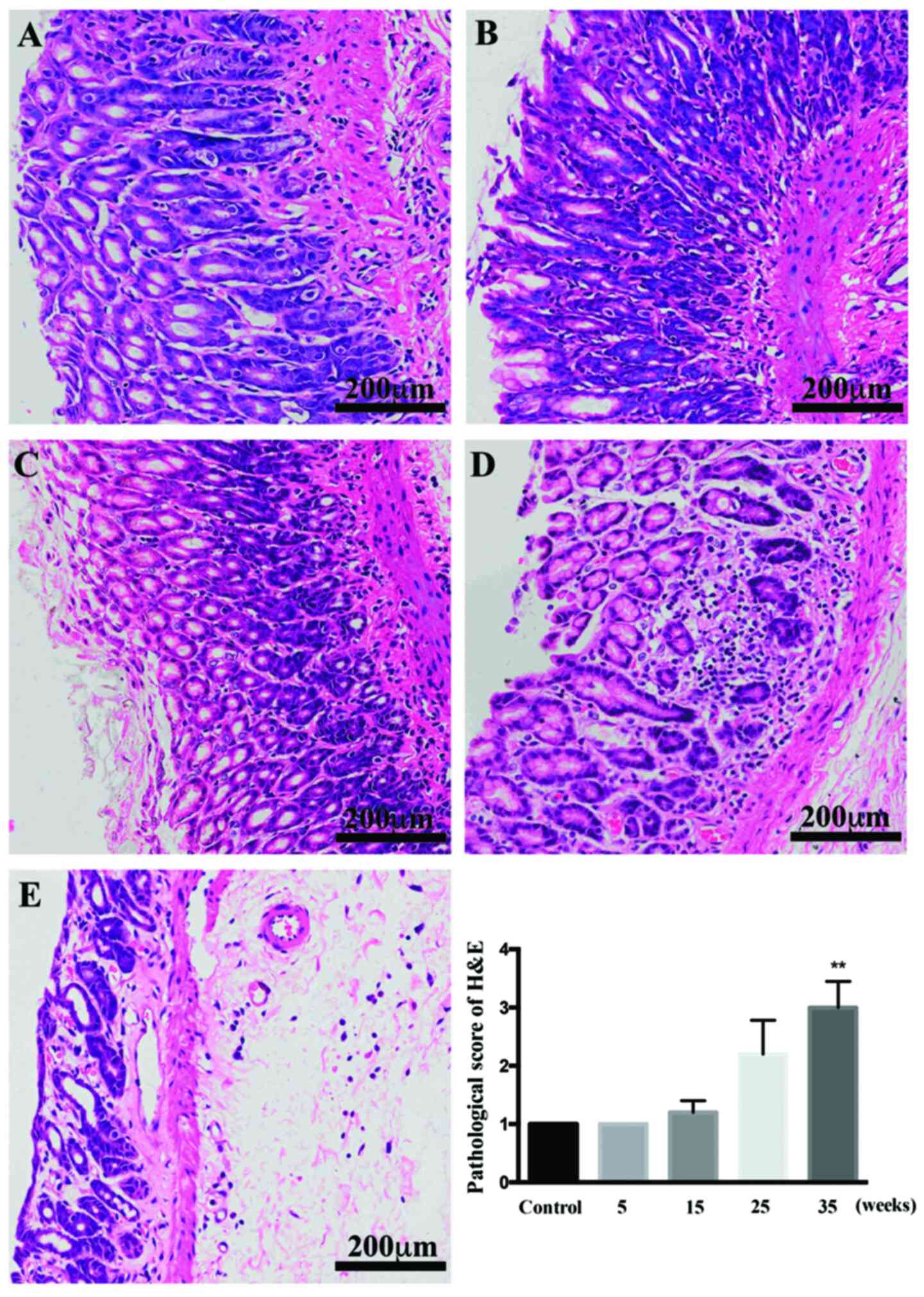
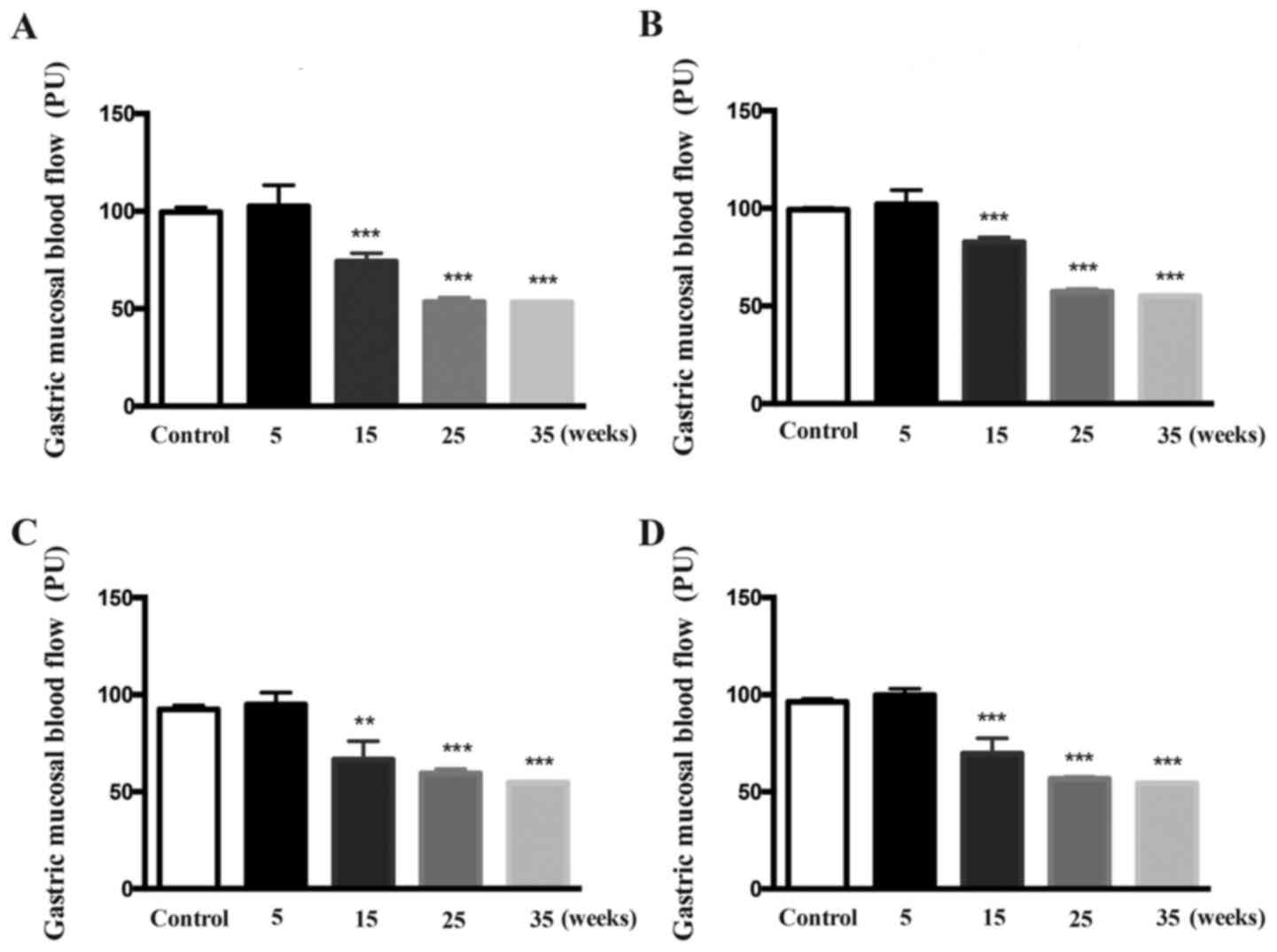
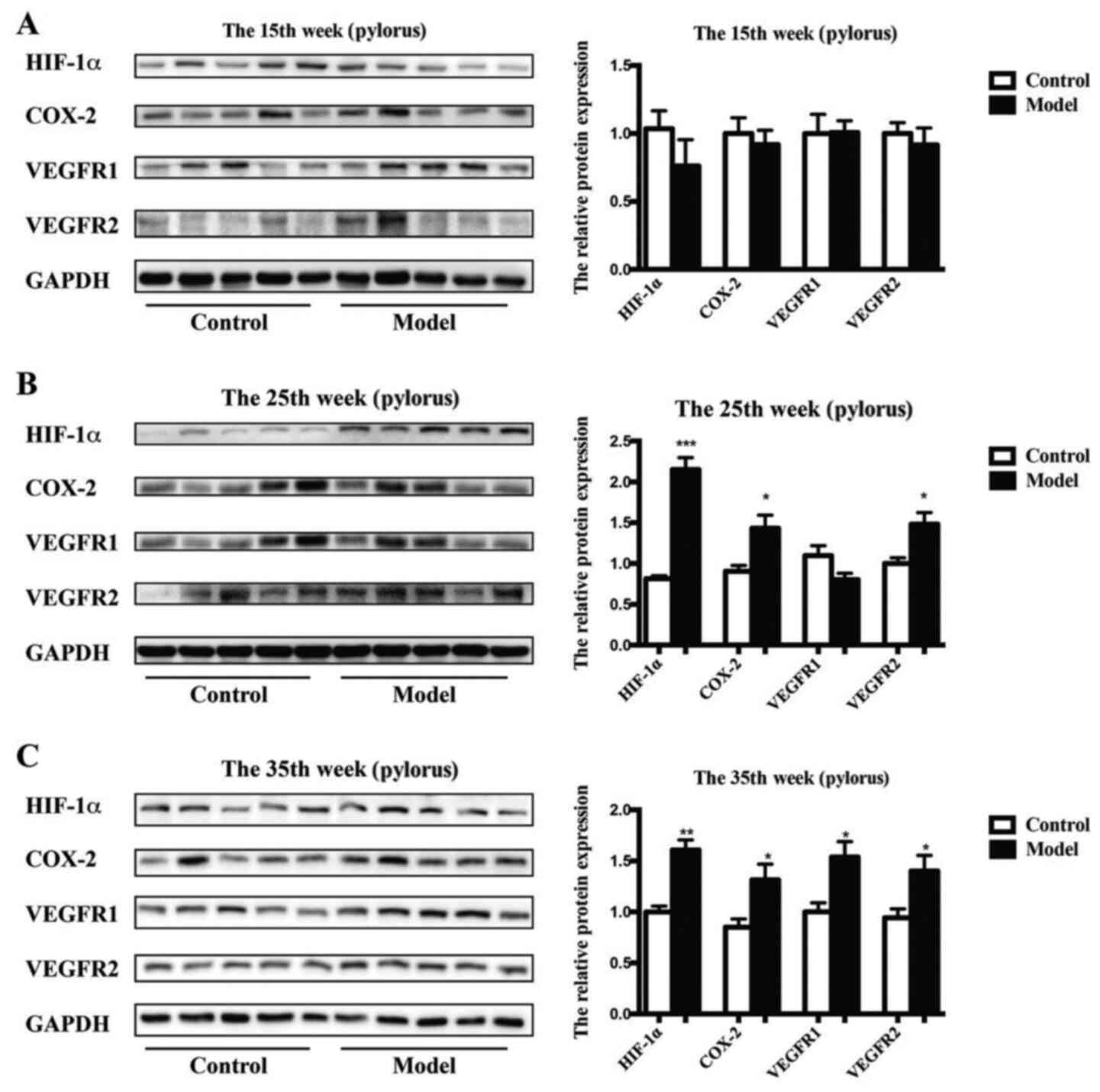
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Forman D and Burley VJ: Gastric cancer:
Global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk
factors. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 20:633–649.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cavatorta O, Scida S, Miraglia C, Barchi
A, Nouvenne A, Leandro G, Meschi T, De' Angelis GL and Di Mario F:
Epidemiology of gastric cancer and risk factors. Acta Biomed.
