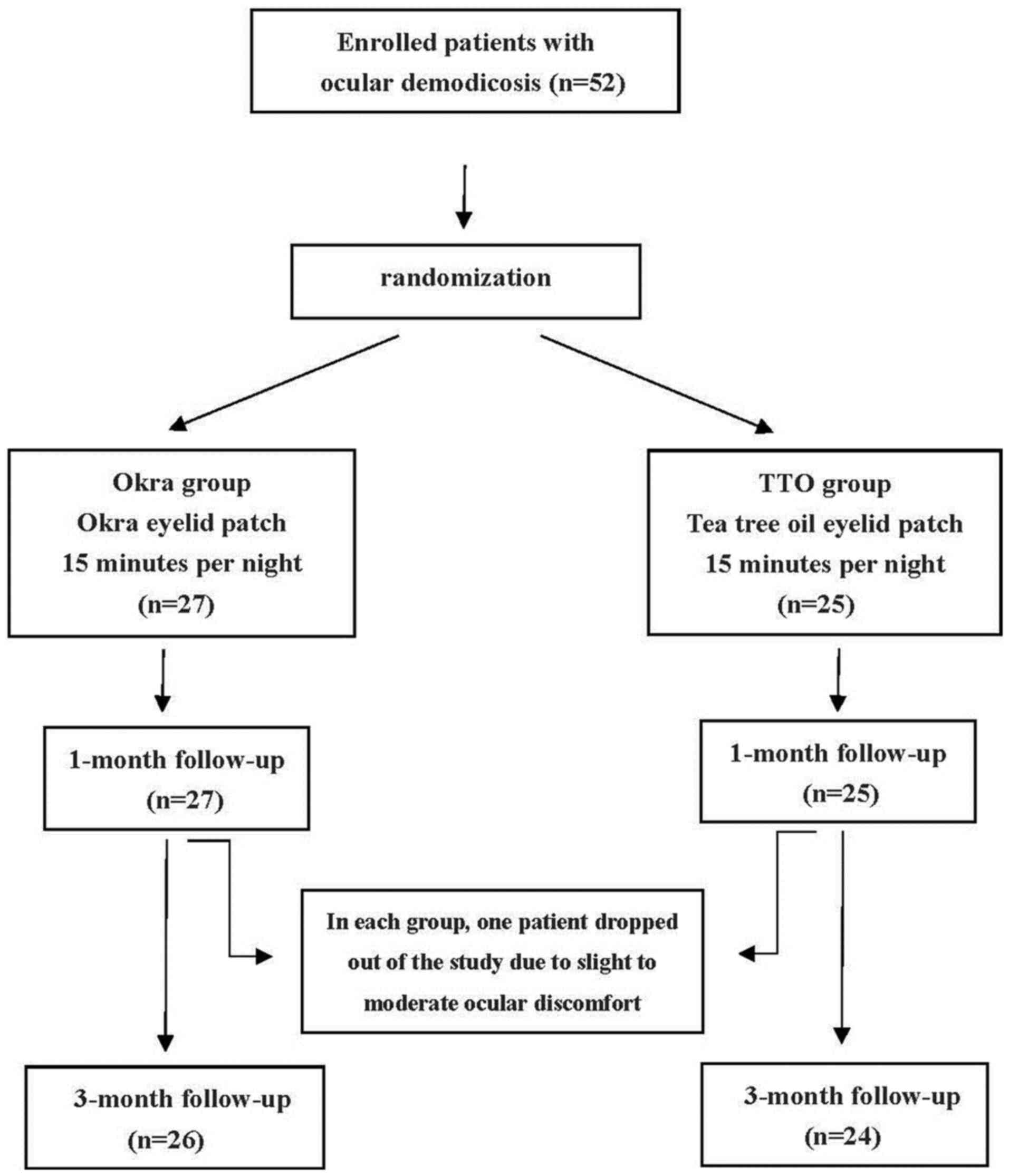
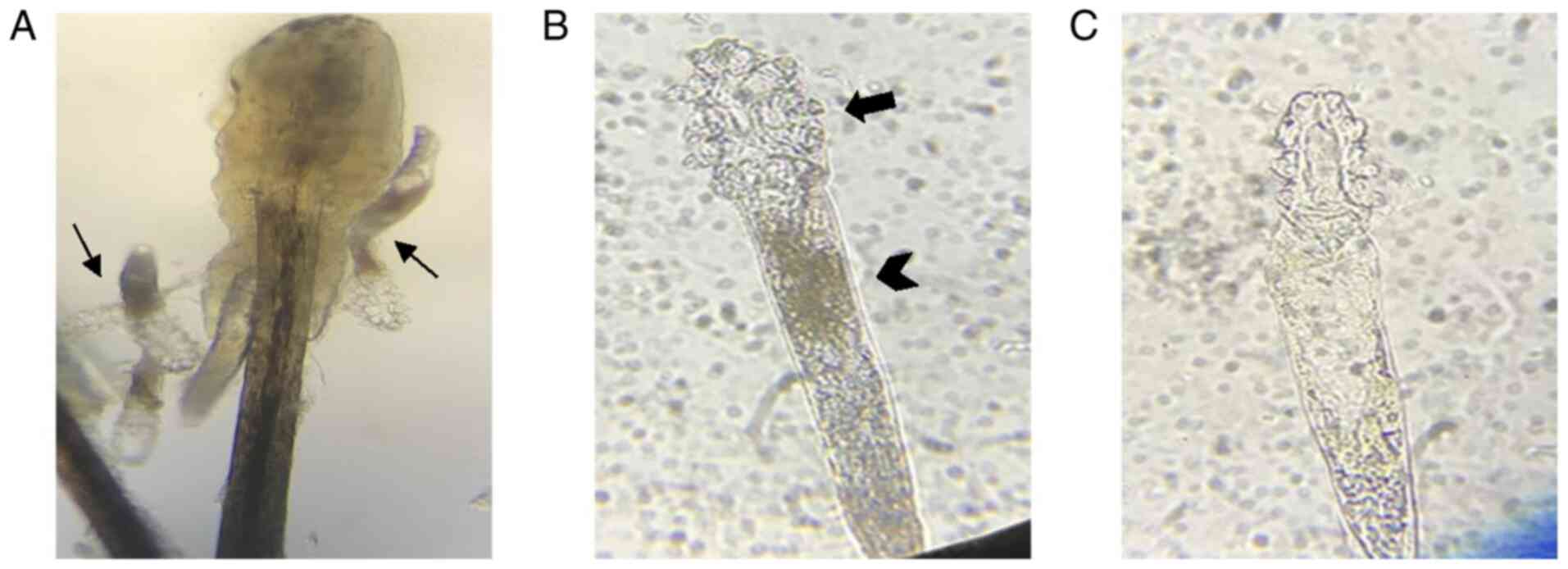
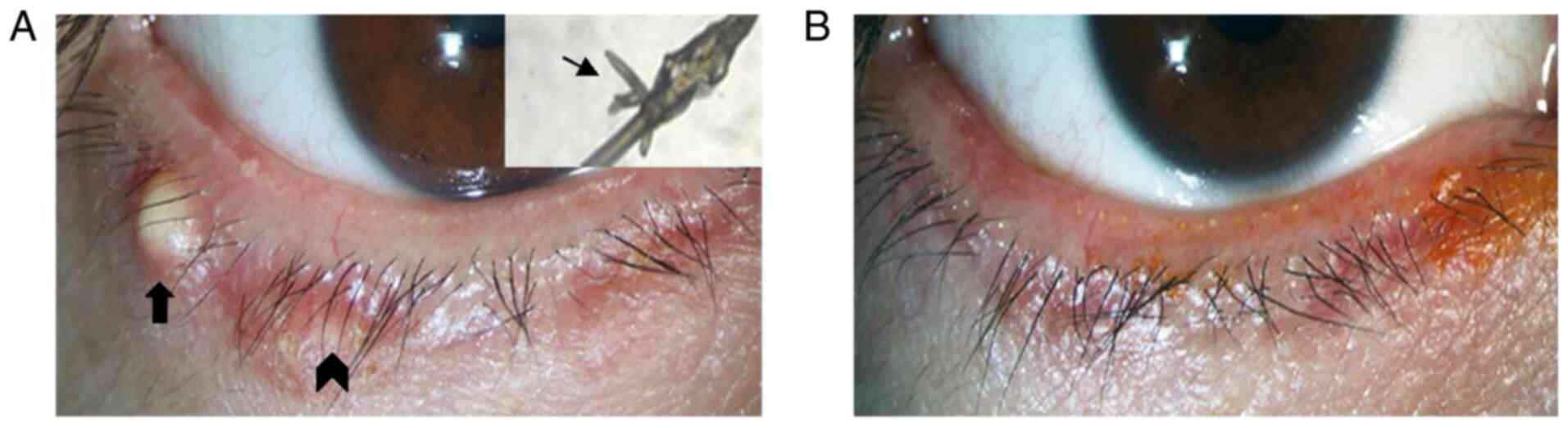
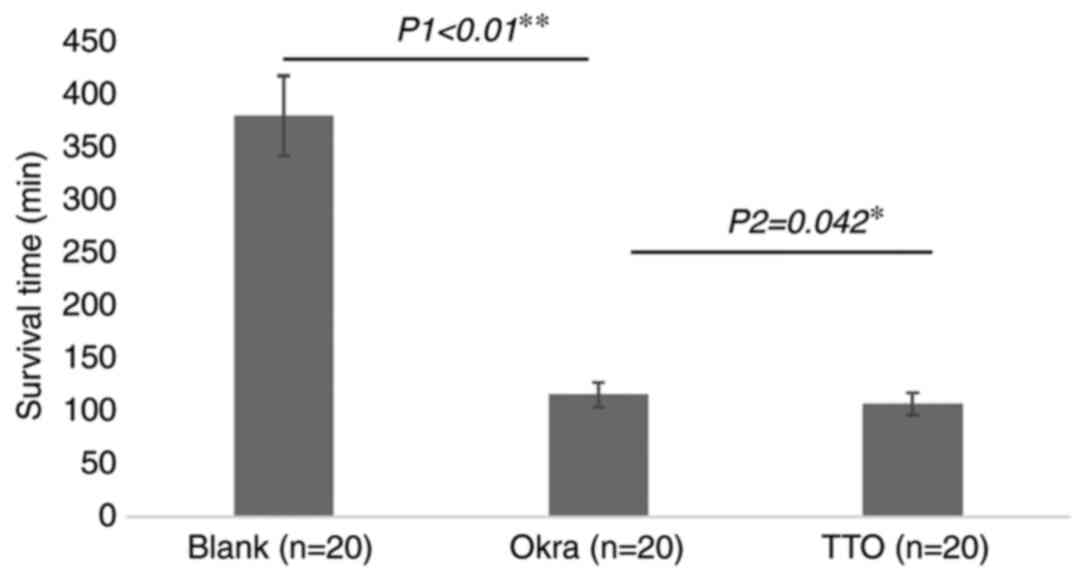
|
1
|
Basta-Juzbasić A, Subić JS and Ljubojević
S: Demodex folliculorum in development of dermatitis
rosaceiformis steroidica and rosacea-related diseases. Clin
Dermatol. 20:135–140. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wesolowska M, Knysz B, Reich A,
Blazejewska D, Czarnecki M, Gladysz A, Pozowski A and Misiuk-Hojlo
M: Prevalence of Demodex spp. in eyelash follicles in
different populations. Arch Med Sci. 10:319–324. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang XB, Ding YH and He W: The
association between Demodex infestation and ocular surface
manifestations in meibomian gland dysfunction. Int J Ophthalmol.
11:589–592. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fromstein SR, Harthan JS, Patel J and
Opitz DL: Demodex blepharitis: Clinical perspectives. Clin
Optom (Auckl). 10:57–63. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Luo X, Li J, Chen C, Tseng S and Liang L:
Ocular demodicosis as a potential cause of ocular surface
inflammation. Cornea. 36 (Suppl 1):S9–S14. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bron AJ, de Paiva CS, Chauhan SK, Bonini
S, Gabison EE, Jain S, Knop E, Markoulli M, Ogawa Y, Perez V, et
al: TFOS DEWS II pathophysiology report. Ocul Surf. 15:438–510.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tomlinson A, Bron AJ, Korb DR, Amano S,
Paugh JR, Pearce EI, Yee R, Yokoi N, Arita R and Dogru M: The
international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: Report of
the diagnosis subcommittee. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
52:2006–2049. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gao YY, Di Pascuale MA, Li W,
Baradaran-Rafii A, Elizondo A, Kuo CL, Raju VK and Tseng SC: In
vitro and in vivo killing of ocular Demodex by tea tree oil.
