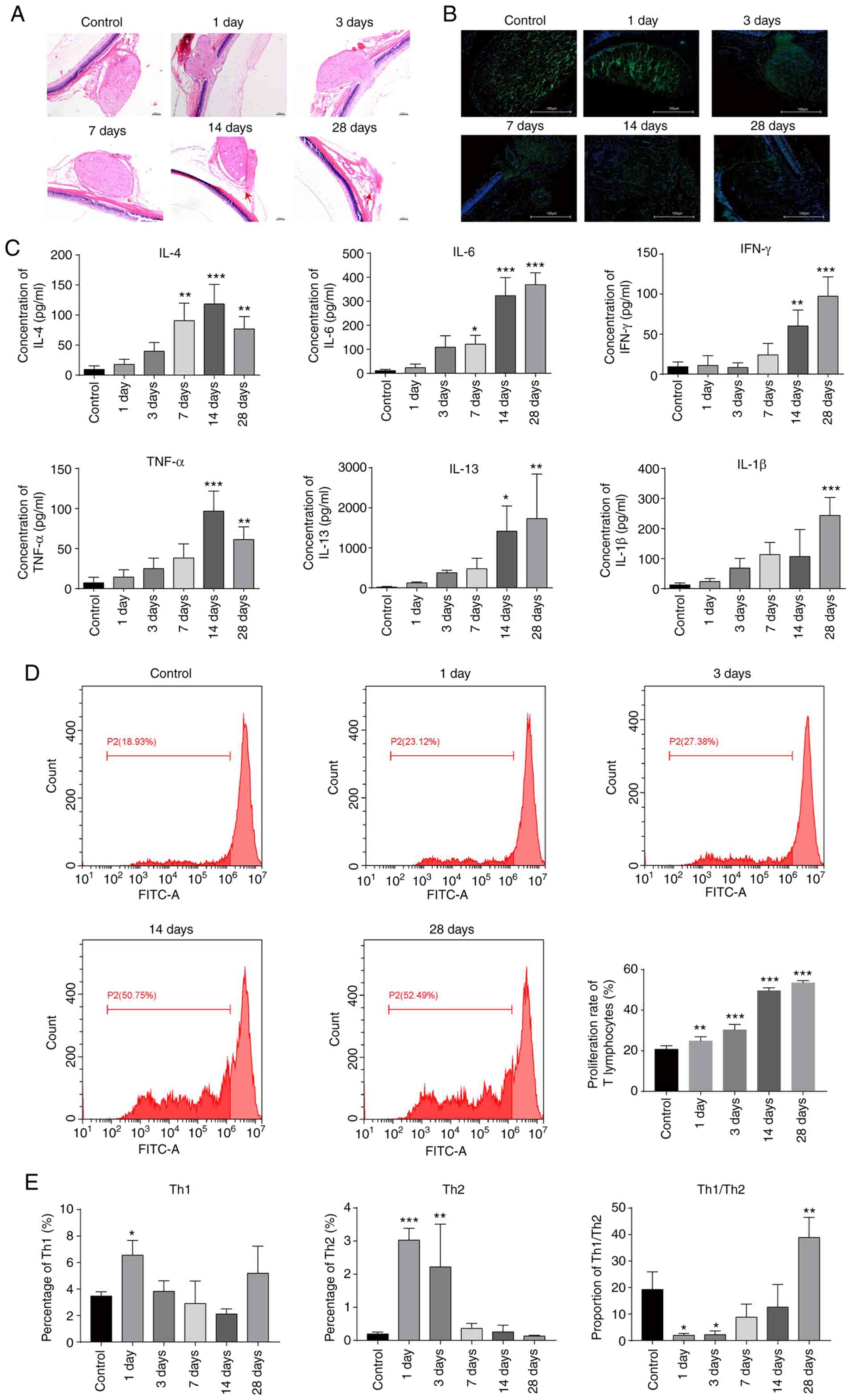
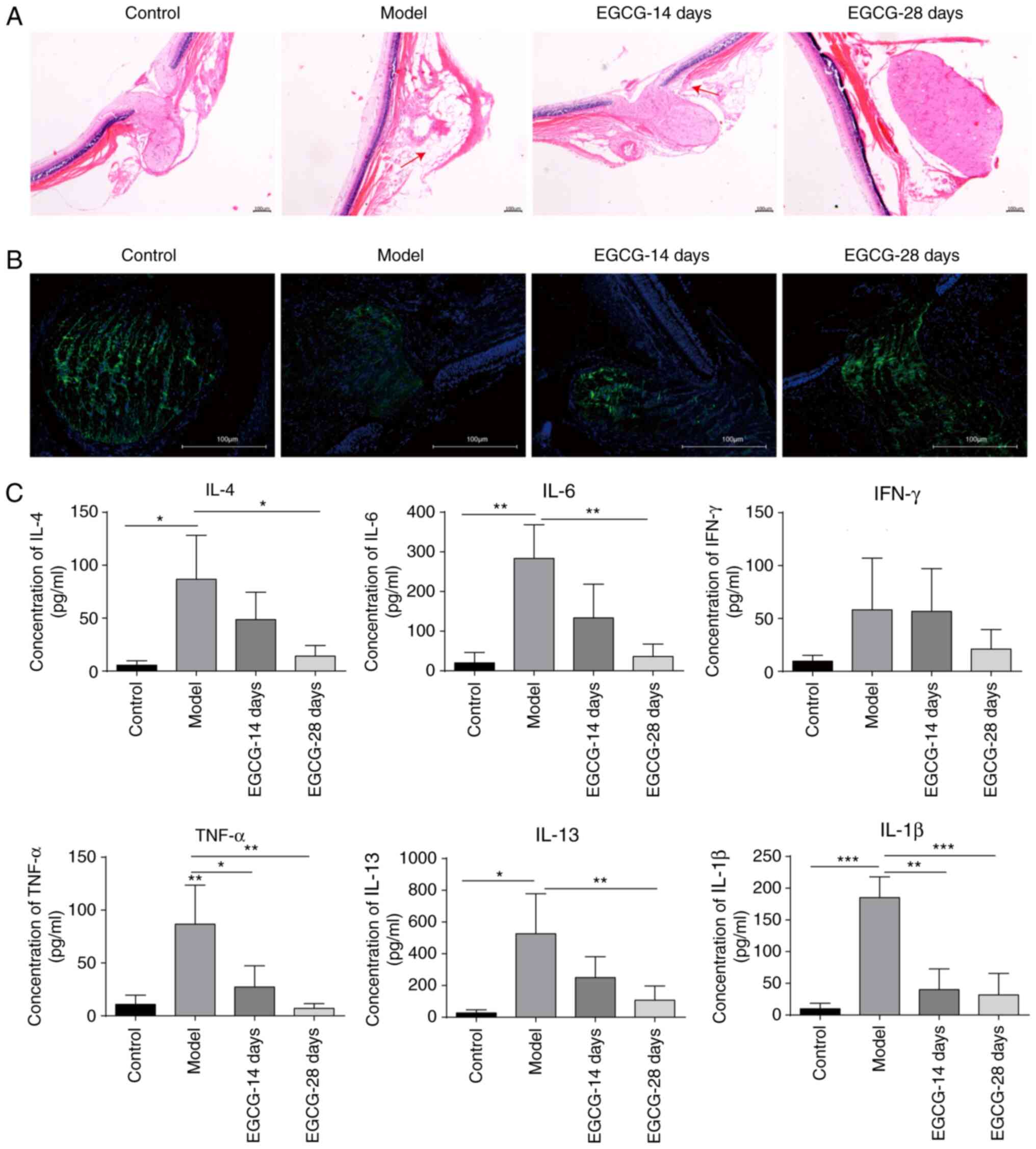
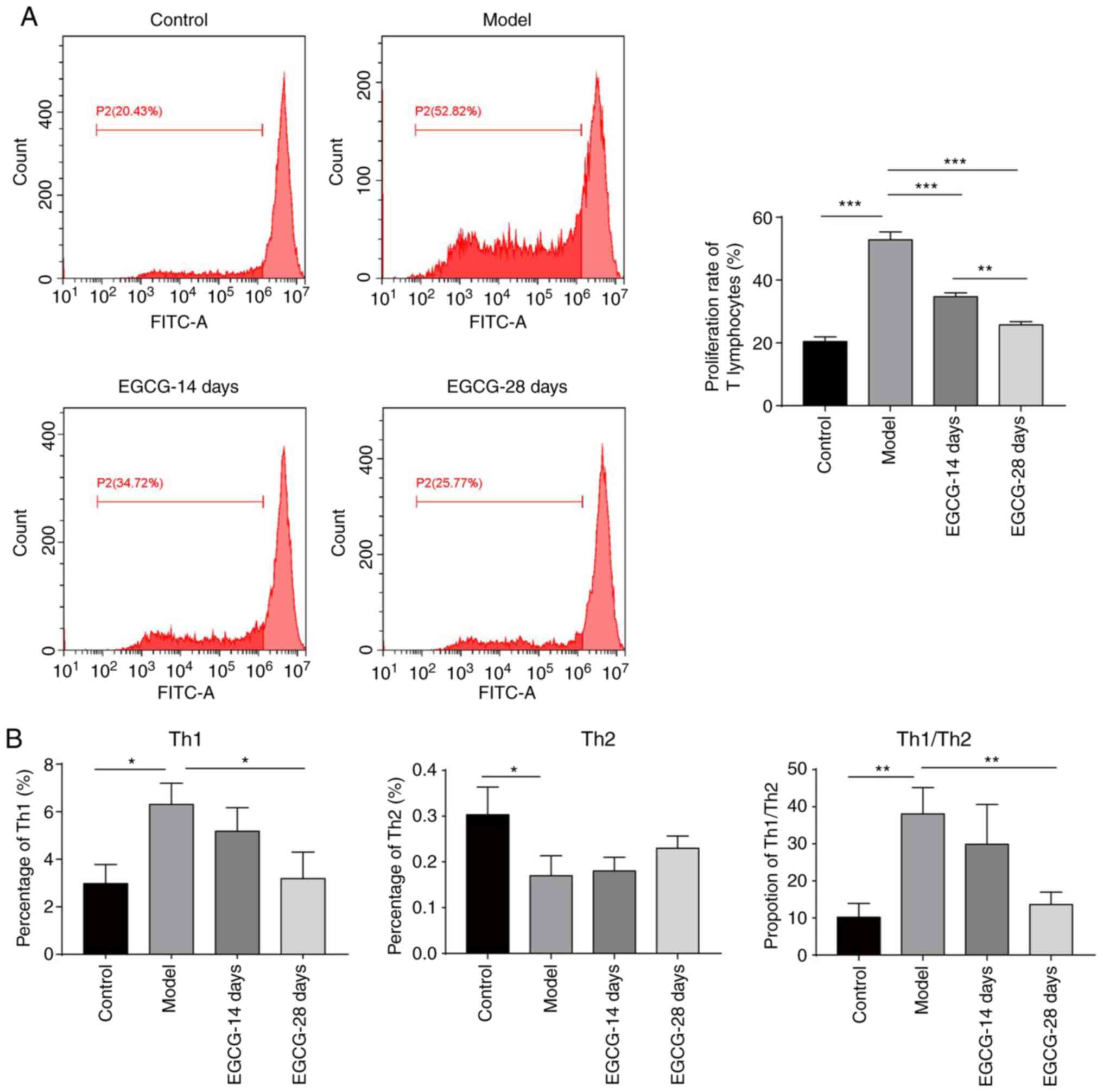
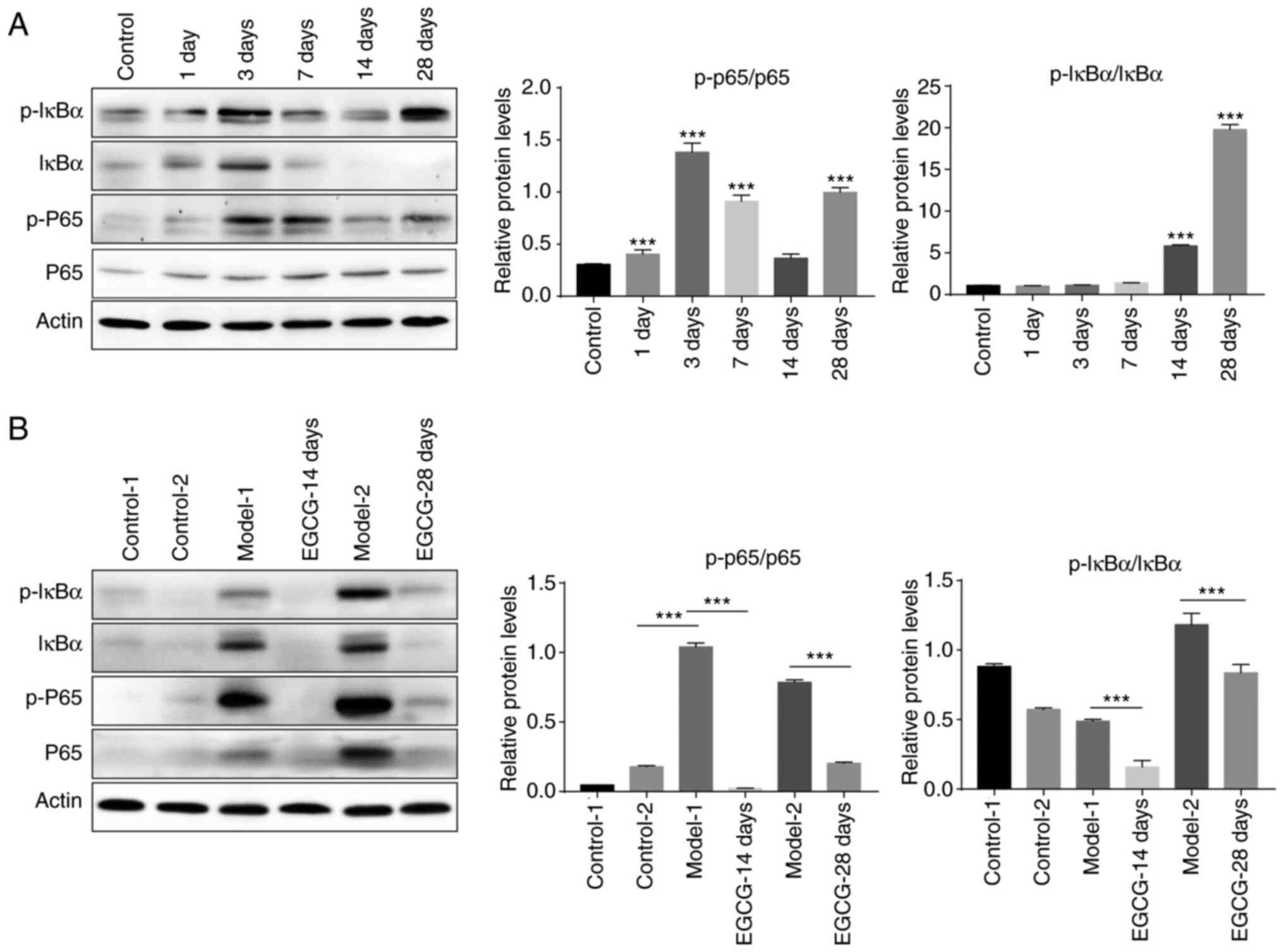
|
1
|
Lei X and Zhao Y: Neovascular glaucoma
regulation by arylsulfonyl indoline-benzamide (ASIB) through
targeting NF-κB signalling pathway. 3 Biotech.
9(211)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Quigley HA: Neuronal death in glaucoma.
Prog Retin Eye Res. 18:39–57. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Foster PJ: The epidemiology of primary
angle closure and associated glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Semin
Ophthalmol. 17:50–58. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shen C, Chen L, Jiang L and Lai TY:
