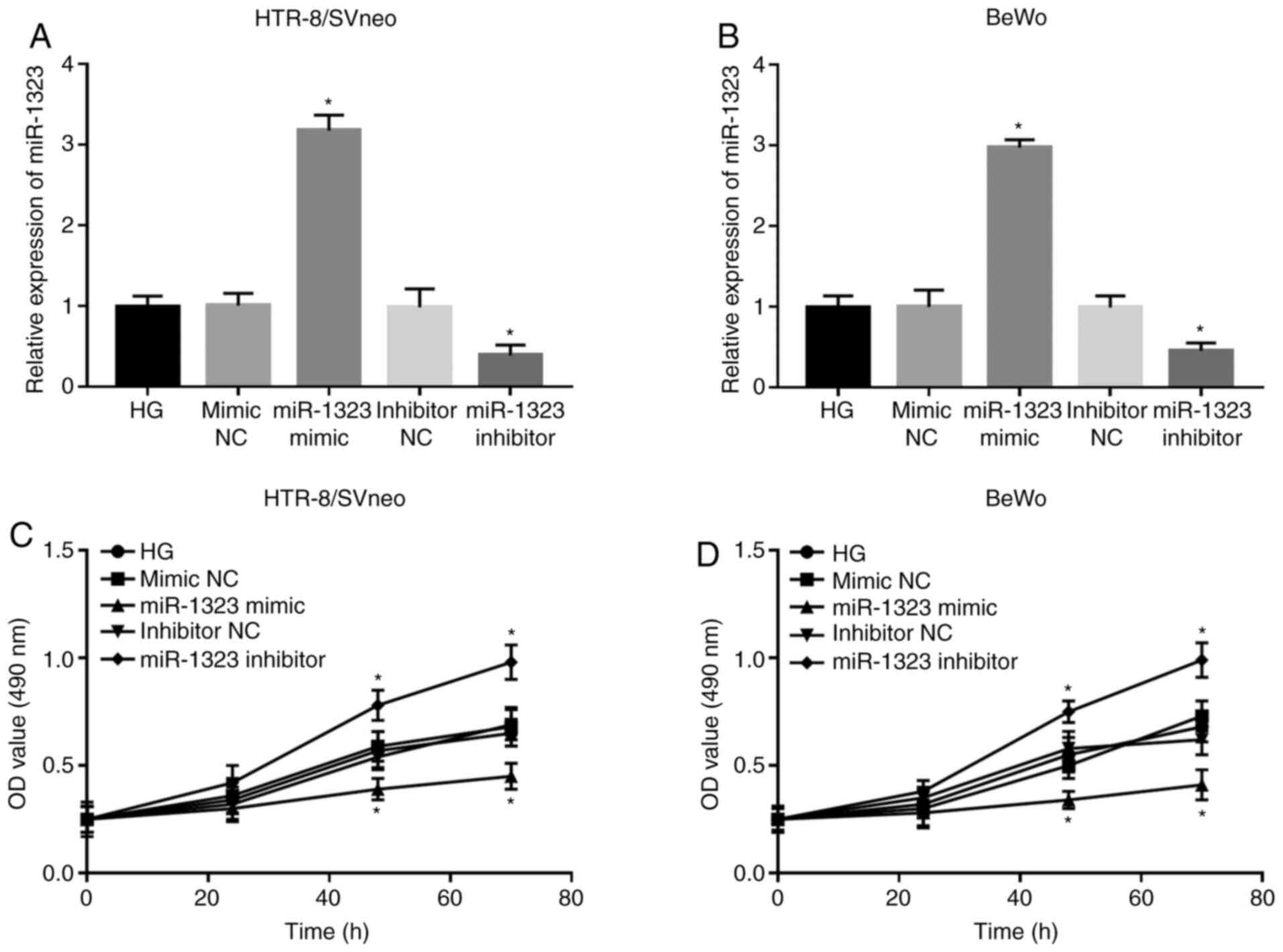
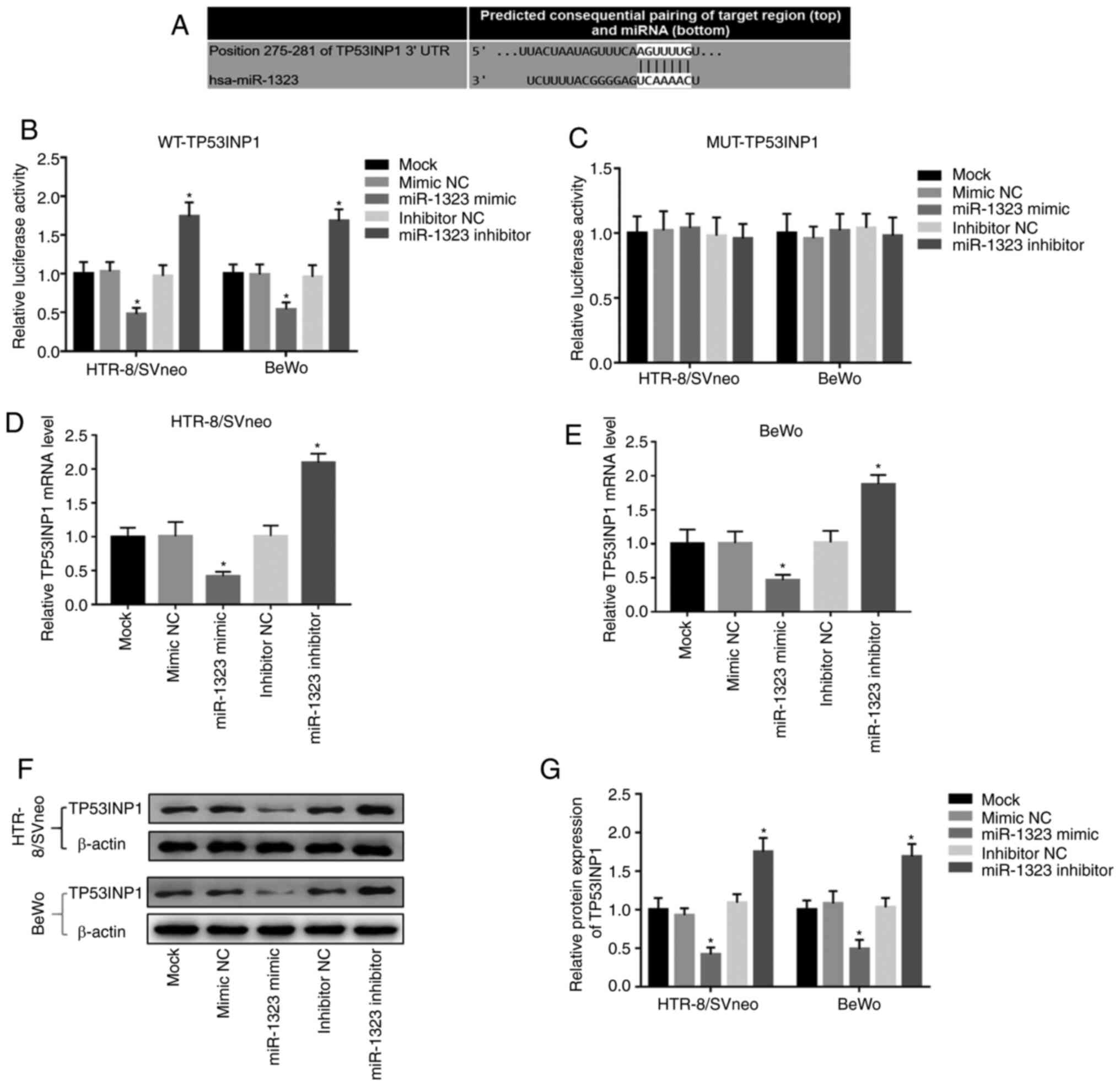
|
1
|
Chiefari E, Arcidiacono B, Foti D and
Brunetti A: Gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated overview. J
Endocrinol Invest. 40:899–909. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lavery JA, Friedman AM, Keyes KM, Wright
JD and Ananth CV: Gestational diabetes in the United States:
Temporal changes in prevalence rates between 1979 and 2010. BJOG.
