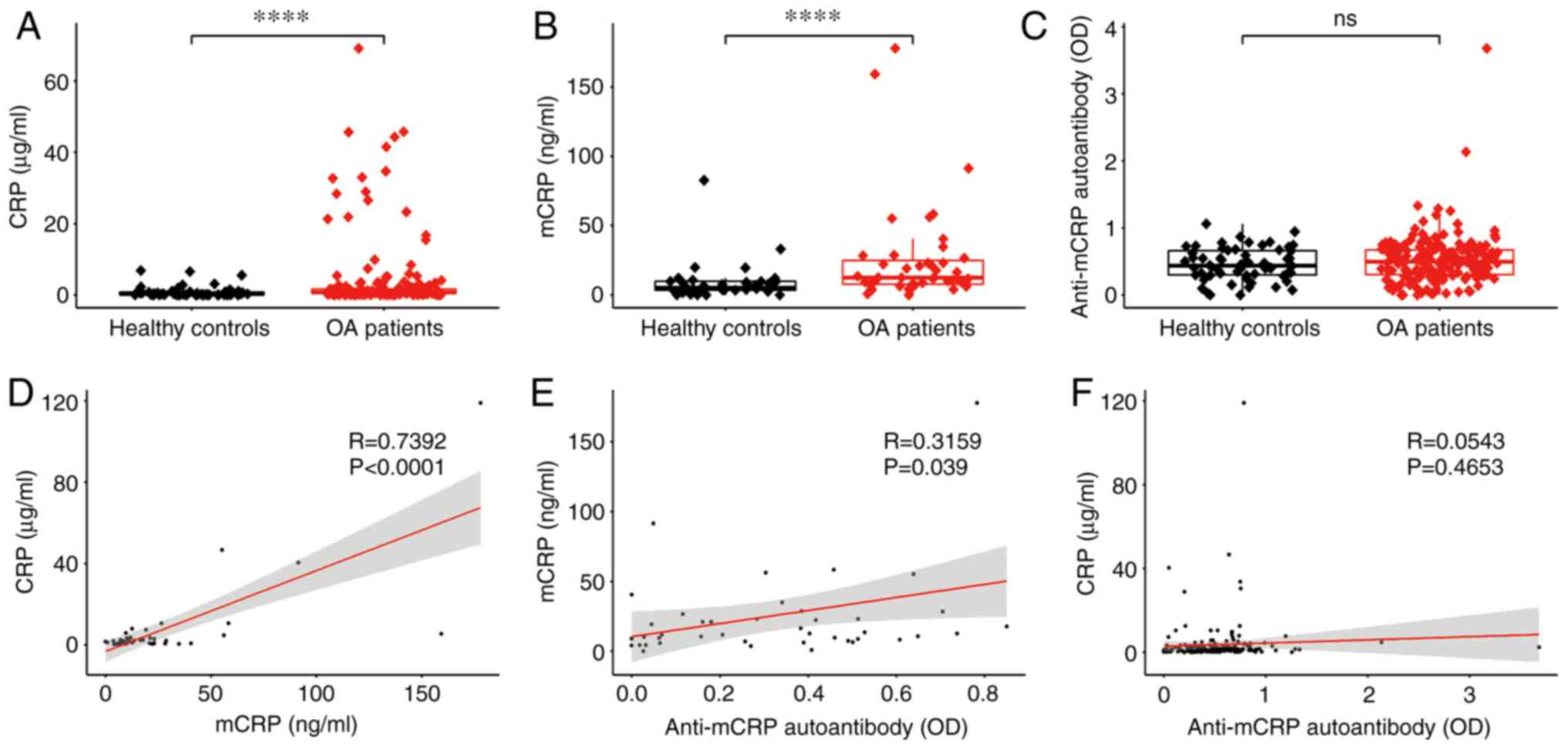
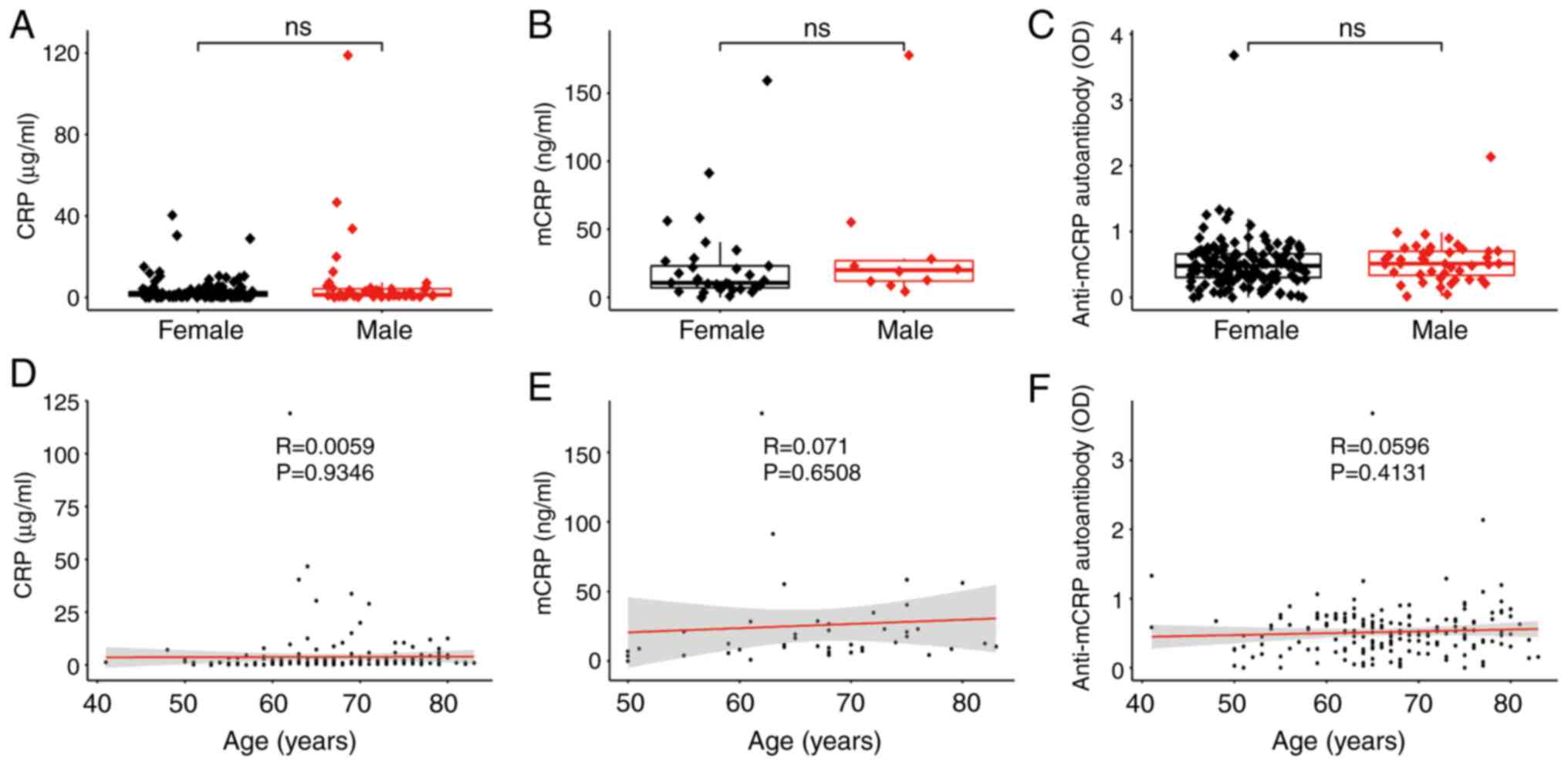
|
1
|
Ringdahl E and Pandit S: Treatment of knee
osteoarthritis. Am Fam Physician. 83:1287–1292. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R, Price
AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis. Lancet.
386:376–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F and Lafeber FP:
Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice.
Lancet. 377:2115–2126. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Towheed TE, Maxwell L, Anastassiades TP,
Shea B, Houpt J, Robinson V, Hochberg MC and Wells G: Glucosamine
therapy for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2005(CD002946)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Uebelhart D, Malaise M, Marcolongo R, de
Vathaire F, Piperno M, Mailleux E, Fioravanti A, Matoso L and
Vignon E: Intermittent treatment of knee osteoarthritis with oral
chondroitin sulfate: A one-year, randomized, double-blind,
multicenter study versus placebo. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
12:269–276. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Benito MJ, Veale DJ, FitzGerald O, van den
Berg WB and Bresnihan B: Synovial tissue inflammation in early and
late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 64:1263–1267. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu-Bryan R: Synovium and the innate
inflammatory network in osteoarthritis progression. Curr Rheumatol
Rep. 15(323)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Du Clos TW: Pentraxins: Structure,
function, and role in inflammation. ISRN Inflamm.
2013(379040)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pepys MB and Hirschfield GM: C-reactive
protein: A critical update. J Clin Invest. 111:1805–1812.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Medzhitov R: Recognition of microorganisms
and activation of the immune response. Nature. 449:819–826.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Schwedler SB, Filep JG, Galle J, Wanner C
and Potempa LA: C-reactive protein: A family of proteins to
regulate cardiovascular function. Am J Kidney Dis. 47:212–222.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Casas JP, Shah T, Hingorani AD, Danesh J
and Pepys MB: C-reactive protein and coronary heart disease: A
critical review. J Intern Med. 264:295–314. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Verma S, Devaraj S and Jialal I: Is
C-reactive protein an innocent bystander or proatherogenic culprit?
