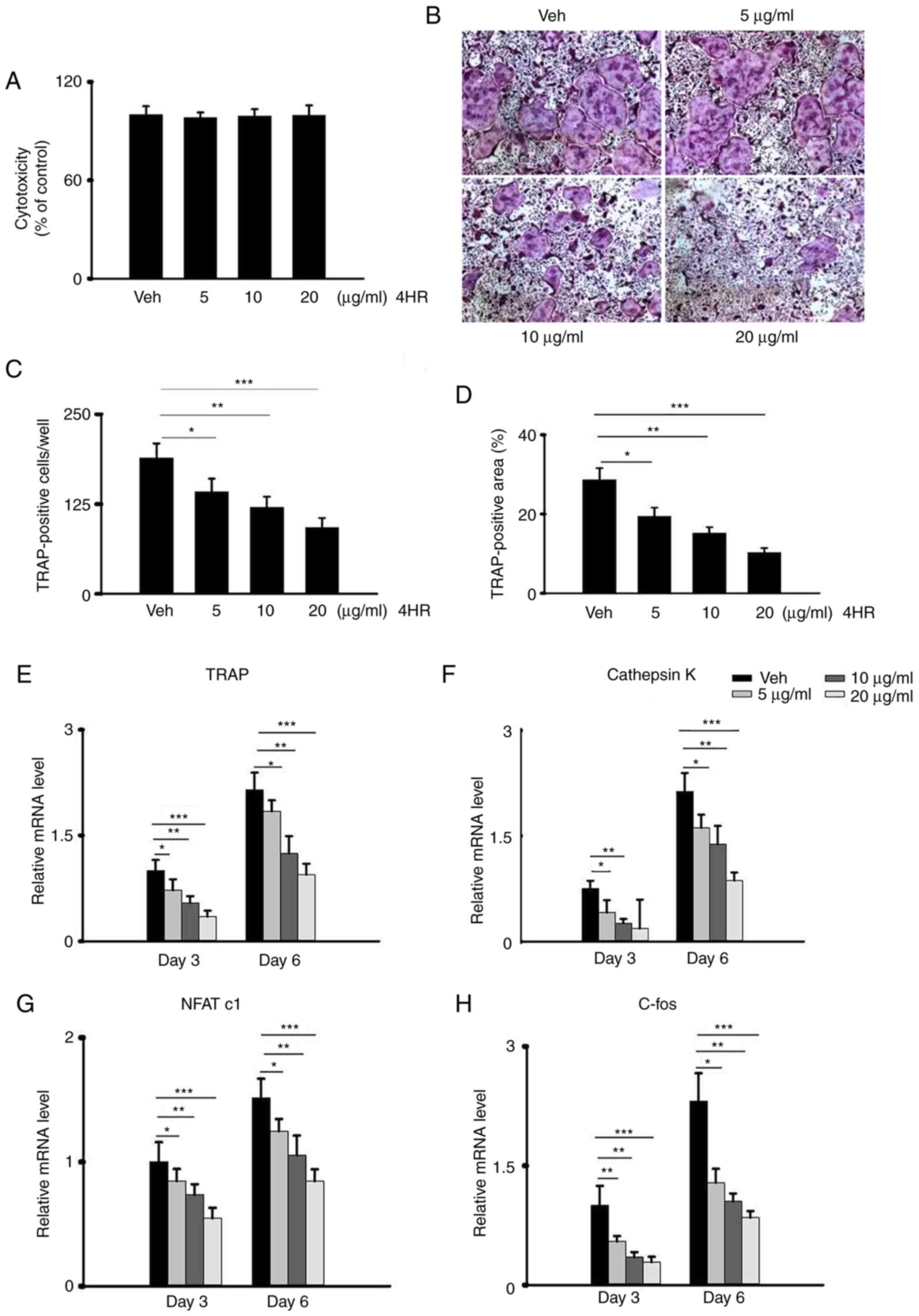
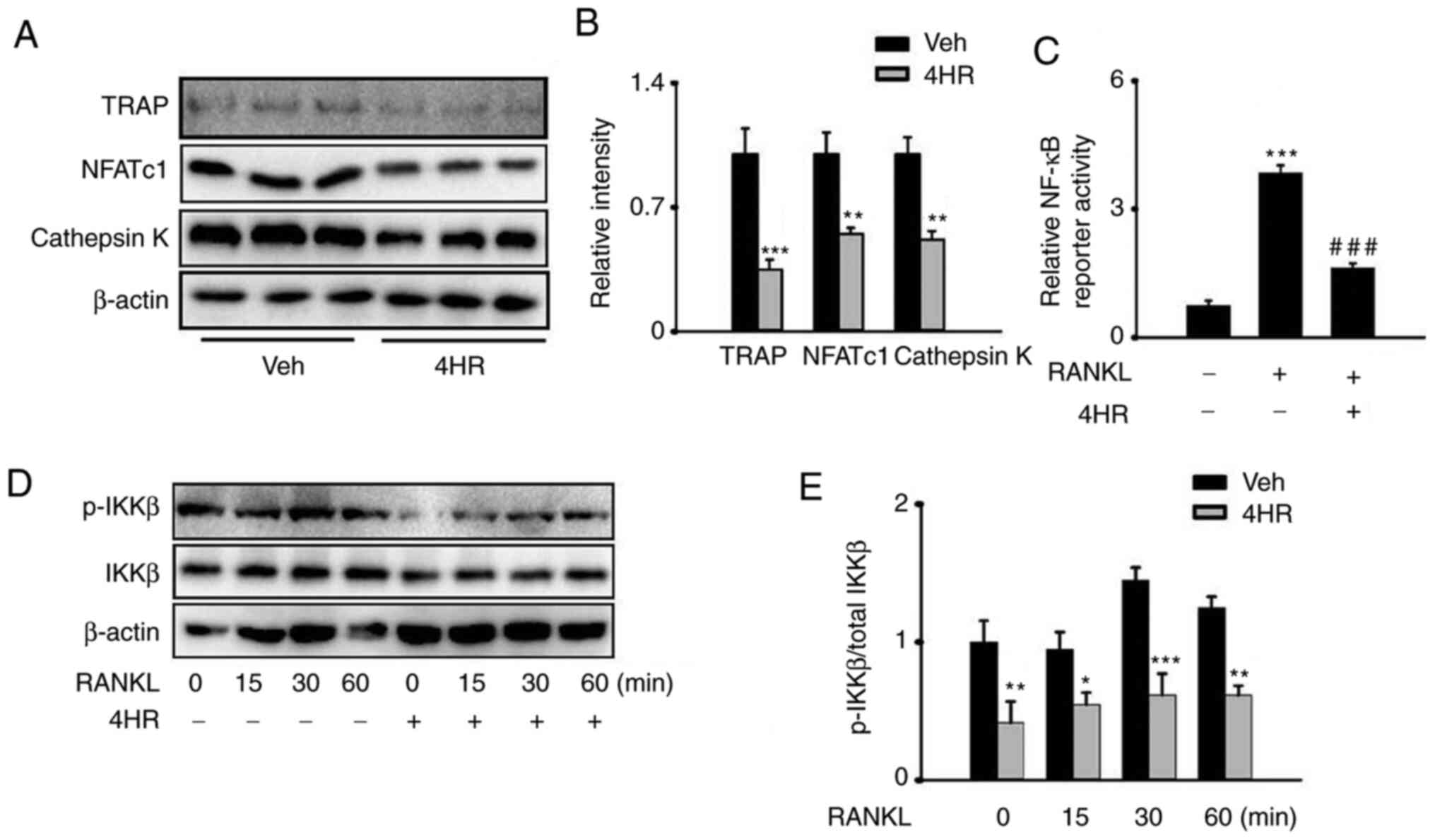
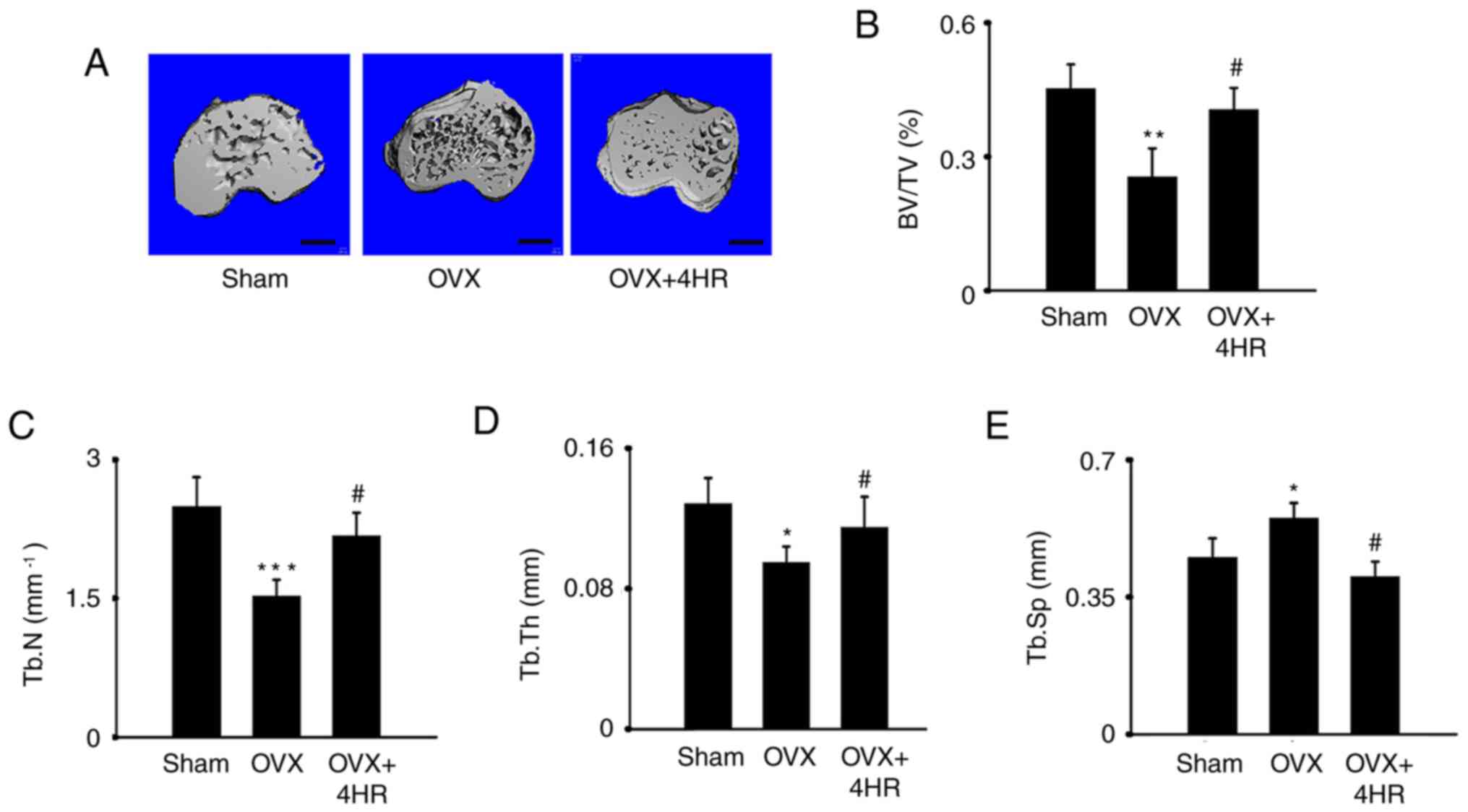
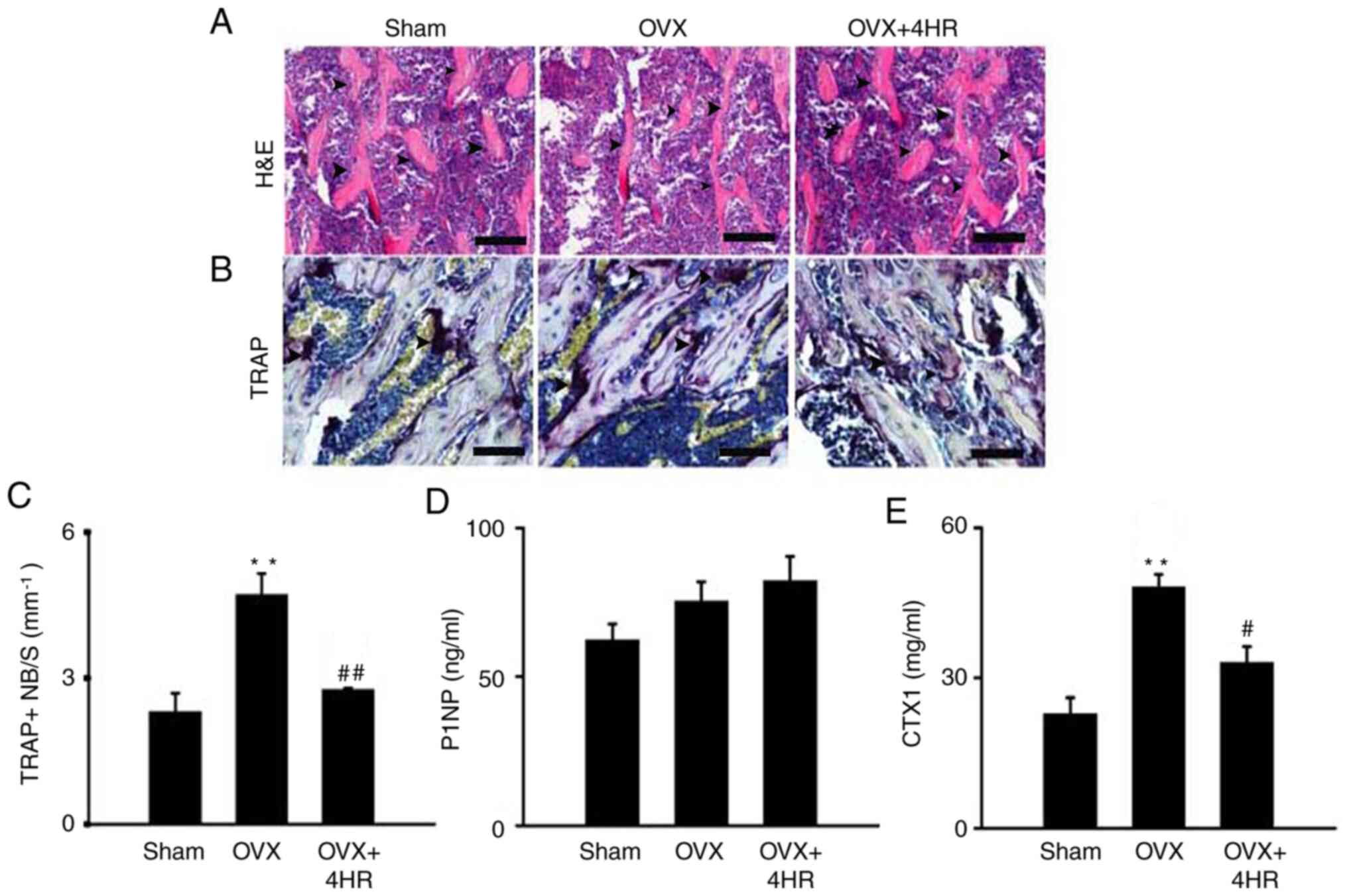
|
1
|
Kanis JA: Assessment of fracture risk and
its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis:
Synopsis of a WHO report. WHO study group. Osteoporos Int.
4:368–381. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergård M,
Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jönsson B and Kanis
JA: Osteoporosis in the European union: Medical management,
epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in
collaboration with the international osteoporosis foundation (IOF)
and the European federation of pharmaceutical industry associations
(EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 8(136)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tom SE, Adachi JD, Anderson FA Jr, Boonen
S, Chapurlat RD, Compston JE, Cooper C, Gehlbach SH, Greenspan SL,
Hooven FH, et al: Frailty and fracture, disability, and falls: A
multiple country study from the global longitudinal study of
osteoporosis in women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 61:327–334.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Johnell O and Kanis J: Epidemiology of
osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 16 (Suppl 2):S3–S7.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Eriksen EF: Cellular mechanisms of bone
remodeling. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 11:219–227. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Wang Z, Duan N, Zhu G, Schwarz EM
and Xie C: Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res.
