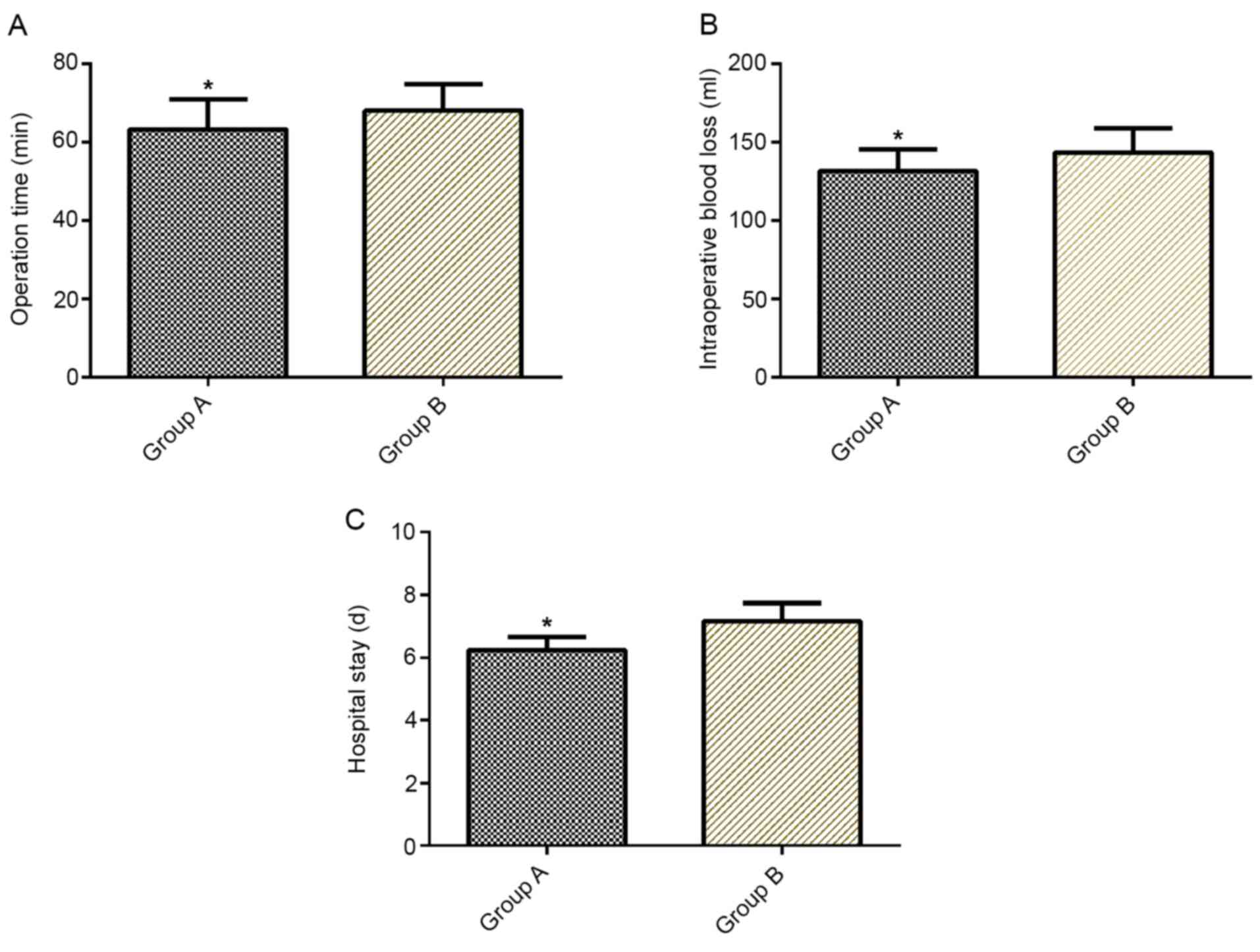
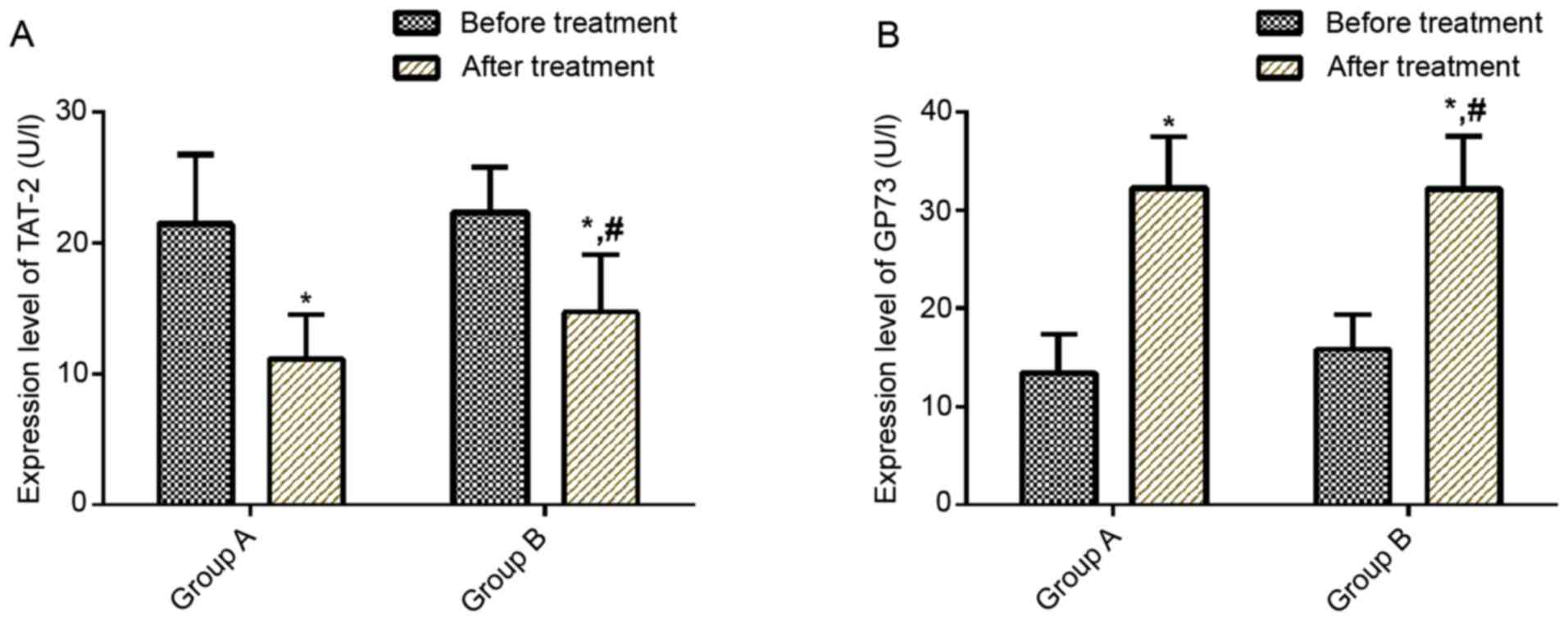
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu HQ, Wang HY, Xie WM, Wu SL, Li ZF,
Zhang XM and Li H: Scanning photoacoustic imaging of submucosal
gastric tumor based on a long focused transducer in phantom and in
vitro experiments. J Innov Opt Health Sci. 12(1950011)2019.
|
|
3
|
Rahman R, Asombang AW and Ibdah JA:
Characteristics of gastric cancer in Asia. World J Gastroenterol.
20:4483–4490. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shen L, Li J, Xu J, Pan H, Dai G, Qin S,
Wang L, Wang J, Yang Z, Shu Y, et al: Bevacizumab plus capecitabine
and cisplatin in Chinese patients with inoperable locally advanced
or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer:
Randomized, double-blind, phase III study (AVATAR study). Gastric
Cancer. 18:168–176. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003-2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yu L, Wu D, Gao H, Balic JJ, Tsykin A, Han
TS, Liu YD, Kennedy CL, Li JK, Mao JQ, et al: Clinical utility of a
STAT3-regulated miRNA-200 family signature with prognostic
potential in early gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:1459–1472.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hondo FY, Kishi H, Safatle-Ribeiro AV,
Pessorrusso FC, Ribeiro U Jr and Maluf-Filho F: Characterization of
the mucin phenotype can predict gastric cancer recurrence after
endoscopic mucosal resection. Arq Gastroenterol. 54:308–314.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim SG, Park CM, Lee NR, Kim J, Lyu DH,
Park SH, Choi IJ, Lee WS, Park SJ, Kim JJ, et al: Long-term
clinical outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients
with early gastric cancer: A prospective multicenter cohort study.
Gut Liver. 12:402–410. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pan J, Zhang X, Shi Y and Pei Q:
Endoscopic mucosal resection with suction vs. endoscopic submucosal
dissection for small rectal neuroendocrine tumors: A meta-analysis.
Scand J Gastroenterol. 53:1139–1145. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Seewald S, Ang TL, Pouw RE, Bannwart F and
Bergman JJ: Management of early-stage adenocarcinoma of the