124:804–813. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Committee on Practice
Bulletins-Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational
diabetes mellitus. Obstet Gynecol. 131:e49–e64. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yung HW, Alnaes-Katjavivi P, Jones CJ,
El-Bacha T, Golic M, Staff AC and Burton GJ: Placental endoplasmic
reticulum stress in gestational diabetes: The potential for
therapeutic intervention with chemical chaperones and antioxidants.
Diabetologia. 59:2240–2250. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Edu A, Teodorescu C, Dobjanschi CG, Socol
ZZ, Teodorescu V, Matei A, Albu DF and Radulian G: Placenta changes
in pregnancy with gestational diabetes. Rom J Morphol Embryol.
57:507–512. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Ji L, Peng Z, Lai R, Zhang X, Xu
Y, Chen Z, Liu R, Zhong Y, Hu H and Wang L: Silencing DAPK3 blocks
the autophagosome-lysosome fusion by mediating SNAP29 in
trophoblast cells under high glucose treatment. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 502(110674)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chang SC and Vivian Yang WC: Hyperglycemia
induces altered expressions of angiogenesis associated molecules in
the trophoblast. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013(457971)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zong S, Li C, Luo C, Zhao X, Liu C, Wang
K, Jia W, Bai M, Yin M, Bao S, et al: Dysregulated expression of
IDO may cause unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion through
suppression of trophoblast cell proliferation and migration. Sci
Rep. 6(19916)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tian FJ, Qin CM, Li XC, Wu F, Liu XR, Xu
WM and Lin Y: Decreased stathmin-1 expression inhibits trophoblast
proliferation and invasion and is associated with recurrent
miscarriage. Am J Pathol. 185:2709–2721. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gao Y, She R, Wang Q, Li Y and Zhang H:
Up-regulation of miR-299 suppressed the invasion and migration of
HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells partly via targeting HDAC2 in
pre-eclampsia. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:1222–1228. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dias S, Pheiffer C, Abrahams Y, Rheeder P
and Adam S: Molecular biomarkers for gestational diabetes mellitus.
Int J Mol Sci. 19(2926)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tryggestad JB, Vishwanath A, Jiang S,
Mallappa A, Teague AM, Takahashi Y, Thompson DM and Chernausek SD:
Influence of gestational diabetes mellitus on human umbilical vein
endothelial cell miRNA. Clin Sci (Lond). 130:1955–1967.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pheiffer C, Dias S, Rheeder P and Adam S:
Decreased expression of circulating miR-20a-5p in South African
women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol Diagn Ther.
22:345–352. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yoffe L, Polsky A, Gilam A, Raff C,
Mecacci F, Ognibene A, Crispi F, Gratacós E, Kanety H, Mazaki-Tovi
S, et al: Early diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus using
circulating microRNAs. Eur J Endocrinol. 181:565–577.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gillet V, Ouellet A, Stepanov Y,
Rodosthenous RS, Croft EK, Brennan K, Abdelouahab N, Baccarelli A
and Takser L: miRNA profiles in extracellular vesicles from serum
early in pregnancies complicated by gestational diabetes mellitus.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 104:5157–5169. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Na Q, Wang D and Song W: Underexpression
of 4 placenta-associated microRNAs in complete hydatidiform moles.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:1075–1080. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Seillier M, Pouyet L, N'Guessan P, Nollet
M, Capo F, Guillaumond F, Peyta L, Dumas JF, Varrault A, Bertrand
G, et al: Defects in mitophagy promote redox-driven metabolic
syndrome in the absence of TP53INP1. EMBO Mol Med. 7:802–818.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang F, Yang C, Xing Z, Liu P, Zhang B,
Ma X, Huang L and Zhuang L: LncRNA GAS5-mediated miR-1323 promotes
tumor progression by targeting TP53INP1 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4013–4023. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabet Care. 35 (Suppl
1):S64–S71. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Tiongco RE, Bituin A, Arceo E, Rivera N
and Singian E: Salivary glucose as a non-invasive biomarker of type
2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Exp Dent. 10:e902–e907. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Gong Y, Zhang DH, You ZH and Li
ZW: DRMDA: Deep representations-based miRNA-disease association
prediction. J Cell Mol Med. 22:472–485. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fang M, Li Y, Wu Y, Ning Z, Wang X and Li
X: miR-185 silencing promotes the progression of atherosclerosis
via targeting stromal interaction molecule 1. Cell Cycle.
