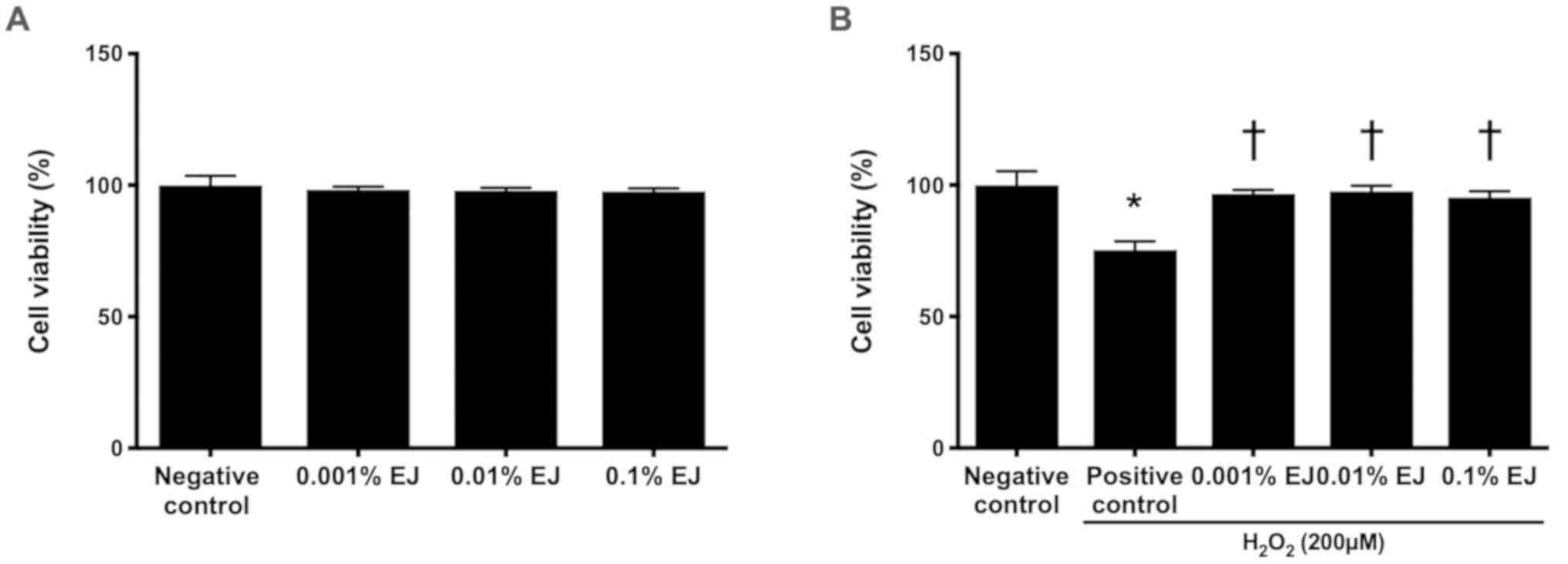
|
1
|
No authors listed. The definition and
classification of dry eye disease. Report of the definition and
classification subcommittee of the international dry eye workshop
(2007). Ocul Surf. 5:75–92. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Paulsen AJ, Cruickshanks KJ, Fischer ME,
Huang GH, Klein BE, Klein R and Dalton DS: Dry eye in the beaver
dam offspring study: Prevalence, risk factors, and health-related
quality of life. Am J Ophthalmol. 157:799–806. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gayton JL: Etiology, prevalence, and
treatment of dry eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 3:405–412.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wan KH, Chen LJ and Young AL: Efficacy and
safety of topical 0.05% cyclosporine eye drops in the treatment of
dry eye syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ocul Surf.
13:213–225. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
You IC, Li Y, Jin R, Ahn M, Choi W and
Yoon KC: Comparison of 0.1%, 0.18%, and 0.3% hyaluronic acid eye
drops in the treatment of experimental dry eye. J Ocul Pharmacol
Ther. 34:557–564. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wakamatsu TH, Dogru M and Tsubota K:
Tearful relations: Oxidative stress, inflammation and eye diseases.