Neuroprotective effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in a mouse
model of chronic glaucoma. Neurosci Lett. 600:132–136.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wong M, Huang P, Li W, Li Y, Zhang SS and
Zhang C: T-helper1/T-helper2 cytokine imbalance in the iris of
patients with glaucoma. PLoS One. 10(e0122184)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang J and Zhao Q: Kaempferitrin inhibits
proliferation, induces apoptosis, and ameliorates inflammation in
human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Phytother
Res. 33:1726–1735. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Niu Y, Dong Q and Li R: Matrine regulates
Th1/Th2 cytokine responses in rheumatoid arthritis by attenuating
the NF-kappaB signaling. Cell Biol Int. 41:611–621. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu B, Lu R, Li H, Zhou Y, Zhang P, Bai L,
Chen D, Chen J, Li J, Yu P, et al: Zhen-wu-tang ameliorates
membranous nephropathy rats through inhibiting NF-κB pathway and
NLRP3 inflammasome. Phytomedicine. 59(152913)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wei HY, Zhang YJ and Zhao SZ: Puerarin
regulates neovascular glaucoma through pigment epitheliumderived
growth factorinduced NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
17:7866–7874. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kar AK, Singh A, Dhiman N, Purohit MP,
Jagdale P, Kamthan M, Singh D, Kumar M, Ghosh D and Patnaik S:
Polymer-assisted in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles with
epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) impregnated wound patch potentiate
controlled inflammatory responses for brisk wound healing. Int J
Nanomedicine. 14:9837–9854. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nguyen T, Payan B, Zambrano A, Du Y,
Bondesson M and Mohan C: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses
neutrophil migration speed in a transgenic zebrafish model
accompanied by reduced inflammatory mediators. J Inflamm Res.
