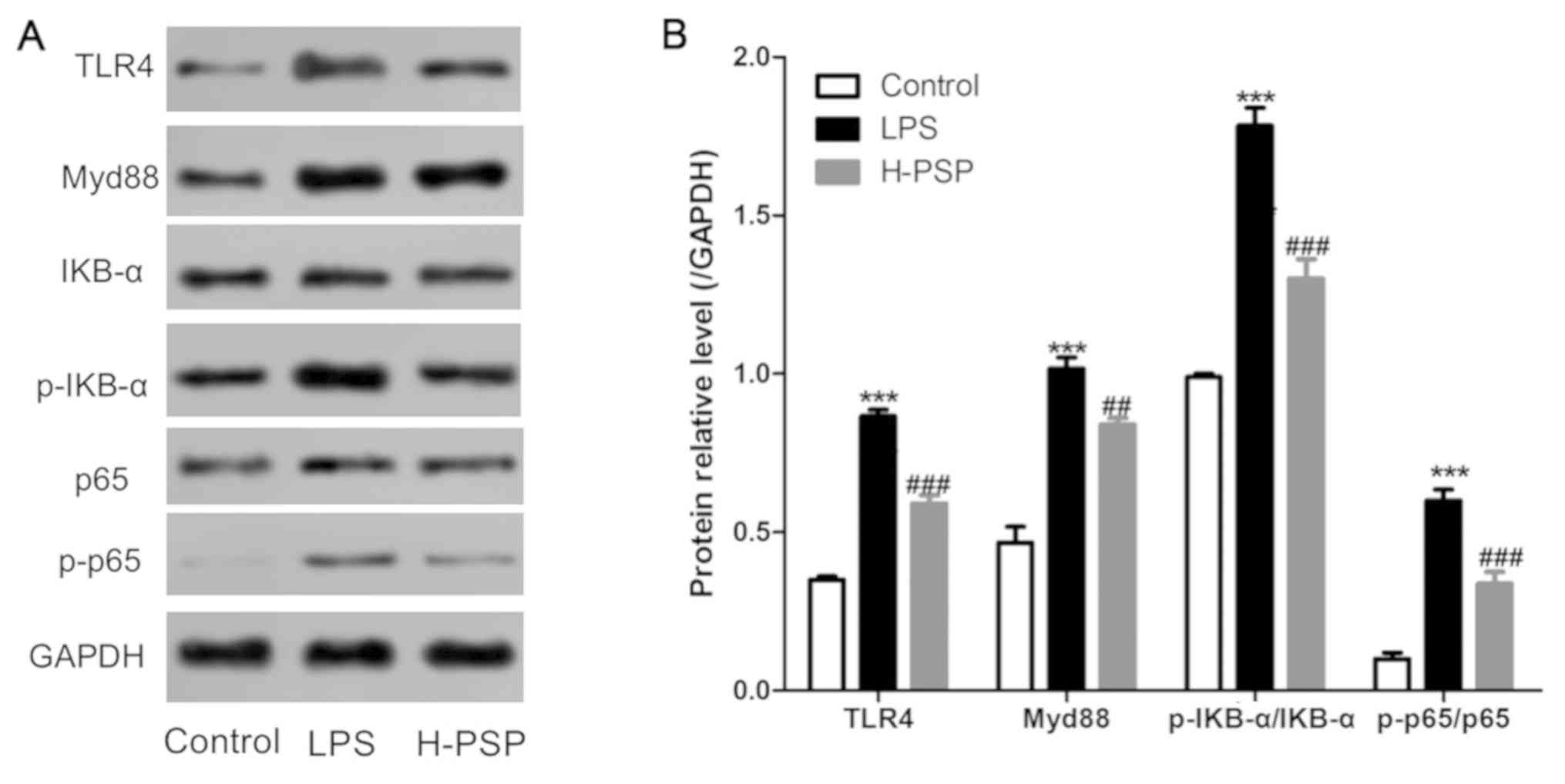
|
1
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
lung injury: A clinical and molecular review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rubenfeld GD and Herridge MS: Epidemiology
and outcomes of acute lung injury. Chest. 131:554–562.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bastarache JA, Ware LB and Bernard GR: The
role of the coagulation cascade in the continuum of sepsis and
acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin
Respir Crit Care Med. 27:365–376. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fujishima S, Morisaki H, Ishizaka A,
Kotake Y, Miyaki M, Yoh K, Sekine K, Sasaki J, Tasaka S, Hasegawa
N, et al: Neutrophil elastase and systemic inflammatory response
syndrome in the initiation and development of acute lung injury
among critically ill patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:333–338.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nie L, Wu W, Lu Z, Zhu G and Liu J: CXCR3
may help regulate the inflammatory response in acute lung injury
via a pathway modulated by IL-10 secreted by CD8+ CD122+ regulatory
T cells. Inflammation. 39:526–533. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Goodman RB, Pugin J, Lee JS and Matthay
MA: Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 14:523–535. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lin SH, Fu J, Wang CJ, Gao F, Feng XY, Liu
Q, Cao J and Xu F: Inflammation elevated IL-33 originating from the
lung mediates inflammation in acute lung injury. Clin Immunol.
