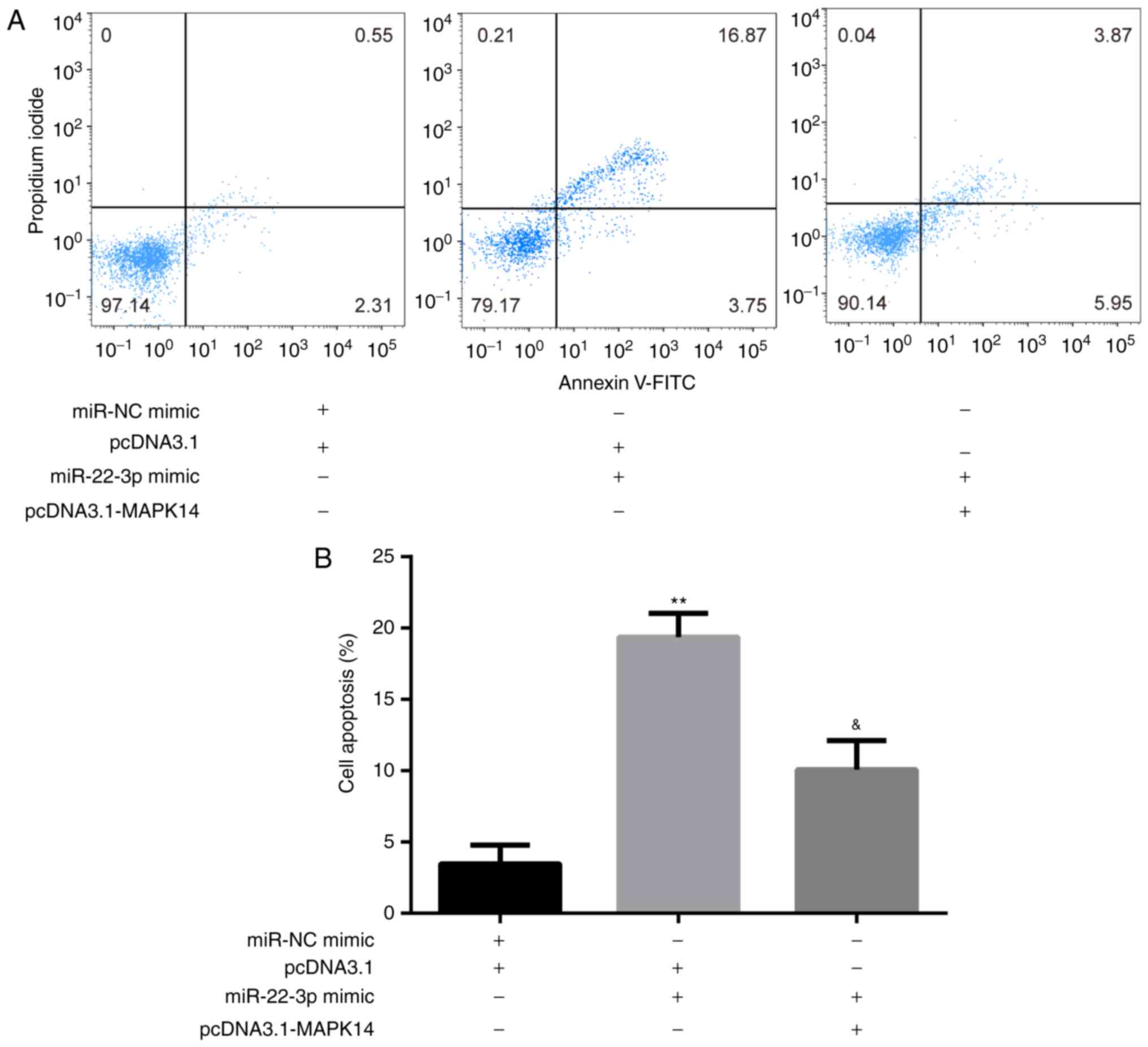
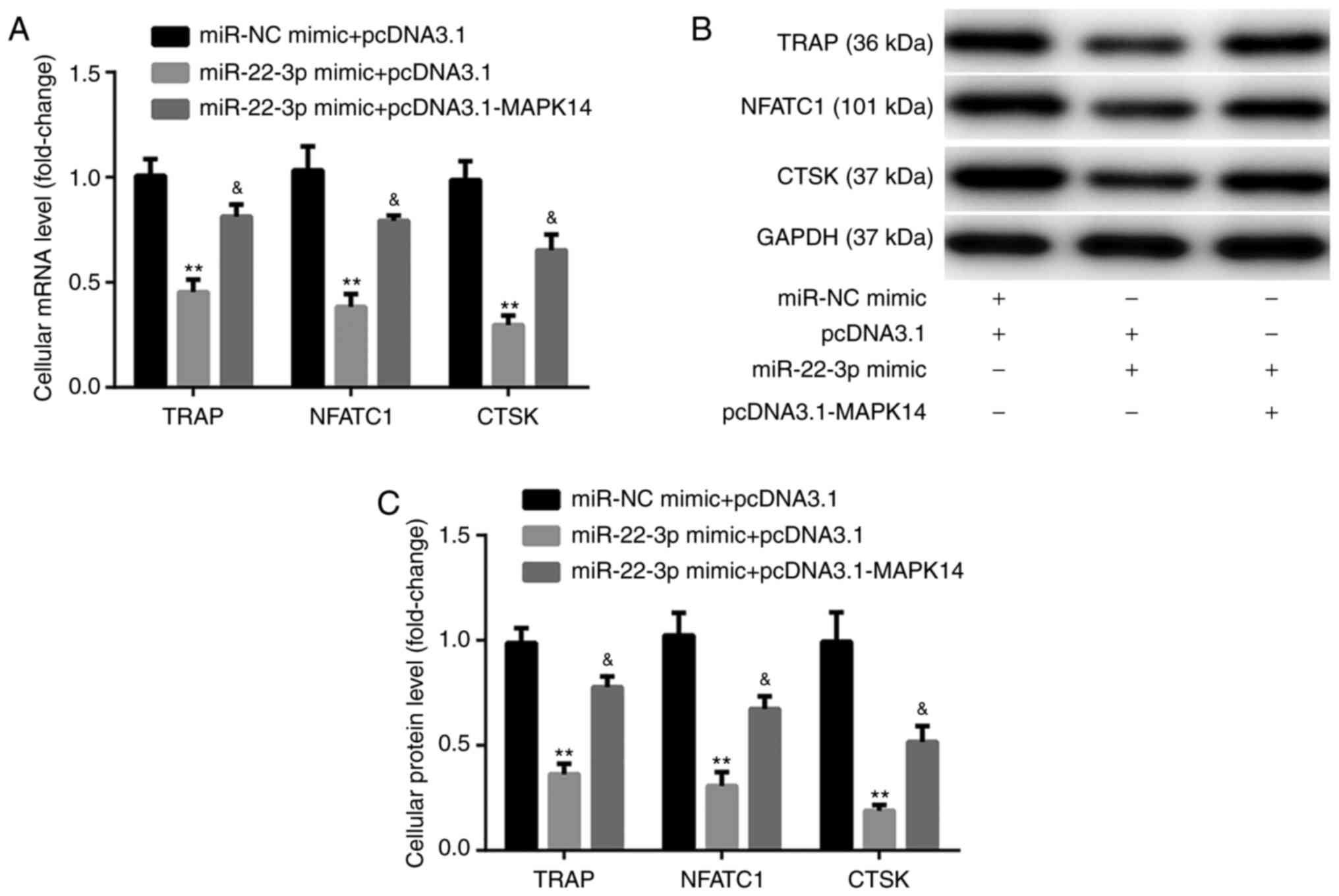
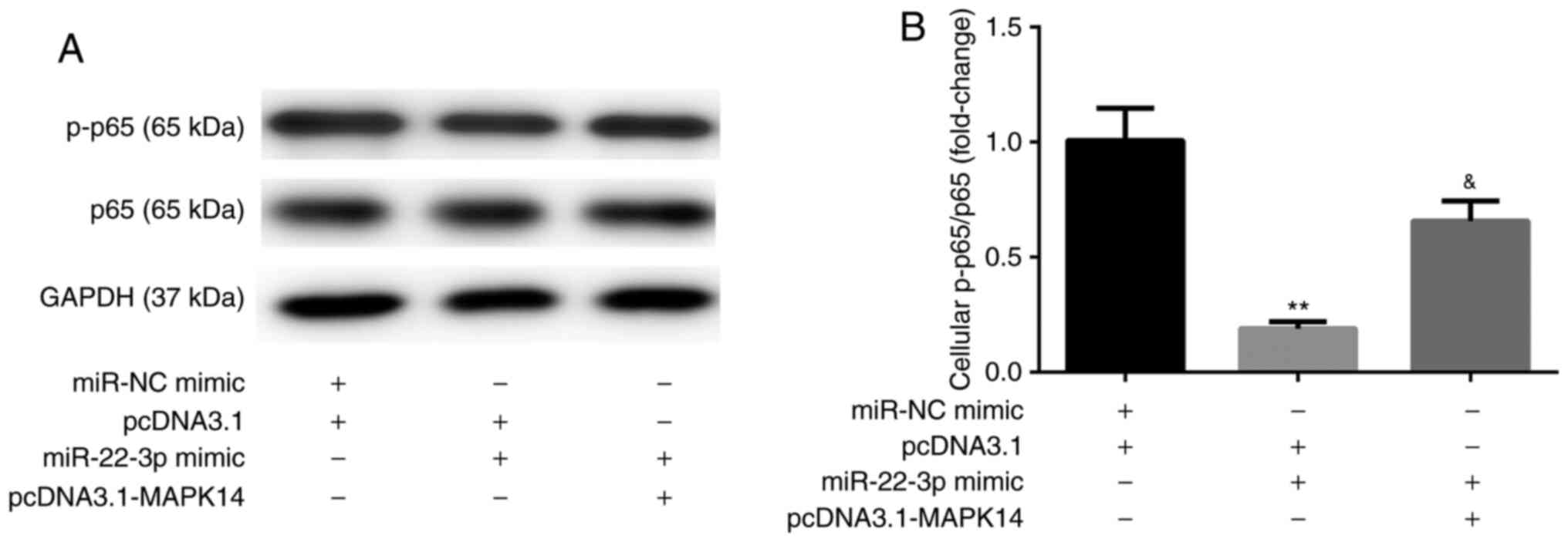
|
1
|
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki
EM, Tanner B, Randall S and Lindsay R: Erratum to: Clinician's
guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.
26:2045–2047. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nguyen BN, Hoshino H, Togawa D and
Matsuyama Y: Cortical thickness index of the proximal femur: A
radiographic parameter for preliminary assessment of bone mineral
density and osteoporosis status in the age 50 years and over
population. Clin Orthop Surg. 10:149–156. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xiao W, Wang Y, Pacios S, Li S and Graves
DT: Cellular and molecular aspects of bone remodeling. Front Oral
Biol. 18:9–16. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Karsenty G: Transcriptional control of
skeletogenesis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 9:183–196.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Manolagas SC: From estrogen-centric to
aging and oxidative stress: A revised perspective of the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 31:266–300.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A,
Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M,
et al: A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA
library sequencing. Cell. 129:1401–1414. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gámez B, Rodriguez-Carballo E and Ventura
F: MicroRNAs and post-transcriptional regulation of skeletal
development. J Mol Endocrinol. 52:R179–R197. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lian JB, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ, Stein
JL, Hassan MQ, Gaur T and Zhang Y: MicroRNA control of bone
formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:212–227.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mizuno Y, Yagi K, Tokuzawa Y,
Kanesaki-Yatsuka Y, Suda T, Katagiri T, Fukuda T, Maruyama M, Okuda
A, Amemiya T, et al: miR-125b inhibits osteoblastic differentiation
by down-regulation of cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 368:267–272. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang FS, Chuang PC, Lin CL, Chen MW, Ke
HJ, Chang YH, Chen YS, Wu SL and Ko JY: MicroRNA-29a protects
against glucocorticoid-induced bone loss and fragility in rats by
orchestrating bone acquisition and resorption. Arthritis Rheum.
65:1530–1540. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kahai S, Lee SC, Lee DY, Yang J, Li M,
Wang CH, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Peng C and Yang BB: MicroRNA miR-378
regulates nephronectin expression modulating osteoblast
differentiation by targeting GalNT-7. PLoS One.
4(e7535)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xia Z, Chen C, Chen P, Xie H and Luo X:
MicroRNAs and their roles in osteoclast differentiation. Front Med.
5:414–419. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
van Wijnen AJ, van de Peppel J, van
Leeuwen JP, Lian JB, Stein GS, Westendorf JJ, Oursler MJ, Im HJ,
Taipaleenmäki H, Hesse E, et al: MicroRNA functions in osteogenesis
and dysfunctions in osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 11:72–82.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Weilner S, Skalicky S, Salzer B, Keider V,
Wagner M, Hildner F, Gabriel C, Dovjak P, Pietschmann P,
Grillari-Voglauer R, et al: Differentially circulating miRNAs after
recent osteoporotic fractures can influence osteogenic
differentiation. Bone. 79:43–51. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma Y, Shan Z, Ma J, Wang Q, Chu J, Xu P,
Qin A and Fan S: Validation of downregulated microRNAs during
osteoclast formation and osteoporosis progression. Mol Med Rep.
