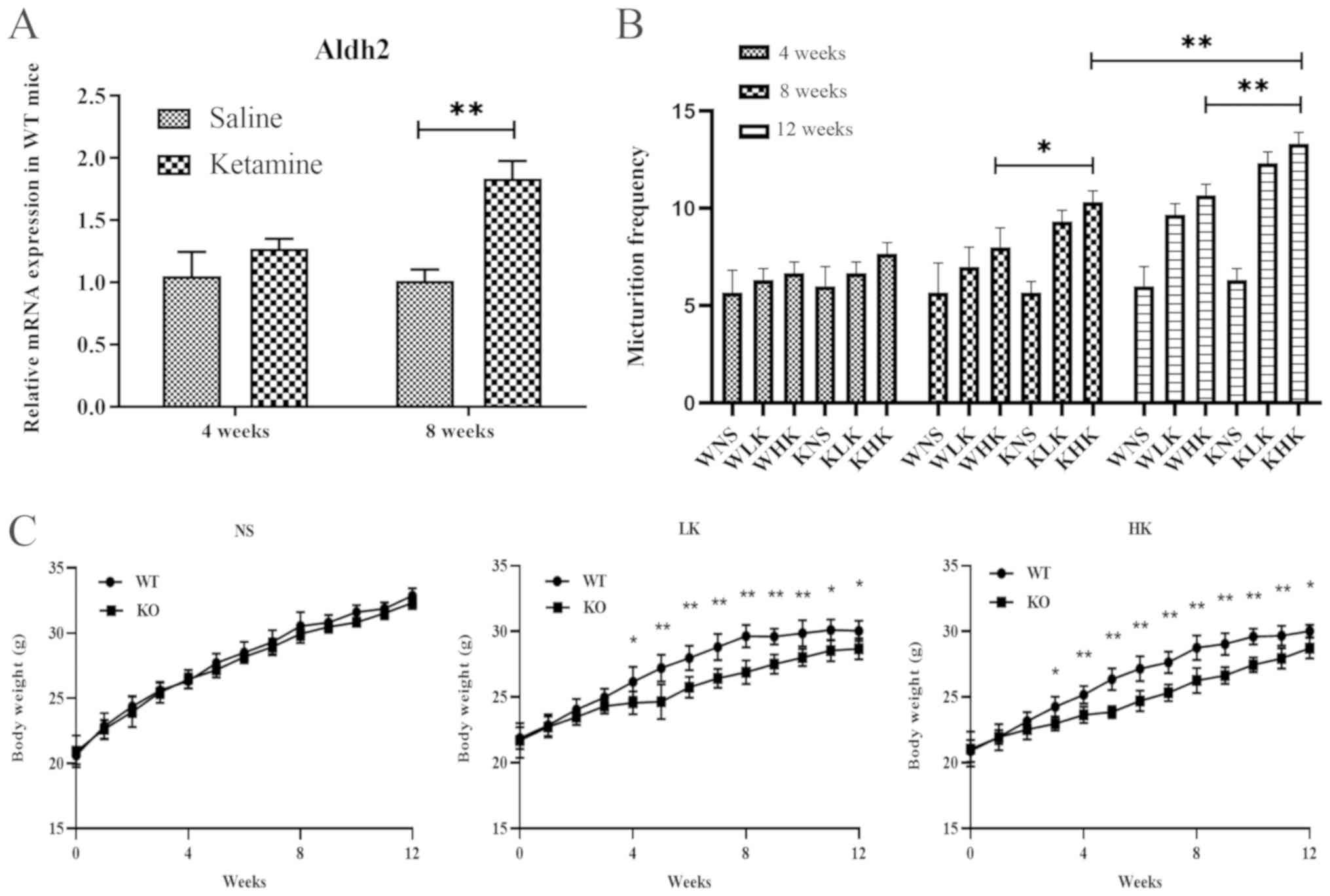
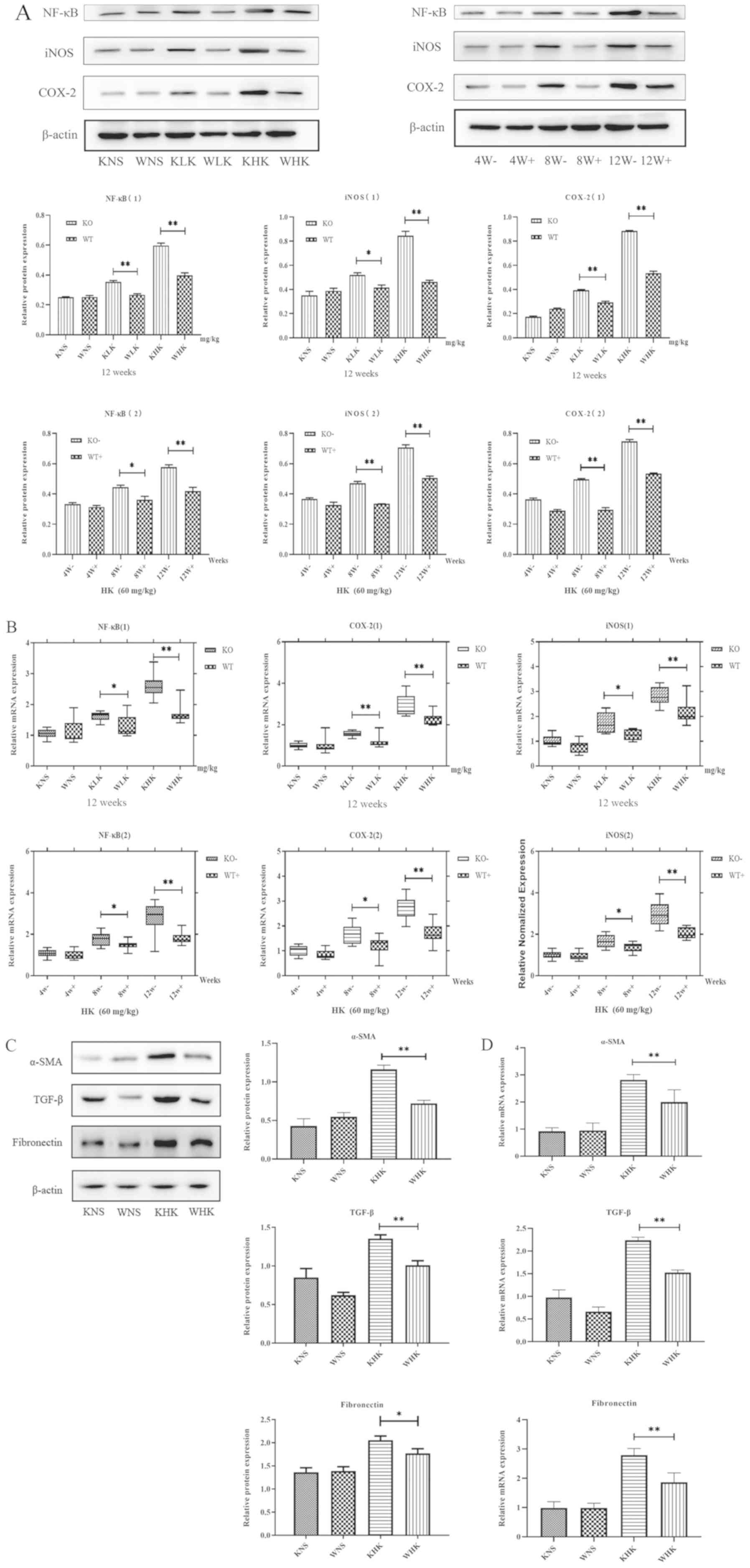
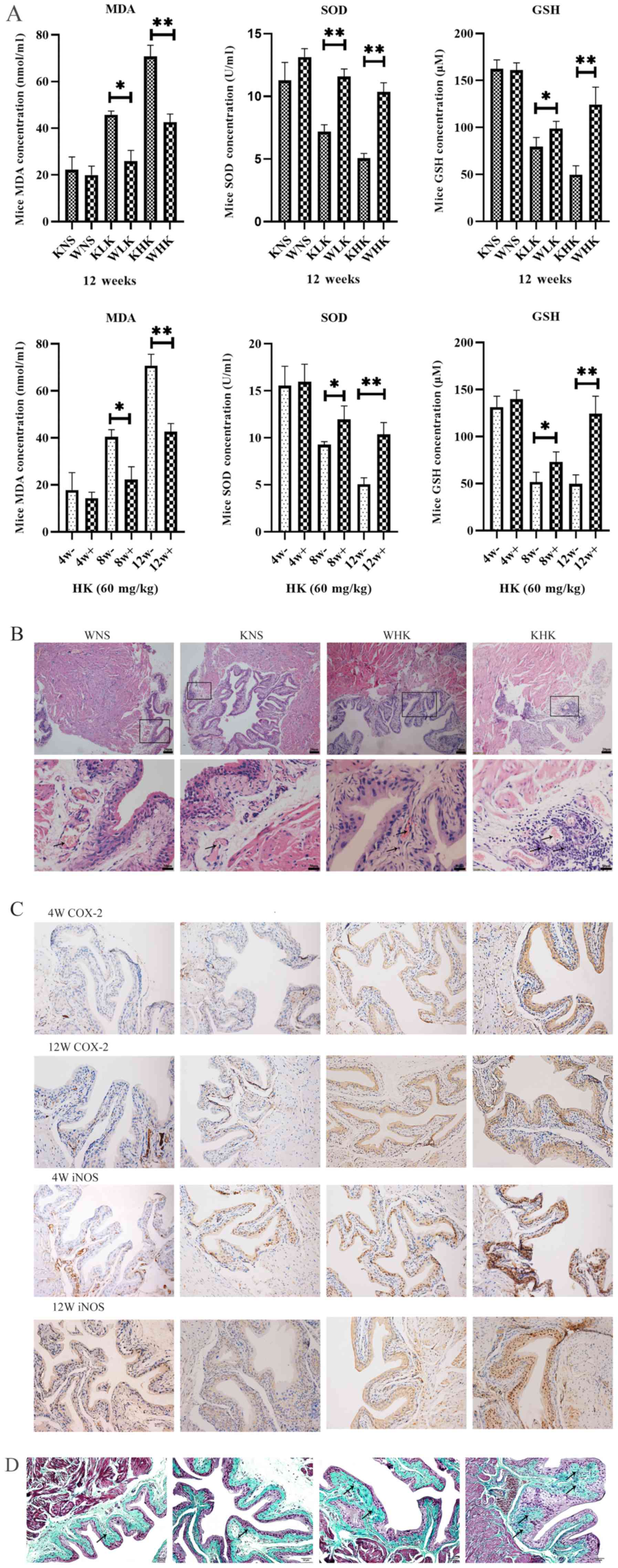
|
1
|
Wang JW, Kivovich V and Gordon L: Ketamine
abuse syndrome: Hepatobiliary and urinary pathology among
adolescents in Flushing, NY. Pediatr Emerg Care. 33:e24–e26.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Persson J: Wherefore ketamine? Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 23:455–60. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Parkin MC, Turfus SC, Smith NW, Halket JM,
Braithwaite RA, Elliott SP, Osselton MD, Cowan DA and Kicman AT:
Detection of ketamine and its metabolites in urine by ultra high
pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 876:137–142.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu KM, Chuang SM, Long CY, Lee YL, Wang
CC, Lu MC, Lin RJ, Lu JH, Jang MY, Wu WJ, et al: Ketamine-induced
ulcerative cystitis and bladder apoptosis involve oxidative stress
mediated by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 309:F318–F331. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu T, Liu S, Ma T, Jia Z, Zhang Z and Wang
A: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 protects against oxidative stress
associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Redox Biol.
11:286–296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bondeva T and Wolf G: Reactive oxygen
species in diabetic nephropathy: Friend or foe? Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 29:1998–2003. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim MJ and Lim Y: Protective effect of
short-term genistein supplementation on the early stage in
diabetes-induced renal damage. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(510212)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jomova K and Valko M: Advances in
metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology.
