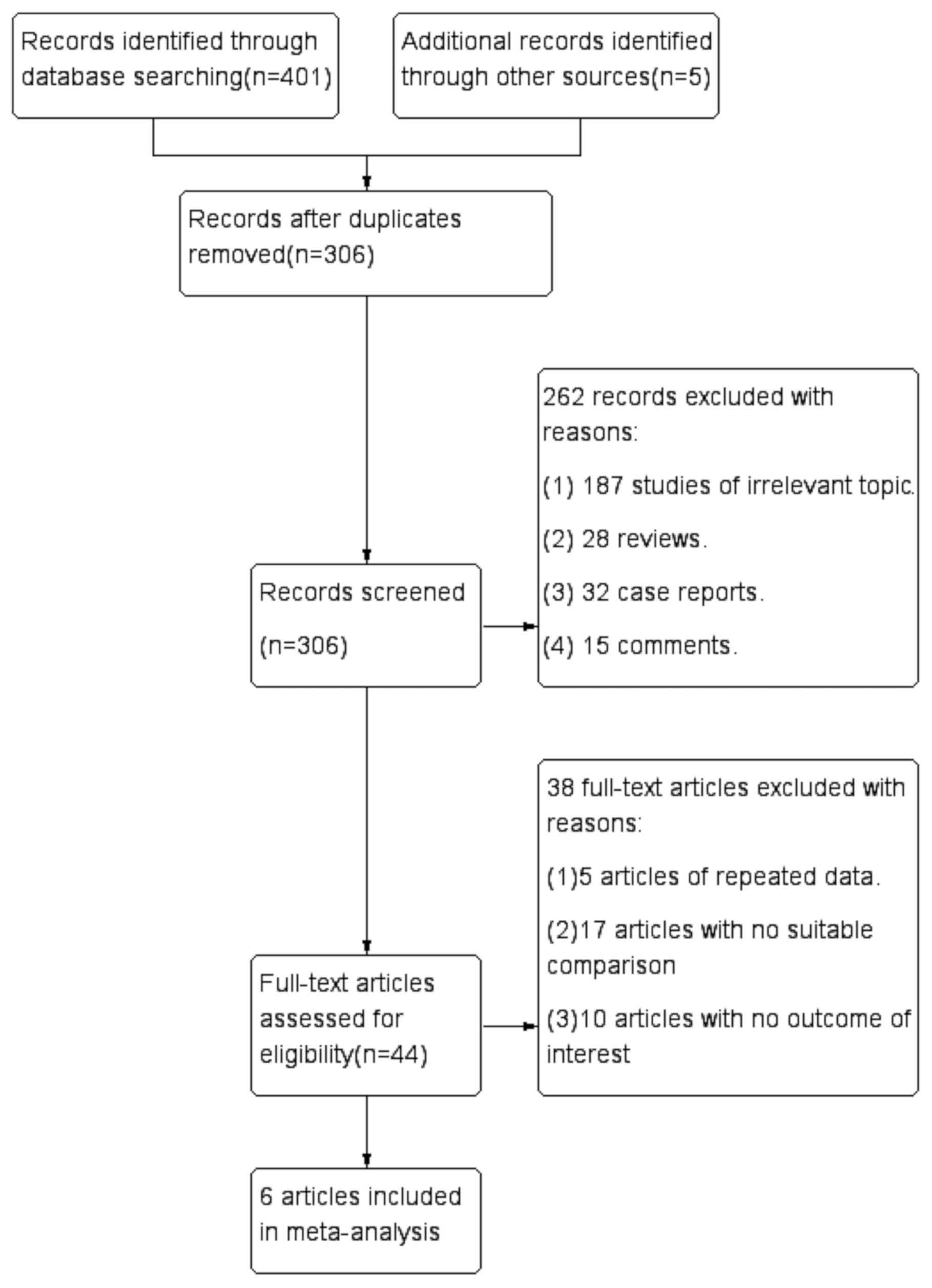
|
1
|
Davies EW, Matza LS, Worth G, Feeny DH,
Kostelec J, Soroka S, Mendelssohn D, McFarlane P and Belozeroff V:
Health state utilities associated with major clinical events in the
context of secondary hyperparathyroidism and chronic kidney disease
requiring dialysis. Health Qual Life Outcomes.
