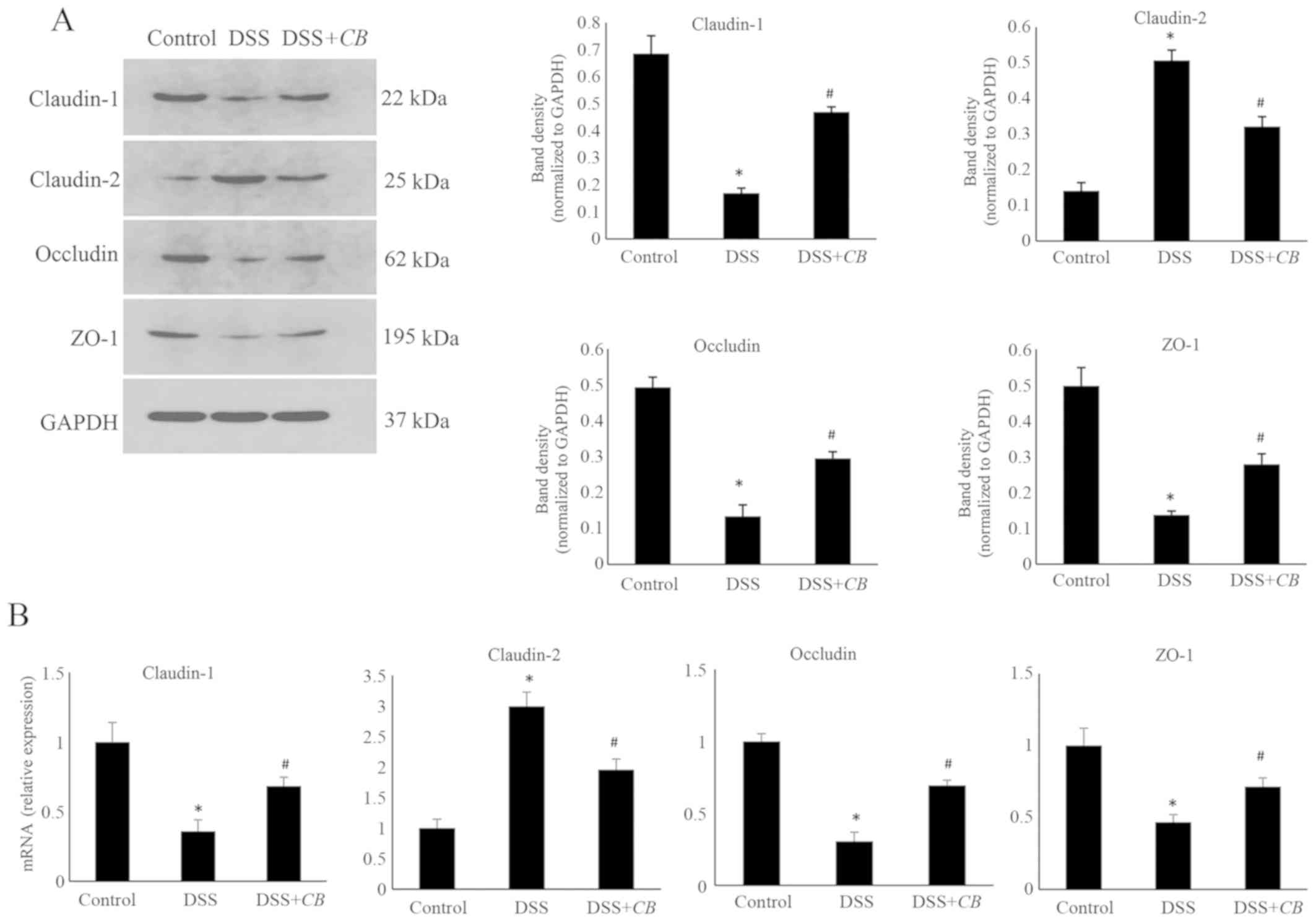
|
1
|
Suzuki T: Regulation of intestinal
epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:631–659. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sanchez de Medina F, Romero-Calvo I,
Mascaraque C and Martinez-Augustin O: Intestinal inflammation and
mucosal barrier function. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:2394–2404.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Suzuki T: Regulation of the intestinal
barrier by nutrients: The role of tight junctions. Anim Sci J.