Arq Bras Oftalmol. 71:72–79. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Uchino Y, Kawakita T, Miyazawa M, Ishii T,
Onouchi H, Yasuda K, Ogawa Y, Shimmura S, Ishii N and Tsubota K:
Oxidative stress induced inflammation initiates functional decline
of tear production. PLoS One. 7(e45805)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shoham A, Hadziahmetovic M, Dunaief JL,
Mydlarski MB and Schipper HM: Oxidative stress in diseases of the
human cornea. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:1047–1055. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yin Y, Zong R, Bao X, Zheng X, Cui H, Liu
Z and Zhou Y: Oxidative stress suppresses cellular autophagy in
corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:3286–3293.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Choi W, Lee JB, Cui L, Li Y, Li Z, Choi
JS, Lee HS and Yoon KC: Therapeutic efficacy of topically applied
antioxidant medicinal plant extracts in a mouse model of
experimental dry eye. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016(4727415)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee HS, Choi JH, Cui L, Li Y, Yang JM, Yun
JJ, Jung JE, Choi W and Yoon KC: Anti-inflammatory and
antioxidative effects of Camellia japonica on human corneal
epithelial cells and experimental dry eye: in vivo and in vitro
study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 58:1196–1207. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cui L, Lee HS, Li Y, Choi JH, Yun JJ, Jung
JE, Choi W and Yoon KC: Experimental and clinical applications of
Chamaecyparis obtusa extracts in dry eye disease. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2017(4523673)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Choi W, Kim JC, Kim WS, Oh HJ, Yang JM,
Lee JB and Yoon KC: Clinical effect of antioxidant glasses
containing extracts of medicinal plants in patients with dry eye
disease: A multi-center, prospective, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. PLoS One. 10(e0139761)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Park SY, Yang HC, Moon JY, Lee NH, Kim SJ,
Kang JH, Lee YK, Park DB, Yoo ES and Kang HK: Induction of the
apoptosis of HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells by Eurya
emarginata. Cancer Lett. 205:31–38. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chung MG and Epperson BK: Clonal and
spatial genetic structure in Eurya emarginata (Theaceae). Heredity
(Edinb). 84 (Pt 2):170–177. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Park SY, Yang HC, Moon JY, Lee NH, Kim SJ,
Kang JH, Lee YK, Park DB, Yoo ES and Kang HK: The cytotoxicity of
eutigosides from Eurya emarginata against HL-60 promyelocytic
leukemia cells. Arch Pharm Res. 28:1047–1052. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Seo EJ, Kuete V, Kadioglu O, Krusche B,
Schröder S, Greten HJ, Arend J, Lee IS and Efferth T:
Antiangiogenic activity and pharmacogenomics of medicinal plants
from traditional korean medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2013(131306)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yang Kuo LM, Zhang LJ, Huang HT, Lin ZH,
Liaw CC, Cheng HL, Lee KH, Morris Natschke SL, Kuo YH and Ho HO:
Antioxidant lignans and chromone glycosides from Eurya
japonica. J Nat Prod. 76:580–587. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim YH, Lee YS and Choi EM: Chrysoeriol
isolated from Eurya cilliata leaves protects MC3T3-E1 cells against
hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of osteoblastic
differentiation. J Appl Toxicol. 30:666–673. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee HJ, Oh TH, Yoon WJ, Kang GJ, Yang EJ,
Park SS, Lee NH, Kang HK and Yoo ES: Eutigoside C inhibits the
production of inflammatory mediators (NO, PGE (2), IL-6) by
down-regulating NF-kappaB and MAP kinase activity in LPS-stimulated
RAW 264.7 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 60:917–924. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Park SY, Lee HJ, Yoon WJ, Kang GJ, Moon
JY, Lee NH, Kim SJ, Kang HK and Yoo ES: Inhibitory effects of
eutigosides isolated from Eurya emarginata on the inflammatory
mediators in RAW264.7 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 28:1244–1250.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim C, Lee IH, Hyun HB, Kim JC, Gyawali R,
Lee SG, Lee J, Kim SH, Shim BS, Cho SK, et al: Supercritical fluid
extraction of citrus iyo hort. ex tanaka pericarp inhibits growth
and induces apoptosis through abrogation of STAT3 regulated gene
products in human prostate cancer xenograft mouse model. Integr
Cancer Ther. 16:227–243. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sookwong P, Suttiarporn P, Boontakham P,
Seekhow P, Wangtueai S and Mahatheeranont S: Simultaneous
quantification of vitamin E, γ-oryzanols and xanthophylls from rice
bran essences extracted by supercritical CO2. Food Chem.
211:140–147. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim H, Roh HS, Kim JE, Park SD, Park WH
and Moon JY: Compound K attenuates stromal cell-derived growth
factor 1 (SDF-1)-induced migration of C6 glioma cells. Nutr Res
Pract. 10:259–264. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kopalli SR, Cha KM, Jeong MS, Lee SH, Sung
JH, Seo SK and Kim SK: Pectinase-treated Panax ginseng ameliorates
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in GC-2 sperm cells and
modulates testicular gene expression in aged rats. J Ginseng Res.
