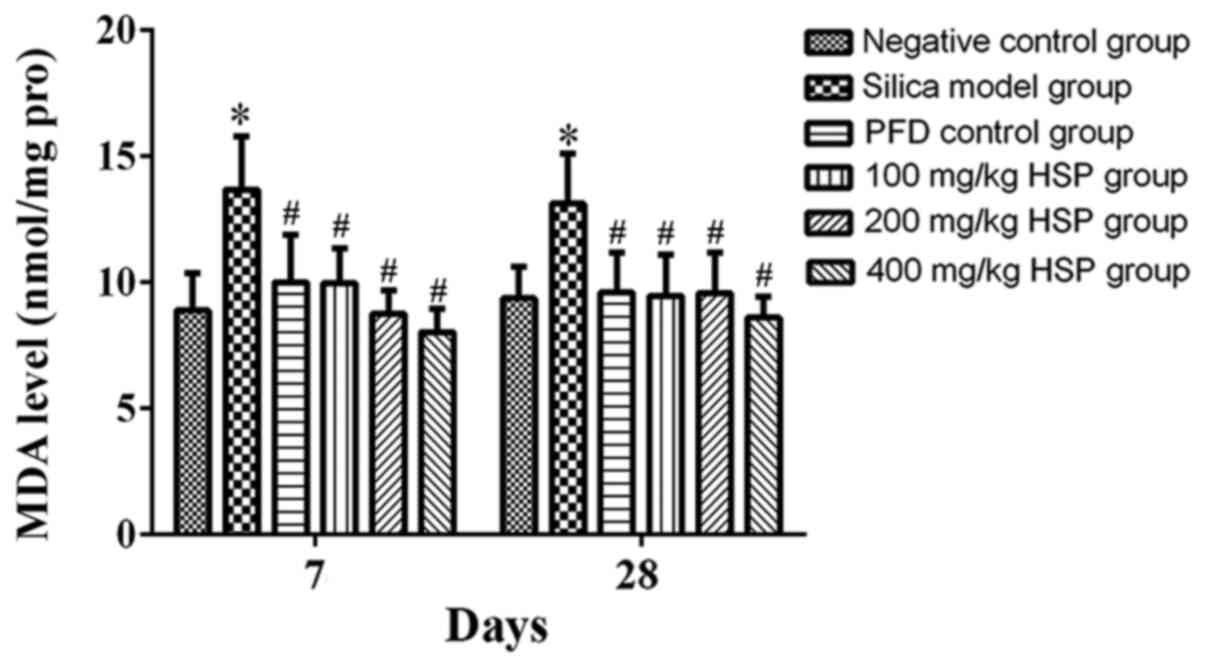
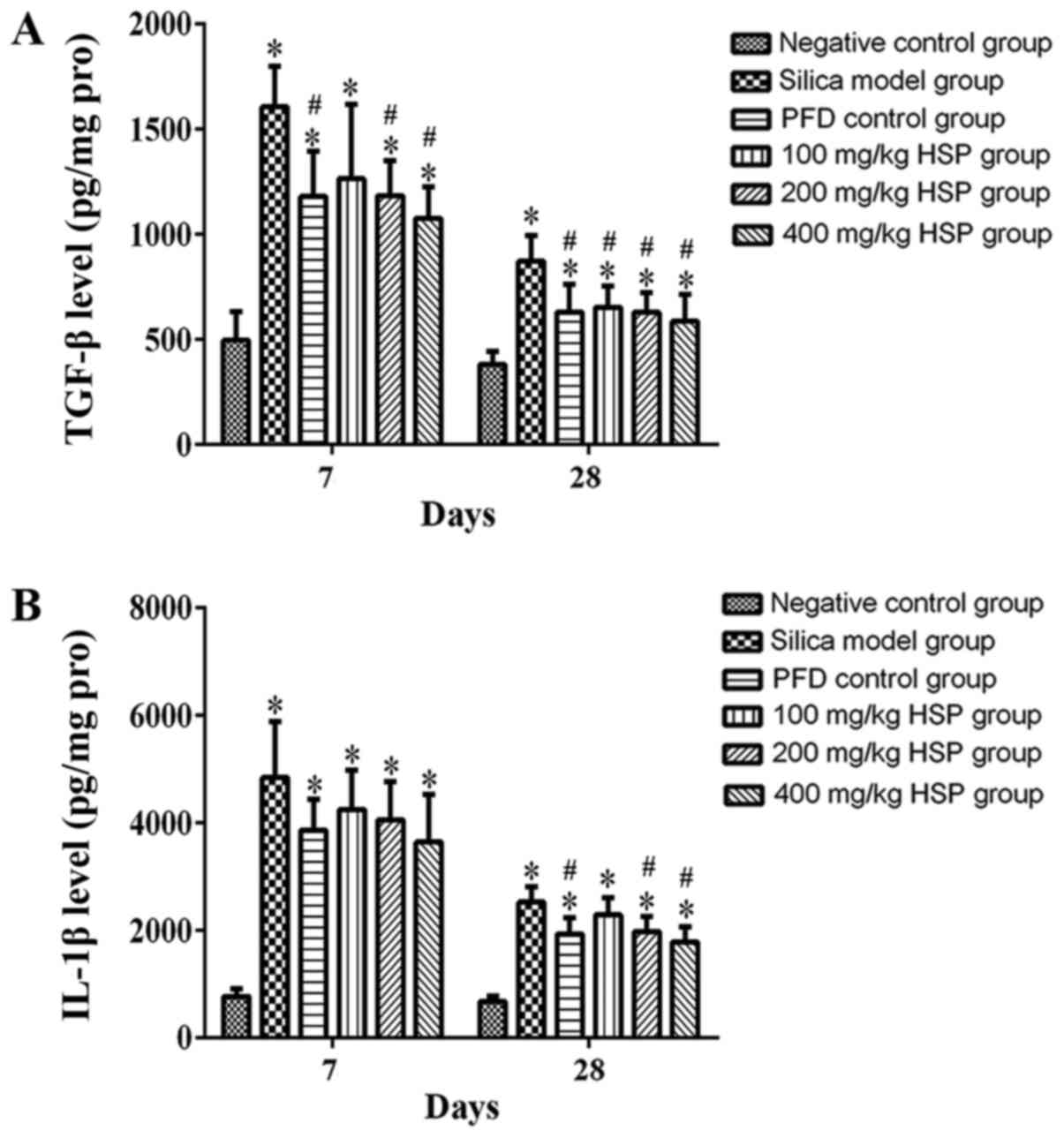
|
1
|
Bissonnette E and Rola-Pleszczynski M:
Pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a murine model of asbestosis
and silicosis. Possible role of tumor necrosis factor.
Inflammation. 13:329–339. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fubini B and Hubbard A: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by
silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1507–1516. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lopes-Pacheco M, Bandeira E and Morales
MM: Cell-based therapy for silicosis. Stem Cells Int.
2016(5091838)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen JJ, Chen L, Liu W and Wang SX:
Effects of Gymnadenia conopse alcohol extract on early protein
profiles in lung tissue of rats exposed to silica. Zhonghua Lao
Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 30:432–435. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Fernandez Alvarez R, Martinez Gonzalez C,
Quero Martinez A, Blanco Perez JJ, Carazo Fernandez L and Prieto
Fernandez A: Guidelines for the diagnosis and monitoring of
silicosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 51:86–93. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rimal B, Greenberg AK and Rom WN: Basic
pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: Current understanding. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 11:169–173. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vallyathan V, Shi XL, Dalal NS, Irr W and
Castranova V: Generation of free radicals from freshly fractured
silica dust. Potential role in acute silica-induced lung injury. Am
