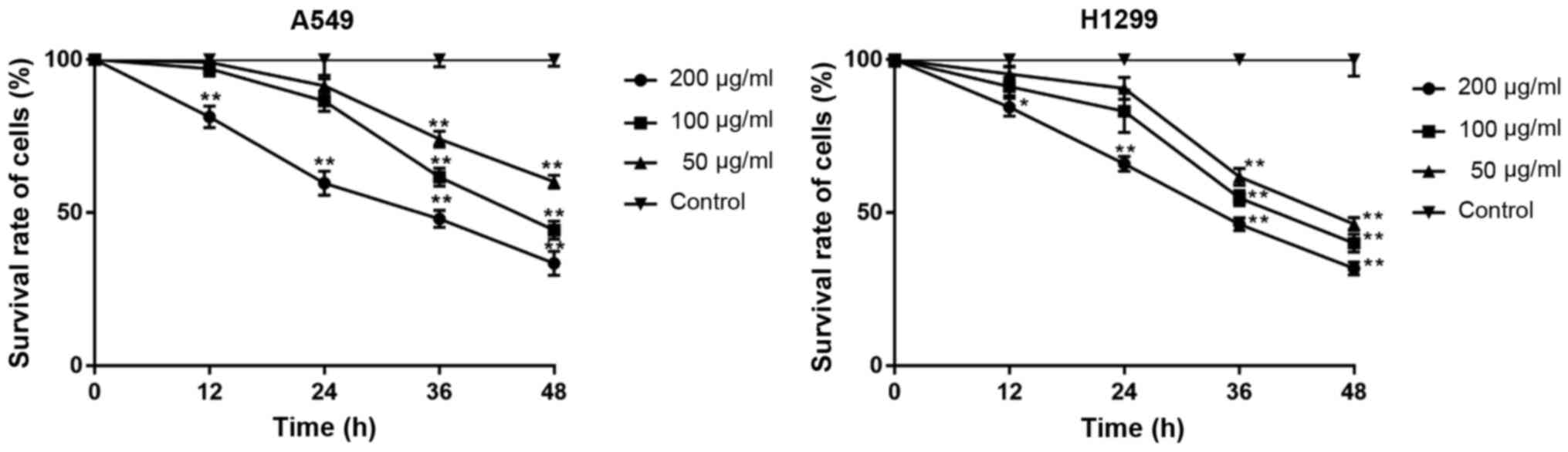
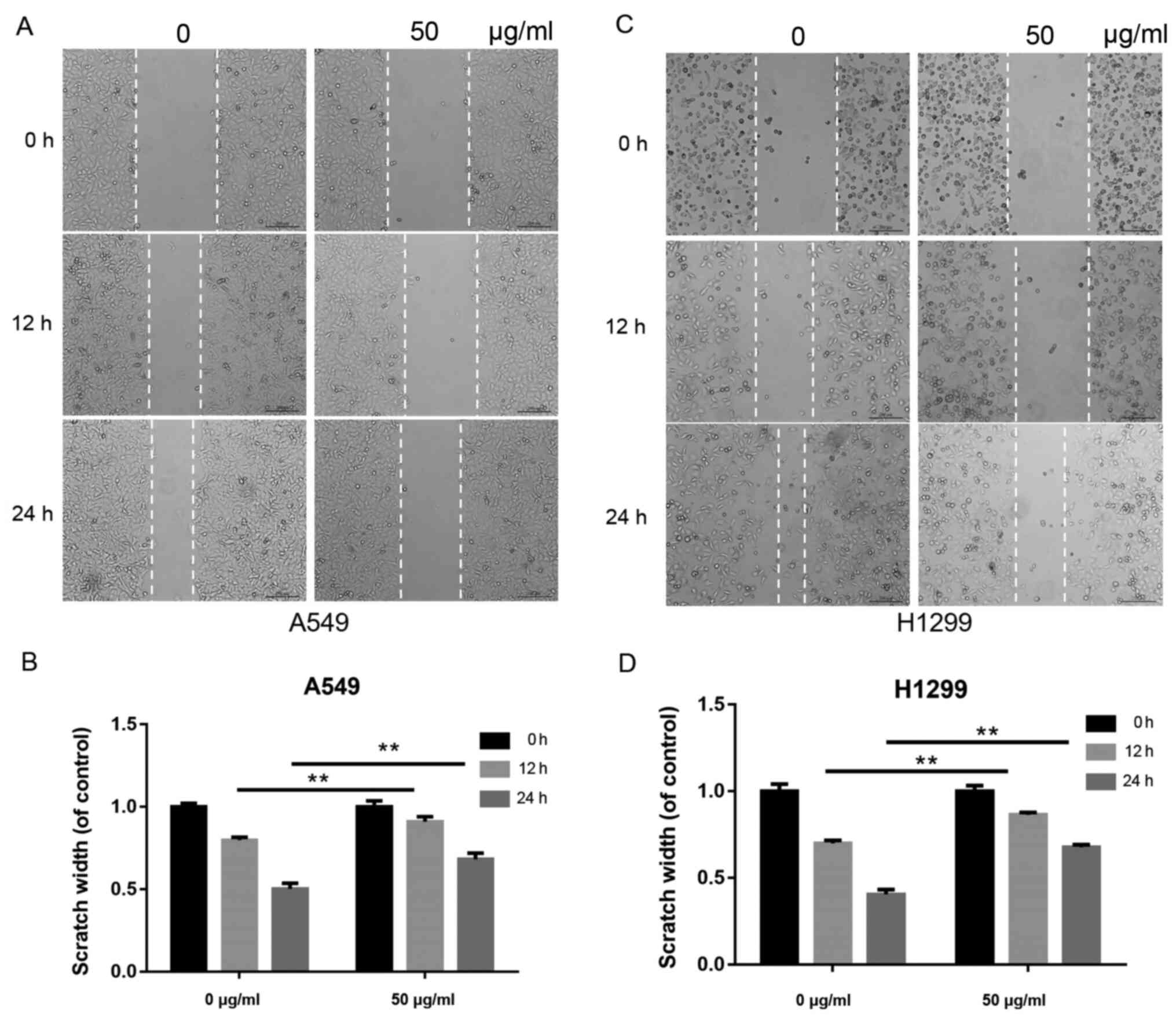
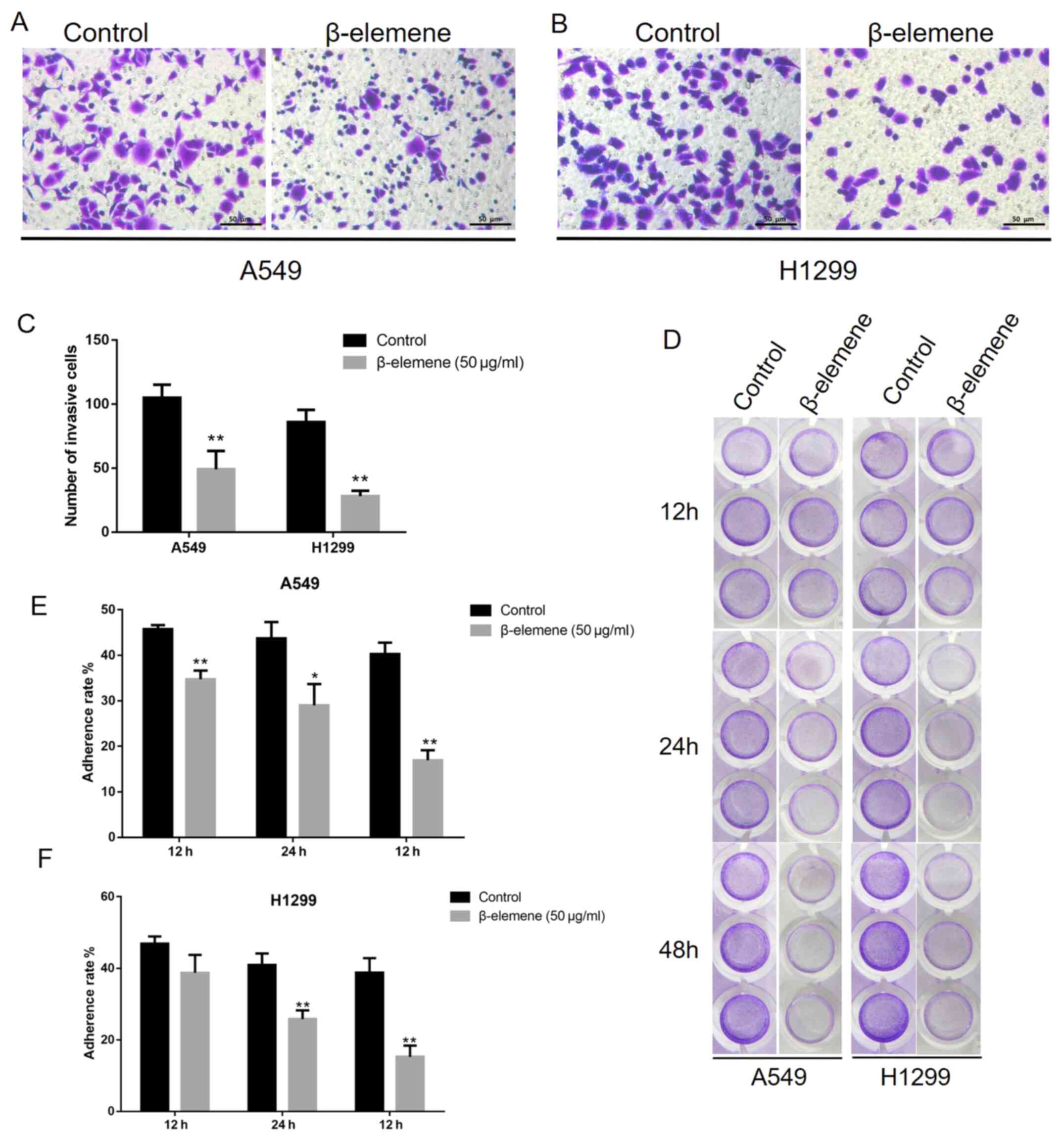
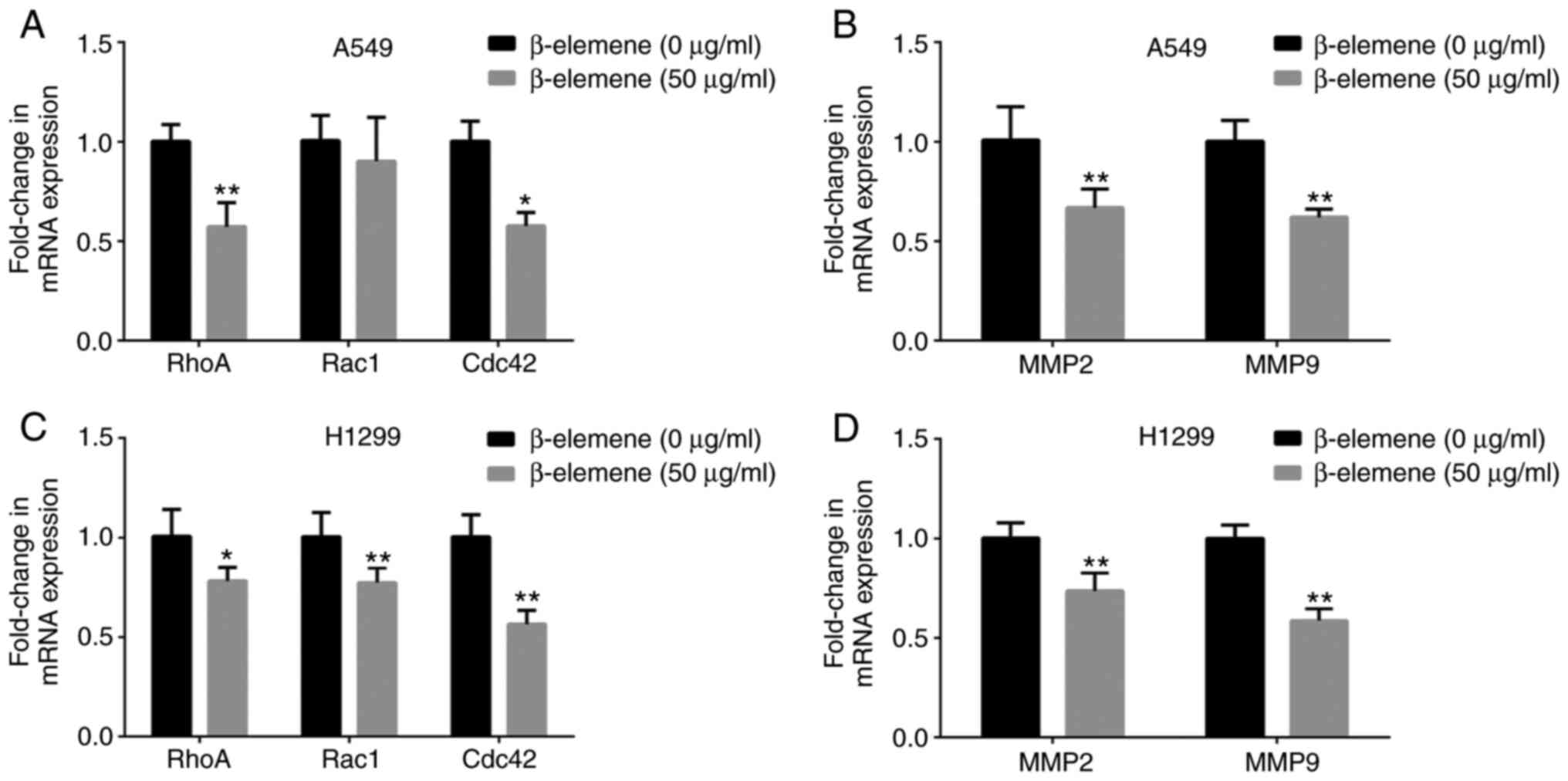
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Paul CD, Mistriotis P and Konstantopoulos
K: Cancer cell motility: Lessons from migration in confined spaces.
Nat Rev Cancer. 17:131–140. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Graham ZA, Gallagher PM and Cardozo CP:
Focal adhesion kinase and its role in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res
Cell Motil. 36:305–315. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Parsons JT, Martin KH, Slack JK, Taylor JM
and Weed SA: Focal adhesion kinase: A regulator of focal adhesion
dynamics and cell movement. Oncogene. 19:5606–5613. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dy GK, Ylagan L, Pokharel S, Miller A,
Brese E, Bshara W, Morrison C, Cance WG and Golubovskaya VM: The