91(e13357)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Andrews C, McLean MH and Durum SK:
Cytokine tuning of intestinal epithelial function. Front Immunol.
9(1270)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rubin DT, Ananthakrishnan AN, Siegel CA,
Sauer BG and Long MD: ACG Clinical Guideline: Ulcerative colitis in
adults. Am J Gastroenterol. 114:384–413. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kornbluth A and Sachar DB: Ulcerative
colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College Of
Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J
Gastroenterol. 105:501–523; quiz 524. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chang J, Leong RW, Wasinger VC, Ip M, Yang
M and Phan TG: Impaired intestinal permeability contributes to
ongoing bowel symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
and mucosal healing. Gastroenterology. 153:723–731.e1.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Luissint AC, Parkos CA and Nusrat A:
Inflammation and the intestinal barrier: Leukocyte-epithelial cell
interactions, cell junction remodeling, and mucosal repair.
Gastroenterology. 151:616–632. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Buckley A and Turner JR: Cell biology of
tight junction barrier regulation and mucosal disease. Cold Spring
Harb Perspect Biol. 10(a029314)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Khor B, Gardet A and Xavier RJ: Genetics
and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature.
474:307–317. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Suau A, Bonnet R, Sutren M, Godon JJ,
Gibson GR, Collins MD and Doré J: Direct analysis of genes encoding
16S rRNA from complex communities reveals many novel molecular
species within the human gut. Appl Environ Microbiol. 65:4799–4807.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J,
Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W and Pettersson S: Host-gut microbiota
metabolic interactions. Science. 336:1262–1267. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hill C, Guarner F, Reid G, Gibson GR,
Merenstein DJ, Pot B, Morelli L, Canani RB, Flint HJ, Salminen S,
et al: Expert consensus document. The international scientific
association for probiotics and prebiotics consensus statement on
the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:506–514. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Schönherr-Hellec S, Klein G, Delannoy J,
Ferraris L, Friedel I, Rozé JC, Butel MJ and Aires J: Comparative
phenotypic analysis of ‘Clostridium neonatale’ and Clostridium
butyricum isolates from neonates. Anaerobe. 48:76–82.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kong Q, He GQ, Jia JL, Zhu QL and Ruan H:
Oral administration of Clostridium butyricum for modulating
gastrointestinal microflora in mice. Curr Microbiol. 62:512–517.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang HB, Wang PY, Wang X, Wan YL and Liu
YC: Butyrate enhances intestinal epithelial barrier function via
up-regulation of tight junction protein Claudin-1 transcription.
Dig Dis Sci. 57:3126–3135. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Peng L, Li ZR, Green RS, Holzman IR and
Lin J: Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating
tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein
kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Nutr. 139:1619–1625.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K,
Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S and Neurath MF: Chemically induced
mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 12:1295–1309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, Gu Y, Fang K, Mao K, Dou J, Fan H,
Zhou C and Wang H: Lactobacillus acidophilus and Clostridium
butyricum ameliorate colitis in murine by strengthening the gut
barrier function and decreasing inflammatory factors. Benef
Microbes. 9:775–787. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dawson PA, Huxley S, Gardiner B, Tran T,
McAuley JL, Grimmond S, McGuckin M and Markovich D: Reduced mucin
sulfonation and impaired intestinal barrier function in the
hyposulfataemic NaS1 null mouse. Gut. 58:910–919. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, Bloemena
E, Peña AS, Meuwissen SG and Van Rees EP: Chronic experimental
colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized
by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 114:385–391.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Matsuoka K and Kanai T: The gut microbiota
and inflammatory bowel disease. Semin Immunopathol. 37:47–55.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zeissig S, Bürgel N, Günzel D, Richter J,
Mankertz J, Wahnschaffe U, Kroesen AJ, Zeitz M, Fromm M and
Schulzke JD: Changes in expression and distribution of claudin 2, 5
and 8 lead to discontinuous tight junctions and barrier dysfunction
in active Crohn's disease. Gut. 56:61–72. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Martini E, Krug SM, Siegmund B, Neurath MF
and Becker C: Mend your fences: The epithelial barrier and its
relationship with mucosal immunity in inflammatory bowel disease.
Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:33–46. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okamoto T, Sasaki M, Tsujikawa T, Fujiyama
Y, Bamba T and Kusunoki M: Preventive efficacy of butyrate enemas
and oral administration of Clostridium butyricum M588 in
dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in rats. J Gastroenterol.
35:341–346. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hayashi A, Sato T, Kamada N, Mikami Y,
Matsuoka K, Hisamatsu T, Hibi T, Roers A, Yagita H, Ohteki T, et
al: A single strain of Clostridium butyricum induces
intestinal IL-10-producing macrophages to suppress acute
experimental colitis in mice. Cell Host Microbe. 13:711–722.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kanai T, Mikami Y and Hayashi A: A
breakthrough in probiotics: Clostridium butyricum regulates
gut homeostasis and anti-inflammatory response in inflammatory
bowel disease. J Gastroenterol. 50:928–939. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Seki H, Shiohara M, Matsumura T, Miyagawa
N, Tanaka M, Komiyama A and Kurata S: Prevention of
antibiotic-associated diarrhea in children by Clostridium
butyricum MIYAIRI. Pediatr Int. 45:86–90. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen L, Li S, Zheng J, Li W, Jiang X, Zhao
X, Li J, Che L, Lin Y, Xu S, et al: Effects of dietary
Clostridium butyricum supplementation on growth performance,
intestinal development, and immune response of weaned piglets
challenged with lipopolysaccharide. J Anim Sci Biotechnol.
9(62)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ye D and Ma TY: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms that mediate basal and tumour necrosis
factor-alpha-induced regulation of myosin light chain kinase gene
activity. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1331–1346. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Al-Sadi R, Guo S, Ye D, Dokladny K,
Alhmoud T, Ereifej L, Said HM and Ma TY: Mechanism of IL-1β
modulation of intestinal epithelial barrier involves p38 kinase and
activating transcription factor-2 activation. J Immunol.
190:6596–6606. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Heller F, Florian P, Bojarski C, Richter
J, Christ M, Hillenbrand B, Mankertz J, Gitter AH, Bürgel N, Fromm
M, et al: Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in
ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions,
apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology. 129:550–564.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kühn R, Löhler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K
and Müller W: Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic
enterocolitis. Cell. 75:263–274. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Franke A, Balschun T, Karlsen TH,
Sventoraityte J, Nikolaus S, Mayr G, Domingues FS, Albrecht M,
Nothnagel M, Ellinghaus D, et al: Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2
and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis
susceptibility. Nat Genet. 40:1319–1323. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kuhn KA, Manieri NA, Liu TC and
Stappenbeck TS: IL-6 stimulates intestinal epithelial proliferation
and repair after injury. PLoS One. 9(e114195)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Inan MS, Rasoulpour RJ, Yin L, Hubbard AK,
Rosenberg DW and Giardina C: The luminal short-chain fatty acid
butyrate modulates NF-kappaB activity in a human colonic epithelial
cell line. Gastroenterology. 118:724–734. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nancey S, Bienvenu J, Coffin B, Andre F,
Descos L and Flourie B: Butyrate strongly inhibits in vitro
stimulated release of cytokines in blood. Dig Dis Sci. 47:921–928.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Mano T, Sinohara R, Sawai Y, Oda N,
Nishida Y, Mokumo T, Asano K, Ito Y, Kotake M, Hamada M, et al:
Changes in lipid peroxidation and free radical scavengers in the
brain of hyper- and hypothyroid aged rats. J Endocrinol.
147:361–365. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Orient A, Donkó A, Szabó A, Leto TL and
Geiszt M: Novel sources of reactive oxygen species in the human
body. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 22:1281–1288. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mårtensson J, Jain A and Meister A:
Glutathione is required for intestinal function. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 87:1715–1719. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kyle ME, Miccadei S, Nakae D and Farber
JL: Superoxide dismutase and catalase protect cultured hepatocytes
from the cytotoxicity of acetaminophen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
149:889–896. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tian T, Wang Z and Zhang J:
Pathomechanisms of oxidative stress in inflammatory bowel disease
and potential antioxidant therapies. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(4535194)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, Saeedsolz
CC, Bayless AJ, Wilson KE, Glover LE, Kominsky DJ, Magnuson A, et
al: Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids
and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function.