173:32–43. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cui X, Wang S, Cao H, Guo H, Li Y, Xu F,
Zheng M, Xi X and Han C: A Review: The bioactivities and
pharmacological applications of Polygonatum sibiricum
polysaccharides. Molecules. 23(1170)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li L, Thakur K, Liao BY, Zhang JG and Wei
ZJ: Antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of polysaccharides
sequentially extracted from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. Int J Biol
Macromol. 114:317–323. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Long T, Liu Z, Shang J, Zhou X, Yu S, Tian
H and Bao Y: Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharides play anti-cancer
effect through TLR4-MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int J Biol
Macromol. 111:813–821. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang HZ, Wang JP, Mi S, Liu HZ, Cui B, Yan
HM, Yan J, Li Z, Liu H, Hua F, et al: TLR4 activity is required in
the resolution of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis after acute
and chronic lung injury. Am J Pathol. 180:275–292. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tao H, Li N, Zhang Z, Mu H, Meng C, Xia H,
Fu L, Xu Y and Zhang S: Erlotinib protects LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice by inhibiting EGFR/TLR4 signaling pathway. Shock.
51:131–138. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Becker CE and O'Neill LAJ: Inflammasomes
in inflammatory disorders: The role of TLRs and their interactions
with NLRs. Semin Immunopathol. 29:239–248. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lin Q, Li M, Fang D, Fang J and Su SB: The
essential roles of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in sterile
inflammatory diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:1422–1432.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu H, Yang Y, Guo S, Yang J, Jiang K, Zhao
G, Qiu C and Deng G: Nuciferine ameliorates inflammatory responses
by inhibiting the TLR4-mediated pathway in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Front Pharmacol.
8(939)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Qi M, Yin L, Xu L, Tao X, Qi Y, Han X,
Wang C, Xu Y, Sun H, Liu K, et al: Dioscin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory kidney injury via the
microRNA let-7i/TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res.
111:509–522. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Verstak B, Nagpal K, Bottomley SP,
Golenbock DT, Hertzog PJ and Mansell A: MyD88 adapter-like
(Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and
TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses. J Biol Chem.
284:24192–24203. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
He W, Qu T, Yu Q, Wang Z, Lv H, Zhang J,
Zhao X and Wang P: LPS induces IL-8 expression through TLR4, MyD88,
NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways in human dental pulp stem cells. Int
Endod J. 46:128–136. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Publication. 327:963–965. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hawkins P, Prescott MJ, Carbone L,
Dennison N, Johnson C, Makowska IJ, Marquardt N, Readman G, Weary
DM and Golledge HD: A good death? Report of the second Newcastle
Meeting on Laboratory Animal Euthanasia. Animals (Basel).