prognostic significance of focal adhesion kinase expression in
stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 9:1278–1284.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu C, Li Y, Xing Y, Cao B, Yang F, Yang
T, Ai Z, Wei Y and Jiang J: The interaction between cancer stem
cell marker CD133 and Src protein promotes focal adhesion kinase
(FAK) phosphorylation and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
291:15540–15550. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Baquero P, Jiménez-Mora E, Santos A, Lasa
M and Chiloeches A: TGFβ induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
of thyroid cancer cells by both the BRAF/MEK/ERK and Src/FAK
pathways. Mol Carcinog. 55:1639–1654. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee JJ, van de Ven RAH, Zaganjor E, Ng MR,
Barakat A, Demmers JJ, Finley LWS, Gonzalez Herrera KN, Hung YP,
Harris IS, et al: Inhibition of epithelial cell migration and
Src/FAK signaling by SIRT3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:7057–7062.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ward KK, Tancioni I, Lawson C, Miller NL,
Jean C, Chen XL, Uryu S, Kim J, Tarin D, Stupack DG, et al:
Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity prevents
anchorage-independent ovarian carcinoma cell growth and tumor
progression. Clin Exp Metastasis. 30:579–594. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chikara S, Lindsey K, Borowicz P,
Christofidou-Solomidou M and Reindl KM: Enterolactone alters
FAK-Src signaling and suppresses migration and invasion of lung
cancer cell lines. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17(30)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Logue JS, Cartagena-Rivera AX and Chadwick
RS: c-Src activity is differentially required by cancer cell
motility modes. Oncogene. 37:2104–2121. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li P, Zhou X, Sun W, Sheng W, Tu Y, Yu Y,
Dong J, Ye B, Zheng Z and Lu M: Elemene induces apoptosis of human
gastric cancer cell line BGC-823 via extracellular signal-regulated
kinase (ERK)1/2 signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 23:809–817.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pan Y, Wang W, Huang S, Ni W, Wei Z, Cao
Y, Yu S, Jia Q, Wu Y, Chai C, et al: Beta-elemene inhibits breast
cancer metastasis through blocking pyruvate kinase M2 dimerization
and nuclear translocation. J Cell Mol Med. 23:6846–6858.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chang Z, Gao M, Zhang W, Song L, Jia Y and
Qin Y: Beta-elemene treatment is associated with improved outcomes
of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surg Oncol.
