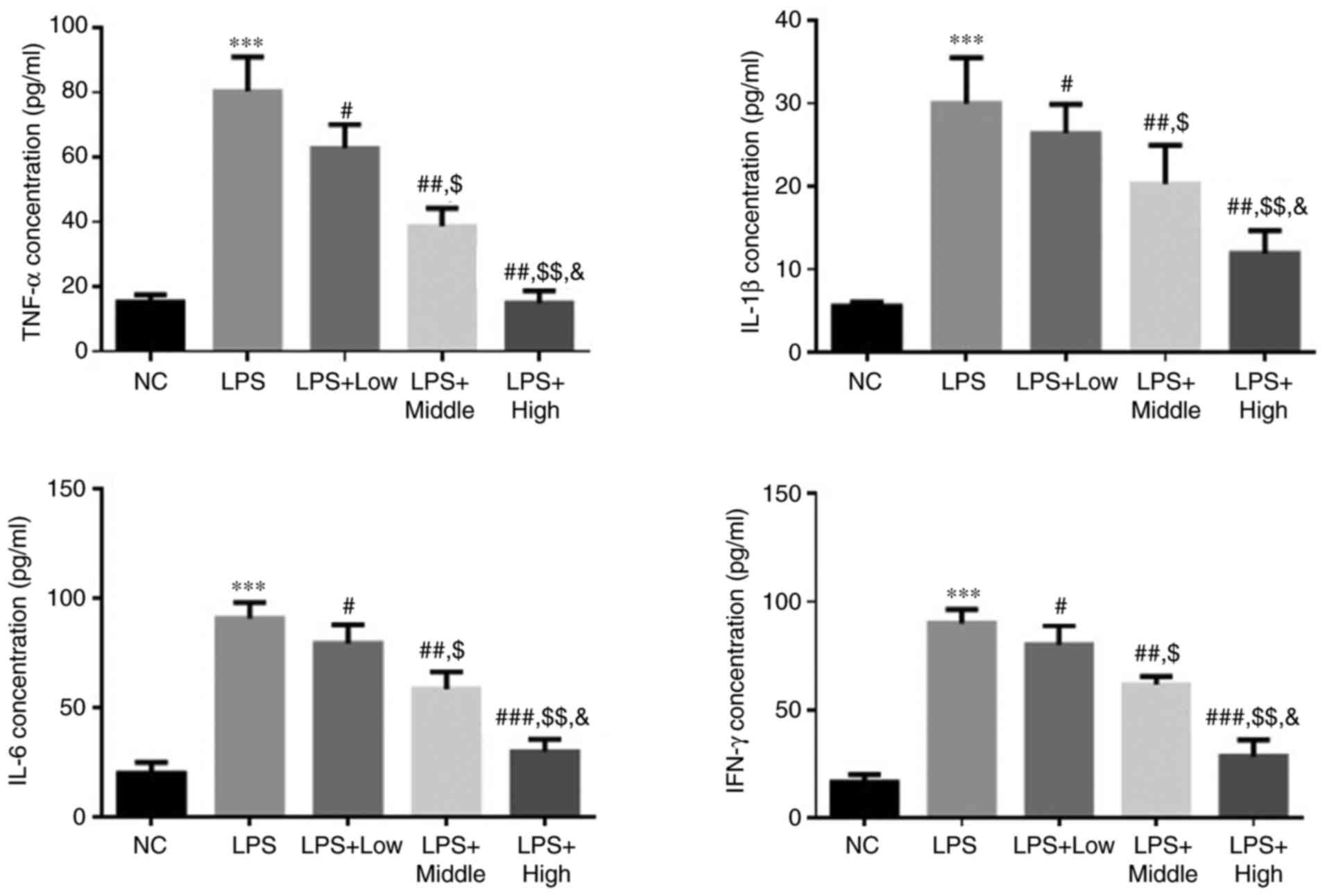
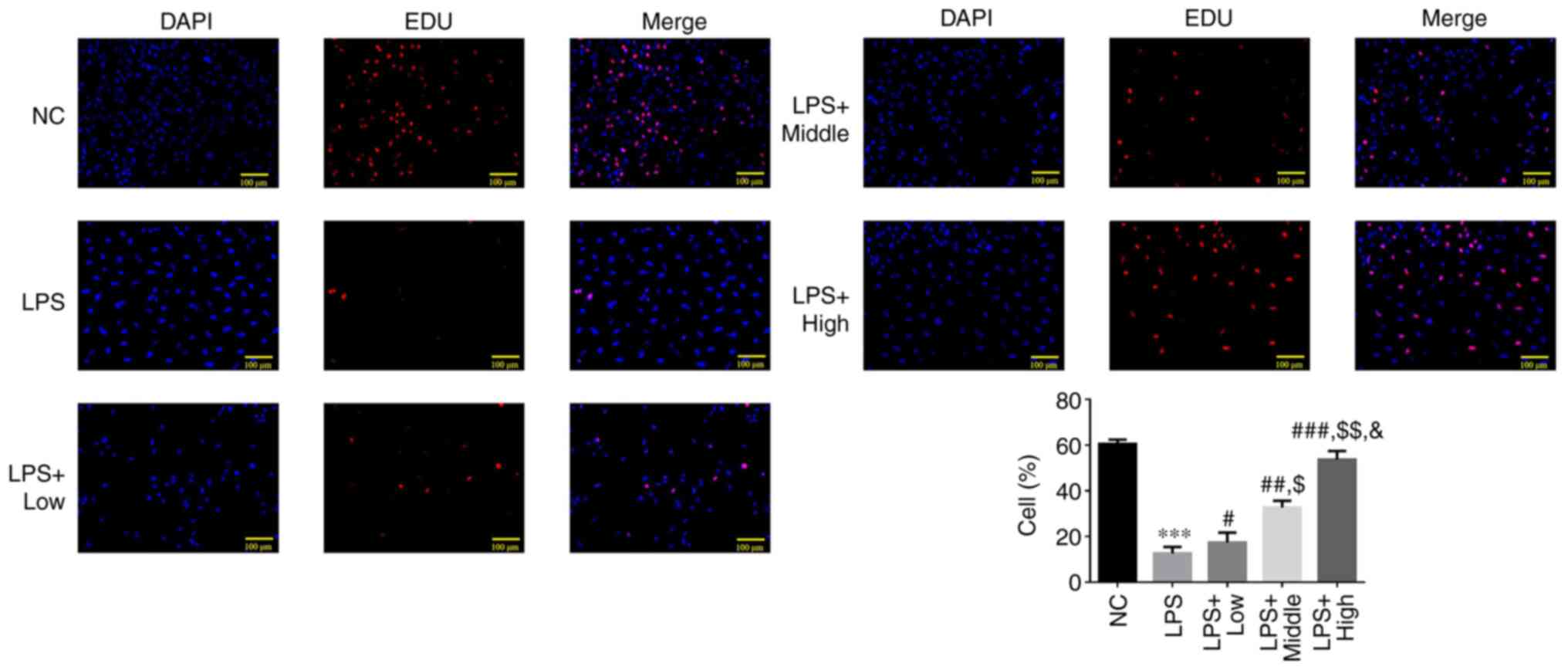
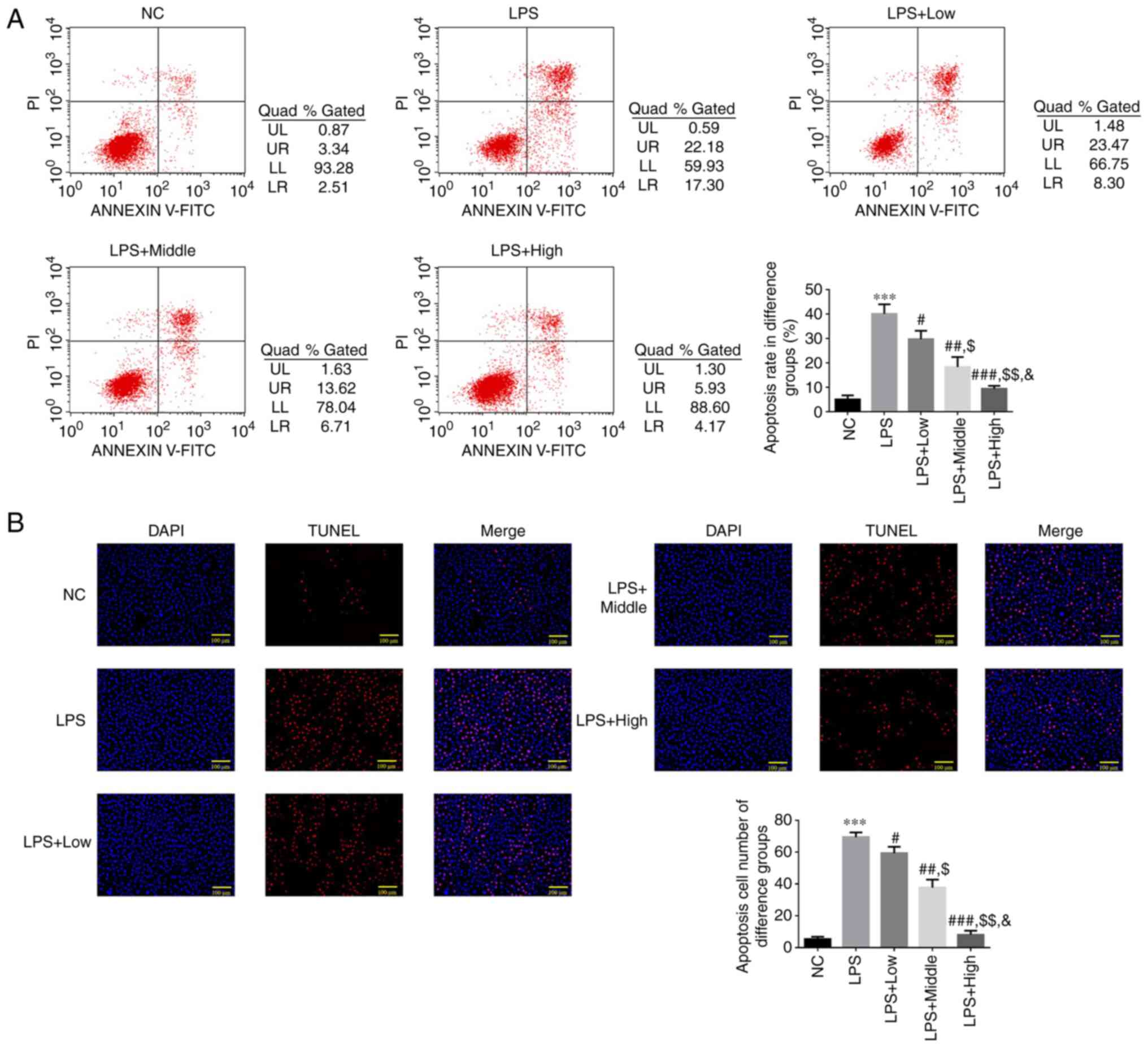
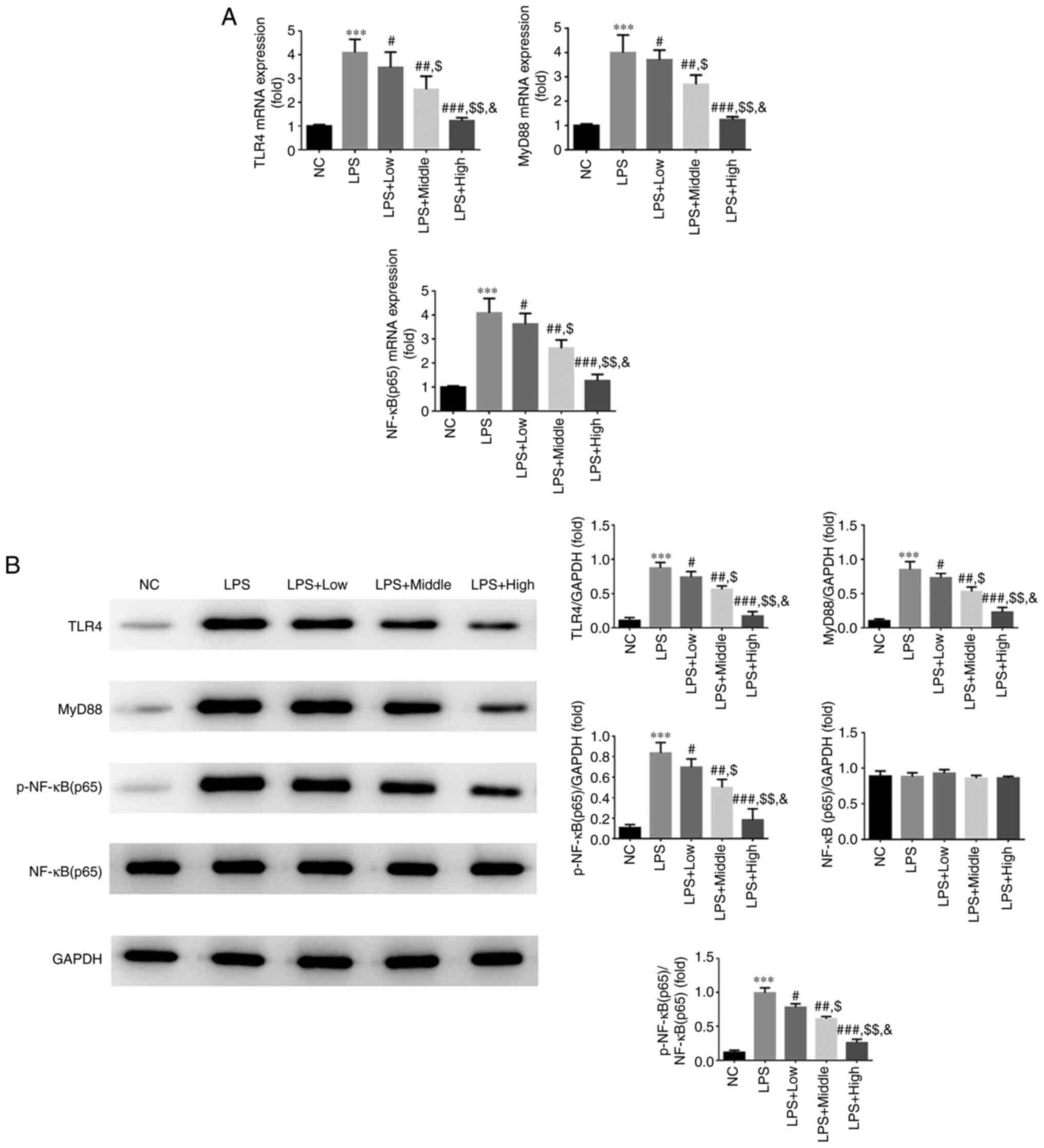
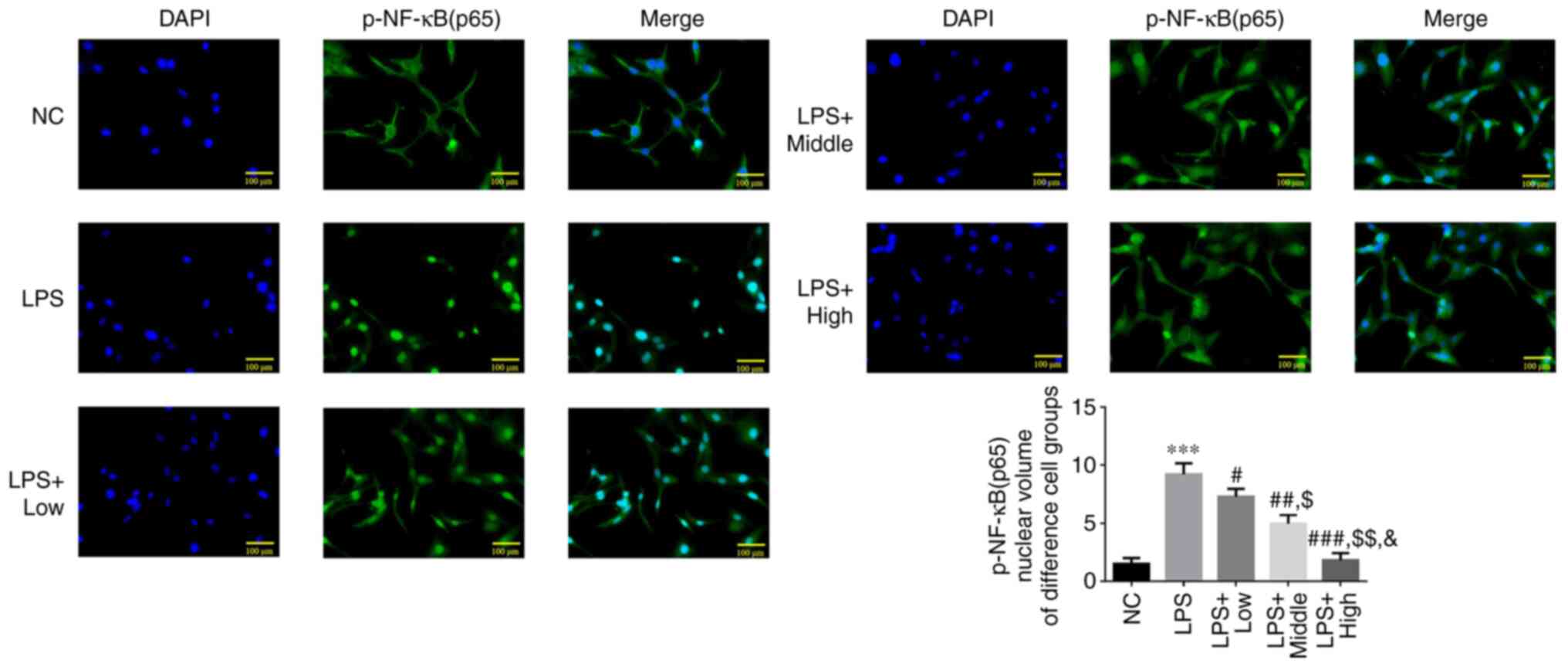
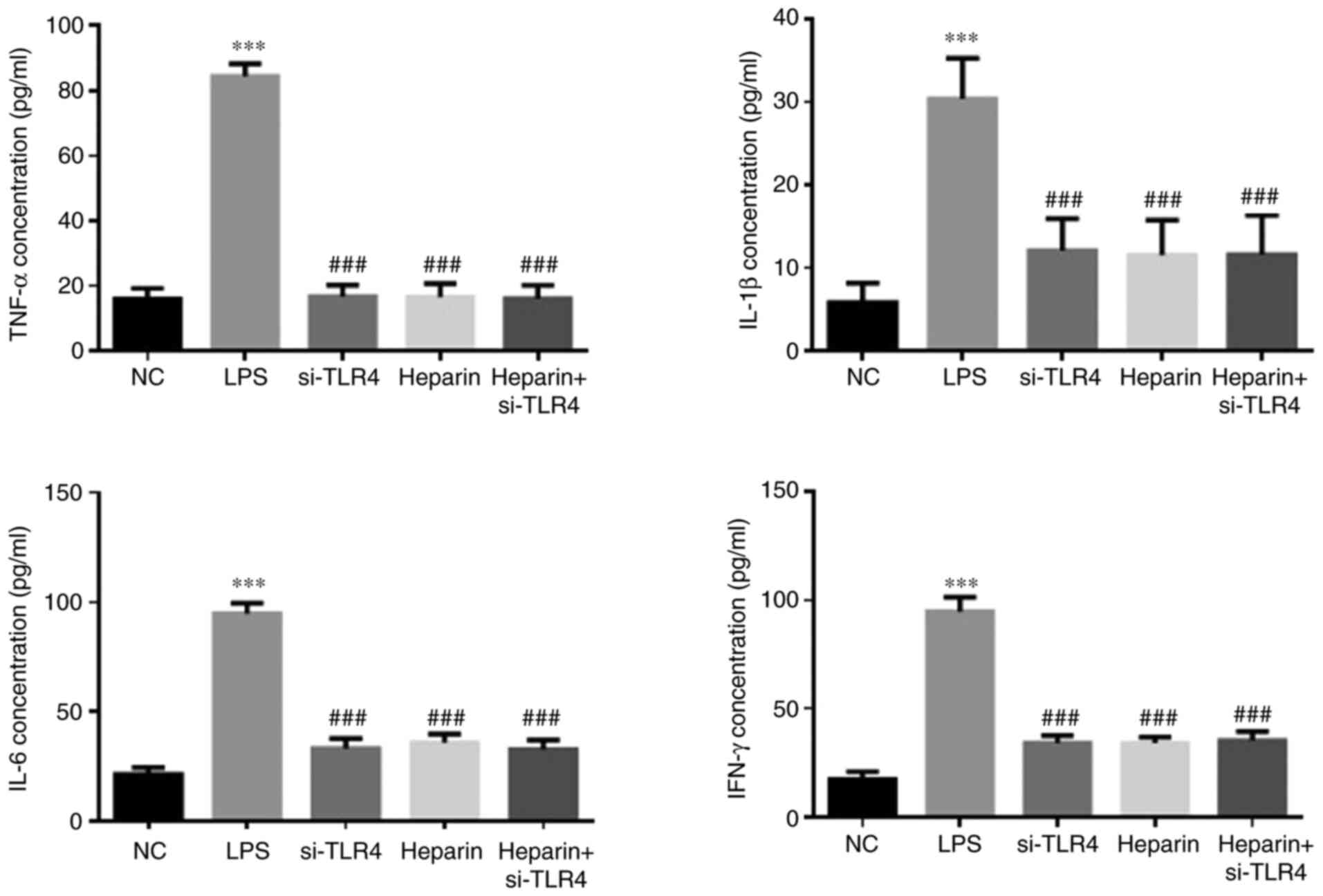
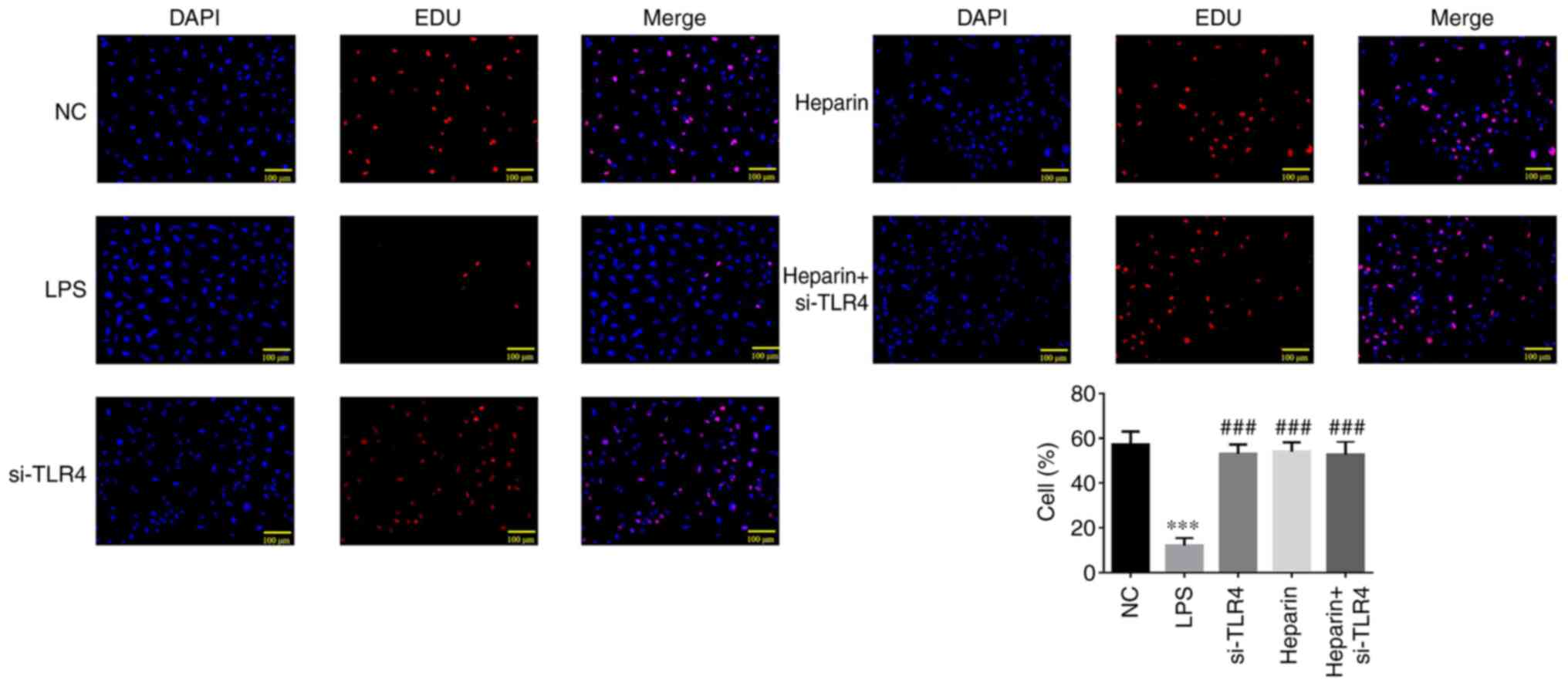