13(90)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lewis R: Mineral and bone disorders in
chronic kidney disease: New insights into mechanism and management.
Ann Clin Biochem. 49:432–440. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wei Y, Lin J, Yang F, Li X, Hou Y, Lu R,
Shi X, Liu Z and Du Y: Risk factors associated with secondary
hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease. Exp
Ther Med. 12:1206–1212. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Isakova T, Nickolas TL, Denburg M,
Yarlagadda S, Weiner DE, Gutiérrez OM, Bansal V, Rosas SE, Nigwekar
S, Yee J, et al: KDOQI US commentary on the 2017 KDIGO clinical
practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation,
prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and
bone disorder (CKD-MBD). Am J Kidney Dis. 70:737–751.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Goettsch C, Iwata H and Aikawa E:
Parathyroid hormone: Critical brigde between bone metabolism and
cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
34:1333–1335. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Grams ME and Coresh J: Assessing risk in
chronic kidney disease: A methodological review. Nat Rev Nephrol.
9:18–25. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ye H, Ye P, Zhang Z, Hou A, Liang Z and
Kong Y: A bayesian network analysis on comparative efficacy of
treatment strategies for dialysis patients with secondary
hyperparathyroidism. Exp Ther Med. 17:531–540. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Naves-Díaz M, Passlick-Deetjen J,
Guinsburg A, Marelli C, Fernández-Martín JL, Rodríguez-Puyol D and
Cannata-Andía JB: Calcium, phosphorus, PTH and death rates in a
large sample of dialysis patients from Latin America. The CORES
Study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:1938–1947. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Komaba H, Taniguchi M, Wada A, Iseki K,
Tsubakihara Y and Fukagawa M: Parathyroidectomy and survival among
Japanese hemodialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Kidney Int. 88:350–359. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ifudu O: Care of patients undergoing
hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 339:1054–1062. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Martin KJ, González EA, Gellens M, Hamm
LL, Abboud H and Lindberg J: 19-Nor-1-α-25-dihydroxyvitamin D2
(paricalcitol) safely and effectively reduces the levels of intact
parathyroid hormone in patients on hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
9:1427–1432. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ross EA, Tian J, Abboud H, Hippensteel R,
Melnick JZ, Pradhan RS, Williams LA, Hamm LL and Sprague SM: Oral
paricalcitol for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in
patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Am J Nephrol.
28:97–106. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mittman N, Desiraju B, Meyer KB,
Chattopadhyay J and Avram MM: Treatment of secondary
hyperparathyroidism in ESRD: A 2 -year-single-center cross-over
study. Kidney Int. (Suppl 8):S33–S36. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Block GA, Martin KJ, de Francisco AL,
Turner SA, Avram MM, Suranyi MG, Hercz G, Cunningham J, Abu-Alfa
AK, Messa P, et al: Cinacalcet for secondary hyperparathyroidism in
patients receiving hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 350:1516–1525.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Block GA, Zeig S, Sugihara J, Chertow GM,
Chi EM, Turner SA and Bushinsky DA: TARGET Investigators. Combined
therapy with cinacalcet and low doses of vitamin D sterols in
patients with moderate to severe secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 23:2311–2318. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fishbane S, Shapiro WB, Corry DB, Vicks
SL, Roppolo M, Rappaport K, Ling X, Goodman WG, Turner S and
Charytan C: Cinacalcet HCl and concurrent low-dose vitamin D
improves treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in dialysis
patients compared with vitamin D alone, the ACHIEVE study results.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 3:1718–1725. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Block GA, Zaun D, Smits G, Persky M,
Brillhart S, Nieman K, Liu J and St Peter WL: Cinacalcet
hydrochloride treatment significantly improves all-cause and
cardiovascular survival in a large cohort of hemodialysis patients.
Kidney Int. 78:578–589. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow
C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, Clarke M, Devereaux PJ, Kleijnen J
and Moher D: The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews
and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare
interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ.