Rev Respir Dis. 138:1213–1219. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ghio AJ, Kennedy TP, Whorton AR, Crumbliss
AL, Hatch GE and Hoidal JR: Role of surface complexed iron in
oxidant generation and lung inflammation induced by silicates. Am J
Physiol. 263:L511–L518. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Elmarakby AA and Sullivan JC: Relationship
between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic
nephropathy. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:49–59. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu MW, Liu R, Wu HY, Li YY, Su MX, Dong
MN, Zhang W and Qian CY: Radix puerariae extracts ameliorate
paraquat-induced pulmonary fibrosis by attenuating follistatin-like
1 and nuclear factor erythroid 2p45-related factor-2 signalling
pathways through downregulation of miRNA-21 expression. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 16(11)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Borensztajn K, Crestani B and Kolb M:
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: From epithelial injury to
biomarkers-insights from the bench side. Respiration. 86:441–452.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kusaka T, Nakayama M, Nakamura K, Ishimiya
M, Furusawa E and Ogasawara K: Effect of silica particle size on
macrophage inflammatory responses. PLoS One.
9(e92634)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wintergerst ES, Maggini S and Hornig DH:
Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune
function. Ann Nutr Metab. 51:301–323. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ribeiro D, Freitas M, Silva AMS, Carvalho
F and Fernandes E: Antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of
carotenoids and their oxidation products. Food Chem Toxicol.
