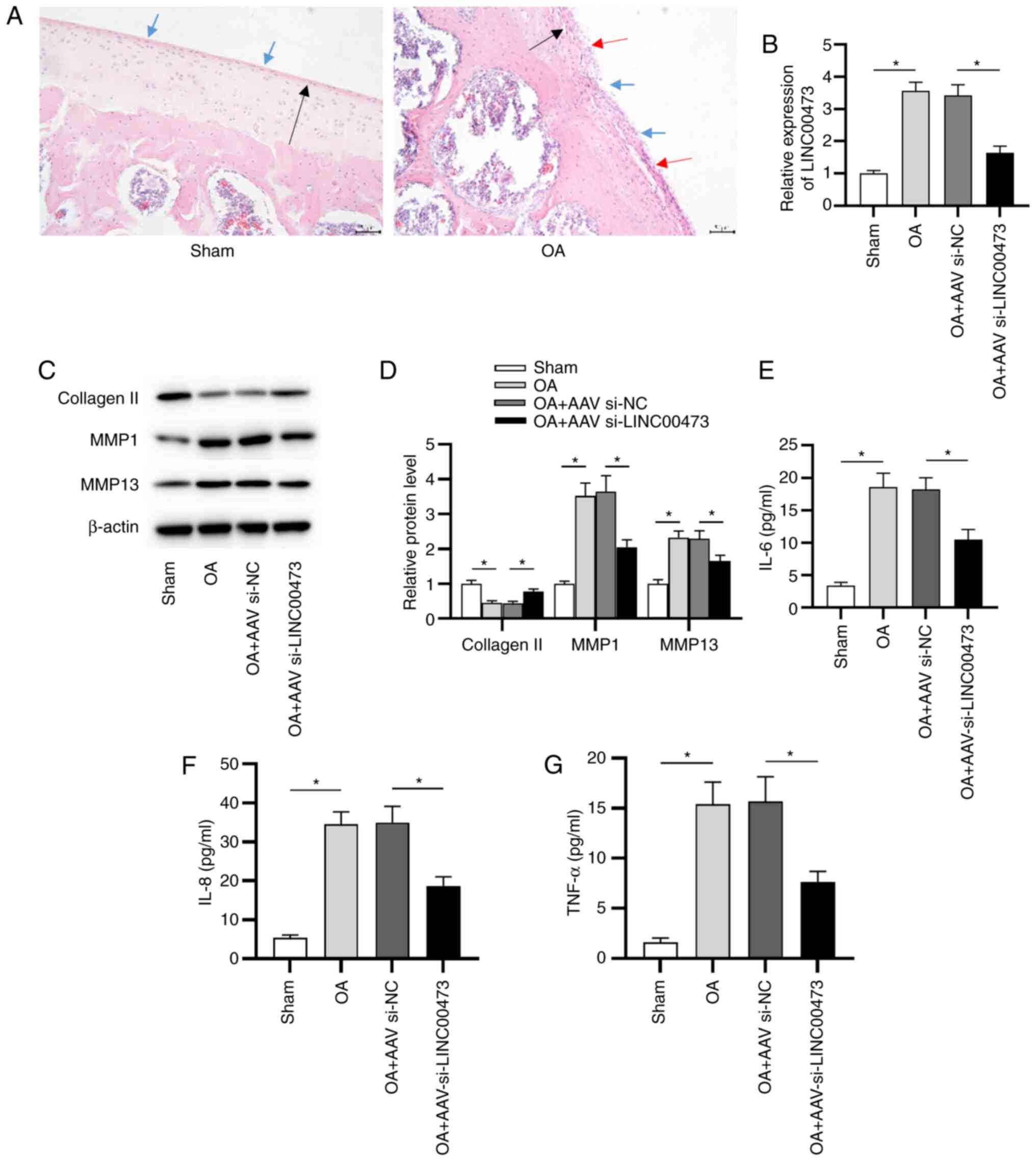
|
1
|
Palazzo C, Nguyen C, Lefevre-Colau MM,
Rannou F and Poiraudeau S: Risk factors and burden of
osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 59:134–138. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu-Bryan R: Inflammation and
intracellular metabolism: New targets in OA. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 23:1835–1842. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Maldonado M and Nam J: The role of changes
in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of
inflammation on the pathology of osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int.
2013(284873)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Perez Martin A: Symptoms. Localizations:
Knee, hip, hands, spine, other localizations. Aten Primaria. 46
(Suppl 1):S11–S17. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Spanish).
|
|
5
|
Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR and
Goldring MB: Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:1697–1707. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Majeed MH, Sherazi SAA, Bacon D and Bajwa
ZH: Pharmacological treatment of pain in osteoarthritis: A
descriptive review. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 20(88)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xu YK, Zhu FG, Feng EY, Fan CL, Yu GS, Wei
YZ and Xie LH: External therapies of traditional Chinese medicine
combined with sodium hyaluronate injected in articular cavity
therapy on knee osteoarthritis: Meta-analysis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao
Za Zhi. 43:1934–1939. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Richards MM, Maxwell JS, Weng L, Angelos
MG and Golzarian J: Intra-articular treatment of knee
osteoarthritis: From anti-inflammatories to products of
regenerative medicine. Phys Sportsmed. 44:101–108. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG:
Analyzing MiRNA-LncRNA interactions. Methods Mol Biol.
