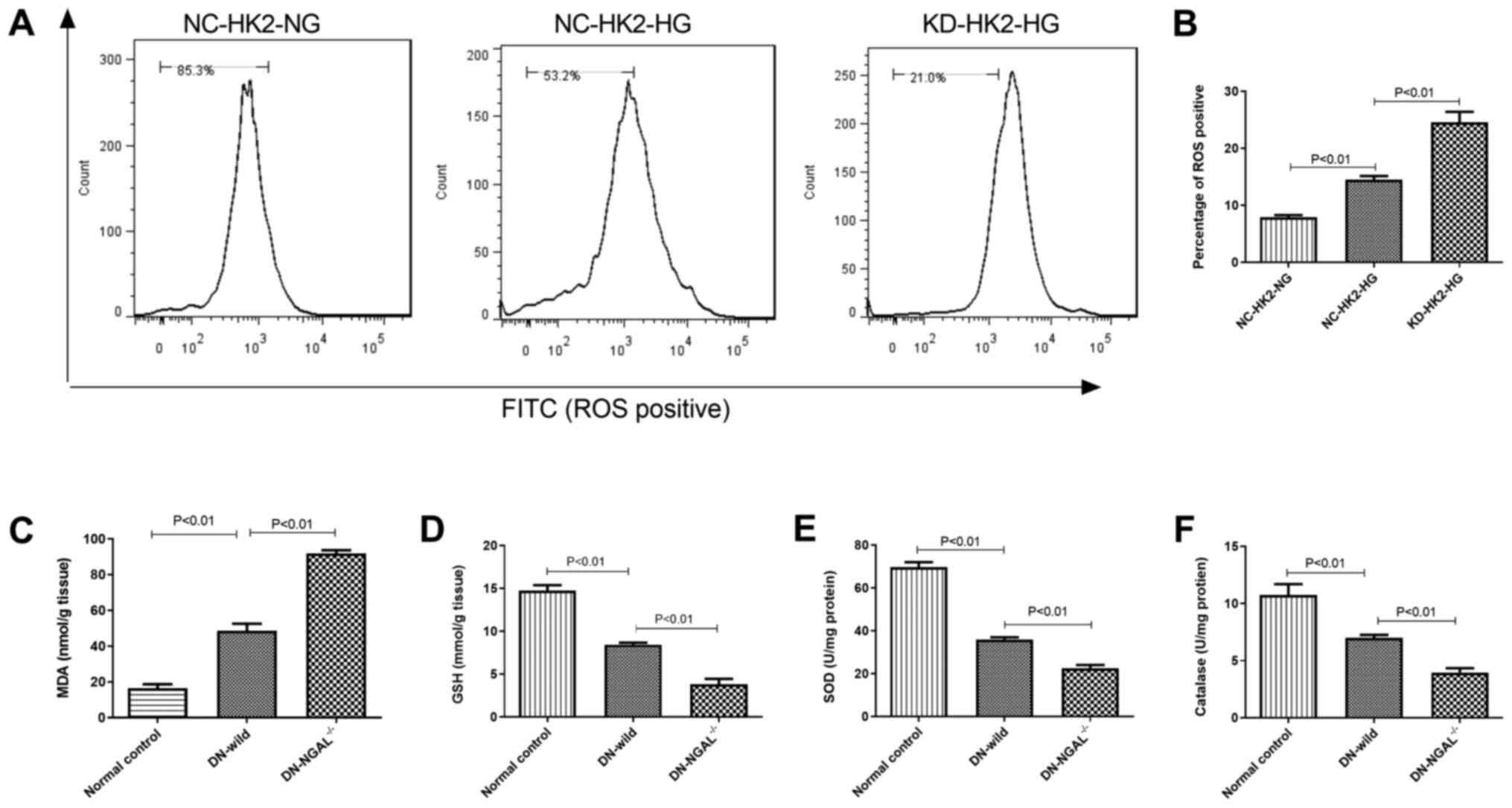
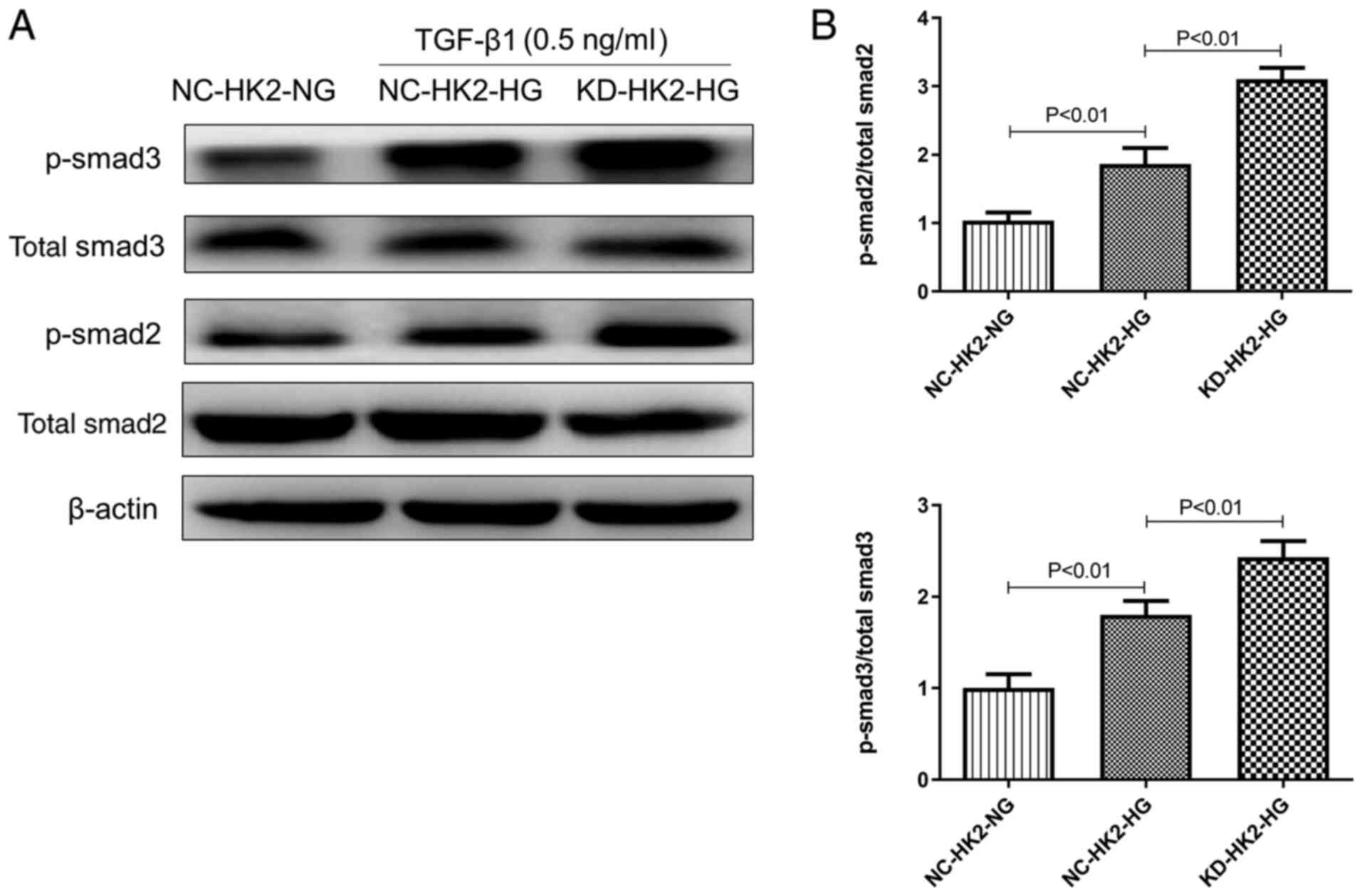
|
1
|
Papadopoulou-Marketou N, Margeli A,
Papassotiriou I, Chrousos GP, Kanaka-Gantenbein C and Wahlberg J:
NGAL as an early predictive marker of diabetic nephropathy in
children and young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes
Res. 2017(7526919)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sadar S, Kaspate D and Vyawahare N:
Protective effect of L-glutamine against diabetes-induced
nephropathy in experimental animal: Role of KIM-1, NGAL, TGF-β1,
and collagen-1. Ren Fail. 38:1483–1495. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Scelo G and Larose TL: Epidemiology and
risk factors for kidney cancer. J Clin Oncol.