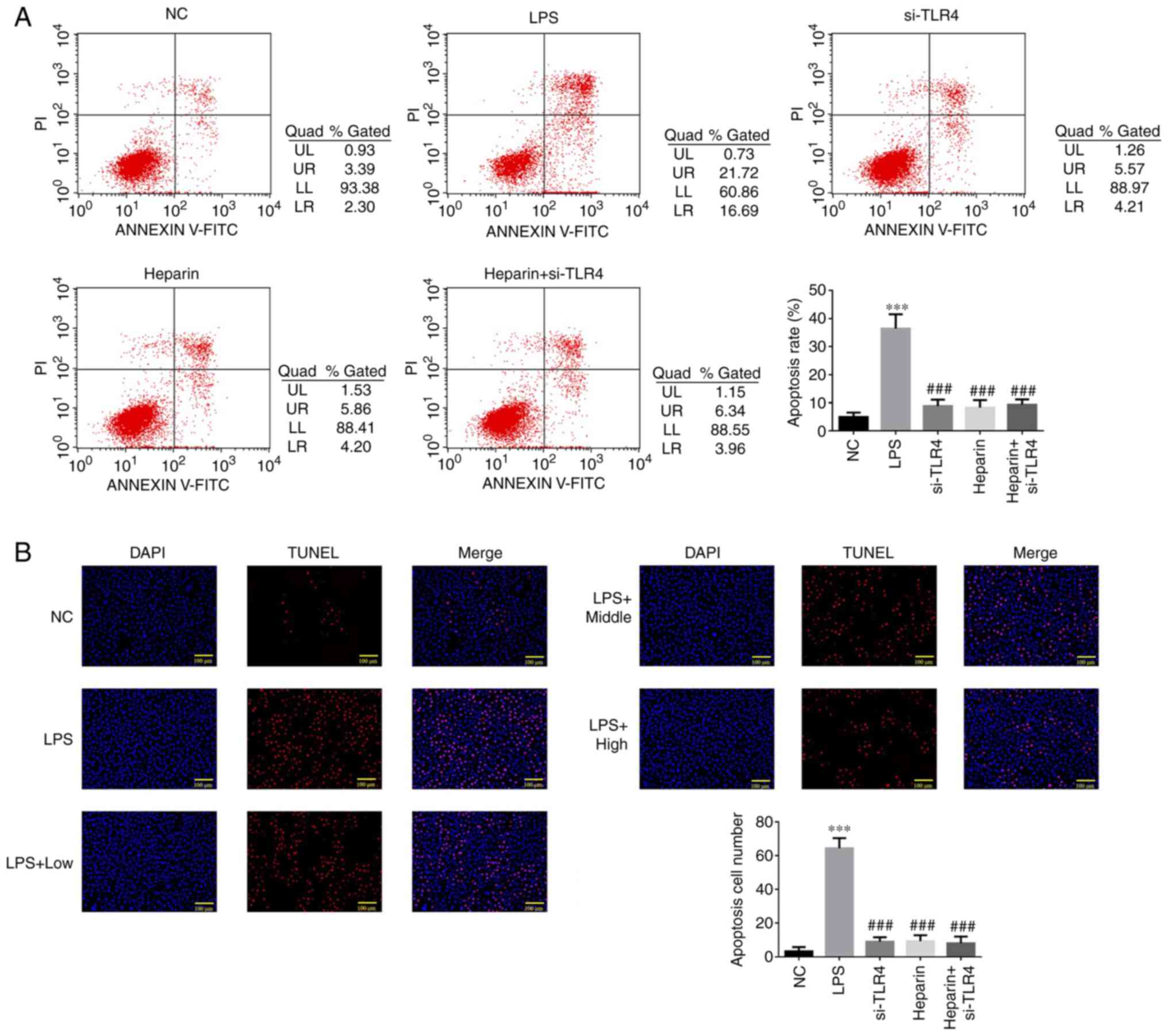
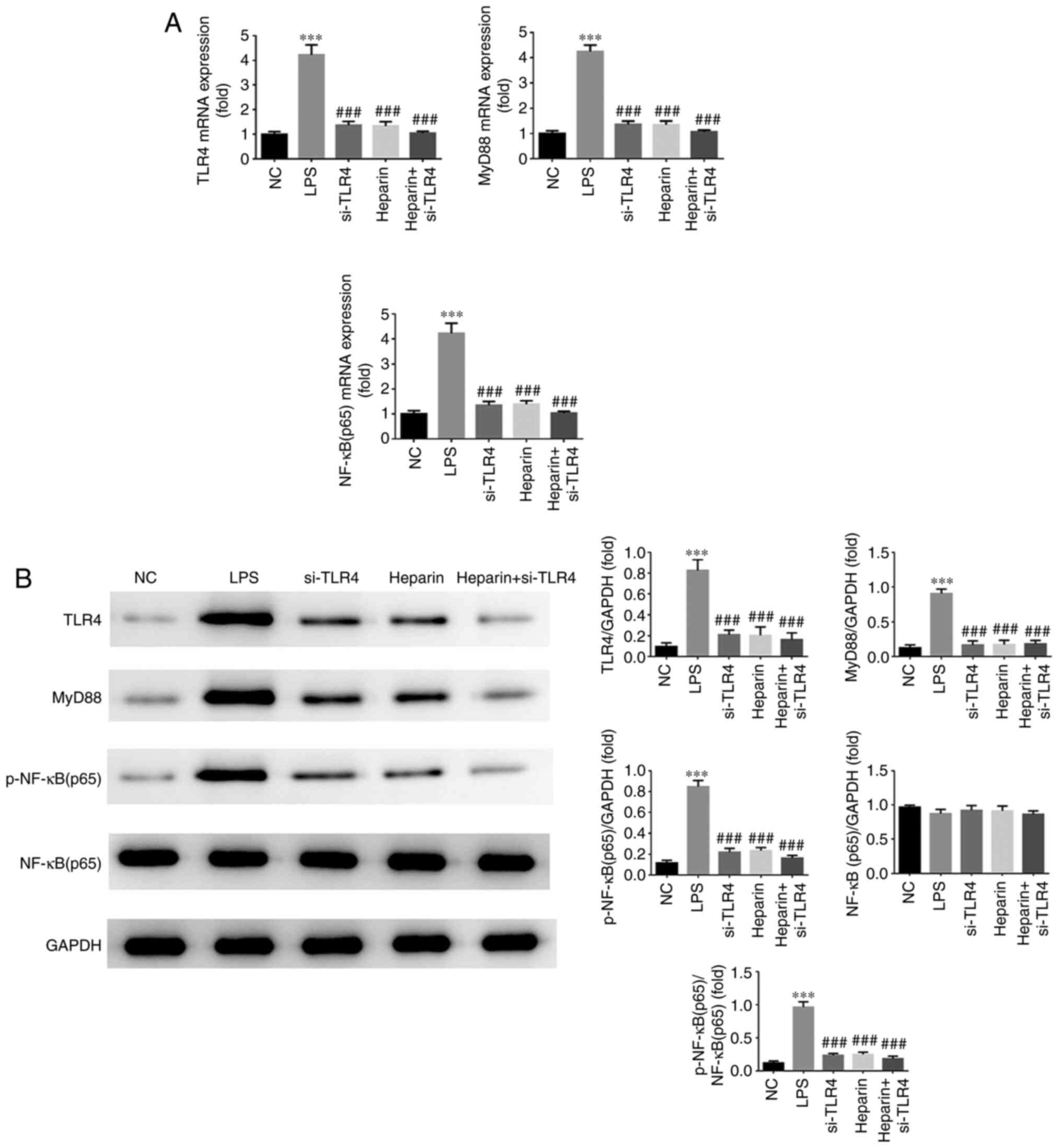
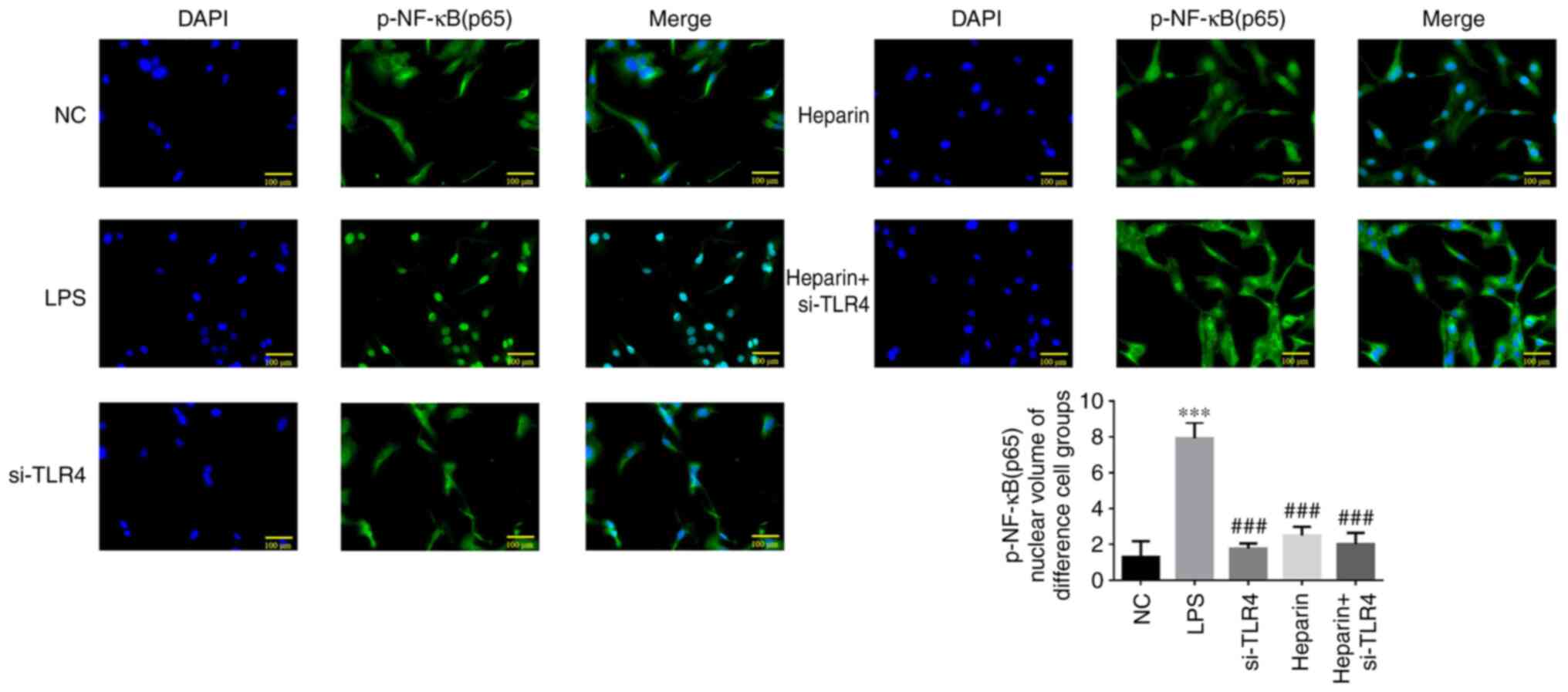
|
1
|
Stanhewicz AE, Wenner MM and Stachenfeld
NS: Sex differences in endothelial function important to vascular
health and overall cardiovascular disease risk across the lifespan.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 315:H1569–H1588. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Widlansky ME, Gokce N, Keaney JF Jr and
Vita JA: The clinical implication of endothelial dysfunction. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 42:1149–1160. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rajendran P, Rengarajan T, Thangavel J,
Nishigaki Y, Sakthisekaran D, Sethi G and Nishigaki I: The vascular
endothelium and human diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 9:1057–1069.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sturtzel C: Endothelial cells. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1003:71–91. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hergenreider E, Heydt S, Tréguer K,
Boettger T, Horrevoets AJ, Zeiher AM, Scheffer MP, Frangakis AS,
Yin X, Mayr M, et al: Atheroprotective communication between
endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat Cell
Biol Feb. 14:249–256. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang AL and Vita JA: Effects of systemic
inflammation on endothelium dependent vasodilation. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 16:15–20. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kolluru GK, Bir SC and Kevil CG:
Endothelial dysfunction and diabetes: Effects on angiogenesis,
vascular remodeling, and wound healing. Int J Vasc Med.