13:2273–2280. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mäkitie RE, Hackl M, Niinimäki R, Kakko S,
Grillari J and Mäkitie O: Altered microRNA profile in osteoporosis
caused by impaired WNT signaling. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
103:1985–1996. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhao H, Han X, Zhao T, Qu
P, Li G and Wang W: Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated miR-22-3p
from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell promotes osteogenic
differentiation via FTO inhibition. Stem Cell Res Ther.
11(227)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
World Health Organization. Assessment of
fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Report of a WHO Study Group. World Health Organ Tech
Rep Ser. 843:1–129. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hemingway F, Cheng X, Knowles HJ, Estrada
FM, Gordon S and Athanasou NA: In vitro generation of mature human
osteoclasts. Calcif Tissue Int. 89:389–395. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sørensen MG, Henriksen K, Schaller S,
Henriksen DB, Nielsen FC, Dziegiel MH and Karsdal MA:
Characterization of osteoclasts derived from CD14+
monocytes isolated from peripheral blood. J Bone Miner Metab.
25:36–45. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cheng P, Chen C, He HB, Hu R, Zhou HD, Xie
H, Zhu W, Dai RC, Wu XP, Liao EY, et al: miR-148a regulates
osteoclastogenesis by targeting V-maf musculoaponeurotic
fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog B. J Bone Miner Res. 28:1180–1190.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jing D, Hao J, Shen Y, Tang G, Li ML,
Huang SH and Zhao ZH: The role of microRNAs in bone remodeling. Int
J Oral Sci. 7:131–143. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
García Palacios V, Robinson LJ, Borysenko
CW, Lehmann T, Kalla SE and Blair HC: Negative regulation of
RANKL-induced osteoclastic differentiation in RAW264.7 cells by
estrogen and phytoestrogens. J Biol Chem. 280:13720–13727.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Down-regulation
of miR-21 biogenesis by estrogen action contributes to osteoclastic
apoptosis. J Cell Biochem. 114:1217–1222. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kagiya T and Nakamura S: Expression
profiling of microRNAs in RAW264.7 cells treated with a combination
of tumor necrosis factor alpha and RANKL during osteoclast
differentiation. J Periodontal Res. 48:373–385. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shibuya H, Nakasa T, Adachi N, Nagata Y,
Ishikawa M, Deie M, Suzuki O and Ochi M: Overexpression of
microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast
differentiation. Mod Rheumatol. 23:674–685. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cao L, Liu W, Zhong Y, Zhang Y, Gao D, He
T, Liu Y, Zou Z, Mo Y, Peng S, et al: Linc02349 promotes
osteogenesis of human umbilical cord-derived stem cells by acting
as a competing endogenous RNA for miR-25-3p and miR-33b-5p. Cell
Prolif. 53(e12814)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cargnello M and Roux PP: Activation and
function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated
protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 75:50–83. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Thamodaran V and Bruce AW: p38 (Mapk14/11)
occupies a regulatory node governing entry into primitive endoderm
differentiation during preimplantation mouse embryo development.
Open Biol. 6(160190)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Caverzasio J, Higgins L and Ammann P:
Prevention of trabecular bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency
by a selective p38alpha inhibitor. J Bone Miner Res. 23:1389–1397.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Thouverey C and Caverzasio J: Ablation of
p38α MAPK signaling in osteoblast lineage cells protects mice from
bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency. Endocrinology.
156:4377–4387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cong Q, Jia H, Li P, Qiu S, Yeh J, Wang Y,
Zhang ZL, Ao J, Li B and Liu H: p38α MAPK regulates proliferation
and differentiation of osteoclast progenitors and bone remodeling
in an aging-dependent manner. Sci Rep. 7(45964)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jovicic A, Zaldivar Jolissaint JF, Moser
R, Silva Santos MF and Luthi-Carter R: MicroRNA-22 (miR-22)
overexpression is neuroprotective via general anti-apoptotic
effects and may also target specific Huntington's disease-related
mechanisms. PLoS One. 8(e54222)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kwon M, Kim JM, Lee K, Park SY, Lim HS,
Kim T and Jeong D: Synchronized cell cycle arrest promotes
osteoclast differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 17(1292)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Boyce BF: Advances in osteoclast biology
reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J
Bone Miner Res. 28:711–722. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|