36(JCO2018791905)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tarchini R, Bottini E, Botti P, Talassi E,
Baraldi O, Lambertini D, Gaetti L and Bellomi A: Type 2 diabetic
nephropathy: Clinical course and prevention proposals 2004. G Ital
Nefrol. 22 (Suppl 31):S15–S19. 2005.PubMed/NCBI(In Italian).
|
|
5
|
Leehey DJ, Singh AK, Alavi N and Singh R:
Role of angiotensin II in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. (Suppl
77):S93–S98. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang S, Wang D, Xue N, Lai F, Ji M, Jin J
and Chen X: Nicousamide protects kidney podocyte by inhibiting the
TGFβ receptor II phosphorylation and AGE-RAGE signaling. Am J
Transl Res. 9:115–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang S, Li Y, Li H, Zheng X and Chen X:
Renal-protective effect of nicousamide on hypertensive nephropathy
in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biomed Rep. 1:34–40.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Oh SM, Park G, Lee SH, Seo CS, Shin HK and
Oh DS: Assessing the recovery from prerenal and renal acute kidney
injury after treatment with single herbal medicine via activity of
the biomarkers HMGB1, NGAL and KIM-1 in kidney proximal tubular
cells treated by cisplatin with different doses and exposure times.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 17(544)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kaul A, Behera MR, Rai MK, Mishra P,
Bhaduaria DS, Yadav S, Agarwal V, Karoli R, Prasad N, Gupta A and
Sharma RK: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: As a
predictor of early diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Indian J Nephrol. 28:53–60. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cowland JB and Borregaard N: Molecular
characterization and pattern of tissue expression of the gene for
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin from humans. Genomics.
45:17–23. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Borregaard N, Sehested M, Nielsen BS,
Sengeløv H and Kjeldsen L: Biosynthesis of granule proteins in
normal human bone marrow cells. Gelatinase is a marker of terminal
neutrophil differentiation. Blood. 85:812–817. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ,
Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S and Aderem A: Lipocalin 2 mediates an
innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating
iron. Nature. 432:917–921. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Venge P, Douhan-Håkansson L, Garwicz D,
Peterson C, Xu S and Pauksen K: Human neutrophil lipocalin as a
superior diagnostic means to distinguish between acute bacterial
and viral infections. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 22:1025–1032.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mishra J, Mori K, Ma Q, Kelly C, Yang J,
Mitsnefes M, Barasch J and Devarajan P: Amelioration of ischemic
acute renal injury by neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 15:3073–3082. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mori K and Nakao K: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin as the real-time indicator of
active kidney damage. Kidney Int. 71:967–970. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bolignano D, Coppolino G, Campo S, Aloisi
C, Nicocia G, Frisina N and Buemi M: Urinary neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is associated with severity
of renal disease in proteinuric patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
23:414–416. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Li Z, Chen Y, Wu H, Zhang S and
Chen X: Prediction value of serum NGAL in the diagnosis and
prognosis of experimental acute and chronic kidney injuries.
Biomolecules. 10(981)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mauro C, Pacifico F, Lavorgna A, Mellone
S, Iannetti A, Acquaviva R, Formisano S, Vito P and Leonardi A:
ABIN-1 binds to NEMO/IKKgamma and co-operates with A20 in
inhibiting NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem. 281:18482–18488. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yan YM, Ai J, Zhou LL, Chung ACK, Li R,
Nie J, Fang P, Wang XL, Luo J, Hu Q, et al: Lingzhiols,
unprecedented rotary door-shaped meroterpenoids as potent and
selective inhibitors of p-Smad3 from ganoderma lucidum. Org Lett.