59:99–107. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kikuta J and Ishii M: Bone imaging:
Osteoclast and osteoblast dynamics. Methods Mol Biol. 1763:1–9.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Roodman GD: Cell biology of the
osteoclast. Exp Hematol. 27:1229–1241. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Datta HK, Ng WF, Walker JA, Tuck SP and
Varanasi SS: The cell biology of bone metabolism. J Clin Pathol.
61:577–587. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zaidi M: Skeletal remodeling in health and
disease. Nat Med. 13:791–801. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Trouvin AP and Goëb V: Receptor activator
of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin: Maintaining the
balance to prevent bone loss. Clin Interv Aging. 5:345–354.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Boyce BF and Xing L: Functions of
RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 473:139–146. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lewiecki EM: Denosumab: A promising drug
for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Womens Health
(Lond). 2:517–525. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Eastell R, Christiansen C, Grauer A,
Kutilek S, Libanati C, McClung MR, Reid IR, Resch H, Siris E,
Uebelhart D, et al: Effects of denosumab on bone turnover markers
in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 26:530–537.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kendler DL, Roux C, Benhamou CL, Brown JP,
Lillestol M, Siddhanti S, Man HS, San Martin J and Bone HG: Effects
of denosumab on bone mineral density and bone turnover in
postmenopausal women transitioning from alendronate therapy. J Bone
Miner Res. 25:72–81. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gupta G and Aronow WS: Treatment of
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Compr Ther. 33:114–119.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lewiecki EM: Denosumab in postmenopausal
osteoporosis: What the clinician needs to know. Ther Adv
Musculoskelet Dis. 1:13–26. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Silva I and Branco JC: Denosumab: Recent
update in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Acta Reumatol Port.
37:302–313. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim MK, Yoon CS, Kim SG, Park YW, Lee SS
and Lee SK: Effects of 4-hexylresorcinol on protein expressions in
RAW 264.7 cells as determined by immunoprecipitation high
performance liquid chromatography. Sci Rep. 9(3379)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rabbani GH, Gilman RH, Kabir I and Mondel
G: The treatment of fasciolopsis buski infection in children: A
comparison of thiabendazole, mebendazole, levamisole, pyrantel
pamoate, hexylresorcinol and tetrachloroethylene. Trans R Soc Trop
Med Hyg. 79:513–515. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim SG, Lee SW, Park YW, Jeong JH and Choi
JY: 4-hexylresorcinol inhibits NF-κB phosphorylation and has a
synergistic effect with cisplatin in KB cells. Oncol Rep.
26:1527–1532. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
He J, Zhu Q, Dong X, Pan H, Chen J and
Zheng ZP: Oxyresveratrol and ascorbic acid O/W microemulsion:
Preparation, characterization, anti-isomerization and potential
application as antibrowning agent on fresh-cut lotus root slices.
Food Chem. 214:269–276. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Choi KH, Kim DW, Lee SK, Kim SG and Kim
TW: The administration of 4-hexylresorcinol accelerates orthodontic
tooth movement and increases the expression level of bone turnover
markers in ovariectomized rats. Int J Mol Sci.
21(1526)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhao L, Guan H, Song C, Wang Y, Liu C, Cai
C, Zhu H, Liu H, Zhao L and Xiao J: YAP1 is essential for
osteoclastogenesis through a TEADs-dependent mechanism. Bone.
110:177–186. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bae S, Lee MJ, Mun SH, Giannopoulou EG,
Yong-Gonzalez V, Cross JR, Murata K, Giguère V, van der Meulen M
and Park-Min KH: MYC-dependent oxidative metabolism regulates
osteoclastogenesis via nuclear receptor ERRα. J Clin Invest.
127:2555–2568. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: Single-step
method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem.
