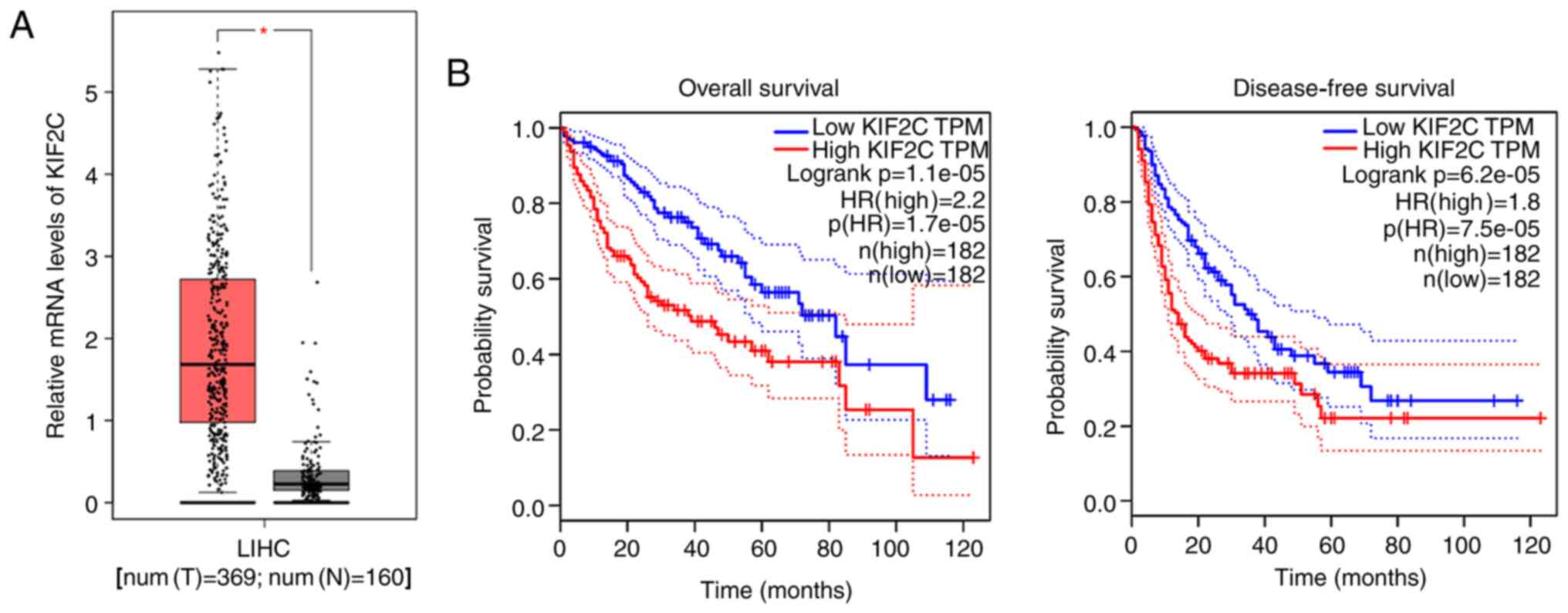
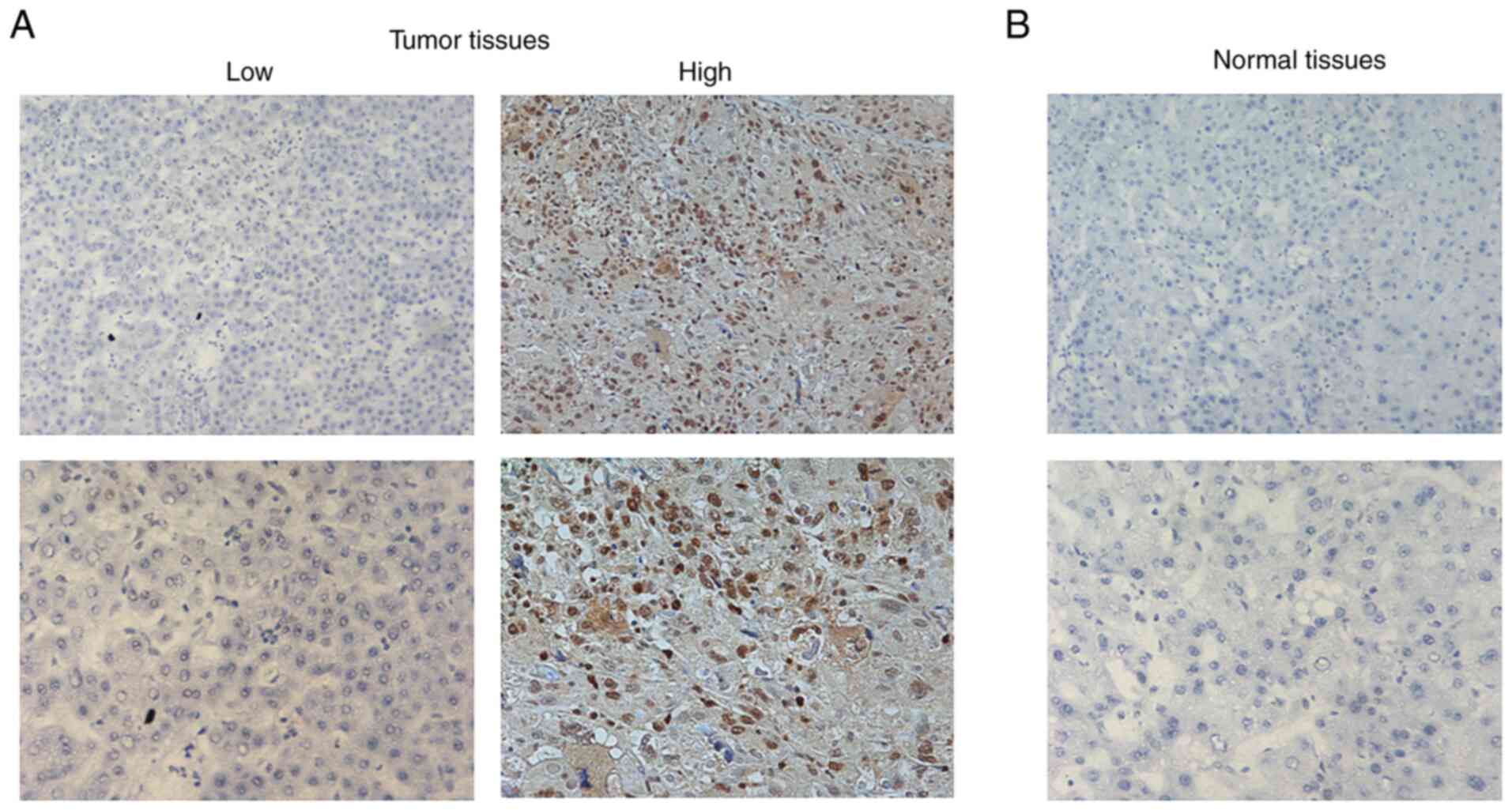
|
1
|
Rahmani F, Ziaeemehr A, Shahidsales S,
Gharib M, Khazaei M, Ferns GA, Ryzhikov M, Avan A and Hassanian SM:
Role of regulatory miRNAs of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in the
pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol.
235:4146–4152. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ninio L, Nissani A, Meirson T, Domovitz T,
Genna A, Twafra S, Srikanth KD, Dabour R, Avraham E, Davidovich A,
et al: Hepatitis C virus enhances the invasiveness of
hepatocellular carcinoma via egfr-mediated invadopodia formation
and activation. Cells. 8(E1395)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang Q, Chen W, Lv X, Weng Q, Chen M, Cui
R, Liang G and Ji J: Piperlongumine, a novel TrxR1 inhibitor,
induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by ROS-mediated
ER stress. Front Pharmacol. 10(1180)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Di Tommaso L, Spadaccini M, Donadon M,
Personeni N, Elamin A, Aghemo A and Lleo A: Role of liver biopsy in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 25:6041–6052.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wege H, Li J and Ittrich H: Treatment
lines in hepatocellular carcinoma. Visc Med. 35:266–272.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Choi SH and Seong J: Strategic application
of radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol.
24:114–134. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhu XD and Sun HC: Emerging agents and