15:5488–5491. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Ma J, Sheng L, Zhang D, Chen X,
Yang J and Wang D: Total coumarins from Hydrangea paniculata show
renal protective effects in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney
injury via anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Front
Pharmacol. 8(872)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sen Z, Weida W, Jie M, Li S, Dongming Z
and Xiaoguang C: Coumarin glycosides from Hydrangea
paniculata slow down the progression of diabetic nephropathy by
targeting Nrf2 anti-oxidation and smad2/3-mediated profibrosis.
Phytomedicine. 57:385–395. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nørgaard SA, Sand FW, Sørensen DB, Abelson
KS and Søndergaard H: Softened food reduces weight loss in the
streptozotocin-induced male mouse model of diabetic nephropathy.
Lab Anim. 52:373–383. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
National Technical Committee for
Standardization of Laboratory Animals.
|
|
25
|
Naito T, Ma LJ, Yang H, Zuo Y, Tang Y, Han
JY, Kon V and Fogo AB: Angiotensin type 2 receptor actions
contribute to angiotensin type 1 receptor blocker effects on kidney
fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F683–F691.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Pörsti I, Fan M, Kööbi P, Jolma P,
Kalliovalkama J, Vehmas TI, Helin H, Holthöfer H, Mervaala E, Nyman
T and Tikkanen I: High calcium diet down-regulates kidney
angiotensin-converting enzyme in experimental renal failure. Kidney
Int. 66:2155–2166. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li P, Ma LL, Xie RJ, Xie YS, Wei RB, Yin
M, Wang JZ and Chen XM: Treatment of 5/6 nephrectomy rats with
sulodexide: A novel therapy for chronic renal failure. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 33:644–651. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aunapuu M, Pechter U, Arend A, Suuroja T
and Ots M: Ultrastructural changes in the remnant kidney (after 5/6
nephrectomy) glomerulus after losartan and atenolol treatment.
Medicina (Kaunas). 39:975–979. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fernandes SM, Cordeiro PM, da Fonseca CD
and Vattimo MF: The role of oxidative stress in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats. Arch
Endocrinol Metab. 60:443–449. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Han H, Cao A, Wang L, Guo H, Zang Y, Li Z,
Zhang X and Peng W: Huangqi decoction ameliorates
streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic nephropathy through antioxidant
and regulation of the TGF-β/MAPK/PPAR-γ signaling. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:1934–1944. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang S, Yang J, Li H, Li Y, Liu Y, Zhang
D, Zhang F, Zhou W and Chen X: Skimmin, a coumarin, suppresses the
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in wistar rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 692:78–83. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sen Z, Weida W, Li Y, Zhaojun L, Nina X
and Xiaoguang C: Nicousamide attenuates renal dysfunction and
glomerular injury in remnant kidneys by inhibiting TGF-β1
internalisation and renin activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 845:74–84.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Han M, Li Y, Liu M, Li Y and Cong B: Renal
neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin expression in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in the rat. BMC
Nephrol. 13(25)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Papadopoulou-Marketou N, Paschou SA,
Marketos N, Adamidi S, Adamidis S and Kannaka-Gantenbein C:
Diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Minerva Med. 109:218–228.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Pérez-Morales RE, Del Pino MD, Valdivielso
JM, Ortiz A, Mora-Fernández C and Navarro-González :
Inflammation in diabetic kidney diseases. Nephron. 143:12–16.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shang W and Wang Z: The update of NGAL in
acute kidney injury. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 18:1211–1217.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Feigerlová E and Battaglia-Hsu SF: IL-6
signaling in diabetic nephropathy: From pathophysiology to
therapeutic perspectives. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 37:57–65.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ma Q, Devarajan SR and Devarajan P:
Amelioration of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by
recombinant neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. Ren Fail.
38:1476–1482. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Han M, Li Y, Wen D, Liu M, Ma Y and Cong
B: NGAL protects against endotoxin-induced renal tubular cell
damage by suppressing apoptosis. BMC Nephrol.
19(168)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Higgins SP, Tang Y, Higgins CE, Mian B,
Zhang W, Czekay RP, Samarakoon R, Conti DJ and Higgins PJ:
TGF-β1/p53 signaling in renal fibrogenesis. Cell Signal. 43:1–10.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|