12:231–239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yelins'ka AM, Liashenko LI and Kostenko
VO: Quercetin potentiates antiradical properties of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate in periodontium of rats under systemic
and local administration of lipopolisaccharide of salmonella typhi.
Wiad Lek. 72:1499–1503. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Jia R, Celi P, Ding X, Bai S, Zeng
Q, Mao X, Xu S and Zhang K: Green tea polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves the antioxidant capacity of
eggs. Food Funct. 11:534–543. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sharifi-Rad M, Pezzani R, Redaelli M,
Zorzan M, Imran M, Ahmed Khalil A, Salehi B, Sharopov F, Cho WC and
Sharifi-Rad J: preclinical pharmacological activities of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate in signaling pathways: An update on
cancer. Molecules. 25(467)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Md Nesran ZN, Shafie NH, Ishak AH, Mohd
Esa N, Ismail A and Md Tohid SF: Induction of endoplasmic reticulum
stress pathway by green tea epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) in
colorectal cancer cells: Activation of PERK/p-eIF2α/ATF4 and IRE1α.
Biomed Res Int. 2019(3480569)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Chen L, Lu T, Xie Y, Li C, Jia Z
and Cao J: ERα36 is an effective target of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 12:3222–3234. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mao L, Hochstetter D, Yao L, Zhao Y, Zhou
J, Wang Y and Xu P: Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epigallocatechin
Gallate (EGCG) attenuates neuroinflammation in palmitic
acid-stimulated BV-2 microglia and high-fat diet-induced obese
mice. Int J Mol Sci. 20(5081)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang D, Gao Q, Wang T, Kan Z, Li X, Hu L,
Peng CY, Qian F, Wang Y and Granato D: Green tea polyphenols and
epigallocatechin-3-gallate protect against perfluorodecanoic acid
induced liver damage and inflammation in mice by inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome activation. Food Res Int. 127(108628)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Karatas A, Dagli AF, Orhan C, Gencoglu H,
Ozgen M, Sahin N, Sahin K and Koca SS: Epigallocatechin 3-gallate
attenuates arthritis by regulating Nrf2, HO-1, and cytokine levels
in an experimental arthritis model. Biotechnol Appl Biochem.
