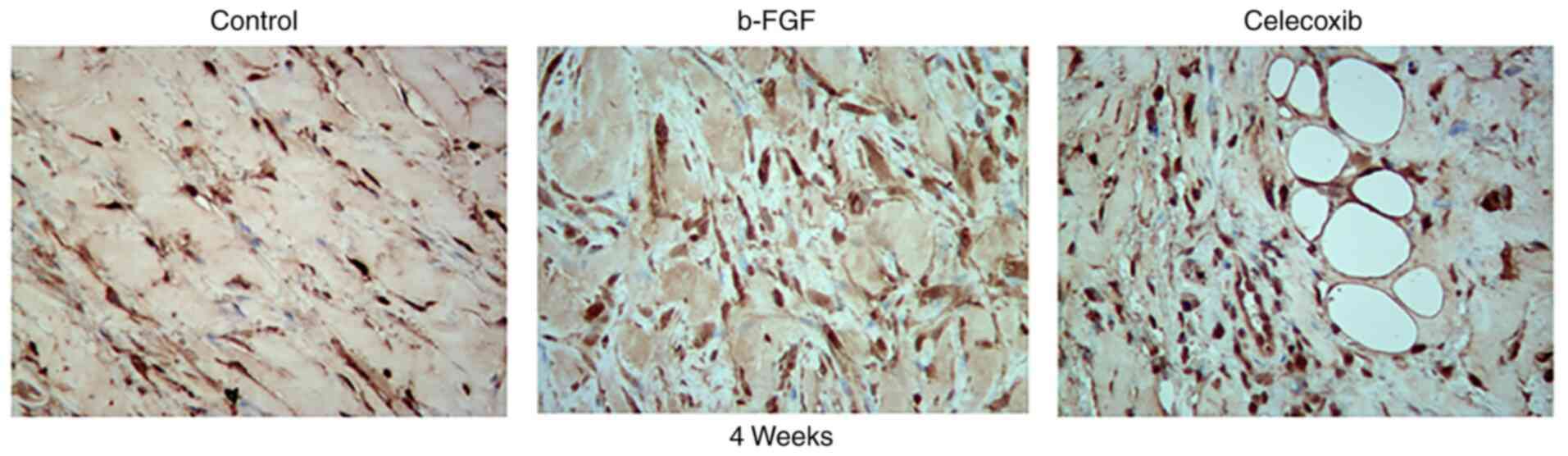
|
1
|
You Y, Li Y, Xiao Y and Zhang J:
Propranolol vs. steroids in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas:
A meta-analysis. Mol Clin Oncol. 15(156)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang Q, Xiang B, Chen S and Ji Y: Efficacy
and safety of oral atenolol for the treatment of infantile
haemangioma: A systematic review. Australas J Dermatol. 60:181–185.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Satterfield KR and Chambers CB: Current
treatment and management of infantile hemangiomas. Surv Ophthalmol.
64:608–618. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Itinteang T, Vishvanath A, Day DJ and Tan
ST: Mesenchymal stem cells in infantile haemangioma. J Clin Pathol.
64:232–236. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Li K, Li L, Xu C and Xiang
B: Signaling pathways in the development of infantile hemangioma. J
Hematol Oncol. 7(13)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Koki AT and Masferrer JL: Celecoxib: A
specific COX-2 inhibitor with anticancer properties. Cancer
Control. 9:28–35. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xie C, Xu X, Wang X, Wei S, Shao L, Chen
J, Cai J and Jia L: Cyclooxygenase-2 induces angiogenesis in
pancreatic cancer mediated by prostaglandin E2. Oncol
Lett. 16:940–948. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li J, Hao Q, Cao W, Vadgama JV and Wu Y:
Celecoxib in breast cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer Manag
Res. 10:4653–4667. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li F, Fan C, Zeng B, Zhang C, Chai Y, Liu
S and Ouyang Y: Celecoxib suppresses fibroblast proliferation and
collagen expression by inhibiting ERK1/2 and SMAD2/3
phosphorylation. Mol Med Rep. 5:827–831. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Esbona K, Inman D, Saha S, Jeffery J,
Schedin P, Wilke L and Keely P: COX-2 modulates mammary tumor
progression in response to collagen density. Breast Cancer Res.
18(35)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Oak NR, Gumucio JP, Flood MD, Saripalli
AL, Davis ME, Harning JA, Lynch EB, Roche SM, Bedi A and Mendias
CL: Inhibition of 5-LOX, COX-1, and COX-2 increases tendon healing
and reduces muscle fibrosis and lipid accumulation after rotator
cuff repair. Am J Sports Med. 42:2860–2868. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yuan SM, Guo Y, Zhou XJ, Shen WM and Chen
HN: Rosiglitazone accentuates the adipogenesis of
hemangioma-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced by adipogenic
media. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:1741–1746. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu XW, Wei D, Gao YS, Du HZ, Yu BY, Li RM,
Qian CM, Luo XJ, Yuan ST, Wang JS and Sun L: Synergistic
combination of DT-13 and Topotecan inhibits aerobic glycolysis in
human gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells via NM IIA/EGFR/HK II axis. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:6622–6634. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yuan SM, Guo Y, Wang Q, Xu Y, Wang M, Chen
HN and Shen WM: Over-expression of PPAR-γ2 gene enhances the
adipogenic differentiation of hemangioma-derived mesenchymal stem
cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 8:115817–115828.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chu TH, Chan HH, Kuo HM, Liu LF, Hu TH,
Sun CK, Kung ML, Lin SW, Wang EM, Ma YL, et al: Celecoxib
suppresses hepatoma stemness and progression by up-regulating PTEN.
