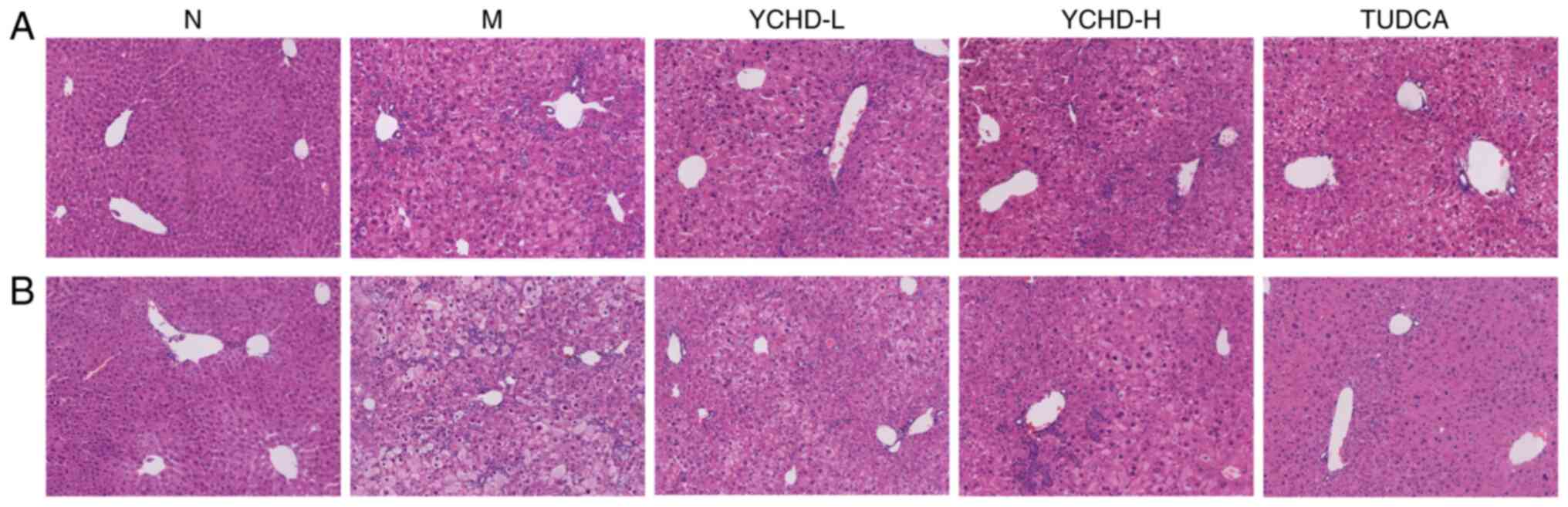
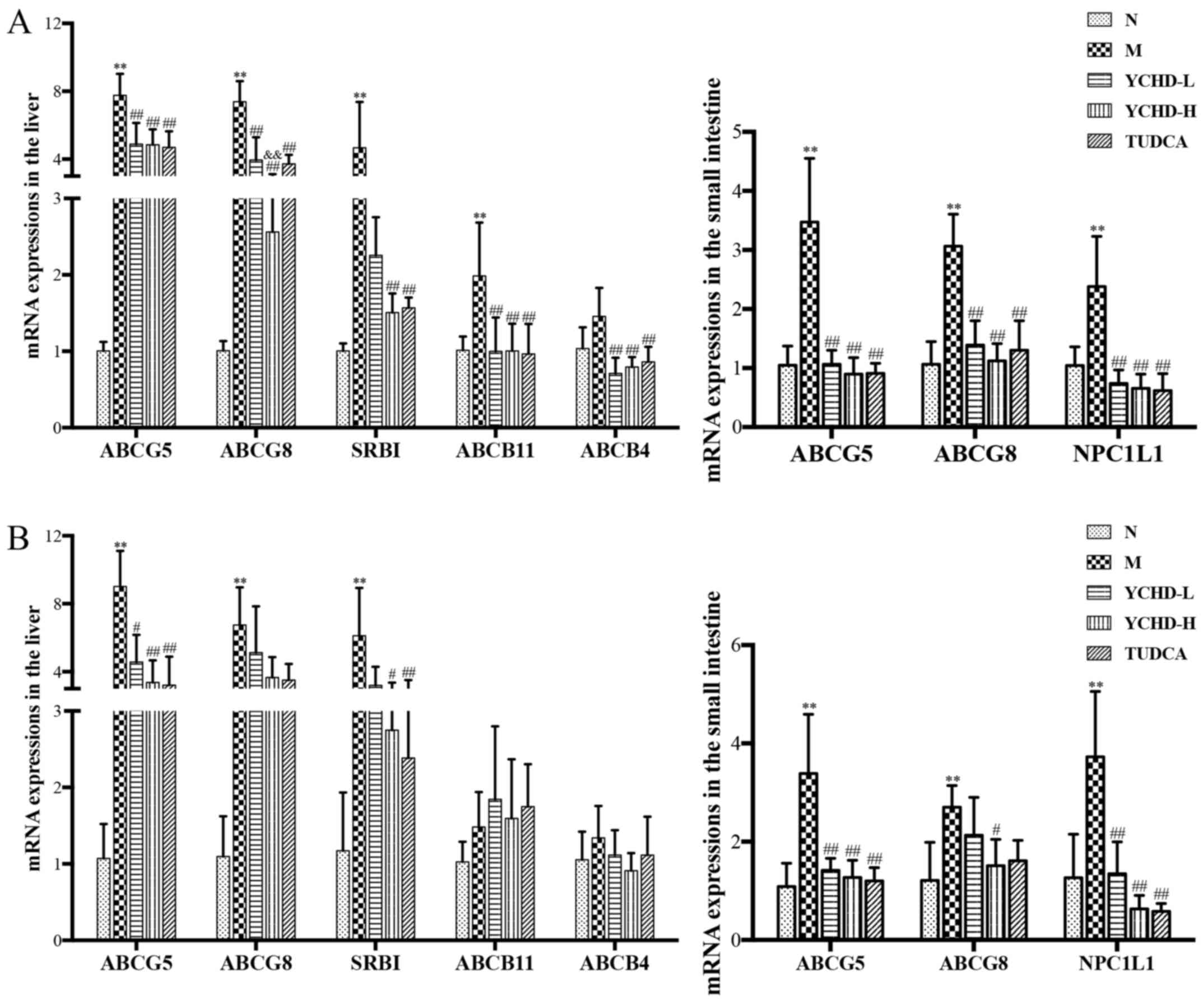
|
1
|
Stinton LM and Shaffer EA: Epidemiology of
gallbladder disease: Cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver.
6:172–187. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhu L, Aili A, Zhang C, Saiding A and
Abudureyimu K: Prevalence of and risk factors for gallstones in
Uighur and Han Chinese. World J Gastroenterol. 20:14942–14949.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Littlefield A and Lenahan C:
Cholelithiasis: Presentation and management. J Midwifery Womens
Health. 64:289–297. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Reshetnyak VI: Concept of the pathogenesis
and treatment of cholelithiasis. World J Hepatol. 4:18–34.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cremer A and Arvanitakis M: Diagnosis and
management of bile stone disease and its complications. Minerva
Gastroenterol Dietol. 62:103–129. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Venneman NG and van Erpecum KJ:
Pathogenesis of gallstones. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
39:171–183, vii. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dikkers A, Freak de Boer J, Annema W,
Groen AK and Tietge UJ: Scavenger receptor BI and ABCG5/G8
differentially impact biliary sterol secretion and reverse
cholesterol transport in mice. Hepatology. 58:293–303.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Van Erpecum KJ: Pathogenesis of
cholesterol and pigment gallstones: An update. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 35:281–287. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hoekstra M and Sorci-Thomas M:
Rediscovering scavenger receptor type BI: Surprising new roles for
the HDL receptor. Curr Opin Lipidol. 28:255–260. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chan J and Vandeberg JL: Hepatobiliary
transport in health and disease. Clin Lipidol. 7:189–202.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Patel SB, Graf GA and Temel RE: ABCG5 and
ABCG8: More than a defense against xenosterols. J Lipid Res.
59:1103–1113. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Krawczyk M, Lütjohann D, Schirin-Sokhan R,
Villarroel L, Nervi F, Pimentel F, Lammert F and Miquel JF:
Phytosterol and cholesterol precursor levels indicate increased
cholesterol excretion and biosynthesis in gallstone disease.
Hepatology. 55:1507–1517. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Reboul E, Soayfane Z, Goncalves A,
Cantiello M, Bott R, Nauze M, Tercé F, Collet X and Coméra C:
Respective contributions of intestinal Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 and
scavenger receptor class B type I to cholesterol and tocopherol
uptake: In vivo v. in vitro studies. Br J Nutr. 107:1296–1304.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Vinarova L, Vinarov Z, Tcholakova S,
Denkov ND, Stoyanov S and Lips A: The mechanism of lowering
cholesterol absorption by calcium studied by using an in vitro
digestion model. Food Funct. 7:151–163. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Portincasa P, Ciaula AD, Bonfrate L and
Wang DQ: Therapy of gallstone disease: What it was, what it is,
what it will be. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 3:7–20.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address: simpleeasloffice@easloffice.eu.