120:681–699. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Koleckar V, Kubikova K, Rehakova Z, Kuca
K, Jun D, Jahodar L and Opletal L: Condensed and hydrolysable
tannins as antioxidants influencing the health. Mini Rev Med Chem.
8:436–447. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vitenberga Z and Pilmane M: Inflammatory,
anti-inflammatory and regulatory cytokines in relatively healthy
lung tissue as an essential part of the local immune system. Biomed
Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 161:164–173.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Joubert KD, Awori Hayanga J, Strollo DC,
Lendermon EA, Yousem SA, Luketich JD, Ensor CR and Shigemura N:
Outcomes after lung transplantation for patients with occupational
lung diseases. Clin Transplant. 33(e13460)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Amirshahrokhi K and Bohlooli S: Effect of
methylsulfonylmethane on paraquat-induced acute lung and liver
injury in mice. Inflammation. 36:1111–1121. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sathiyamoorthy G, Sehgal S and Ashton RW:
Pirfenidone and nintedanib for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. South Med J. 110:393–398. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meyer KC and Decker CA: Role of
pirfenidone in the management of pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Clin Risk
Manag. 13:427–437. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini
S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM,
Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, et al: A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in
patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med.
370:2083–2092. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bahri S, Mies F, Ben Ali R, Mlika M,
Jameleddine S, Entee KM and Shlyonsky V: Rosmarinic acid
potentiates carnosic acid induced apoptosis in lung fibroblasts.
PLoS One. 12(e0184368)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Iranshahi M, Rezaee R, Parhiz H,
Roohbakhsh A and Soltani F: Protective effects of flavonoids
against microbes and toxins: The cases of hesperidin and
hesperetin. Life Sci. 137:125–132. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ma H, Feng X and Ding S: Hesperetin
attenuates ventilator-induced acute lung injury through inhibition
of NF-kB-mediated inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 769:333–341.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Roohbakhsh A, Parhiz H, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Molecular mechanisms behind the biological
effects of hesperidin and hesperetin for the prevention of cancer
and cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci. 124:64–74. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bai X, Yang P, Zhou Q, Cai B, Buist-Homan
M, Cheng H, Jiang J, Shen D, Li L, Luo X, et al: The protective
effect of the natural compound hesperetin against fulminant
hepatitis in vivo and in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 174:41–56.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. 8th edition. National Academies Press, Washington, DC,
2011.
|
|
29
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yang YT, Zhang Y, Yu GC, Chen YJ, Bo CX,
Jia Q and Shao H: Lung fibrosis and changes in autophagy-related
proteins in rats exposed to silica dust. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei
Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 36:890–895. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Nardi J, Nascimento S, Goethel G, Gauer B,
Sauer E, Fão N, Cestonaro L, Peruzzi C, Souza J and Garcia SC:
Inflammatory and oxidative stress parameters as potential early
biomarkers for silicosis. Clin Chim Acta. 484:305–313.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Castranova V and Vallyathan V: Silicosis
and coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Environ Health Perspect. 108
(Suppl 4):S675–S684. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lapp NL and Castranova V: How silicosis
and coal workers' pneumoconiosis develop-a cellular assessment.
Occup Med. 8:35–56. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu N, Cao F, Li Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Z and
Guan W: Study of quercetin on pulmonary fibrosis by silica
particles. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 43:814–818. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Wang JY, Yu GC, Jia Q, Li C, Shao LL, Sai
LL and Shao H: Preliminary analysis of differential expression of
miRNA-423-5p and miRNA-26a-5p in lung tissue of early silicotic
rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 37:7–12.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Zhao Y, Xu G, Li H, Chang M, Guan Y, Li Y,
Wu W and Yao S: Overexpression of endogenous lipoic acid synthase
attenuates pulmonary fibrosis induced by crystalline silica in
mice. Toxicol Lett. 323:57–66. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hubbard AK, Thibodeau M and Giardina C:
Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating silica-induced
adhesion molecule expression in mice. J Environ Pathol Toxicol
Oncol. 20 (Suppl 1):S45–S51. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hubbard AK, Timblin CR, Shukla A, Rincon M
and Mossman BT: Activation of NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression
by silica in lungs of luciferase reporter mice. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 282:L968–L975. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Karlmark KR, Weiskirchen R, Zimmermann HW,
Gassler N, Ginhoux F, Weber C, Merad M, Luedde T, Trautwein C and
Tacke F: Hepatic recruitment of the inflammatory Gr1+ monocyte
subset upon liver injury promotes hepatic fibrosis. Hepatology.