26:333–337. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zou S, Wang C, Cui Z, Guo P, Meng Q, Shi
X, Gao Y, Yang G and Han Z: β-Elemene induces apoptosis of human
rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via reactive
oxygen species-dependent activation of p38 mitogen-activated
protein kinase. Pharmacol Rep. 68:7–11. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Guo Z, Liu Z, Yue H and Wang J:
Beta-elemene increases chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil through
down-regulating microRNA-191 expression in colorectal carcinoma
cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:7032–7039. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jiang Z, Jacob JA, Loganathachetti DS,
Nainangu P and Chen B: β-Elemene: Mechanistic studies on cancer
cell interaction and its chemosensitization effect. Front
Pharmacol. 8(105)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu X, Xu M, Li N, Li Z, Li H, Shao S, Zou
K and Zou L: β-elemene inhibits tumor-promoting effect of M2
macrophages in lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
490:514–520. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Machacek M, Hodgson L, Welch C, Elliott H,
Pertz O, Nalbant P, Abell A, Johnson GL, Hahn KM and Danuser G:
Coordination of Rho GTPase activities during cell protrusion.
Nature. 461:99–103. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wu L, Zhao KQ, Wang W, Cui LN, Hu LL,
Jiang XX, Shuai J and Sun YP: Nuclear receptor coactivator 6
promotes HTR-8/SVneo cell invasion and migration by activating
NF-κB-mediated MMP9 transcription. Cell Prolif.
53(e12876)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lu Q, Huang Y, Wu J, Guan Y, Du M, Wang F,
Liu Z, Zhu Y, Gong G, Hou H, et al: T-cadherin inhibits invasion
and migration of endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis. Hum
Reprod. 35:145–156. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van Zijl F, Krupitza G and Mikulits W:
Initial steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial
transmigration. Mutat Res. 728:23–34. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Li Y, Zhang Y, Song J, Wang Q,
Zheng L and Liu D: Beta-elemene blocks epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 through
Smad3-mediated down-regulation of nuclear transcription factors.
PLoS One. 8(e58719)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang G, Li X, Huang F, Zhao J, Ding H,
Cunningham C, Coad JE, Flynn DC, Reed E and Li QQ: Antitumor effect
of beta-elemene in non-small-cell lung cancer cells is mediated via
induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptotic cell death. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 62:881–893. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao SY, Wu J, Zheng F, Tang Q, Yang LJ,
Li L, Wu WY and Hann SS: β-elemene inhibited expression of DNA
methyltransferase 1 through activation of ERK1/2 and AMPKα
signalling pathways in human lung cancer cells: the role of Sp1. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:630–641. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Deng M, Zhang Y, Liu B, Chen Y, Song H, Yu
R, Che X, Qu X, Liu Y, Hu X, et al: β-Elemene inhibits peritoneal
metastasis of gastric cancer cells by modulating FAK/Claudin-1
signaling. Phytother Res. 33:2448–2456. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
McLean GW, Carragher NO, Avizienyte E,
Evans J, Brunton VG and Frame MC: The role of focal-adhesion kinase
in cancer - a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:505–515. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lai IR, Chu PY, Lin HS, Liou JY, Jan YJ,
Lee JC and Shen TL: Phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase at
Tyr397 in gastric carcinomas and its clinical significance. Am J
Pathol. 177:1629–1637. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tungsukruthai S, Sritularak B and
Chanvorachote P: Cycloartobiloxanthone inhibits migration and
invasion of lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37:6311–6319.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Dwyer SF and Gelman IH:
Cross-phosphorylation and interaction between Src/FAK and
MAPKAP5/PRAK in early focal adhesions controls cell motility. J
Cancer Biol Res. 2(2)2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Aspenström P: The intrinsic GDP/GTP
exchange activities of Cdc42 and Rac1 are critical determinants for
their specific effects on mobilization of the actin filament
system. Cells. 8(8)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Webb AH, Gao BT, Goldsmith ZK, Irvine AS,
Saleh N, Lee RP, Lendermon JB, Bheemreddy R, Zhang Q, Brennan RC,
et al: Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 decreases cellular migration,
and angiogenesis in in vitro models of retinoblastoma. BMC Cancer.
17(434)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|