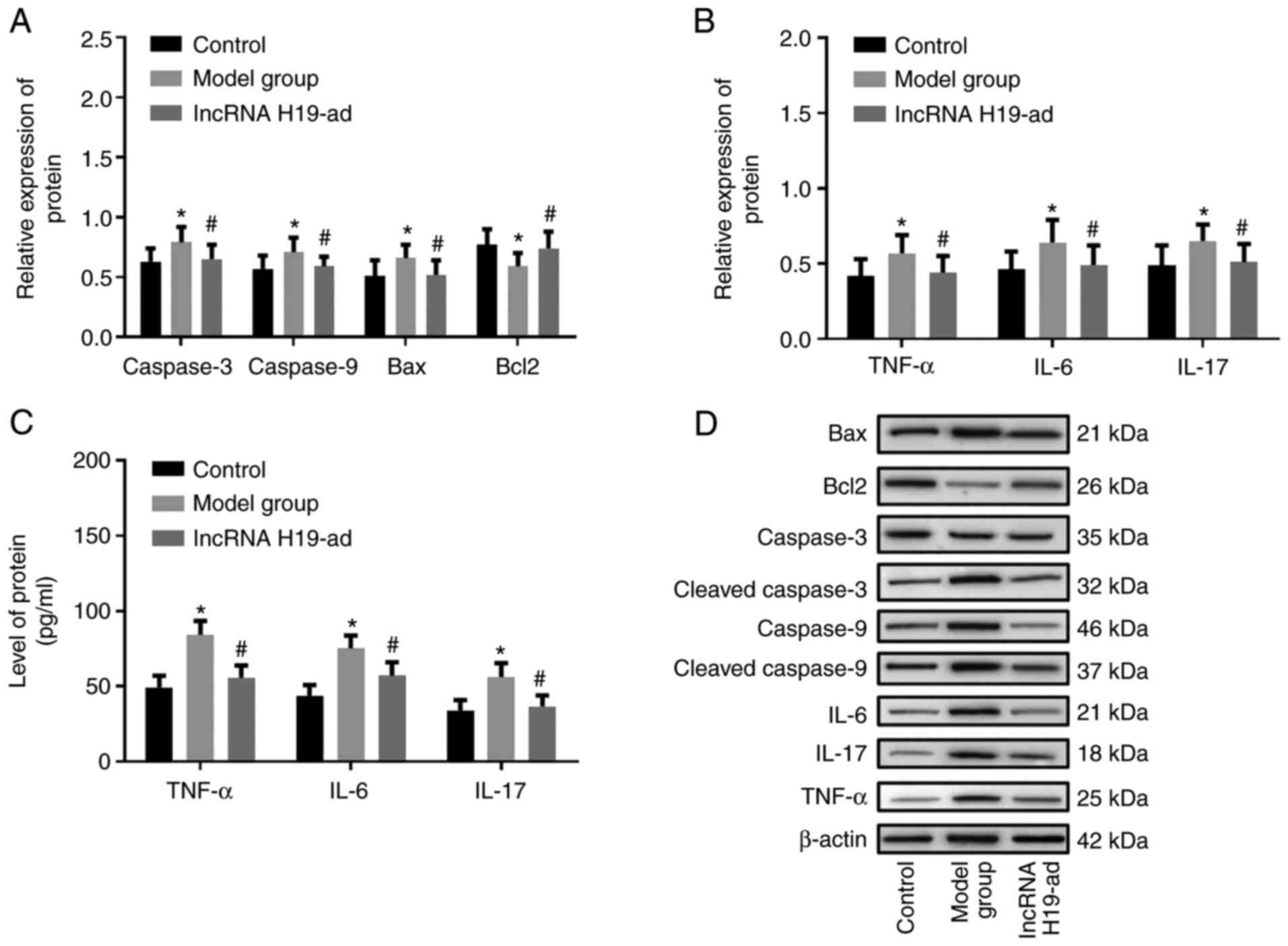
|
1
|
Lever A and Mackenzie I: Sepsis:
Definition, epidemiology, and diagnosis. BMJ. 335:879–883.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Martin-Loeches I, Guia MC, Vallecoccia MS,
Suarez D, Ibarz M, Irazabal M, Ferrer R and Artigas A: Risk factors
for mortality in elderly and very elderly critically ill patients
with sepsis: A prospective, observational, multicenter cohort
study. Ann Intensive Care. 9(26)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gómez H and Kellum JA: Sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 22:546–553.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Cai Y and Zang QS: Cardiac
autophagy in sepsis. Cells. 8(141)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shao IY, Elkind MSV and Boehme AK: Risk
factors for stroke in patients with sepsis and bloodstream
infections. Stroke. 50:1046–1051. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen X, Wang T, Song L and Liu X:
Activation of multiple toll-like receptors serves different roles
in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 18:443–450.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu J, Yan X and Jin G: Ulinastatin
protects rats from sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing
the JAK-STAT3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:2554–2559.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zheng H, Liang W, He W, Huang C, Chen Q,
Yi H, Long L, Deng Y and Zeng M: Ghrelin attenuates sepsis-induced
acute lung injury by inhibiting the NF-κB, iNOS, and Akt signaling
in alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
317:L381–L391. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Park I, Kim M, Choe K, Song E, Seo H,
Hwang Y, Ahn J, Lee SH, Lee JH, Jo YH, et al: Neutrophils disturb
pulmonary microcirculation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur
Respir J. 53(1800786)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zou Y, Bao S, Wang F, Guo L, Zhu J, Wang
J, Deng X and Li J: FN14 blockade on pulmonary microvascular
endothelial cells improves the outcome of sepsis-induced acute lung
injury. Shock. 49:213–220. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Aziz M, Ode Y, Zhou M, Ochani M, Holodick
NE, Rothstein TL and Wang P: B-1a cells protect mice from
sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Mol Med. 24(26)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Gong S, Wang F, Niu M, Wei G, He
Z, Gu T, Jiang Y, Liu A and Chen P: Granisetron protects
polymicrobial sepsis-induced acute lung injury in mice. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 508:1004–1010. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Englert JA, Bobba C and Baron RM:
Integrating molecular pathogenesis and clinical translation in
sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. JCI Insight.