Br J Ophthalmol. 89:1468–1473. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Doreddula SK, Bonam SR, Gaddam DP, Desu
BS, Ramarao N and Pandy V: Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant,
antistress, and nootropic activities of aqueous and methanolic seed
extracts of ladies finger (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) in
mice. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014(519848)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Adelakun OE, Oyelade OJ, Ade-Omowaye BI,
Adeyemi IA and Van de Venter M: Chemical composition and the
antioxidative properties of nigerian okra seed (Abelmoschus
esculentus Moench) flour. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:1123–1126.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liao H, Dong W, Shi X, Liu H and Yuan K:
Analysis and comparison of the active components and antioxidant
activities of extracts from Abelmoschus esculentus L.
Pharmacogn Mag. 8:156–161. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cho CW, Han CJ, Rhee YK, Lee YC, Shin KS,
Shin JS, Lee KT and Hong HD: Cheonggukjang polysaccharides enhance
immune activities and prevent cyclophosphamide-induced
immunosuppression. Int J Biol Macromol. 72:519–525. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Durazzo A, Lucarini M, Novellino E, Souto
EB, Daliu P and Santini A: Abelmoschus esculentus (L.):
Bioactive components' beneficial properties-focused on antidiabetic
role-for sustainable health applications. Molecules.
24(38)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mairuae N, Cheepsunthorn P, Cheepsunthorn
CL and Tongjaroenbuangam W: Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus
Linn) inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators in
BV2 microglial cells. Trop J Pharm Res. 16(1285)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang X, Yin Y, Yue L and Gong L:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors aggravate
depression-associated dry eye via activating the NF-κB pathway.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 60:407–419. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang FM, Fan D, Yang XQ, Zhu FH, Shao MJ,
Li Q, Liu YT, Lin ZM, Cao SQ, Tang W, et al: The artemisinin analog
SM934 alleviates dry eye disease in rodent models by regulating
TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin: Aug 3, 2020 (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
17
|
Gao YY, Di Pascuale MA, Li W, Liu DT,
Baradaran-Rafii A, Elizondo A, Kawakita T, Raju VK and Tseng SC:
High prevalence of Demodex in eyelashes with cylindrical
dandruff. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:3089–3094. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kheirkhah A, Blanco G, Casas V and Tseng
SC: Fluorescein dye improves microscopic evaluation and counting of
demodex in blepharitis with cylindrical dandruff. Cornea.
26:697–700. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Salem DA, El-Shazly A, Nabih N, El-Bayoumy
Y and Saleh S: Evaluation of the efficacy of oral ivermectin in
comparison with ivermectin-metronidazole combined therapy in the
treatment of ocular and skin lesions of Demodex
folliculorum. Int J Infect Dis. 17:e343–e347. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Song N and Gong L: Therapeutic
effect of intense pulsed light on ocular demodicosis. Curr Eye Res.
44:250–256. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Schiffman RM, Christianson MD, Jacobsen G,
Hirsch JD and Reis BL: Reliability and validity of the ocular
surface disease index. Arch Ophthalmol. 118:615–621.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yokoi N, Georgiev GA, Kato H, Komuro A,
Sonomura Y, Sotozono C, Tsubota K and Kinoshita S: Classification
of fluorescein breakup patterns: A novel method of differential
diagnosis for dry eye. Am J Ophthalmol. 180:72–85. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lemp MA: Report of the national eye
institute/industry workshop on clinical trials in dry eyes. CLAO J.
21:221–232. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bevins CL and Liu FT: Rosacea: Skin innate
immunity gone awry? Nat Med. 13:904–906. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao YY, Di Pascuale MA, Elizondo A and
Tseng SC: Clinical treatment of ocular demodecosis by lid scrub
with tea tree oil. Cornea. 26:136–143. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tighe S, Gao YY and Tseng SC:
Terpinen-4-ol is the most active ingredient of tea tree oil to kill
Demodex mites. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2(2)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Koo H, Kim TH, Kim KW, Wee SW, Chun YS and
Kim JC: Ocular surface discomfort and Demodex: Effect of tea
tree oil eyelid scrub in Demodex blepharitis. J Korean Med
Sci. 27:1574–1579. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Messing J, Thöle C, Niehues M, Shevtsova
A, Glocker E, Borén T and Hensel A: Antiadhesive properties of
Abelmoschus esculentus (Okra) immature fruit extract against
Helicobacter pylori adhesion. PLoS One. 9(e84836)2014.