50:261–274. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Barrett EG, Johnston C, Oberdorster G and
Finkelstein JN: Antioxidant treatment attenuates cytokine and
chemokine levels in murine macrophages following silica exposure.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 158:211–220. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kehrer JP, Lee YC and Solem SM: Comparison
of in vitro and in vivo rates of collagen synthesis in normal and
damaged lung tissue. Exp Lung Res. 10:187–201. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cheresh P, Kim SJ, Tulasiram S and Kamp
DW: Oxidative stress and pulmonary fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1832:1028–1040. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vallyathan V, Mega JF, Shi X and Dalal NS:
Enhanced generation of free radicals from phagocytes induced by
mineral dusts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 6:404–413.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Srinivasan BP, Nag TC,
Srivastava S, Saxena R and Jha KA: Hesperetin rescues retinal
oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and apoptosis in diabetic rats.
Microvasc Res. 87:65–74. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Anlar HG, Bacanli M, İritaş S, Bal C, Kurt
T, Tutkun E, Yilmaz OH and Basaran N: Effects of occupational
silica exposure on oxidative stress and immune system parameters in
ceramic workers in Turkey. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 80:688–696.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pocernich CB and Butterfield DA: Elevation
of glutathione as a therapeutic strategy in Alzheimer disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:625–630. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Peter C, Braidy N, Zarka M, Welch J and
Bridge W: Therapeutic approaches to modulating glutathione levels
as a pharmacological strategy in Alzheimer's disease. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 12:298–313. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Townsend DM, Tew KD and Tapiero H: The
importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother.
57:145–155. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sacco R, Eggenhoffner R and Giacomelli L:
Glutathione in the treatment of liver diseases: Insights from
clinical practice. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 62:316–324.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nuttall SL, Martin U, Sinclair AJ and
Kendall MJ: Glutathione: In sickness and in health. Lancet.
351:645–646. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Julius M, Lang CA, Gleiberman L, Harburg
E, DiFranceisco W and Schork A: Glutathione and morbidity in a
community-based sample of elderly. J Clin Epidemiol. 47:1021–1026.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Karkale S, Khurana A, Saifi MA, Godugu C
and Talla V: Oropharyngeal administration of silica in Swiss mice:
A robust and reproducible model of occupational pulmonary fibrosis.
Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 51:32–40. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kliment CR and Oury TD: Oxidative stress,
extracellular matrix targets, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Free Radic Biol Med. 49:707–717. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wu FJ, Xue Y, Liu XF, Xue CH, Wang JF, Du
L, Takahashi K and Wang YM: The protective effect of
eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids from sea cucumber
Cucumaria frondosa on oxidative stress in PC12 cells and SAMP8
mice. Neurochem Int. 64:9–17. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen MC, Ye YY, Ji G and Liu JW:
Hesperidin upregulates heme oxygenase-1 to attenuate hydrogen
peroxide-induced cell damage in hepatic L02 cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 58:3330–3335. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kheradmand E, Hajizadeh Moghaddam A and
Zare M: Neuroprotective effect of hesperetin and nano-hesperetin on
recognition memory impairment and the elevated oxygen stress in rat
model of Alzheimer's disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:1096–1101.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rahman I and MacNee W: Oxidative stress
and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation. Eur Respir J.
16:534–554. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YMW and
Anathy V: Oxidative stress in chronic lung disease: From
mitochondrial dysfunction to dysregulated redox signaling. Mol
Aspects Med. 63:59–69. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dong X, Li X, Li M, Chen M, Fan Q and Wei
W: Antiinflammation and antioxidant effects of thalidomide on
pulmonary fibrosis in mice and human lung fibroblasts.
Inflammation. 40:1836–1846. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kawasaki H: A mechanistic review of
silica-induced inhalation toxicity. Inhal Toxicol. 27:363–377.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Bonner JC: Regulation of PDGF and its
receptors in fibrotic diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
15:255–273. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Phan SH: Genesis of the myofibroblast in
lung injury and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 9:148–152.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Saito A and Nagase T: Hippo and TGF-β
interplay in the lung field. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
309:L756–L767. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhu L, Fu X, Chen X, Han X and Dong P: M2
macrophages induce EMT through the TGF-β/Smad2 signaling pathway.