esophagus: Endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal
dissection. Dig Dis Sci. 63:2146–2154. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hu JS, Wu DW, Liang S and Miao XY: GP73, a
resident Golgi glycoprotein, is sensibility and specificity for
hepatocellular carcinoma of diagnosis in a hepatitis B-endemic
Asian population. Med Oncol. 27:339–345. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Riener MO, Stenner F, Liewen H, Soll C,
Breitenstein S, Pestalozzi BC, Samaras P, Probst-Hensch N,
Hellerbrand C, Müllhaupt B, et al: Golgi phosphoprotein 2 (GOLPH2)
expression in liver tumors and its value as a serum marker in
hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology. 49:1602–1609.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sun Y, Yang H, Mao Y, Xu H, Zhang J, Li G,
Lu X, Sang X, Zhao H, Zhong S, et al: Increased Golgi protein 73
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue correlates with tumor
aggression but not survival. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:1207–1212.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fujimura T, Ohta T, Kitagawa H, Fushida S,
Nishimura GI, Yonemura Y, Elnemr A, Miwa K and Nakanuma Y:
Trypsinogen expression and early detection for peritoneal
dissemination in gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 69:71–75.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Itkonen O: Human trypsinogens in the
pancreas and in cancer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 70:136–143.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ichikawa Y, Koshikawa N, Hasegawa S,
Ishikawa T, Momiyama N, Kunizaki C, Takahashi M, Moriwaki Y,
Akiyama H, Yamaoka H, et al: Marked increase of trypsin(ogen) in
serum of linitis plastica (gastric cancer, borrmann 4) patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 6:1385–1388. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Esaki M, Suzuki S, Hayashi Y, Yokoyama A,
Abe S, Hosokawa T, Tsuruta S, Minoda Y, Hata Y, Ogino H, et al:
Propensity score-matching analysis to compare clinical outcomes of
endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in the
postoperative and non-operative stomachs. BMC Gastroenterol.
