Immunol. 16:17–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lei Q, Liu H, Peng Y and Xiao P: In silico
target fishing and pharmacological profiling for the isoquinoline
alkaloids of Macleaya cordata (Bo Luo Hui). Chin Med.
10(37)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Freitas K, Carroll FI and Damaj MI: The
antinociceptive effects of nicotinic receptors α7-positive
allosteric modulators in murine acute and tonic pain models. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 344:264–275. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jiang B, Snipes-Magaldi L, Dennehy P,
Keyserling H, Holman RC, Bresee J, Gentsch J and Glass RI:
Cytokines as mediators for or effectors against rotavirus disease
in children. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 10:995–1001. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Khadem A, Soler L, Everaert N and Niewold
TA: Growth promotion in broilers by both oxytetracycline and
Macleaya cordata extract is based on their anti-inflammatory
properties. Br J Nutr. 112:1110–1118. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vrba J, Orolinova E and Ulrichova J:
Induction of heme oxygenase-1 by Macleaya cordata extract and its
constituent sanguinarine in RAW264. .7 cells. Fitoterapia.
83:329–335. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fagone P, Patti F, Mangano K, Mammana S,
Coco M, Touil-Boukoffa C, Chikovani T, Di Marco R and Nicoletti F:
Heme oxygenase-1 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells
correlates with disease activity in multiple sclerosis. J
Neuroimmunol. 261:82–86. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ronco C, Ronco F and Mccullough PA: A call
to action to develop integrated curricula in cardiorenal medicine.
Rev Cardiovasc Med. 18:93–99. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jin J, Liu Y, Huang L and Tan H: Advances
in epigenetic regulation of vascular aging. Rev Cardiovasc Med.
20:19–25. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yilmaz E, Coskun EI, Gul M, Sahin N,
Tuncay G and Simsek Y: Nuclear factor-kappa β pathway and
endometrial cancer: A pilot study. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
38:536–540. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tian JS, Zhai QJ, Zhao Y, Chen R and Zhao
LD: 2-(2-benzofuranyl)-2-imidazoline (2-BFI) improved the
impairments in AD rat models by inhibiting oxidative stress,
inflammation and apoptosis. J Integr Neurosci. 16:385–400.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fagone P, Mazzon E, Cavalli E, Bramanti A,
Petralia MC, Mangano K, Al-Abed Y, Bramati P and Nicoletti F:
Contribution of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor
superfamily of cytokines in the pathogenesis of preclinical and
human multiple sclerosis: In silico and in vivo evidences. J
Neuroimmunol. 322:46–56. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Presti M, Mazzon E, Basile MS, Petralia
MC, Bramanti A, Colletti G, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F and Fagone P:
Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and
functionally-related genes, D-DT, CD74, CD44, CXCR2 and CXCR4, in
glioblastoma. Oncol Lett. 16:2881–2886. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lang T, Lee JPW, Elgass K, Pinar AA, Tate
MD, Aitken EH, Fan H, Creed SJ, Deen NS, Traore DAK, et al:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is required for NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Nat Commun. 9(2223)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gandhi GR, Santos VS, Denadai M, da Silva
Calisto VK, de Souza Siqueira Quintans J, de Oliveira E Silva AM,
de Souza Araújo AA, Narain N, Cuevas LE, Júnior LJQ and Gurgel RQ:
Cytokines in the management of rotavirus infection: A systematic
review of in vivo studies. Cytokine. 96:152–160. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Feng N, Kim B, Fenaux M, Nguyen H, Vo P,
Omary MB and Greenberg HB: Role of interferon in homologous and
heterologous rotavirus infection in the intestines and
extraintestinal organs of suckling mice. J Virol. 82:7578–7590.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liu M, Zhao G, Cao S, Zhang Y, Li X and
Lin X: Development of certain protein kinase inhibitors with the
components from traditional chinese medicine. Front Pharmacol.
7(523)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mammana S, Bramanti P, Mazzon E, Cavalli
E, Basile MS, Fagone P, Petralia MC, McCubrey JA, Nicoletti F and
Mangano K: Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in
animal models of multiple sclerosis. Oncotarget. 9:8263–8277.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Horie R, Nakamura O, Yamagami Y, Mori M,
Nishimura H, Fukuoka N and Yamamoto T: Apoptosis and antitumor
effects induced by the combination of an mTOR inhibitor and an
autophagy inhibitor in human osteosarcoma MG63 cells. Int J Oncol.
48:37–44. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yin Y, Dang W, Zhou X, Xu L, Wang W, Cao
W, Chen S, Su J, Cai X, Xiao S, et al: PI3K-Akt-mTOR axis sustains
rotavirus infection via the 4E-BP1 mediated autophagy pathway and
represents an antiviral target. Virulence. 9:83–98. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Raible DJ, Frey LC and Brooks-Kayal AR:
Effects of JAK2-STAT3 signaling after cerebral insults. JAKSTAT.
3(e29510)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sansone P and Bromberg J: Targeting the
interleukin6/Jak/stat pathway in human malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
30:1005–1014. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cui J, Zhang F, Cao W, Wang Y, Liu J, Liu
X, Chen T, Li L, Tian J and Yu B: Erythropoietin alleviates
hyperglycaemia-associated inflammation by regulating macrophage
polarization via the JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway. Mol Immunol.
101:221–228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang X, Jia J, Yu Z, Duanmu Z, He H, Chen
S and Qu C: Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3/SOCS3 signaling attenuates
atherosclerosis in rabbit. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
20(133)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li CH, Xu LL, Zhao JX, Sun L, Yao ZQ, Deng
XL, Liu R, Yang L, Xing R and Liu XY: CXCL16 upregulates RANKL
expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through the
JAK2/STAT3 and p38/MAPK signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 65:193–202.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Holdbrooks AT, De Sarno P, Rowse
AL, Yanagisawa LL, McFarland BC, Harrington LE, Raman C, Sabbaj S,
Benveniste EN and Qin H: Therapeutic efficacy of suppressing the
Jak/STAT pathway in multiple models of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 192:59–72. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Villarino AV, Kanno Y, Ferdinand JR and
O'Shea JJ: Mechanisms of Jak/STAT signaling in immunity and
disease. J Immunol. 194:21–27. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|