162:156–159. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun X, Gao X, Deng Z, Zhang L, McGilvray
K, Gadomski BC, Amra S, Bao G and Huard J: High bone
microarchitecture, strength, and resistance to bone loss in MRL/MpJ
mice correlates with activation of different signaling pathways and
systemic factors. FASEB J. 34:789–806. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Farahzadi R, Fathi E and Vietor I:
Mesenchymal stem cells could be considered as a candidate for
further studies in cell-based therapy of alzheimer's disease via
targeting the signaling pathways. ACS Chem Neurosci. 11:1424–1435.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Deng Y, Lu J, Li W, Wu A, Zhang X, Tong W,
Ho KK, Qin L, Song H and Mak KK: Reciprocal inhibition of YAP/TAZ
and NF-κB regulates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation. Nat
Commun. 9(4564)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Idris AI: Ovariectomy/orchidectomy in
rodents. Methods Mol Biol. 816:545–551. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huo J and Sun X: Effect of astragalus
polysaccharides on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Genet
Mol Res. 15:2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gao X, Usas A, Tang Y, Lu A, Tan J,
Schneppendahl J, Kozemchak AM, Wang B, Cummins JH, Tuan RS and
Huard J: A comparison of bone regeneration with human mesenchymal
stem cells and muscle-derived stem cells and the critical role of
BMP. Biomaterials. 35:6859–6870. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lee Y, Kim HJ, Park CK, Kim YG, Lee HJ,
Kim JY and Kim HH: MicroRNA-124 regulates osteoclast
differentiation. Bone. 56:383–389. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Takada J, Dinavahi R, Miyauchi A, Hamaya
E, Hirama T, Libanati C, Nakamura Y, Milmont CE and Grauer A:
Relationship between P1NP, a biochemical marker of bone turnover,
and bone mineral density in patients transitioned from alendronate
to romosozumab or teriparatide: A post hoc analysis of the
STRUCTURE trial. J Bone Miner Metab. 38:310–315. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu S, Zhang Y, Wang J, Li K, Tan K, Liang
K, Shen J, Cai D, Jin D, Li M, et al: TSC1 regulates osteoclast
podosome organization and bone resorption through mTORC1 and
Rac1/Cdc42. Cell Death Differ. 25:1549–1566. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Xu S, Li K, Tan K, Liang K, Wang
J, Shen J, Zou W, Hu L, Cai D, et al: mTORC1 inhibits NF-κB/NFATc1
signaling and prevents osteoclast precursor differentiation, in
vitro and in mice. J Bone Miner Res. 32:1829–1840. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lorenzo J, Horowitz M and Choi Y:
Osteoimmunology: Interactions of the bone and immune system. Endocr
Rev. 29:403–440. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin TH, Pajarinen J, Lu L, Nabeshima A,
Cordova LA, Yao Z and Goodman SB: NF-κB as a therapeutic target in
inflammatory-associated bone diseases. Adv Protein Chem Struct
Biol. 107:117–154. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Abu-Amer Y: NF-κB signaling and bone
resorption. Osteoporos Int. 24:2377–2386. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu TT, Liu DM, Xuan Y, Zhao L, Sun LH,
Zhao DD, Wang XF, He Y, Guo XZ, Du R, et al: The association
between the baseline bone resorption marker CTX and incident
dysglycemia after 4 years. Bone Res. 5(17020)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Thurairaja R, Iles RK, Jefferson K,
McFarlane JP and Persad RA: Serum amino-terminal propeptide of type
1 procollagen (P1NP) in prostate cancer: A potential predictor of
bone metastases and prognosticator for disease progression and
survival. Urol Int. 76:67–71. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Boyce BF, Xiu Y, Li J, Xing L and Yao Z:
NF-κB-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol Metab
(Seoul). 30:35–44. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Silva I and Branco JC: Rank/Rankl/opg:
Literature review. Acta Reumatol Port. 36:209–218. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Onal M, Xiong J, Chen X, Thostenson JD,
Almeida M, Manolagas SC and O'Brien CA: Receptor activator of
nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) protein expression by B
lymphocytes contributes to ovariectomy-induced bone loss. J Biol
Chem. 287:29851–29860. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Salamanna F, Borsari V, Contartese D,
Nicoli Aldini N and Fini M: Link between estrogen deficiency
osteoporosis and susceptibility to bone metastases: A way towards
precision medicine in cancer patients. Breast. 41:42–50.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kanis JA, Cooper C, Rizzoli R and
Reginster JY: Scientific Advisory Board of the European Society for
Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis (ESCEO) and the
Committees of Scientific Advisors and National Societies of the
International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). European guidance for
the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal
women. Osteoporos Int. 30:3–44. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|