2012(918267)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Park KH and Park WJ: Endothelial
dysfunction: Clinical implication in cardiovascular disease and
therapeutic approaches. J Korean Med Sci. 30:1213–1225.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhong L, Simard MJ and Huot J: Endothelial
microRNAs regulating the NF-κB pathway and cell adhesion molecules
during inflammation. FASEB J. 32:4070–4084. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Onishi A, St Ange K, Dordick JS and
Linhardt RJ: Heparin and anticoagulation. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 21:1372–1392. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ong CS, Marcum JA, Zehr KJ and Cameron DE:
A century of heparin. Ann Thorac Surg. 108:955–958. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
McLaughlin K, Nadeem L, Wat J, Baczyk D,
Lye SJ and Kingdom JC: Low molecular weight heparin promotes
transcription and release of placental growth factor from
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
318:H1008–H1017. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen J, Wang H, Gao C, Liu D, Fan Y, Li W,
Chen Y and Pan S: Tetramethylpyrazine alleviates LPS-induced
inflammatory injury in HUVECs by inhibiting Rho/ROCK pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 514:329–335. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Haarmann R, Ibrahim M, Stevanovic M,
Bredemeier R and Schleiff E: The properties of the outer membrane
localized Lipid A transporter LptD. J Phys Condens Matter.
22(454124)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wan X, Wang PX, Zhou L and Xiang Q: Gene
expression of toll-like receptors in the liver, lungs and spleen in
mice after endotoxin challenge. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 16:73–76. 2004.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Luo Y, Du Y, Zhang X and
Fu J: Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting
microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/ TLR4/ NF-κB pathways in BV2
cells. Mol Immunol. 116:29–37. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xiao Q, Zhu X, Yang S, Wang J, Yin R, Song
J, Ma A and Pan X: LPS induces CXCL16 expression in HUVECs through
the miR-146a-mediated TLR4 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
69:143–149. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li Y, Zhu H, Wei X, Li H, Yu Z, Zhang H
and Liu W: LPS induces HUVEC angiogenesis in vitro through
miR-146a-mediated TGF-β1 inhibition. Am J Transl Res. 15:591–600.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cox D, Kerrigan SW and Watson SP:
Platelets and the innate immune system: Mechanisms of
bacterial-induced platelet activation. J Thromb Haemost.
9:1097–1107. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cheng X, Yang YL, Yang H, Wang YH and Du
GH: Kaempferol alleviates LPS-induced neuroinflammation and BBB
dysfunction in mice via inhibiting HMGB1 release and
down-regulating TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:29–35.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gu J, Su S, Guo J, Zhu Y, Zhao M and Duan
JA: Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of the combination
of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae against focal cerebral
ischaemia via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway in MCAO
rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 70:268–277. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li C, Ai G, Wang Y, Lu Q, Luo C, Tan L,
Lin G, Liu Y, Li Y, Zeng H, et al: Oxyberberine, a novel gut
microbiota-mediated metabolite of berberine, possesses superior
anti-colitis effect: Impact on intestinal epithelial barrier, gut
microbiota profile and TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB pathway. Pharmacol Res.
152(104603)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li H, Zhong X, Li W and Wang Q: Effects of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on experimental periodontitis and
AhR/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in a mouse model. J Appl Oral
Sci. 27(e20180713)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim SY, Jin CY, Kim CH, Yoo YH, Choi SH,
Kim GY, Yoon HM, Park HT and Choi YH: Isorhamnetin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in BV2 microglia
by inactivating NF-κB, blocking the TLR4 pathway and reducing ROS
generation. Int J Mol Med. 43:682–692. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim DC, Quang TH, Oh H and Kim YC:
Steppogenin isolated from Cudrania tricuspidata shows
Antineuroinflammatory effects via NF-κB and MAPK pathways in
LPS-Stimulated BV2 and primary rat microglial cells. Molecules.
22(2130)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu X, Lan P, Hou X, Han Q, Lu N, Li T,
Jiao C, Zhang J, Zhang C and Tian Z: HBV inhibits LPS-induced NLRP3
inflammasome activation and IL-1β production via suppressing the
NF-κB pathway and ROS production. J Hepatol. 66:693–702.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kauppinen A, Suuronen T, Ojala J,
Kaarniranta K and Salminen A: Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB
and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic
disorders. Cell Signal. 25:1939–1948. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pober JS and Sessa WC: Evolving functions
of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nature Rev Immunol.
7:803–815. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A,
Perrini S, Laviola L and Giorgino F: Oxidative stress and reactive
oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with
cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. 100:1–19.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bischoff J: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Circ Res. 124:1163–1165. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Deanfield JE, Halcox JP and Rabelink TJ:
Endothelial function and dysfunction: Testing and clinical
relevance. Circulation. 115:1285–1295. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|