40:185–195. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dalal S, Zha Q, Singh M and Singh K:
Osteopontin-stimulated apoptosis in cardiac myocytes involves
oxidative stress and mitochondrial death pathway: Role of a
pro-apoptotic protein BIK. Mol Cell Biochem. 418:1–11.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yoon KC, De Paiva CS, Qi H, Chen Z, Farley
WJ, Li DQ, Stern ME and Pflugfelder SC: Desiccating environmental
stress exacerbates autoimmune lacrimal keratoconjunctivitis in
non-obese diabetic mice. J Autoimmun. 30:212–221. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yoon KC, Ahn KY, Choi W, Li Z, Choi JS,
Lee SH and Park SH: Tear production and ocular surface changes in
experimental dry eye after elimination of desiccating stress.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:7267–7273. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pauly A, Brignole-Baudouin F, Labbė A,
Liang H, Warnet JM and Baudouin C: New tools for the evaluation of
toxic ocular surface changes in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:5473–5483. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oh HJ, Li Z, Park SH and Yoon KC: Effect
of hypotonic 0.18% sodium hyaluronate eyedrops on inflammation of
the ocular surface in experimental dry eye. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther.
30:533–542. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sung MS, Li Z, Cui L, Choi JS, Choi W,
Park MJ, Park SH and Yoon KC: Effect of topical
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside in a mouse
model of experimental dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
56:3149–3158. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dogru M, Kojima T, Simsek C and Tsubota K:
Potential role of oxidative stress in ocular surface inflammation
and dry eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:DES163–DES168.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Devasagayam TP, Tilak JC, Boloor KK, Sane
KS, Ghaskadbi SS and Lele RD: Free radicals and antioxidants in
human health: Current status and future prospects. J Assoc
Physicians India. 52:794–804. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alió JL, Artola A, Serra A, Ayala MJ and
Mulet ME: Effect of topical antioxidant therapy on experimental
infectious keratitis. Cornea. 14:175–179. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gritz DC, Montes C, Atalla LR, Wu GS,
Sevanian A and Rao NA: Histochemical localization of superoxide
production in experimental autoimmune uveitis. Curr Eye Res.
10:927–931. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Erol Tinaztepe Ö, Ay M and Eser E: Nuclear
and mitochondrial DNA of age-related cataract patients are
susceptible to oxidative damage. Curr Eye Res. 42:583–588.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pinazo Durán MD, Gallego Pinazo R, García
Medina JJ, Zanon Moreno V, Nucci C, Dolz Marco R, Martínez Castillo
S, Galbis Estrada C, Marco Ramírez C, López-Gálvez MI, et al:
Oxidative stress and its downstream signaling in aging eyes. Clin
Interv Aging. 9:637–652. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Craig JP, Nichols KK, Akpek EK, Caffery B,
Dua HS, Joo CK, Liu Z, Nelson JD, Nichols JJ, Tsubota K, et al:
TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report. Ocul Surf.
15:276–283. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nakamura S, Shibuya M, Nakashima H,
Hisamura R, Masuda N, Imagawa T, Uehara M and Tsubota K:
Involvement of oxidative stress on corneal epithelial alterations
in a blink-suppressed dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:1552–1558. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Uchino Y, Kawakita T, Ishii T, Ishii N and
Tsubota K: A new mouse model of dry eye disease: Oxidative stress
affects functional decline in the lacrimal gland. Cornea. 31 (Suppl
1):S63–S67. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wakamatsu TH, Dogru M, Matsumoto Y, Kojima
T, Kaido M, Ibrahim OM, Sato EA, Igarashi A, Ichihashi Y, Satake Y,
et al: Evaluation of lipid oxidative stress status in Sjögren
syndrome patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:201–210.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Liu H, Zeng W and Wei J: Edaravone
protects against hyperosmolarity-induced oxidative stress and
apoptosis in primary human corneal epithelial cells. PLoS One.
12(e0174437)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Deng R, Hua X, Li J, Chi W, Zhang Z, Lu F,
Zhang L, Pflugfelder SC and Li DQ: Oxidative stress markers induced
by hyperosmolarity in primary human corneal epithelial cells. PLoS
One. 10(e0126561)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee HS, Jang JY, Lee SH, Im SK and Yoon
KC: Clinical effectiveness of topical cyclosporine a 0.05% after
laser epithelial keratomileusis. Cornea. 32:e150–e155.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Holland EJ, Darvish M, Nichols KK, Jones L
and Karpecki PM: Efficacy of topical ophthalmic drugs in the
treatment of dry eye disease: A systematic literature review. Ocul
Surf. 17:412–423. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|