18:682–695. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu Y, Bi X, Xiong J, Han W, Xiao T, Xu X,
Yang K, Liu C, Jiang W, He T, et al: MicroRNA-34a promotes renal
fibrosis by downregulation of klotho in tubular epithelial cells.
Mol Ther. 27:1051–1065. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhou X, Xiang C and Zheng X: miR-132
serves as a diagnostic biomarker in gestational diabetes mellitus
and its regulatory effect on trophoblast cell viability. Diagn
Pathol. 14(119)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Qi S and Wang X: Decreased expression of
miR-185 in serum and placenta of patients with gestational diabetes
mellitus. Clin Lab. 65:2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I: The
potential of miRNAs for diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of
breast cancer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 245 (Suppl
1):S34–S39. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang M, Zhao L and Sun M: Diagnostic value
of miR-103 in patients with sepsis and noninfectious SIRS and its
regulatory role in LPS-induced inflammatory response by targeting
TLR4. Int J Genomics. 2020(2198308)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu W, Zhao X, Zhang YJ, Fang GW and Xue
Y: MicroRNA-375 as a potential serum biomarker for the diagnosis,
prognosis, and chemosensitivity prediction of osteosarcoma. J Int
Med Res. 46:975–983. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhao H, Zheng C, Wang Y, Hou K, Yang X,
Cheng Y, Che X, Xie S, Wang S, Zhang T, et al: miR-1323 promotes
cell migration in lung adenocarcinoma by targeting Cbl-b and is an
early prognostic biomarker. Front Oncol. 10(181)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xu Y and Liu M: MicroRNA-1323
downregulation promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer
cells by targeting tumor protein D52. J Biochem. 168:83–91.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Peng HY, Li MQ and Li HP: High glucose
suppresses the viability and proliferation of HTR8/SVneo cells
through regulation of the miR137/PRKAA1/IL6 axis. Int J Mol Med.
42:799–810. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ji L and Li X: Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is
a tumor suppressor in choriocarcinoma by upregulation of
microRNA-211. J Cell Physiol. 234:22911–22920. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Peng HY, Li MQ and Li HP: miR-137
restricts the viability and migration of HTR-8/SVneo cells by
downregulating FNDC5 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr Mol
Med. 19:494–505. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nishimoto M, Nishikawa S, Kondo N,
Wanifuchi-Endo Y, Hato Y, Hisada T, Dong Y, Okuda K, Sugiura H,
Kato H, et al: Prognostic impact of TP53INP1 gene expression in
estrogen receptor α-positive breast cancer patients. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 49:567–575. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Du J, Yang ST, Liu J, Zhang KX and Leng
JY: Silence of LncRNA GAS5 protects cardiomyocytes H9c2 against
hypoxic injury via sponging miR-142-5p. Mol Cells. 42:397–405.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li N, Cui T, Guo W, Wang D and Mao L:
miR-155-5p accelerates the metastasis of cervical cancer cell via
targeting TP53INP1. Onco Targets Ther. 12:3181–3196.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ye W, Liang F, Ying C, Zhang M, Feng D and
Jiang X: Downregulation of microRNA-3934-5p induces apoptosis and
inhibits the proliferation of neuroblastoma cells by targeting
TP53INP1. Exp Ther Med. 18:3729–3736. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dou J, Tu D, Zhao H and Zhang X: LncRNA
PCAT18/miR-301a/TP53INP1 axis is involved in gastric cancer cell
viability, migration, and invasion. J Biochem. 168:547–555.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Abou-Kheir W, Barrak J, Hadadeh O and
Daoud G: HTR-8/SVneo cell line contains a mixed population of
cells. Placenta. 50:1–7. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|