regimens for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol.
12(110)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li L, Qian M, Chen IH, Finkelstein D,
Onar-Thomas A, Johnson M, Calabrese C, Bahrami A, López-Terrada DH,
Yang JJ, et al: Acquisition of cholangiocarcinoma traits during
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma development in mice. Am J Pathol.
188:656–671. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Manning AL, Ganem NJ, Bakhoum SF,
Wagenbach M, Wordeman L and Compton DA: The kinesin-13 proteins
Kif2a, Kif2b, and Kif2c/MCAK have distinct roles during mitosis in
human cells. Mol Biol Cell. 18:2970–2979. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gwon MR, Cho JH and Kim JR: Mitotic
centromere-associated kinase (MCAK/Kif2C) regulates cellular
senescence in human primary cells through a p53-dependent pathway.
FEBS Lett. 586:4148–4156. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bakhoum SF, Thompson SL, Manning AL and
Compton DA: Genome stability is ensured by temporal control of
kinetochore-microtubule dynamics. Nat Cell Biol. 11:27–35.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jiang K, Wang J, Liu J, Ward T, Wordeman
L, Davidson A, Wang F and Yao X: TIP150 interacts with and targets
MCAK at the microtubule plus ends. EMBO Rep. 10:857–865.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lee T, Langford KJ, Askham JM,
Brüning-Richardson A and Morrison EE: MCAK associates with EB1.