1402:271–286. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kazemzadeh M, Safaralizadeh R and Orang
AV: LncRNAs: Emerging players in gene regulation and disease
pathogenesis. J Genet. 94:771–784. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mathieu EL, Belhocine M, Dao LT, Puthier D
and Spicuglia S: Functions of lncRNA in development and diseases.
Med Sci (Paris). 30:790–796. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
12
|
Xie F, Liu YL, Chen XY, Li Q, Zhong J, Dai
BY, Shao XF and Wu GB: Role of MicroRNA, LncRNA, and exosomes in
the progression of osteoarthritis: A review of recent literature.
Orthop Surg. 12:708–716. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhou Q, Huang XR, Yu J, Yu X and Lan HY:
Long noncoding RNA Arid2-IR is a novel therapeutic target for renal
inflammation. Mol Ther. 23:1034–1043. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cai L, Tu L, Li T, Yang X, Ren Y, Gu R,
Zhang Q, Yao H, Qu X, Wang Q and Tian J: Downregulation of lncRNA
UCA1 ameliorates the damage of dopaminergic neurons, reduces
oxidative stress and inflammation in Parkinson's disease through
the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 75(105734)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Wang F, Chen G, He R and Yang L:
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes osteoarthritis by modulating miR-150-5p/AKT3
axis. Cell Biosci. 9(54)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zheng Y, Sun S, Yu M and Fu X:
Identification of potential hub-lncRNAs in ischemic stroke based on
Subpathway-LNCE method. J Cell Biochemistry. 120:12832–12842.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu D, Xu Y, Zou Y, Zuo Q, Huang S, Wang S,
Lu X, He X, Wang J, Wang T and Sun L: Long noncoding RNA 00473 is
involved in preeclampsia by LSD1 binding-regulated TFPI2
transcription in trophoblast cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
12:381–392. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen Y, Lin Y, Bai Y, Cheng D and Bi Z: A
long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-associated competing endogenous RNA
(ceRNA) network identifies eight lncRNA biomarkers in patients with
osteoarthritis of the knee. Med Sci Monit. 25:2058–2065.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kong F, Jin J, Lv X, Han Y, Liang X, Gao Y
and Duan X: Long noncoding RNA RMRP upregulation aggravates
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by sponging miR-206 to
target ATG3 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:716–725.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li X, Zeng L, Cao C, Lu C, Lian W, Han J,
Zhang X, Zhang J, Tang T and Li M: Long noncoding RNA MALAT1
regulates renal tubular epithelial pyroptosis by modulated miR-23c
targeting of ELAVL1 in diabetic nephropathy. Exp Cell Res.
350:327–335. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shen H, Wang Y, Shi W, Sun G, Hong L and
Zhang Y: LncRNA SNHG5/miR-26a/SOX2 signal axis enhances
proliferation of chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 50:191–198. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. Washington, DC, National Academies Press (US), 2011.
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Shen S, Li Z, Li W and Weng X:
MIR-140-5p affects chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and
inflammation by targeting HMGB1 in osteoarthritis. Inflamm Res.
69:63–73. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cheng C, Shan W, Huang W, Ding Z, Cui G,
Liu F, Lu W, Xu J, He W and Yin Z: ACY-1215 exhibits
anti-inflammatory and chondroprotective effects in human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes via inhibition of STAT3 and NF-κB
signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 109:2464–2471.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Yu T, Jin H, Zhao C and Wang Y:
Knockdown MiR-302b alleviates LPS-induced injury by targeting Smad3
in C28/I2 chondrocytic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:733–743.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fernandes JC, Martel-Pelletier J and
Pelletier JP: The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis
pathophysiology. Biorheology. 39:237–246. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Charlier E, Deroyer C, Ciregia F, Malaise
O, Neuville S, Plener Z, Malaise M and de Seny D: Chondrocyte
dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol.
165:49–65. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Goldring MB and Otero M: Inflammation in
osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 23:471–478. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Lin J, Zhou X, Chen X, Chen AC,
Pi B, Pan G, Pei M, Yang H, Liu T and He F: Melatonin prevents
osteoarthritis-induced cartilage degradation via targeting
MicroRNA-140. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019(9705929)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang P, Sun J, Liang C, Gu B, Xu Y, Lu H,
Cao B and Xu H: lncRNA IGHC γ Acts as a ceRNA to regulate
macrophage inflammation via the miR-6891-3p/TLR4 axis in
osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020(9743037)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen H and Chen L: An integrated analysis
of the competing endogenous RNA network and co-expression network
revealed seven hub long non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Bone
Joint Res. 9:90–98. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PJN: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ren Y, Hu J, Tan J, Tang X, Li Q, Yang H,
Liu C, He Q, Zou K, Sun X and Tan B: Incidence and risk factors of
symptomatic knee osteoarthritis among the Chinese population:
Analysis from a nationwide longitudinal study. BMC Public Health.