89:82–87. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Adamu MA, Weck MN, Gao L and Brenner H:
Incidence of chronic atrophic gastritis: Systematic review and
meta-analysis of follow-up studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 25:439–448.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Park YH and Kim N: Review of atrophic
gastritis and intestinal metaplasia as a premalignant lesion of
gastric cancer. J Cancer Prev. 20:25–40. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhao J, Zhao J, Du F, Zhang Y, Shen G, Zhu
H, Ji F, Ma F, Dong L, Kan J, et al: Cardia and non-cardia gastric
cancer have similar stage-for-stage prognoses after R0 resection: A
large-scale, multicenter study in China. J Gastrointest Surg.
20:700–707. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Devesa SS, Blot WJ and Fraumeni JF Jr:
Changing patterns in the incidence of esophageal and gastric
carcinoma in the United States. Cancer. 83:2049–2053.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Powell J and McConkey CC: Increasing
incidence of adenocarcinoma of the gastric cardia and adjacent
sites. Br J Cancer. 62:440–443. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cavaleiro-Pinto M, Peleteiro B, Lunet N
and Barros H: Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric
cardia cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes
Control. Netherlands. 22:375–387. 2011.
|
|
10
|
Yoon H and Kim N: Diagnosis and management
of high risk group for gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 9:5–17.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hipgrave DB, Chang S, Li X and Wu Y: Salt
and sodium intake in China. JAMA. 315:703–705. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bergin IL, Sheppard BJ and Fox JG:
Helicobacter pylori infection and high dietary salt
independently induce atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia
in commercially available outbred Mongolian gerbils. Dig Dis Sci.
48:475–485. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
D'Elia L, Rossi G, Ippolito R, Cappuccio
FP and Strazzullo P: Habitual salt intake and risk of gastric
cancer: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Clin Nutr.
31:489–498. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Song JH, Kim YS, Heo NJ, Lim JH, Yang SY,
Chung GE and Kim JS: High salt intake is associated with atrophic
gastritis with intestinal metaplasia. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 26:1133–1138. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Montani A, Sasazuki S, Inoue M, Higuchi K,
Arakawa T and Tsugane S: Food/nutrient intake and risk of atrophic
gastritis among the Helicobacter pylori-infected population
of northeastern Japan. Cancer Sci. 94:372–377. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wiseman M: The second World Cancer
Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research expert report
Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: A
global perspective. Proc Nutr Soc. 67:253–256. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim J, Park S and Nam BH: Gastric cancer
and salt preference: A population-based cohort study in Korea. Am J
Clin Nutr. 91:1289–1293. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ling L, Tao H, Lu L, Qianqian S and Mingyu
S: Summary and review of animal models for chronic atrophic
gastritis and precancerous lesions of gastric cancer. Chinese J Exp
Trand Med Formulae. 24:1–8. 2018.
|
|
19
|
Fuhua L, Xiaoguang Q, Junhua L and Mei L:
Research progress on animal models of chronic atrophic gastritis.
Chinese Med Moedern distance Educ China. 16:18–19. 2018.
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Xia R, Zhang B and Li C: Chronic
atrophic gastritis: A review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.
37:241–259. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sipponen P and Maaroos HI: Chronic
gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 50:657–667. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee JY, Kim N, Nam RH, Choi YJ, Seo JH,
Lee HS, Oh JC and Lee DH: No correlation of inflammation with
colonization of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach of mice
fed high-salt diet. J Cancer Prev. 19:144–151. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Toyoda T, Tsukamoto T, Yamamoto M, Ban H,
Saito N, Takasu S, Shi L, Saito A, Ito S, Yamamura Y, et al: Gene
expression analysis of a Helicobacter pylori-infected and
high-salt diet-treated mouse gastric tumor model: Identification of
CD177 as a novel prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer.