C-reactive protein promotes atherothrombosis. Circulation.
113:2135–2150; discussion 2150. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bharadwaj D, Stein MP, Volzer M, Mold C
and Du Clos TW: The major receptor for C-reactive protein on
leukocytes is fcgamma receptor II. J Exp Med. 190:585–590.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Marjon KD, Marnell LL, Mold C and Du Clos
TW: Macrophages activated by C-reactive protein through Fc gamma RI
transfer suppression of immune thrombocytopenia. J Immunol.
182:1397–1403. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Lee PY, Sobel ES, Narain S, Satoh M,
Segal MS, Reeves WH and Richards HB: Increased expression of
FcgammaRI/CD64 on circulating monocytes parallels ongoing
inflammation and nephritis in lupus. Arthritis Res Ther.
11(R6)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu Y, Potempa LA, El Kebir D and Filep JG:
C-reactive protein and inflammation: Conformational changes affect
function. Biol Chem. 396:1181–1197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Potempa LA, Maldonado BA, Laurent P, Zemel
ES and Gewurz H: Antigenic, electrophoretic and binding alterations
of human C-reactive protein modified selectively in the absence of
calcium. Mol Immunol. 20:1165–1175. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Potempa LA, Yao ZY, Ji SR, Filep JG and Wu
Y: Solubilization and purification of recombinant modified
C-reactive protein from inclusion bodies using reversible anhydride
modification. Biophys Rep. 1:18–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li HY, Wang J, Meng F, Jia ZK, Su Y, Bai
QF, Lv LL, Ma FR, Potempa LA, Yan YB, et al: An intrinsically
disordered motif mediates diverse actions of monomeric C-reactive
protein. J Biol Chem. 291:8795–8804. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ying SC, Gewurz H, Kinoshita CM, Potempa
LA and Siegel JN: Identification and partial characterization of
multiple native and neoantigenic epitopes of human C-reactive
protein by using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 143:221–228.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ying SC, Shephard E, de Beer FC, Siegel
JN, Harris D, Gewurz BE, Fridkin M and Gewurz H: Localization of
sequence-determined neoepitopes and neutrophil digestion fragments
of C-reactive protein utilizing monoclonal antibodies and synthetic
peptides. Mol Immunol. 29:677–687. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kohn MD, Sassoon AA and Fernando ND:
Classifications in brief: Kellgren-lawrence classification of
osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 474:1886–1893.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Petersson IF, Boegard T, Saxne T, Silman
AJ and Svensson B: Radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee
classified by the Ahlback and Kellgren & Lawrence systems for
the tibiofemoral joint in people aged 35-54 years with chronic knee
pain. Ann Rheum Dis. 56:493–496. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Macri EM, Runhaar J, Damen J, Oei EH and
Bierma-Zeinstra SM: Kellgren & Lawrence grading in cohort
studies: Methodological update and implications illustrated using
data from the CHECK cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). Jan 15,
2021. (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1002/acr.24563.
|
|
27
|
Emrani PS, Katz JN, Kessler CL, Reichmann
WM, Wright EA, McAlindon TE and Losina E: Joint space narrowing and
Kellgren-Lawrence progression in knee osteoarthritis: An analytic
literature synthesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 16:873–882.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
The R Core Team: R: A language and
environment for statistical computing. Reference index. https://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/fullrefman.pdf.
Accessed October 10, 2020.
|
|
29
|
Woolf AD and Pfleger B: Burden of major
musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 81:646–656.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li HY, Liu XL, Liu YT, Jia ZK, Filep JG,
Potempa LA, Ji SR and Wu Y: Matrix sieving-enforced retrograde
transcytosis regulates tissue accumulation of C-reactive protein.
Cardiovasc Res. 115:440–452. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pepys MB, Hirschfield GM, Tennent GA,
Gallimore JR, Kahan MC, Bellotti V, Hawkins PN, Myers RM, Smith MD,
Polara A, et al: Targeting C-reactive protein for the treatment of
cardiovascular disease. Nature. 440:1217–1221. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Griselli M, Herbert J, Hutchinson WL,
Taylor KM, Sohail M, Krausz T and Pepys MB: C-reactive protein and
complement are important mediators of tissue damage in acute
myocardial infarction. J Exp Med. 190:1733–1740. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Diehl EE, Haines GK III, Radosevich JA and
Potempa LA: Immunohistochemical localization of modified C-reactive
protein antigen in normal vascular tissue. Am J Med Sci. 319:79–83.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schwedler SB, Amann K, Wernicke K, Krebs
A, Nauck M, Wanner C, Potempa LA and Galle J: Native C-reactive
protein increases whereas modified C-reactive protein reduces
atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Circulation.