6(50)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang CH, Yang ML, Tsai CH, Li YC, Lin YJ
and Kuan YH: Ginkgo biloba leaves extract (EGb 761) attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of
oxidative stress and NF-κB-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
pathway. Phytomedicine. 20:303–309. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Leung WS, Yang ML, Lee SS, Kuo CW, Ho YC,
Huang-Liu R, Lin HW and Kuan YH: Protective effect of zerumbone
reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via
antioxidative enzymes and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
46:194–200. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tao J, Zhang J, Ling Y, McCall CE and Liu
TF: Mitochondrial sirtuin 4 resolves immune tolerance in monocytes
by rebalancing glycolysis and glucose oxidation homeostasis. Front
Immunol. 9(419)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang B, Liu ZY, Li YY, Luo Y, Liu ML,
Dong HY, Wang YX, Liu Y, Zhao PT, Jin FG, et al: Antiinflammatory
effects of matrine in LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Eur J
Pharm Sci. 44:573–579. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang W, Luo F, Lu Q, Liu J, Li P, Wang X,
Fu Y, Hao K, Yan T and Ding X: The protective effect of Trillin
LPS-induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation
and oxidative state. Chem Biol Interact. 243:127–134.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu J, Zhang YY, Guo L, Li H and Chen DF:
Bupleurum polysaccharides attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation via modulating Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. PLoS
One. 8(e78051)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Caudrillier A, Kessenbrock K, Gilliss BM,
Nguyen JX, Marques MB, Monestier M, Toy P, Werb Z and Looney MR:
Platelets induce neutrophil extracellular traps in
transfusion-related acute lung injury. J Clin Invest.
122:2661–2671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Narasaraju T, Yang E, Samy RP, Ng HH, Poh
WP, Liew AA, Phoon MC, van Rooijen N and Chow VT: Excessive
neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to acute
lung injury of influenza pneumonitis. Am J Pathol. 179:199–210.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhi-Tao LI, Sun JX, Zhu HX and Chu ZF:
Extracting of Polygonatum polysaccharides and its antimicrobial
activity. Food Res Dev. 38:36–37. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Zheng CY, Wang HF and Zhang TT: Studies on
the anti-micromial and anti-inflammatory activities of Polygonatum
cyrtonema Hua. polysaccharides. J Anhui Norm Univsity. 33:272–276.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Jiang Q, Yi M, Guo Q, Wang C, Wang H, Meng
S, Liu C, Fu Y, Ji H and Chen T: Protective effects of polydatin on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through
TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:370–376.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Akhter N, Hasan A, Shenouda S, Wilson A,
Kochumon S, Ali S, Tuomilehto J, Sindhu S and Ahmad R: TLR4/MyD88
-mediated CCL2 production by lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin):
Implications for metabolic inflammation. J Diabetes Metab Disord.
17:77–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rocha DM, Caldas AP, Oliveira LL, Bressan
J and Hermsdorff HH: Saturated fatty acids trigger TLR4-mediated
inflammatory response. Atherosclerosis. 244:211–215.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Doyle SL and O'Neill LAJ: Toll-like
receptors: From the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into
transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1102–1113. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
O'Neill LAJ and Bowie AG: The family of
five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:353–364. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang Z, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Qian Y,
Matsumoto K and Li X: Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated
kinase-dependent IL-1-induced signaling complexes phosphorylate
TAK1 and TAB2 at the plasma membrane and activate TAK1 in the
cytosol. Mol Cell Biol. 22:7158–7167. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Monick MM and Hunninghake GW: Activation
of second messenger pathways in alveolar macrophages by endotoxin.
Eur Respir J. 20:210–222. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Perkins ND: Integrating cell-signalling
pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
8:49–62. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dolinay T, Kim YS, Howrylak J, Hunninghake
GM, An CH, Fredenburgh L, Massaro AF, Rogers A, Gazourian L,
Nakahira K, et al: Inflammasome-regulated cytokines are critical
mediators of acute lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
185:1225–1234. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Montravers P, Chollet-Martin S, Marmuse
JP, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA and Desmonts JM: Lymphatic release of
cytokines during acute lung injury complicating severe
pancreatitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 152:1527–1533.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Barreto TR, Costola-de-Souza C, Margatho
RO, Queiroz-Hazarbassanov N, Rodrigues SC, Felício LF, Palermo-Neto
J and Zager A: Repeated Domperidone treatment modulates pulmonary
cytokines in LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 56:43–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lin S, Wu H, Wang C, Xiao Z and Xu F:
Regulatory T cells and acute lung injury: Cytokines, uncontrolled
inflammation, and therapeutic implications. Front Immunol.
9(1545)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|