BMC Gastroenterol. 13(122)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Amara S, Alotaibi D and Tiriveedhi V:
NFAT5/STAT3 interaction mediates synergism of high salt with IL-17
towards induction of VEGF-A expression in breast cancer cells.
Oncol Lett. 12:933–943. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Amara S and Tiriveedhi V: Inflammatory
role of high salt level in tumor microenvironment (Review). Int J
Oncol. 50:1477–1481. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Li J, Zhu L and Cui W: Effect of
three methods for activating blood circulation on early stage
apoptosis in rats with chronic atrophic gastric complicated
precancerous lesion. Chinese J Integr Tradit West Med. 28:448–450.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shimizu N, Inada KI, Tsukamoto T,
Nakanishi H, Ikehara Y, Yoshikawa A, Kaminishi M, Kuramoto S and
Tatematsu M: New animal model of glandular stomach carcinogenesis
in Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori and
treated with a chemical carcinogen. J Gastroenterol. 34:61–66.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Honda S, Fujioka T, Tokieda M, Satoh R,
Nishizono A and Nasu M: Development of Helicobacter
pylori-induced gastric carcinoma in mongolian gerbils. Cancer
Res. 58:4255–4259. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi XY, Zhao FZ, Dai X, Ma LS, Dong XY and
Fang J: Effect of jianpiyiwei capsule on gastric precancerous
lesions in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 8:608–612. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Dong Xi, Lei D, Jun G, Ningli C, Huibin Q
and Jinyan L: Experimental study on the relationship between cell
proliferation and apoptosis and the expression of the related gene
in rats with duodenogastric reflux. J Xi'an Jiaotong Univ Sci.
25:261–265. 2004.
|
|
32
|
Wei Y, Yang J, Yang H and Song Y:
Experimental effect of Yiqi Huayu Jiedu principle on chronic
atrophic gastritis with dysplasia rats. Chinese J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 20:916–919. 2011.
|
|
33
|
Si J, Zhou W, Wu J, Cao Q, Xiang Z, Jiang
L, Lü W and Huang H: Establishment of an animal model of chronic
atrophic gastritis and a study on the factors inducing atrophy.
Chin Med J (Engl). 114:1323–1325. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gu J, Hu X, Shao W, Ji T, Yang W, Zhuo H,
Jin Z, Huang H, Chen J, Huang C and Lin D: Metabolomic analysis
reveals altered metabolic pathways in a rat model of gastric
carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 7:60053–60073. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tsukamoto H, Mizoshita T, Katano T,
Hayashi N, Ozeki K, Ebi M, Shimura T, Mori Y, Tanida S, Kataoka H,
et al: Preventive effect of rebamipide on
N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced gastric carcinogenesis
in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 67:271–277. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu J, Shen W, Pei B, Wang X, Sun D, Li Y,
Xiu L, Liu X, Lu Y, Zhang X and Yue X: Xiao Tan He Wei Decoction
reverses MNNG-induced precancerous lesions of gastric carcinoma in
vivo and vitro: Regulation of apoptosis through NF-κB pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 108:95–102. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ren J, Yang Y, Qu X, Ying L, Yang M and
Yan N: Evaluation of a compound modling method with
N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine for establishing chronic
atrophic gastritis model rats. J Tradit Chinese Med. 58:1961–1964.
2017.
|
|
38
|
Tsukamoto T, Mizoshita T and Tatematsu AM:
Animal models of stomach carcinogenesis. Toxicol Pathol.
35:636–648. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang XQ, Terry PD and Yan H: Review of
salt consumption and stomach cancer risk: Epidemiological and
biological evidence. World J Gastroenterol. 15:2204–2213.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kato S, Matsukura N, Matsuda N, Yamashita
N, Naito Z and Tajiri T: How to evaluate mRNA gene expressions of
cancer related cytokines for the infectious diseases including
stomach and liver carcinogenesis and prevention. Cancer Res.