|
|
29
|
Lengsfeld C, Titgemeyer F, Faller G and
Hensel A: Glycosylated compounds from okra inhibit adhesion of
Helicobacter pylori to human gastric mucosa. J Agric Food
Chem. 52:1495–1503. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wahyuningsih SPA, Pramudya M, Putri IP,
Winarni D, Savira NII and Darmanto W: Crude polysaccharides from
okra pods (Abelmoschus esculentus) grown in indonesia
enhance the immune response due to bacterial infection. Adv
Pharmacol Sci. 2018(8505383)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Polito L, Bortolotti M, Maiello S,
Battelli MG and Bolognesi A: Plants producing ribosome-inactivating
proteins in traditional medicine. Molecules.
21(1560)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu JX, Sun YH and Li CP: Volatile oils of
Chinese crude medicines exhibit antiparasitic activity against
human Demodex with no adverse effects in vivo. Exp
Ther Med. 9:1304–1308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lehnhardt Pires C, Rodrigues SD, Bristot
D, Gaeta HH, de Oliveira Toyama D, Lobo Farias WR and Toyama MH:
Evaluation of macroalgae sulfated polysaccharides on the leishmania
(L.) amazonensis promastigote. Mar Drugs. 11:934–943.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jiang MH, Zhu L and Jiang JG:
Immunoregulatory actions of polysaccharides from Chinese herbal
medicine. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1367–1402. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shui G and Peng LL: An improved method for
the analysis of major antioxidants of hibiscus esculentus Linn. J
Chromatogr A. 1048:17–24. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen H, Jiao H, Cheng Y, Xu K, Jia X, Shi
Q, Guo S, Wang M, Du L and Wang F: In vitro and in vivo
immunomodulatory activity of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus
L.) polysaccharides. J Med Food. 19:253–265. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hu L, Yu W, Li Y, Prasad N and Tang Z:
Antioxidant activity of extract and its major constituents from
okra seed on rat hepatocytes injured by carbon tetrachloride.
Biomed Res Int. 2014(341291)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Khomsug P, Thongjaroe W, Pakdeenaro N,
Suttajit M and Chantirati P: Antioxidative activities and phenolic
content of extracts from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.).
Res J Biol Sci. 5:310–313. 2010.
|
|
39
|
Chi W, Hua X, Chen X, Bian F, Yuan X,
Zhang L, Wang X, Chen D, Deng R, Li Z, et al: Mitochondrial DNA
oxidation induces imbalanced activity of NLRP3/NLRP6 inflammasomes
by activation of caspase-8 and BRCC36 in dry eye. J Autoimmun.
80:65–76. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Saravanan S, Pandikumar P, Pazhanivel N,
Paulraj MG and Ignacimuthu S: Hepatoprotective role of
Abelmoschus esculentus (Linn.) moench., on carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver injury. Toxicol Mech Methods.
23:528–536. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Powell FC: Clinical practice. Rosacea. N
Engl J Med. 352:793–803. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li J, O'Reilly N, Sheha H, Katz R, Raju
VK, Kavanagh K and Tseng SC: Correlation between ocular
Demodex infestation and serum immunoreactivity to bacillus
proteins in patients with facial rosacea. Ophthalmology.
117:870–877.e1. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Baldwin HE: Diagnosis and treatment of
rosacea: State of the art. J Drugs Dermatol. 11:725–730.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huang CN, Wang CJ, Lee YJ and Peng CH:
Active subfractions of Abelmoschus esculentus substantially
prevent free fatty acid-induced β cell apoptosis via inhibiting
dipeptidyl peptidase-4. PLoS One. 12(e0180285)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Mollick MMR, Bhowmick B, Mondal D, Maity
D, Rana D, Dash SK, Chattopadhyay S, Roy S, Sarkar J, Acharya K, et
al: Anticancer (in vitro) and antimicrobial effect of gold
nanoparticles synthesized using Abelmoschus esculentus (L.)
pulp extract via a green route. RSC Adv. 4:37838–37848. 2014.
|