Oncotarget. 5:1475–1490. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Atiakshin D, Buchwalow I and Tiemann M:
Mast cells and collagen fibrillogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol.
154:21–40. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen L, Li J, Zhang J, Dai C, Liu X, Wang
J, Gao Z, Guo H, Wang R, Lu S, et al: S100A4 promotes liver
fibrosis via activation of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol.
62:156–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wnęk A, Andrzejewska E, Kobos J, Taran K
and Przewratil P: Molecular and immunohistochemical expression of
apoptotic proteins Bax, Bcl-2 and Caspase 3 in infantile hemangioma
tissues as an effect of propranolol treatment. Immunol Lett.
185:27–31. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yuan SM, Chen RL, Chen HN, Shen WM and
Zhou XJ: The role of the expression of PPAR-gamma gene in the
adipogenesis in hemangioma evolution. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 29:45–48. 2013.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Ishay-Ronen D, Diepenbruck M, Kalathur
RKR, Sugiyama N, Tiede S, Ivanek R, Bantug G, Morini MF, Wang J,
Hess C and Christofori G: Gain fat-lose metastasis: Converting
invasive breast cancer cells into adipocytes inhibits cancer
metastasis. Cancer Cell. 35:17–32.e6. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Veglia F, Tyurin VA, Blasi M, De Leo A,
Kossenkov AV, Donthireddy L, To TKJ, Schug Z, Basu S, Wang F, et
al: Fatty acid transport protein 2 reprograms neutrophils in
cancer. Nature. 569:73–78. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tian F, Zhang YJ and Wang YH: Effects of
celecoxib on expression of PPARγ and NF-κB in type 2 diabetes rats
with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
24:590–595. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Lima LH, Farah ME, Gum G, Ko P and de
Carvalho RAP: Sustained and targeted episcleral delivery of
celecoxib in a rabbit model of retinal and choroidal
neovascularization. Int J Retina Vitreous. 4(31)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bundscherer A, Hafner C, Maisch T, Becker
B, Landthaler M and Vogt T: Antiproliferative and proapoptotic
effects of rapamycin and celecoxib in malignant melanoma cell
lines. Oncol Rep. 19:547–553. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Maggi LB Jr, Sadeghi H, Weigand C, Scarim
AL, Heitmeier MR and Corbett JA: Anti-inflammatory actions of
15-deoxy-delta 12,14-prostaglandin J2 and troglitazone: Evidence
for heat shock-dependent and -independent inhibition of
cytokine-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression.
Diabetes. 49:346–355. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Harbi S, Wang R, Gregory M, Hanson N,
Kobylarz K, Ryan K, Deng Y, Lopez P, Chiriboga L and Mignatti P:
Infantile hemangioma originates from a dysregulated but not fully
transformed multipotent stem cell. Sci Rep. 6(35811)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li HH, Lou Y, Zhang RR, Xie J and Cao DS:
Propranolol accelerats hemangioma stem cell transformation into
adipocyte. Ann Plast Surg. 83:e5–e13. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
England RW, Hardy KL, Kitajewski AM, Wong
A, Kitajewski JK, Shawber CJ and Wu JK: Propranolol promotes
accelerated and dysregulated adipogenesis in hemangioma stem cells.
Ann Plast Surg. 73 (Suppl 1):S119–S124. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wei D, Wang L, He Y, Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese
JL and Xie K: Celecoxib inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in and reduces angiogenesis and metastasis of human
pancreatic cancer via suppression of Sp1 transcription factor
activity. Cancer Res. 64:2030–2038. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Knopfová L and Smarda J: The use of Cox-2
and PPARγ signaling in anti-cancer therapies. Exp Ther Med.
1:257–264. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mingyuan X, Qianqian P, Shengquan X,
Chenyi Y, Rui L, Yichen S and Jinghong X: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α activates transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling
and increases collagen deposition in dermal fibroblasts.
Oncotarget. 9:3188–3197. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ma Y, Kakudo N, Morimoto N, Lai F,
Taketani S and Kusumoto K: Fibroblast growth factor-2 stimulates
proliferation of human adipose-derived stem cells via Src
activation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10(350)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang Y, Xia T, Zhi W, Wei L, Weng J, Zhang
C and Li X: Promotion of skin regeneration in diabetic rats by
electrospun core-sheath fibers loaded with basic fibroblast growth
factor. Biomaterials. 32:4243–4254. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li F, Liu S, Ouyang Y, Fan C, Wang T,
Zhang C, Zeng B, Chai Y and Wang X: Effect of celecoxib on
proliferation, collagen expression, ERK1/2 and SMAD2/3
phosphorylation in NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 678:1–5.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fairweather M, Heit YI, Buie J, Rosenberg
LM, Briggs A, Orgill DP and Bertagnolli MM: Celecoxib inhibits
early cutaneous wound healing. J Surg Res. 194:717–724.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Olson JM, Haas AW, Lor J, McKee HS and
Cook ME: A comparison of the anti-inflammatory effects of Cis-9,
trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid to celecoxib in the
collagen-induced arthritis model. Lipids. 52:151–159.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Salib CG, Reina N, Trousdale WH, Limberg
AK, Tibbo ME, Jay AG, Robin JX, Turner TW, Jones CR, Paradise CR,
et al: Inhibition of COX-2 pathway as a potential prophylaxis
against arthrofibrogenesis in a rabbit model of joint contracture.
J Orthop Res. 37:2609–2620. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|