66(871)2006.
|
|
41
|
Leung WK, Wu K, Wong CYP, Cheng AS, Ching
AK, Chan AW, Chong WW, Go MY, Yu J, To KF, et al: Transgenic
cyclooxygenase-2 expression and high salt enhanced susceptibility
to chemical-induced gastric cancer development in mice.
Carcinogenesis. 29:1648–1654. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Takahashi M and Hasegawa R: Enhancing
effects of dietary salt on both initiation and promotion stages of
rat gastric carcinogenesis. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 16:169–182.
1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen Z, Li K, Bi J and Wang B: Sodium
intake, salt taste and gastric cancer risk according to
Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking, histological type
and tumor site in China. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 13:2481–2484.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
You W, Blot WJ, Chang YS, Ershow AG, Yang
Z, An Q, Henderson B, Xu GW, Fraumeni JF Jr and Wang TG: Diet and
high risk of stomach cancer in shandong, China. Cancer Res.
48:3518–3523. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu S, E Z and Liu S: Examination of the
gastric mucosal vessels in chronic gastritis by color Doppler flow
imaging. Chinese J Ultrasound Med. 17:45–46. 2001.
|
|
46
|
Pousa ID and Gisbert JP: Gastric
angiogenesis and Helicobacter pylori infection. Rev Esp
Enferm Dig. 98:527–541. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
47
|
Mirzoeva S, Kim ND, Chiu K, Franzen CA,
Bergan RC and Pelling JC: Inhibition of HIF-1 alpha and VEGF
expression by the chemopreventive bioflavonoid apigenin is
accompanied by Akt inhibition in human prostate carcinoma PC3-M
cells. Mol Carcinog. 47:686–700. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Huang SP, Wu MS, Shun CT, Wang HP, Hsieh
CY, Kuo ML and Lin JT: Cyclooxygenase-2 increases hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor to promote
angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. J Biomed Sci. 12:229–241.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Stoeltzing O, Liu W, Reinmuth N, Fan F,
Parikh AA, Bucana CD, Evans DB, Semenza GL and Ellis LM: Regulation
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and angiogenesis by an insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor autocrine loop in human pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol.
163:1001–1011. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Liu LZ, Jing Y, Jiang LL, Jiang XE, Jiang
Y, Rojanasakul Y and Jiang BH: Acacetin inhibits VEGF expression,
tumor angiogenesis and growth through AKT/HIF-1α pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 413:299–305. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Park SA, Jeong MS, Ha KT and Jang SB:
Structure and function of vascular endothelial growth factor and
its receptor system. BMB Rep. 51:73–78. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liu D, He Q and Liu C: Correlations among
Helicobacter pylori infection and the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric
mucosa with intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 25:795–799. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hu H, Zheng H and Lu X: Effects of
‘Weiqiyin Drink’ in reversing chronic atrophic gastritis
complicated with precancerous morbid cells. Chinese J Integr Tradit
West Med Gastro-spleen. 9:32–34. 2001.
|
|
54
|
Naomoto Y, Gunduz M, Takaoka M, Okawa T,
Gunduz E, Nobuhisa T, Kobayashi M, Shirakawa Y, Yamatsuji T, Sonoda
R, et al: Heparanase promotes angiogenesis through Cox-2 and
HIF1alpha. Med Hypotheses. 68:162–165. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Tarnawski AS, Ahluwalia A and Jones MK:
Angiogenesis in gastric mucosa: An important component of gastric
erosion and ulcer healing and its impairment in aging. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29 (Suppl 4):S112–S123. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Isobe T, Aoyagi K, Koufuji K, Shirouzu K,
Kawahara A, Taira T and Kage M: Clinicopathological significance of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1α) expression in gastric
cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 18:293–304. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kopparapu PK, Boorjian SA, Robinson BD,
Downes M, Gudas LJ, Mongan NP and Persson JL: Expression of VEGF
and its receptors VEGFR1/VEGFR2 is associated with invasiveness of
bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:2381–2390. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|