283:65–87. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Choi YJ, Kim HS, Lee J, Chung J, Lee JS,
Choi JS, Yoon TR, Kim HK and Chung HY: Down-regulation of oxidative
stress and COX-2 and iNOS expressions by dimethyl lithospermate in
aged rat kidney. Arch Pharm Res. 37:1032–1038. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin HC, Lee HS, Chiueh TS, Lin YC, Lin HA,
Lin YC, Cha TL and Meng E: Histopathological assessment of
inflammation and expression of inflammatory markers in patients
with ketamine-induced cystitis. Mol Med Rep. 11:2421–2428.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ge W, Guo R and Ren J: AMP-dependent
kinase and autophagic flux are involved in aldehyde
dehydrogenase-2-induced protection against cardiac toxicity of
ethanol. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1736–48. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Clarke TK, Adams MJ, Davies G, Howard DM,
Hall LS, Padmanabhan S, Murray AD, Smith BH, Campbell A, Hayward C,
et al: Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and
genetic overlap with other health-related traits in UK Biobank
(N=112 117). Mol Psychiatry. 22:1376–1384. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu S, Chen J, Dong P, Zhang S, He Y, Sun
L, Zhu J, Cheng Y, Li X, Tang A, et al: Global gene expression
profiling identifies ALDH2, CCNE1 and SMAD3 as potential prognostic
markers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
14(836)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Andrew AS, Gui J, Hu T, Wyszynski A,
Marsit CJ, Kelsey KT, Schned AR, Tanyos SA, Pendleton EM, Ekstrom
RM, et al: Genetic polymorphisms modify bladder cancer recurrence
and survival in a USA population-based prognostic study. BJU Int.
115:238–247. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ferreira-Teixeira M, Parada B,
Rodrigues-Santos P, Alves V, Ramalho JS, Caramelo F, Sousa V, Reis
F and Gomes CM: Functional and molecular characterization of cancer
stem-like cells in bladder cancer: A potential signature for
muscle-invasive tumors. Oncotarget. 6:36185–201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chuang SM, Lu JH, Lin KL, Long CY, Lee YC,
Hsiao HP, Tsai CC, Wu WJ, Yang HJ and Juan YS: Epigenetic
regulation of COX2 expression by DNA hypomethylation via NFkappaB
activation in ketamineinduced ulcerative cystitis. Int J Mol Med.
44:797–812. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jin S, Chen J, Chen L, Histen G, Lin Z,
Gross S, Hixon J, Chen Y, Kung C, Chen Y, et al: ALDH2(E487K)
mutation increases protein turnover and promotes murine
hepatocarcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:9088–9093.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yeung LY, Rudd JA, Lam WP, Mak YT and Yew
DT: Mice are prone to kidney pathology after prolonged ketamine
addiction. Toxicol Lett. 191:275–278. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gu D, Huang J, Yin Y, Shan Z, Zheng S and
Wu P: Long-term ketamine abuse induces cystitis in rats by
impairing the bladder epithelial barrier. Mol Biol Rep. 41:7313–22.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Choi JW, Kim JH, Cho SC, Ha MK, Song KY,
Youn HD and Park SC: Malondialdehyde inhibits an AMPK-mediated
nuclear translocation and repression activity of ALDH2 in
transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 404:400–406.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hu JF, Wang HX, Li HH, Hu J, Yu Y and Gao
QQ: Inhibition of ALDH2 expression aggravates renal injury in a rat
sepsis syndrome model. Exp Ther Med. 14:2249–2254. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wimborne HJ, Hu J, Takemoto K, Nguyen N,
Jaeschke H, Lemasters JJ and Zhong Z: Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2
activation decreases acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by prevention of
mitochondrial depolarization. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
396(114982)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu T, Liu SY, Ma TT, Jia ZY, Zhang ZF and
Wang AM: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 protects against oxidative stress
associated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Redox Biol.
11:286–296. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tang S, Huang T, Jing H, Huang Z, Chen H,
Fan Y, Zhong J and Zhou J: Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 acts as a
potential genetic target for renal fibrosis. Life Sci.
239(117015)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mali VR, Pan G, Deshpande M, Thandavarayan
RA, Xu J, Yang XP and Palaniyandi SS: Cardiac mitochondrial
respiratory dysfunction and tissue damage in chronic hyperglycemia
correlate with reduced aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 activity. PLoS One.
