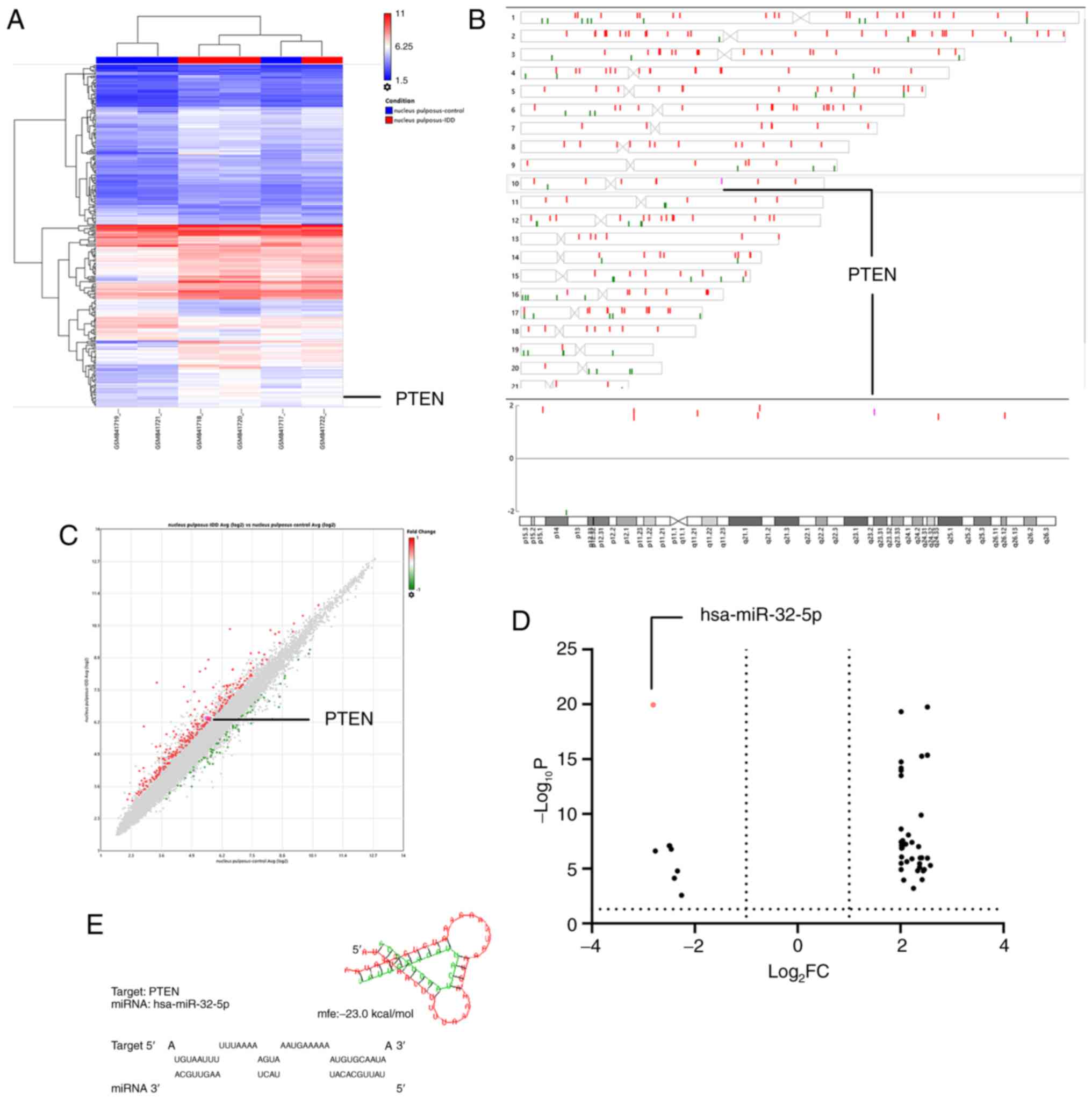
|
1
|
Ji ML, Jiang H, Zhang XJ, Shi PL, Li C, Wu
H, Wu XT, Wang YT, Wang C and Lu J: Preclinical development of a
microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat
Commun. 9(5051)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sloan SR Jr, Wipplinger C, Kirnaz S,
Navarro-Ramirez R, Schmidt F, McCloskey D, Pannellini T,
Schiavinato A, Härtl R and Bonassar LJ: Combined nucleus pulposus
augmentation and annulus fibrosus repair prevents acute
intervertebral disc degeneration after discectomy. Sci Transl Med.