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis and
treatment of gallstones. J Hepatol. 65:146–181. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen Q, Zhang Y, Li S, Chen S, Lin X, Li C
and Asakawa T: Mechanisms underlying the prevention and treatment
of cholelithiasis using traditional chinese medicine. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2019(2536452)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang A, Sun H, Yuan Y, Sun W, Jiao G and
Wang X: An in vivo analysis of the therapeutic and synergistic
properties of Chinese medicinal formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang based on
its active constituents. Fitoterapia. 82:1160–1168. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang J, Cheung F, Tan HY, Hong M, Wang N,
Yang J, Feng Y and Zheng Q: Identification of the active compounds
and significant pathways of yinchenhao decoction based on network
pharmacology. Mol Med Rep. 16:4583–4592. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Zhang A, Wang P, Sun H, Wu G, Sun
W, Lv H, Jiao G, Xu H, Yuan Y, et al: Metabolomics coupled with
proteomics advancing drug discovery toward more agile development
of targeted combination therapies. Mol Cell Proteomics.
12:1226–1238. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen Z, Ma X, Zhao Y, Wang J, Zhang Y, Li
J, Wang R, Zhu Y, Wang L and Xiao X: Yinchenhao decoction in the
treatment of cholestasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 168:208–216. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li JY, Cao HY, Sun L, Sun RF, Wu C, Bian
YQ, Dong S, Liu P and Sun MY: Therapeutic mechanism of Yin-Chen-Hao
decoction in hepatic diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 23:1125–1138.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Asakawa T, Yagi M, Tanaka Y, Asagiri K,
Kobayashi H, Egami H, Tanikawa K and Kage M: The herbal medicine
Inchinko-to reduces hepatic fibrosis in cholestatic rats. Pediatr
Surg Int. 28:379–384. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang B, Sun MY, Long AH, Cao HY, Ren S,
Bian YQ, Lu X, Gu HT, Liu CH and Liu P: Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang
alleviates biliary obstructive cirrhosis in rats by inhibiting
biliary epithelial cell proliferation and activation. Pharmacogn
Mag. 11:417–425. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Man-ting L, Ying F and Shao-Dong C: Effect
and mechanism of Yinchenhao Decoction in preventing lipid metabolic
disturbance for rats fed on high fat diet. China J Tradit Chin Med
Pharm. 26:2428–2430. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Lv J, Jin S, Yuan H, Han J, Fu S, Jin S,
Guo JJ and Xiao X: Rational daily administration times of
yinchenhao decoction in rats with jaundice based on PD/PK. Chin
Herb Med. 4:150–156. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Yi YX, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Ma NH, Shi F, Kang
P, Cai ZZ and Zhang T: Yinchenhao decoction ameliorates
alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate induced intrahepatic cholestasis in
rats by regulating phase II metabolic enzymes and transporters.
Front Pharmacol. 9(510)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Sun H, Zhang A, Jiao G, Sun W and
Yuan Y: Pharmacokinetics screening for multi-components absorbed in
the rat plasma after oral administration traditional Chinese
medicine formula Yin-Chen-Hao-Tang by ultra performance liquid
chromatography-electrospray ionization/quadrupole-time-of-flight
mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition methods.
Analyst. 136:5068–5076. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yan J, Xie G, Liang C, Hu Y, Zhao A, Huang
F, Hu P, Liu P, Jia W and Wang X: Herbal medicine Yinchenhaotang
protects against α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis in
rats. Sci Rep. 7(4211)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cheng L, Huang C and Chen Z:
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced
depression like behavior in mice via the inhibition of
neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress. Pharmacology.
103:93–100. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
National Research Council: Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals:
Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal
Care. In: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Washington DC, 2011.
|
|
32
|
Committee IACaU: Institutional animal care
and use committee guidebook. In: Office of Laboratory Animal
Welfare. National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, 2002.
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Jiao L, He C, Sun H, Cai Q, Han T
and Hu H: Alteration of gut microbiota in association with
cholesterol gallstone formation in mice. BMC Gastroenterol.
17(74)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M and Ahmad N: Dose
translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J.