18(125)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hahn KY, Park CH, Lee YK, Chung H, Park
JC, Shin SK, Lee YC, Kim HI, Cheong JH, Hyung WJ, et al:
Comparative study between endoscopic submucosal dissection and
surgery in patients with early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc.
32:73–86. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yuan Y: A survey and evaluation of
population-based screening for gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Med.
10:72–80. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lamb CA, Kennedy NA, Raine T, Hendy PA,
Smith PJ, Limdi JK, Hayee B, Lomer MCE, Parkes GC, Selinger C, et
al: IBD guidelines eDelphi consensus group: British Society of
Gastroenterology consensus guidelines on the management of
inflammatory bowel disease in adults. Gut. 68 (Suppl 3):s1–s106.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Askar H, Di Gianfilippo R, Ravida A,
Tattan M, Majzoub J and Wang HL: Incidence and severity of
postoperative complications following oral, periodontal, and
implant surgeries: A retrospective study. J Periodontol.
90:1270–1278. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Buckland G, Travier N, Huerta JM,
Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Siersema PD, Skeie G, Weiderpass E, Engeset
D, Ericson U, Ohlsson B, et al: Healthy lifestyle index and risk of
gastric adenocarcinoma in the EPIC cohort study. Int J Cancer.
137:598–606. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ghoshal UC, Kumar S, Krishnani N, Kumari
N, Chourasia D and Tripathi S: Serological assessment of gastric
intestinal metaplasia and atrophy using pepsinogen-I, pepsinogen-II
and gastrin-17 levels in a low incidence area of gastric cancer
endemic for H. pylori infection. Trop Gastroenterol.
32:292–298. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K, Goto O,
Kodashima S, Yamamichi N and Omata M: Long-term outcomes of
endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal
squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 70:860–866.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Onozato Y, Kakizaki S, Ishihara H, Iizuka
H, Sohara N, Okamura S, Mori M and Itoh H: Endoscopic submucosal
dissection for rectal tumors. Endoscopy. 39:423–427.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Saito Y, Uraoka T, Matsuda T, Emura F,
Ikehara H, Mashimo Y, Kikuchi T, Fu KI, Sano Y and Saito D:
Endoscopic treatment of large superficial colorectal tumors: A case
series of 200 endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video).
Gastrointest Endosc. 66:966–973. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Meng Y, Li W, Han L, Zhang Q, Gong W, Cai
J, Li A, Yan Q, Lai Q, Yu J, et al: Long-term outcomes of
endoscopic submucosal dissection versus laparoscopic resection for
gastric stromal tumors less than 2 cm. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
32:1693–1697. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bang CS, Baik GH, Shin IS, Suk KT, Yoon JH
and Kim DJ: Endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric
subepithelial tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean
J Intern Med (Korean Assoc Intern Med). 31:860–871. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Park JC, Lee SK, Seo JH, Kim YJ, Chung H,
Shin SK and Lee YC: Predictive factors for local recurrence after
endoscopic resection for early gastric cancer: Long-term clinical
outcome in a single-center experience. Surg Endosc. 24:2842–2849.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ryu SJ, Kim BW, Kim BG, Kim JH, Kim JS,
Kim JI, Park JM, Oh JH, Kim TH, Kim JJ, et al: Endoscopic
submucosal dissection versus surgical resection for early gastric
cancer: A retrospective multicenter study on immediate and
long-term outcome over 5 years. Surg Endosc. 30:5283–5289.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Song WC, Qiao XL and Gao XZ: A comparison
of endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and radical surgery for
early gastric cancer: A retrospective study. World J Surg Oncol.
13(309)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen LG, Wang HJ, Yao HB, Guan TP, Wu F,
He XJ, Ma YY, Tao HQ and Ye ZY: GP73 is down-regulated in gastric
cancer and associated with tumor differentiation. World J Surg
Oncol. 11(132)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rong L, Cai Y, Nian W, Wang X, Liang J, He
Y and Zhang J: Efficacy comparison between surgical resection and
endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer in a
domestic single center. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi.
21:190–195. 2018.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|