20(1491)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Callahan LF, Ambrose KR, Albright AL,
Altpeter M, Golightly YM, Huffman KF, Nelson AE and Weisner SE:
Public Health interventions for osteoarthritis-updates on the
osteoarthritis Action Alliance's efforts to address the 2010 OA
Public Health Agenda Recommendations. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 37 (Suppl
120):S31–S39. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vargas Negrin F, Medina Abellan MD,
Hermosa Hernan JC and de Felipe Medina R: Treatment of patients
with osteoarthritis. Aten Primaria. 46 (Suppl 1):S39–S61.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Spanish).
|
|
39
|
Hermann W, Lambova S and Muller-Ladner U:
Current treatment options for osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev.
14:108–116. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hwang HS and Kim HA: Chondrocyte apoptosis
in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26035–26054. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Minguzzi M, Cetrullo S, D'Adamo S,
Silvestri Y, Flamigni F and Borzi RM: Emerging players at the
intersection of chondrocyte loss of maturational arrest, oxidative
stress, senescence and low-grade inflammation in osteoarthritis.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018(3075293)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ryu JH, Shin Y, Huh YH, Yang S, Chun CH
and Chun JS: Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha regulates Fas-mediated
chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction.
Cell Death Differ. 19:440–450. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu Q, Zhang X, Dai L, Hu X, Zhu J, Li L,
Zhou C and Ao Y: Long noncoding RNA related to cartilage injury
promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:969–978. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Nanus DE, Wijesinghe SN, Pearson MJ,
Hadjicharalambous MR, Rosser A, Davis ET, Lindsay MA and Jones SW:
Obese osteoarthritis patients exhibit an inflammatory synovial
fibroblast phenotype, which is regulated by the long non coding RNA
MALAT1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72:609–619. 2019.
|
|
45
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
De Smet EG, Van Eeckhoutte HP, Avila Cobos
F, Blomme E, Verhamme FM, Provoost S, Verleden SE, Venken K, Maes
T, Joos GF, et al: The role of miR-155 in cigarette smoke-induced
pulmonary inflammation and COPD. Mucosal Immunol. 13:423–436.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhang Y, Peng B and Han Y: MiR-182
alleviates the development of cyanotic congenital heart disease by
suppressing HES1. Eur J Pharmacol. 836:18–24. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chang T, Xie J, Li H, Li D, Liu P and Hu
Y: MicroRNA-30a promotes extracellular matrix degradation in
articular cartilage via downregulation of Sox9. Cell Prolif.
49:207–218. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang G, Wu Y, Xu D and Yan X: Long
Noncoding RNA UFC1 promotes proliferation of chondrocyte in
osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge for miR-34a. DNA Cell Biol.
35:691–695. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Li S, Luo Y, Liu Y and Yu N: LncRNA
PVT1 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis in osteoarthritis by acting as
a sponge for miR-488-3p. DNA Cell Biol. 36:571–580. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Li YF, Li SH, Liu Y and Luo YT: Long
noncoding RNA CIR promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix
degradation in osteoarthritis by acting as a sponge For Mir-27b.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:602–610. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pan W, Yu H, Zheng B, Gao Y, Li P, Huang
Q, Xie C and Ge X: Upregulation of MiR-369-3p suppresses cell
migration and proliferation by targeting SOX4 in Hirschsprung's
disease. J Pediatr Surg. 52:1363–1370. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chen L, Li Q, Wang J, Jin S, Zheng H, Lin
J, He F, Zhang H, Ma S, Mei J and Yu J: MiR-29b-3p promotes
chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates the occurrence and
development of osteoarthritis by targeting PGRN. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3347–3359. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yu J and Liu SL: Emerging role of LY6E in
virus-host interactions. Viruses. 11(1020)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Feng X, Huang J, Liu Y, Xiao L, Wang D,
Hua B, Tsao BP and Sun L: Identification of interferon-inducible
genes as diagnostic biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus.
Clin Rheumatol. 34:71–79. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Komatsuda A, Wakui H, Iwamoto K, Ozawa M,
Togashi M, Masai R, Maki N, Hatakeyama T and Sawada K: Up-regulated
expression of Toll-like receptors mRNAs in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Clin Exp Immunol. 152:482–487. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
He W, Wei D, Cai Chen S, Li S and Chen W:
Altered long non-coding RNA Transcriptomic Profiles in Ischemic
Stroke. Hum Gene Ther. 29:719–732. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|