Cell Host Microbe. 17:662–671. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kaczmarczyk MM, Miller MJ and Freund GG:
The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of
type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer.
Metabolism. 61:1058–1066. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W,
Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, Grueter CA, Lim H, Saunders LR, Stevens RD,
et al: Suppression of oxidative stress by beta-hydroxybutyrate, an
endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science. 339:211–214.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rosignoli P, Fabiani R, De Bartolomeo A,
Spinozzi F, Agea E, Pelli MA and Morozzi G: Protective activity of
butyrate on hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in isolated human
colonocytes and HT29 tumour cells. Carcinogenesis. 22:1675–1680.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Citi S: Intestinal barriers protect
against disease. Science. 359:1097–1098. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Suzuki H, Tani K and Fujiyoshi Y: Crystal
structures of claudins: Insights into their intermolecular
interactions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1397:25–34. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Inai T, Kobayashi J and Shibata Y:
Claudin-1 contributes to the epithelial barrier function in MDCK
cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 78:849–855. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Milatz S, Krug SM, Rosenthal R, Günzel D,
Müller D, Schulzke JD, Amasheh S and Fromm M: Claudin-3 acts as a
sealing component of the tight junction for ions of either charge
and uncharged solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1798:2048–2057.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Van Itallie C, Rahner C and Anderson JM:
Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular
conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J
Clin Invest. 107:1319–1327. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Amasheh S, Schmidt T, Mahn M, Florian P,
Mankertz J, Tavalali S, Gitter AH, Schulzke JD and Fromm M:
Contribution of claudin-5 to barrier properties in tight junctions
of epithelial cells. Cell Tissue Res. 321:89–96. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yu AS, Enck AH, Lencer WI and Schneeberger
EE: Claudin-8 expression in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
augments the paracellular barrier to cation permeation. J Biol
Chem. 278:17350–17359. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Amasheh S, Meiri N, Gitter AH, Schöneberg
T, Mankertz J, Schulzke JD and Fromm M: Claudin-2 expression
induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial
cells. J Cell Sci. 115:4969–4976. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Alexandre MD, Jeansonne BG, Renegar RH,
Tatum R and Chen YH: The first extracellular domain of claudin-7
affects paracellular Cl-permeability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
357:87–91. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Fujita H, Chiba H, Yokozaki H, Sakai N,
Sugimoto K, Wada T, Kojima T, Yamashita T and Sawada N:
Differential expression and subcellular localization of claudin-7,
-8, -12, -13, and -15 along the mouse intestine. J Histochem
Cytochem. 54:933–944. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dörfel MJ and Huber O: Modulation of tight
junction structure and function by kinases and phosphatases
targeting occludin. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2012(807356)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Xiao Z, Liu L, Tao W, Pei X, Wang G and
Wang M: Clostridium tyrobutyricum protect intestinal barrier
function from LPS-induced apoptosis via P38/JNK signaling pathway
in IPEC-J2 Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1779–1792.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Daly K and Shirazi-Beechey SP: Microarray
analysis of butyrate regulated genes in colonic epithelial cells.
DNA Cell Biol. 25:49–62. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Kandel ES and Hay N: The regulation and
activities of the multifunctional serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB.
Exp Cell Res. 253:210–229. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Manning BD and Toker A: AKT/PKB signaling:
Navigating the network. Cell. 169:381–405. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Wang H, Ji Y, Wu G, Sun K, Sun Y, Li W,
Wang B, He B, Zhang Q, Dai Z and Wu Z: l-tryptophan activates
mammalian target of rapamycin and enhances expression of tight
junction proteins in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. J Nutr.
145:1156–1162. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Yan H and Ajuwon KM: Butyrate modifies
intestinal barrier function in IPEC-J2 cells through a selective
upregulation of tight junction proteins and activation of the Akt
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 12(e0179586)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhao Y, Chen F, Wu W, Sun M, Bilotta AJ,
Yao S, Xiao Y, Huang X, Eaves-Pyles TD, Golovko G, et al: GPR43
mediates microbiota metabolite SCFA regulation of antimicrobial
peptide expression in intestinal epithelial cells via activation of
mTOR and STAT3. Mucosal Immunol. 11:752–762. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|