112:1016–1023. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ullah N, Ma FR, Han J, Liu XL, Fu Y, Liu
YT, Liang YL, Ouyang H and Li HY: Monomeric C-reactive protein
regulates fibronectin mediated monocyte adhesion. Mol Immunol.
117:122–130. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li QY, Li HY, Fu G, Yu F, Wu Y and Zhao
MH: Autoantibodies against C-reactive protein influence complement
activation and clinical course in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 28:3044–3054. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tan Y, Yu F, Yang H, Chen M, Fang Q and
Zhao MH: Autoantibodies against monomeric C-reactive protein in
sera from patients with lupus nephritis are associated with disease
activity and renal tubulointerstitial lesions. Hum Immunol.
69:840–844. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yao Z, Zhang Y and Wu H: Regulation of
C-reactive protein conformation in inflammation. Inflamm Res.
68:815–823. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ji SR, Wu Y, Zhu L, Potempa LA, Sheng FL,
Lu W and Zhao J: Cell membranes and liposomes dissociate C-reactive
protein (CRP) to form a new, biologically active structural
intermediate: mCRP(m). FASEB J. 21:284–294. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ji SR, Wu Y, Potempa LA, Qiu Q and Zhao J:
Interactions of C-reactive protein with low-density lipoproteins:
Implications for an active role of modified C-reactive protein in
atherosclerosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:648–661.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ji SR, Wu Y, Potempa LA, Liang YH and Zhao
J: Effect of modified C-reactive protein on complement activation:
A possible complement regulatory role of modified or monomeric
C-reactive protein in atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 26:935–941. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Khreiss T, Jozsef L, Potempa LA and Filep
JG: Loss of pentameric symmetry in C-reactive protein induces
interleukin-8 secretion through peroxynitrite signaling in human
neutrophils. Circ Res. 97:690–697. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Fernandez-Torres J, Zamudio-Cuevas Y,
Lopez-Reyes A, Garrido-Rodríguez D, Martínez-Flores K, Lozada CA,
Muñóz-Valle JF, Oregon-Romero E and Martínez-Nava GA: Gene-gene
interactions of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in knee
osteoarthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 45:1089–1098. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang Y, Fan X, Xing L and Tian F: Wnt
signaling: A promising target for osteoarthritis therapy. Cell
Commun Signal. 17(97)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu Z, Ren Y, Mirando AJ, Wang C, Zuscik
MJ, O'Keefe RJ and Hilton MJ: Notch signaling in postnatal joint
chondrocytes, but not subchondral osteoblasts, is required for
articular cartilage and joint maintenance. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 24:740–751. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu Z, Chen J, Mirando AJ, Wang C, Zuscik
MJ, O'Keefe RJ and Hilton MJ: A dual role for NOTCH signaling in
joint cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis. Sci Signal.
8(ra71)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Choi MC, Jo J, Park J, Kang HK and Park Y:
NF-κB signaling pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage destruction.
Cells. 8(734)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang LB, Man ZT, Li W, Zhang W, Wang XQ
and Sun S: Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response
through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol. 87:249–257.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Trovato FM,
Weinberg AM, Al-Wasiyah MK, Alqahtani MH and Mobasheri A:
Biomarkers of chondrocyte apoptosis and autophagy in
osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:20560–20575. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xue JF, Shi ZM, Zou J and Li XL:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of
articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats
with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1252–1261.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Koura HM, Zaki SM, Ismail NA, Salama EE,
El Lebedy DH and Effat LK: Relationship between biochemical bone
markers and bone mineral density in patients with phenylketonuria
under restricted diet. Iran J Pediatr. 24:23–28, Epub 2013 Dec 31.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu Y, Ge J, Chen D, Weng Y, Du H, Sun Y
and Zhang Q: Osteoprotegerin deficiency leads to deformation of the
articular cartilage in femoral head. J Mol Histol. 47:475–483.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kovacs B, Vajda E and Nagy EE: Regulatory
effects and interactions of the Wnt and OPG-RANKL-RANK signaling at
the bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
20(4653)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sproston NR and Ashworth JJ: Role of
C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection. Front
Immunol. 9(754)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Boras E, Slevin M, Alexander MY, et al:
Monomeric C-reactive protein and Notch-3 co-operatively increase
angiogenesis through PI3K signalling pathway. Cytokine. 69:165–179.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Jia ZK, Li HY, Liang YL, Potempa LA, Ji SR
and Wu Y: Monomeric C-reactive protein binds and neutralizes
receptor activator of NF-κB ligand-induced osteoclast
differentiation. Front Immunol. 9(234)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|