339(b2700)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Higgins JP and Green S: Cochrane handbook
for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Book Series,
2008.
|
|
20
|
Wells GA, Shea B, O'Connell D, Petersen J,
Welch V, Losos M and Tugwell P: The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale(NOS) for
assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses.
Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, 2015. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp.
|
|
21
|
Sharma A, Marshall TS, Khan SS and Johns
B: Cost effectiveness of paricalcitol versus cinacalcet with
low-dose vitamin D for management of secondary hyperparathyroidism
in haemodialysis patients in the USA. Clin Drug Investig.
34:107–115. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zawierucha J, Malyszko J, Malyszko JS,
Prystacki T, Marcinkowski WP and Dryl-Rydzynska T: Three
therapeutic strategies: Cinacalcet, paricalcitol or both in
secondary hyperparathyroidism treatment in hemodialysed patients
during 1-year observational study-A comparison. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 10(40)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sprague SM, Wetmore JB, Gurevich K, Da
Roza G, Buerkert J, Reiner M, Goodman W and Cooper K: Effect of
cinacalcet and vitamin d analogs on fibroblast growth factor-23
during the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin J Am
Society Nephrol. 10:1021–1030. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kukavica N, Resic H, Ajanović S, Groša E,
Prohić N, Ćorić A and Mašnić F: Comparative effectiveness of
cinacalcet (sensipar/mimpara) versus paracalcitol in treatment of
secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients on hemodialysis. Acta Med
Croatica. 65:128–129. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Kaperonis N, Kourvelou C, Sgantzos1 A,
Nastou1 D, Ntatsis G, Ziakka S, Karakasis F, Nikolopoulos V,
Zoubaniotou V, Koutsovasili A, et al: Cinacalcet vs. paricalcitol
in hemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:497–498.
2012.
|
|
26
|
Ketteler M, Martin KJ, Wolf M, Amdahl M,
Cozzolino M, Goldsmith D, Sharma A, Marx S and Khan S: Paricalcitol
versus cinacalcet plus low-dose vitamin D therapy for the treatment
of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients receiving
haemodialysis: Results of the IMPACT SHPT study. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 27:3270–3278. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Andress D: Nonclassical aspects of
differential vitamin D receptor activation, implications for
survival in patients with chronic kidney disease. Drugs.
67:1999–2012. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Dusilová-Sulková S: Vitamin D metabolism
and vitamin D traditional and nontraditional, target organs,
implications for kidney patients. J Ren Care. 35:39–44.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Matuszkiewicz-Rowińska J and Żebrowski P:
Paricalcitol-a selective vitamin D receptor activator for secondary
hyperparathy-roidism in patients with chronic kidney disease. Wiad
Lek. 69:756–759. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zawierucha J, Małyszko J, Małyszko J,
Prystacki T, Marcinkowski W and Dryl-Rydzyńska T: Treatment of
secondary hyperparathyroidism in hemodialysed patients-paricalcitol
with or without cinacalcet. Przegl Lek. 73:229–232. 2016.PubMed/NCBI(In Polish).
|
|
31
|
Soliman AR, Maamoun HA, Soliman MA,
Darwish H and Elbanna E: Cinacalcet versus parathyroidectomy in the
treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism post renal
transplantation. Rom J Intern Med. 54:184–189. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Block GA, Bushinsky DA, Cheng S,
Cunningham J, Dehmel B, Drueke TB, Ketteler M, Kewalramani R,
Martin KJ, Moe SM, et al: Effect of etelcalcetide vs. cinacalcet on
serum parathyroid hormone in patients receiving hemodialysis with
secondary hyperparathyroidism: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
317:156–164. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI
clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in
chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 42 (4 Suppl 3):S1–S201.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ureña-Torres P, Bridges I, Christiano C,
Cournoyer SH, Cooper K, Farouk M, Kopyt NP, Rodriguez M, Zehnder D
and Covic A: Efficacy of cinacalcet with low-dose vitamin D in
incident haemodialysis subjects with secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 28:1241–1254. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|