4(e124061)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Online ahead of
print).
|
|
14
|
Delahanty RJ, Alvarez J, Flynn LM, Sherwin
RL and Jones SS: Development and evaluation of a machine learning
model for the early identification of patients at risk for sepsis.
Ann Emerg Med. 73:334–344. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rezaei M, Mokhtari MJ, Bayat M, Safari A,
Dianatpuor M, Tabrizi R, Asadabadi T and Borhani-Haghighi A: Long
non-coding RNA H19 expression and functional polymorphism rs217727
are linked to increased ischemic stroke risk. BMC Neurol.
21(54)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wan P, Su W, Zhang Y, Li Z, Deng C, Li J,
Jiang N, Huang S, Long E and Zhuo Y: lncRNA H19 initiates
microglial pyroptosis and neuronal death in retinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Differ. 27:176–191.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Thomas AA, Biswas S, Feng B, Chen S,
Gonder J and Chakrabarti S: lncRNA H19 prevents
endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetologia. 62:517–530. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bitarafan S, Yari M, Broumand MA,
Ghaderian SM, Rahimi M, Mirfakhraie R, Azizi F and Omrani MD:
Association of increased levels of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs with risk of
coronary artery disease. Cell J. 20:564–568. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen MJ, Deng J, Chen C, Hu W, Yuan YC and
Xia ZK: lncRNA H19 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition and
metastasis of esophageal cancer via STAT3/EZH2 axis. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 113:27–36. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Cheng Z, Dai L, Jiang T, Jia L,
Jing X, An L, Wang H and Liu M: Knockdown of long noncoding RNA H19
represses the progress of pulmonary fibrosis through the
transforming growth factor β/Smad3 pathway by regulating miR-140.
Mol Cell Biol. 39:e00143–19. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Fang Y, Hu J, Wang Z, Zong H, Zhang L,
Zhang R and Sun L: lncRNA H19 functions as an Aquaporin 1
competitive endogenous RNA to regulate microRNA-874 expression in
LPS sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother. 105:1183–1191. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zheng JF, Guo NH, Zi FM and Cheng J: Long
non-coding RNA H19 promotes tumorigenesis of multiple myeloma by
activating BRD4 signaling by targeting miR-152-3p. Mol Cell Biol.
40:e00382–19. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu XW, Ma T, Cai Q, Wang L, Song HW and
Liu Z: Elevation of serum PARK7 and IL-8 levels is associated with
acute lung injury in patients with severe sepsis/septic shock. J
Intensive Care Med. 34:662–668. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Mélot C and
Vincent JL: Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome
in critically ill patients. JAMA. 286:1754–1758. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xie W, Lu Q, Wang K, Lu J, Gu X, Zhu D,
Liu F and Guo Z: miR-34b-5p inhibition attenuates lung inflammation
and apoptosis in an LPS-induced acute lung injury mouse model by
targeting progranulin. J Cell Physiol. 233:6615–6631.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Murray A, Gow AJ, Venosa A, Andres J,
Malaviya R, Adler D, Yurkow E, Laskin JD and Laskin DL: Assessment
of mustard vesicant lung injury and anti-TNF-α efficacy in rodents
using live-animal imaging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1480:246–256.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chepurnova DA, Samoilova EV, Anisimov AA,
Verin AD and Korotaeva AA: Compounds of IL-6 receptor complex
during acute lung injury. Bull Exp Biol Med. 164:609–611.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gouda MM and Bhandary YP: Acute lung
injury: IL-17A-mediated inflammatory pathway and its regulation by
curcumin. Inflammation. 42:1160–1169. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yin T, Liu MM, Jin RT, Kong J, Wang SH and
Sun WB: miR-152-3p modulates hepatic carcinogenesis by targeting
cyclin-dependent kinase 8. Pathol Res Pract.
215(152406)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li L, Zhang L, Zhao X, Cao J, Li J and Chu
G: Downregulation of miR-152 contributes to the progression of
liver fibrosis via targeting Gli3 in vivo and in vitro. Exp Ther
Med. 18:425–434. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang WL, Yu DJ and Zhong M: lncRNA HAGLROS
accelerates the progression of lung carcinoma via sponging
microRNA-152. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:6531–6538.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Moya L, Meijer J, Schubert S, Matin F and
Batra J: Assessment of miR-98-5p, miR-152-3p, miR-326 and miR-4289
expression as biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 20(1154)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang R, Bai Z, Wen X, Du H, Zhou L, Tang
Z, Yang Z and Ma W: miR-152-3p regulates cell proliferation,
invasion and extracellular matrix expression through by targeting
FOXF1 in keloid fibroblasts. Life Sci. 234(116779)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dong L, Li H, Zhang S and Yang G: miR-148
family members are putative biomarkers for sepsis. Mol Med Rep.
19:5133–5141. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|