Oncogene. 27:2494–2500. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vogt E, Sanhaji M, Klein W, Seidel T,
Wordeman L and Eichenlaub-Ritter U: MCAK is present at centromeres,
midspindle and chiasmata and involved in silencing of the spindle
assembly checkpoint in mammalian oocytes. Mol Hum Reprod.
16:665–684. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shao H, Huang Y, Zhang L, Yuan K, Chu Y,
Dou Z, Jin C, Garcia-Barrio M, Liu X and Yao X: Spatiotemporal
dynamics of Aurora B-PLK1-MCAK signaling axis orchestrates
kinetochore bi-orientation and faithful chromosome segregation. Sci
Rep. 5(12204)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jang CY and Fang G: DDA3 associates with
MCAK and controls chromosome congression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 407:610–614. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Parra MT, Gómez R, Viera A, Page J,
Calvente A, Wordeman L, Rufas JS and Suja JA: A perikinetochoric
ring defined by MCAK and Aurora-B as a novel centromere domain.
PLoS Genet. 2(e84)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gan H, Lin L, Hu N, Yang Y, Gao Y, Pei Y,
Chen K and Sun B: KIF2C exerts an oncogenic role in nonsmall cell
lung cancer and is negatively regulated by miR-325-3p. Cell Biochem
Funct. 37:424–431. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gnjatic S, Cao Y, Reichelt U, Yekebas EF,
Nölker C, Marx AH, Erbersdobler A, Nishikawa H, Hildebrandt Y,
Bartels K, et al: NY-CO-58/KIF2C is overexpressed in a variety of
solid tumors and induces frequent T cell responses in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 127:381–393. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bai Y, Xiong L, Zhu M, Yang Z, Zhao J and
Tang H: Co-expression network analysis identified KIF2C in
association with progression and prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Biomark. 24:371–382. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bie L, Zhao G, Wang YP and Zhang B:
Kinesin family member 2C (KIF2C/MCAK) is a novel marker for
prognosis in human gliomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 114:356–360.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pinato DJ, Mauri FA, Spina P, Cain O,
Siddique A, Goldin R, Victor S, Pizio C, Akarca AU, Boldorini RL,
et al: Clinical implications of heterogeneity in PD-L1
immunohistochemical detection in hepatocellular carcinoma: The
Blueprint-HCC study. Br J Cancer. 120:1033–1036. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa T: Anti-viral therapy to reduce
recurrence and improve survival in hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 19:8861–8866.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Banini BA and Sanyal AJ: The use of cell
free DNA in the diagnosis of HCC. Hepatoma Res.
5(34)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang Y, Zhao Z, Xie C and Zhao Y:
Dual-targeting liposome modified by glutamic hexapeptide and folic
acid for bone metastatic breast cancer. Chem Phys Lipids.
228(104882)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhao Z, Zhao Y, Xie C, Chen C, Lin D, Wang
S, Lin D, Cui X, Guo Z and Zhou J: Dual-active targeting liposomes
drug delivery system for bone metastatic breast cancer: Synthesis
and biological evaluation. Chem Phys Lipids.
223(104785)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hasan S, Abel S, Uemura T, Verma V, Koay
EJ, Herman J, Thai N and Kirichenko A: Liver transplant mortality
and morbidity following preoperative radiotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB (Oxford). 22:770–778. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shimo A, Tanikawa C, Nishidate T, Lin ML,
Matsuda K, Park JH, Ueki T, Ohta T, Hirata K, Fukuda M, et al:
Involvement of kinesin family member 2C/mitotic
centromere-associated kinesin overexpression in mammary
carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 99:62–70. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sanhaji M, Friel CT, Wordeman L, Louwen F
and Yuan J: Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK): A
potential cancer drug target. Oncotarget. 2:935–947.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li C, Zhang Y, Yang Q, Ye F, Sun SY, Chen
ES and Liou YC: NuSAP modulates the dynamics of kinetochore
microtubules by attenuating MCAK depolymerisation activity. Sci
Rep. 6(18773)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ritter A, Kreis NN, Louwen F, Wordeman L
and Yuan J: Molecular insight into the regulation and function of
MCAK. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 51:228–245. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Shen T, Guerois R, Zhang F,
Kuerban H, Lv Y, Gigant B, Knossow M and Wang C: New Insights into
the Coupling between Microtubule Depolymerization and ATP
Hydrolysis by Kinesin-13 Protein Kif2C. J Biol Chem.
290:18721–18731. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang GP, Shen SL, Yu Y, Yue X, Hu WJ and
Li SQ: Kinesin family member 2C aggravates the progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma and interacts with competing endogenous
RNA. J Cell Biochem. 121:4419–4430. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rath O and Kozielski F: Kinesins and
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:527–539. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wojcik EJ, Buckley RS, Richard J, Liu L,
Huckaba TM and Kim S: Kinesin-5: Cross-bridging mechanism to
targeted clinical therapy. Gene. 531:133–149. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|