12(eaay2380)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Madhu V, Boneski PK, Silagi E, Qiu Y,
Kurland I, Guntur AR, Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Hypoxic regulation
of mitochondrial metabolism and mitophagy in nucleus pulposus cells
is dependent on HIF-1α-BNIP3 Axis. J Bone Miner Res. 35:1504–1524.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hamid AA, Gray KP, Shaw G, MacConaill LE,
Evan C, Bernard B, Loda M, Corcoran NM, Van Allen EM, Choudhury AD
and Sweeney CJ: Compound genomic alterations of TP53, PTEN, and RB1
tumor suppressors in localized and metastatic prostate cancer. Eur
Urol. 76:89–97. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Meng J, Zhang W, Wang C, Zhang W, Zhou C,
Jiang G, Hong J, Yan S and Yan W: Catalpol suppresses
osteoclastogenesis and attenuates osteoclast-derived bone
resorption by modulating PTEN activity. Biochem Pharmacol.
171(113715)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: miR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lin Y, Guo W, Chen KW and Xiao ZM:
VO-OHpic attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via PTEN/Akt
pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:2811–2819. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang M, Sun Y, Xu J, Lu J, Wang K, Yang
DR, Yang G, Li G and Chang C: Preclinical studies using miR-32-5p
to suppress clear cell renal cell carcinoma metastasis via altering
the miR-32-5p/TR4/HGF/Met signaling. Int J Cancer. 143:100–112.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhao L, Han T, Li Y, Sun J, Zhang S, Liu
Y, Shan B, Zheng D and Shi J: The lncRNA SNHG5/miR-32 axis
regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by
targeting KLF4. FASEB J. 31:893–903. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu W, Yang J, Feng X, Wang H, Ye S, Yang
P, Tan W, Wei G and Zhou Y: MicroRNA-32 (miR-32) regulates
phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) expression and promotes
growth, migration, and invasion in colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol
Cancer. 12(30)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Nakai T, Mishima T,
Kato S, Grad S, Alini M, Risbud MV, Chan D, Cheah KS, et al:
Exhaustion of nucleus pulposus progenitor cells with ageing and
degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Nat Commun.
3(1264)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Smith LJ, Silverman L, Sakai D, Le Maitre
CL, Mauck RL, Malhotra NR, Lotz JC and Buckley CT: Advancing cell
therapies for intervertebral disc regeneration from the lab to the
clinic: Recommendations of the ORS spine section. JOR Spine.
1(e1036)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peng W, Chen JQ, Liu C, Malu S, Creasy C,
Tetzlaff MT, Xu C, McKenzie JA, Zhang C, Liang X, et al: Loss of
PTEN promotes resistance to T cell-mediated immunotherapy. Cancer
Discov. 6:202–216. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang D, Ma M, Zhou W, Yang B and Xiao C:
Inhibition of miR-32 activity promoted EMT induced by PM2.5
exposure through the modulation of the Smad1-mediated signaling
pathways in lung cancer cells. Chemosphere. 184:289–298.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li H, Jia Y and Wang Y: Targeting HIF-1α
signaling pathway for gastric cancer treatment. Pharmazie. 74:3–7.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ling S, Shan Q, Zhan Q, Ye Q, Liu P, Xu S,
He X, Ma J, Xiang J, Jiang G, et al: USP22 promotes hypoxia-induced
hepatocellular carcinoma stemness by a HIF1α/USP22 positive
feedback loop upon TP53 inactivation. Gut. 69:1322–1334.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu J, Zhang X, Chen K, Cheng Y, Liu S,
Xia M, Chen Y, Zhu H, Li Z and Cao X: CCR7 Chemokine
receptor-inducible inc-Dpf3 restrains dendritic cell migration by
inhibiting HIF-1α-mediated glycolysis. Immunity. 50:600–615.e15.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Stegen S, Laperre K, Eelen G, Rinaldi G,
Fraisl P, Torrekens S, Van Looveren R, Loopmans S, Bultynck G,
Vinckier S, et al: HIF-1α metabolically controls collagen synthesis
and modification in chondrocytes. Nature. 565:511–515.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu FQ, Fang T, Yu LX, Lv GS, Lv HW, Liang
D, Li T, Wang CZ, Tan YX, Ding J, et al: ADRB2 signaling promotes
HCC progression and sorafenib resistance by inhibiting autophagic
degradation of HIF1α. J Hepatol. 65:314–324. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen J and Steidl U: Inhibition of HIF1α
Signaling: A grand slam for MDS therapy? Cancer Discov.
8:1355–1357. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|