22:659–661. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Akiyoshi T, Uchida K, Takase H, Nomura Y
and Takeuchi N: Cholesterol gallstones in alloxan-diabetic mice. J
Lipid Res. 27:915–924. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Carey MC: Critical tables for calculating
the cholesterol saturation of native bile. J Lipid Res. 19:945–955.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Portincasa P, Di Ciaula A, de Bari O,
Garruti G, Palmieri VO and Wang DQ: Management of gallstones and
its related complications. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
10:93–112. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shabanzadeh DM: Incidence of gallstone
disease and complications. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 34:81–89.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Di Ciaula A, Wang DQ, Wang HH, Bonfrate L
and Portincasa P: Targets for current pharmacologic therapy in
cholesterol gallstone disease. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
39:245–264, viii-ix. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Di Ciaula A, Wang DQ, Bonfrate L and
Portincasa P: Current views on genetics and epigenetics of
cholesterol gallstone disease. Cholesterol.
2013(298421)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Simonsen MH, Erichsen R, Froslev T, Rungby
J and Sorensen HT: Postmenopausal estrogen therapy and risk of
gallstone disease: A population-based case-control study. Drug Saf.
36:1189–1197. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lammert F, Gurusamy K, Ko CW, Miquel JF,
Méndez-Sánchez N, Portincasa P, van Erpecum KJ, van Laarhoven CJ
and Wang DQ: Gallstones. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2(16024)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Di Ciaula A, Wang DQ and Portincasa P: An
update on the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstone disease. Curr
Opin Gastroenterol. 34:71–80. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Di Ciaula A, Garruti G, Frühbeck G, De
Angelis M, de Bari O, Wang DQ, Lammert F and Portincasa P: The role
of diet in the pathogenesis of cholesterol gallstones. Curr Med
Chem. 26:3620–3638. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lavoie JM: Dynamics of hepatic and
intestinal cholesterol and bile acid pathways: The impact of the
animal model of estrogen deficiency and exercise training. World J
Hepatol. 8:961–975. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chen LY, Qiao QH, Zhang SC, Chen YH, Chao
GQ and Fang LZ: Metabolic syndrome and gallstone disease. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:4215–4220. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Han T, Zhang D, Fu Z, Sun Y, Yang W and
Yuan C: Retinol-binding protein 4 as a risk factor for cholesterol
gallstone formation. Mol Cell Biochem. 377:219–227. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Andreotti G, Chen J, Gao YT, Rashid A,
Chang SC, Shen MC, Wang BS, Han TQ, Zhang BH, Danforth KN, et al:
Serum lipid levels and the risk of biliary tract cancers and
biliary stones: A population-based study in China. Int J Cancer.
122:2322–2329. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Atamanalp SS, Keles MS, Atamanalp RS,
Acemoglu H and Laloglu E: The effects of serum cholesterol, LDL,
and HDL levels on gallstone cholesterol concentration. Pak J Med
Sci. 29:187–190. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang S, Zhang W, Shi L, Xie A, Shao Y, Ye
Y, Pan X, Lin Z, Li X and Zhang Y: Hepatic CXCL16 is increased in
gallstone accompanied with liver injury. Eur J Clin Invest.
47:667–674. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Makino A, Hullin-Matsuda F, Murate M, Abe
M, Tomishige N, Fukuda M, Yamashita S, Fujimoto T, Vidal H, Lagarde
M, et al: Acute accumulation of free cholesterol induces the
degradation of perilipin 2 and Rab18-dependent fusion of ER and
lipid droplets in cultured human hepatocytes. Mol Biol Cell.
27:3293–3304. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Liu C, Sun M, Wang L, Wang G, Chen G, Liu
C and Liu P: Effects of Yinchenhao Tang and related decoctions on
DMN-induced cirrhosis/fibrosis in rats. Chin Med.
3(1)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Jiang SL, Hu XD and Liu P:
Immunomodulation and liver protection of Yinchenhao decoction
against concanavalin A-induced chronic liver injury in mice. J
Integr Med. 13:262–268. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yago MD, Gonzalez V, Serrano P, Calpena R,
Martínez MA, Martínez-Victoria E and Mañas M: Effect of the type of
dietary fat on biliary lipid composition and bile lithogenicity in
humans with cholesterol gallstone disease. Nutrition. 21:339–347.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Morita SY, Ikeda Y, Tsuji T and Terada T:
Molecular mechanisms for protection of hepatocytes against bile
salt cytotoxicity. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 67:333–340.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Tazuma S, Kanno K, Sugiyama A and
Kishikawa N: Nutritional factors (nutritional aspects) in biliary
disorders: Bile acid and lipid metabolism in gallstone diseases and
pancreaticobiliary maljunction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28 (Suppl
4):S103–S107. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Vazquez MC, Rigotti A and Zanlungo S:
Molecular mechanisms underlying the link between nuclear receptor
function and cholesterol gallstone formation. J Lipids.