67:317–322. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Liu J, Lei Y and Liu M: Potential
ameliorative effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate against
cigarette smoke exposure induced renal and hepatic deficits.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 191(110202)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Singh BN, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): Mechanisms,
perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:1807–1821. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liang L, He L, Zhu M, Chen B and Xiao C:
Protective effects of carnosic acid on retinal ganglion cells in
acute ocular hypertension rats. Int Ophthalmol. 40:1869–1878.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Azarsiz E, Karaca N, Ergun B, Durmuscan M,
Kutukculer N and Aksu G: In vitro T lymphocyte proliferation by
carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester method is helpful
in diagnosing and managing primary immunodeficiencies. J Clin Lab
Anal. 32(e22216)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yin Y, Mitson-Salazar A and Prussin C:
Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow cytometry. Curr Protoc
Immunol. 110:6.24.1–6.24.18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Foster B, Prussin C, Liu F, Whitmire JK
and Whitton JL: Detection of intracellular cytokines by flow
cytometry. Curr Protoc Immunol Chapter. 6(Unit 6 24)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li W, Ma N, Liu MX, Ye BJ, Li YJ, Hu HY
and Tang YH: C1q/TNF-related protein-9 attenuates retinal
inflammation and protects blood-retinal barrier in db/db mice. Eur
J Pharmacol. 853:289–298. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Paula AP, Paula JS, Silva MJ, Rocha EM, De
Moraes CG and Rodrigues ML: Effects of swimming goggles wearing on
intraocular pressure, ocular perfusion pressure, and ocular pulse
amplitude. J Glaucoma. 25:860–864. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sanchez-Sanchez C, Puerto B,
Lopez-Caballero C and Contreras I: Unilateral acute iris
depigmentation and transillumination after glaucoma surgery with
mitomycin application and intracameral moxifloxacin. Am J
Ophthalmol Case Rep. 18(100639)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Otarola F, Virgili G, Shah A, Hu K, Bunce
C and Gazzard G: Ab interno trabecular bypass surgery with Schlemm
s canal microstent (Hydrus) for open angle glaucoma. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 3(CD012740)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dada T, Midha N, Shah P, Sidhu T, Angmo D
and Sihota R: Innovations in glaucoma surgery from Dr. Rajendra
Prasad Centre for Ophthalmic Sciences. Indian J Ophthalmol.
65:103–108. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Weinreb RN, Aung T and Medeiros FA: The
pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: A review. JAMA.
311:1901–1911. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hong S, Kim CY, Lee WS, Shim J, Yeom HY
and Seong GJ: Ocular hypotensive effects of topically administered
agmatine in a chronic ocular hypertensive rat model. Exp Eye Res.
90:97–103. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yu S, Tanabe T and Yoshimura N: A rat
model of glaucoma induced by episcleral vein ligation. Exp Eye Res.
83:758–770. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhong L: A modified chronic ocular
hypertension rat model for retinal ganglion cell neuroprotection.
Front Med. 7:367–377. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Morrison JC, Johnson EC and Cepurna WO:
Hypertonic saline injection model of experimental glaucoma in rats.
Methods Mol Biol. 1695:11–21. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhou J, Mao L, Xu P and Wang Y: Effects of
(-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) on energy expenditure and
microglia-mediated hypothalamic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat
diet. Nutrients. 10(1681)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu D, Perkins JT and Hennig B: EGCG
prevents PCB-126-induced endothelial cell inflammation via
epigenetic modifications of NF-κB target genes in human endothelial
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 28:164–170. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kian K, Khalatbary AR, Ahmadvand H,
Karimpour Malekshah A and Shams Z: Neuroprotective effects of
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) against peripheral nerve
transection-induced apoptosis. Nutr Neurosci. 22:578–586.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Husain S, Abdul Y, Webster C, Chatterjee
S, Kesarwani P and Mehrotra S: Interferon-gamma
(IFN-gamma)-mediated retinal ganglion cell death in human
tyrosinase T cell receptor transgenic mouse. PLoS One.
9(e89392)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Borkenstein A, Faschinger C, Maier R,
Weger M, Theisl A, Demel U, Graninger W, Irene H and Mossböck G:
Measurement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, Fas
ligand, interleukin-1a, and interleukin-1β in the aqueous humor of
patients with open angle glaucoma using multiplex bead analysis.
Mol Vis. 19:2306–2311. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gramlich OW, Ding QJ, Zhu W, Cook A,
Anderson MG and Kuehn MH: Adoptive transfer of immune cells from
glaucomatous mice provokes retinal ganglion cell loss in
recipients. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 3(56)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wax MB, Tezel G, Yang J, Peng G, Patil RV,
Agarwal N, Sappington RM and Calkins DJ: Induced autoimmunity to
heat shock proteins elicits glaucomatous loss of retinal ganglion
cell neurons via activated T-cell-derived fas-ligand. J Neurosci.
28:12085–12096. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Huang P, Zhang SS and Zhang C: The two
sides of cytokine signaling and glaucomatous optic neuropathy. J
Ocul Biol Dis Infor. 2:78–83. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen H, Cho KS, Vu THK, Shen CH, Kaur M,
Chen G, Mathew R, McHam ML, Fazelat A, Lashkari K, et al: Commensal
microflora-induced T cell responses mediate progressive
neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Nat Commun. 9(3209)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|