Cell Biol Int. 41:960–968. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Peteranderl C, Sznajder JI, Herold S and
Lecuona E: Inflammatory responses regulating alveolar ion transport
during pulmonary infections. Front Immunol. 8(446)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Polat FR, Karaboga I, Polat MS, Erboga Z,
Yilmaz A and Guzel S: Effect of hesperetin on inflammatory and
oxidative status in trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced
experimental colitis model. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
64:58–65. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Parhiz H, Roohbakhsh A, Soltani F, Rezaee
R and Iranshahi M: Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of
the citrus flavonoids hesperidin and hesperetin: An updated review
of their molecular mechanisms and experimental models. Phytother
Res. 29:323–331. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Huang AL, Zhang YL, Ding HW, Li B, Huang
C, Meng XM and Li J: Design, synthesis and investigation of
potential anti-inflammatory activity of O-alkyl and O-benzyl
hesperetin derivatives. Int Immunopharmacol. 61:82–91.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Maruoka S
and Horie T: IL-4 and IL-13 induce myofibroblastic phenotype of
human lung fibroblasts through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-dependent
pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 107:1001–1008. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Postlethwaite AE, Holness MA, Katai H and
Raghow R: Human fibroblasts synthesize elevated levels of
extracellular matrix proteins in response to interleukin 4. J Clin
Invest. 90:1479–1485. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Doucet C, Brouty-Boye D, Pottin-Clemenceau
C, Jasmin C, Canonica GW and Azzarone B: IL-4 and IL-13
specifically increase adhesion molecule and inflammatory cytokine
expression in human lung fibroblasts. Int Immunol. 10:1421–1433.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Doucet C, Brouty-Boye D, Pottin-Clemenceau
C, Canonica GW, Jasmin C and Azzarone B: Interleukin (IL) 4 and
IL-13 act on human lung fibroblasts. Implication in asthma. J Clin
Invest. 101:2129–2139. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Antoniou KM, Ferdoutsis E and Bouros D:
Interferons and their application in the diseases of the lung.
Chest. 123:209–216. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Tzortzaki EG, Antoniou KM, Zervou MI,
Lambiri I, Koutsopoulos A, Tzanakis N, Plataki M, Maltezakis G,
Bouros D and Siafakas NM: Effects of antifibrotic agents on
TGF-beta1, CTGF and IFN-gamma expression in patients with
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med. 101:1821–1829.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Ip WKE, Hoshi N, Shouval DS, Snapper S and
Medzhitov R: Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-10 mediated by
metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Science. 356:513–519.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Cyktor JC, Carruthers B, Kominsky RA,
Beamer GL, Stromberg P and Turner J: IL-10 inhibits mature fibrotic
granuloma formation during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J
Immunol. 190:2778–2790. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Palomares O, Martin-Fontecha M, Lauener R,
Traidl-Hoffmann C, Cavkaytar O, Akdis M and Akdis CA: Regulatory T
cells and immune regulation of allergic diseases: Roles of IL-10
and TGF-β. Genes Immun. 15:511–520. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Mlika M, Adigun R and Bhutta BS:
Silicosis. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island,
FL, 2020.
|
|
79
|
Xiao H, Zhang GF, Liao XP, Li XJ, Zhang J,
Lin H, Chen Z and Zhang X: Anti-fibrotic effects of pirfenidone by
interference with the hedgehog signalling pathway in patients with
systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Int J
Rheum Dis. 21:477–486. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Zou WJ, Huang Z, Jiang TP, Shen YP, Zhao
AS, Zhou S and Zhang S: Pirfenidone inhibits proliferation and
promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Med Sci Monit. 23:6107–6113.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Seifirad S, Keshavarz A, Taslimi S, Aran
S, Abbasi H and Ghaffari A: Effect of pirfenidone on pulmonary
fibrosis due to paraquat poisoning in rats. Clin Toxicol (Phila).
50:754–758. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Chahar MK, Sharma N, Dobhal MP and Joshi
YC: Flavonoids: A versatile source of anticancer drugs. Pharmacogn
Rev. 5:1–12. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Wang J, Zhu H, Yang Z and Liu Z:
Antioxidative effects of hesperetin against lead acetate-induced
oxidative stress in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 45:395–398.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Zhang J, Song J, Wu D, Wang J and Dong W:
Hesperetin induces the apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
via mitochondrial pathway mediated by the increased intracellular
reactive oxygen species, ATP and calcium. Med Oncol.
32(101)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Aswar M, Kute P, Mahajan S, Mahajan U,
Nerurkar G and Aswar U: Protective effect of hesperetin in rat
model of partial sciatic nerve ligation induced painful neuropathic
pain: An evidence of anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activity.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 124:101–107. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|