11(e0163158)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu S, Chen JH, Dong P, Zhang SQ, He YY,
Sun L, Zhu JL, Cheng YB, Li XX, Tang AF, et al: Global gene
expression profiling identifies ALDH2, CCNE1 and SMAD3 as potential
prognostic markers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
14(836)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang Q, Wu Q, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhang G,
Chen J, Zhao J and Wu P: Ketamine analog methoxetamine induced
inflammation and dysfunction of bladder in rats. Int J Mol Sci.
18(117)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kim A, Yu HY, Heo J, Song M, Shin JH, Lim
J, Yoon SJ, Kim Y, Lee S, Kim SW, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells
protect against the tissue fibrosis of ketamine-induced cystitis in
rat bladder. Sci Rep. 6(30881)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chiba K, Yamaguchi K, Ando M, Miyake H and
Fujisawa M: Expression pattern of testicular claudin-11 in
infertile men. Urology. 80:1161.e13–e17. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Juan YS, Lee YL, Long CY, Wong JH, Jang
MY, Lu JH, Wu WJ, Huang YS, Chang WC and Chuang SM: Translocation
of NF-κB and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 are enhanced by
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Am J Pathol.
185:2269–2285. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xi XJ, Zeng JJ, Lu Y, Chen SH, Jiang ZW,
He PJ and Mi H: Extracellular vesicles enhance oxidative stress
through P38/NF-kB pathway in ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis.
J Cell Mol Med. 24:7609–7624. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lee YL, Lin KL, Chuang SM, Lee YC, Lu MC,
Wu BN, Wu WJ, Yuan SF, Ho WT and Juan YS: Elucidating mechanisms of
bladder repair after hyaluronan instillation in ketamine-induced
ulcerative cystitis in animal model. Am J Pathol. 187:1945–1959.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Arena A, Zimmer TS, van Scheppingen J,
Korotkov A, Anink JJ, Mühlebner A, Jansen FE, van Hecke W, Spliet
WG, van Rijen PC, et al: Oxidative stress and inflammation in a
spectrum of epileptogenic cortical malformations: Molecular
insights into their interdependence. Brain Pathol. 29:351–365.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chuang SM, Liu KM, Li YL, Jang MY, Lee HH,
Wu WJ, Chang WC, Levin RM and Juan YS: Dual involvements of
cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase expressions in
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Neurourol
Urodyn. 32:1137–1143. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hu VY, Malley S, Dattilio A, Folsom JB,
Zvara P and Vizzard MA: COX-2 and prostanoid expression in
micturition pathways after cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis in the
rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 284:R574–R585.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Oter S, Korkmaz A, Oztas E, Yildirim I,
Topal T and Bilgic H: Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition in
cyclophosphamide induced hemorrhagic cystitis in rats. Urol Res.
32:185–189. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Macedo FY, Mour ão LT, Palheta RC Jr, Juca
DM, Lima RC Jr, Neto Jde S, Magalhaes PJ, Santos AA, Souza MH,
Brito GA and Ribeiro RA: Cyclooxygenase-2 contributes to functional
changes seen on experimental hemorrhagic cystitis induced by
ifosfamide in rat urinary bladder. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
67:935–943. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kumar A, Singh KP, Bali P, Anwar S, Kaul
A, Singh OP, Gupta BK, Kumari N, Noor Alam M, Raziuddin M, et al:
iNOS polymorphism modulates iNOS/NO expression via impaired
antioxidant and ROS content in P. vivax and P. falciparum
infection. Redox Biol. 15:192–206. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Song M, Yu HY, Chun JY, Shin DM, Song SH,
Choo MS and Song YS: The fibrosis of ketamine, a noncompetitive
N-methyl-d-aspartic acid receptor antagonist dose-dependent change
in a ketamine-induced cystitis rat model. Drug Chem Toxicol.
39:206–212. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shen CH, Wang SC, Wang ST, Lin SM, Wu JD,
Lin CT and Liu YW: Evaluation of urinary bladder fibrogenesis in a
mouse model of long-term ketamine injection. Mol Med Rep.
14:1880–1890. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|