2012(547643)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fracchia M, Pellegrino S, Secreto P, Gallo
L, Masoero G, Pera A and Galatola G: Biliary lipid composition in
cholesterol microlithiasis. Gut. 48:702–706. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Pasternak A, Matyja A, Gil K, Gajda M,
Tomaszewski KA, Gajda M, Tomaszewski KA, Matyja M, Walocha JA and
Kulig J: Interstitial cajal-like cells and bile lithogenicity in
the pathogenesis of gall-stone disease. Pol Przegl Chir.
85:311–316. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ioannou GN, Landis CS, Jin GY, Haigh WG,
Farrell GC, Kuver R, Lee SP and Savard C: cholesterol crystals in
hepatocyte lipid droplets are strongly associated with human
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatol Commun. 3:776–791.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhao B, Natarajan R and Ghosh S: Human
liver cholesteryl ester hydrolase: Cloning, molecular
characterization, and role in cellular cholesterol homeostasis.
Physiol Genomics. 23:304–310. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Di Ciaula A, Wang DQ, Garruti G, Wang HH,
Grattagliano I, de Bari O and Portincasa P: Therapeutic reflections
in cholesterol homeostasis and gallstone disease: A review. Curr
Med Chem. 21:1435–1447. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hoekstra M, Van Berkel TJ and Van Eck M:
Scavenger receptor BI: A multi-purpose player in cholesterol and
steroid metabolism. World J Gastroenterol. 16:5916–5924.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Stender S, Frikke-Schmidt R, Nordestgaard
BG and Tybjaerg-Hansen A: The ABCG5/8 cholesterol transporter and
myocardial infarction versus gallstone disease. J Am Coll Cardiol.
63:2121–2128. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Dikkers A and Tietge UJ: Biliary
cholesterol secretion: More than a simple ABC. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:5936–5945. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Stokes CS and Lammert F: Transporters in
cholelithiasis. Biol Chem. 393:3–10. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Xie M, Kotecha VR, Andrade JDP, Fox JG and
Carey MC: Augmented cholesterol absorption and sarcolemmal sterol
enrichment slow small intestinal transit in mice, contributing to
cholesterol cholelithogenesis. J Physiol. 590:1811–1824.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wang LJ and Song BL: Niemann-Pick C1-Like
1 and cholesterol uptake. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1821:964–972.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Yoon JH, Choi HS, Jun DW, Yoo KS, Lee J,
Yang SY and Kuver R: ATP-binding cassette sterol transporters are
differentially expressed in normal and diseased human gallbladder.
Dig Dis Sci. 58:431–439. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Wang LJ, Wang J, Li N, Ge L, Li BL and
Song BL: Molecular characterization of the NPC1L1 variants
identified from cholesterol low absorbers. J Biol Chem.
286:7397–7408. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Zhou X, Seto SW, Chang D, Kiat H,
Razmovski-Naumovski V, Chan K and Bensoussan A: Synergistic effects
of Chinese herbal medicine: A comprehensive review of methodology
and current research. Front Pharmacol. 7(201)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Zhang A, Sun H, Qiu S and Wang X:
Advancing drug discovery and development from active constituents
of yinchenhao tang, a famous traditional Chinese medicine formula.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013(257909)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Cai FF, Wu R, Song YN, Xiong AZ, Chen XL,
Yang MD, Yang L, Hu Y, Sun MY and Su SB: Yinchenhao decoction
alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating bile acid metabolism and
TGF-β/Smad/ERK signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 8(15367)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Mase A, Makino B, Tsuchiya N, Yamamoto M,
Kase Y, Takeda S and Hasegawa T: Active ingredients of traditional
Japanese (kampo) medicine, inchinkoto, in murine concanavalin
A-induced hepatitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 127:742–749. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chen SD, Fan Y and Xu WJ: Effects of
yinchenhao decoction for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats and
study of the mechanism. J Tradit Chin Med. 31:220–223.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Li Y, Pan H, Li X, Jiang N, Huang L, Lu Y
and Shi F: Role of intestinal microbiota-mediated genipin
dialdehyde intermediate formation in geniposide-induced
hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
377(114624)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|