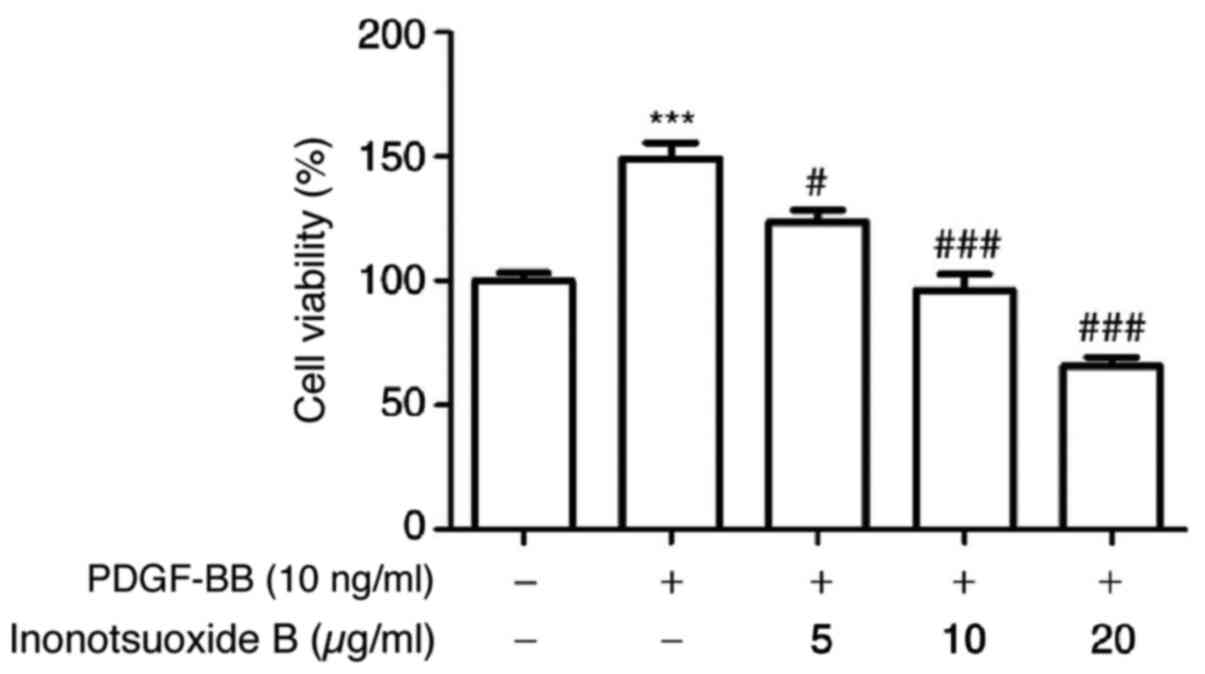
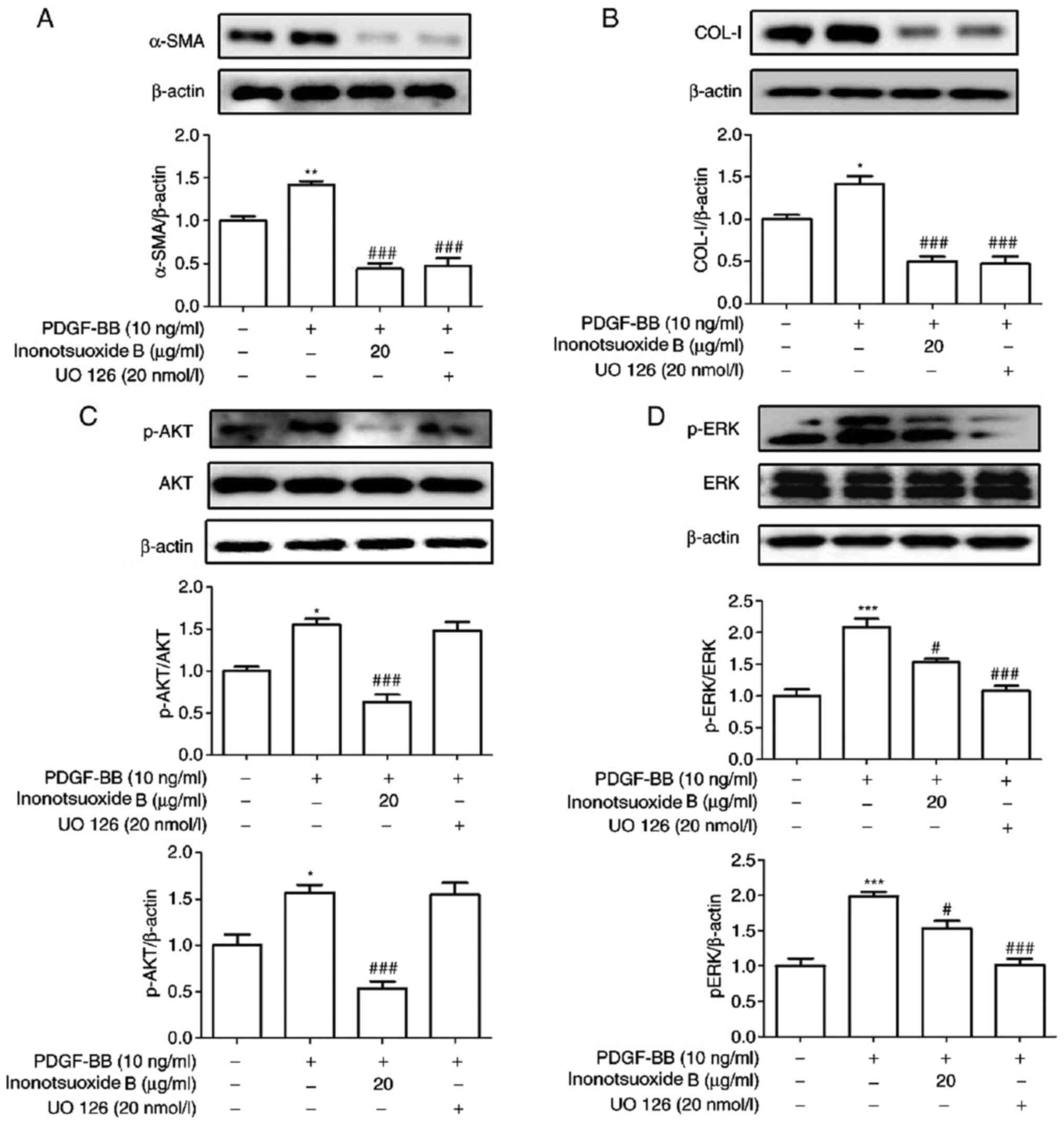
|
1
|
Ping J, Li JT, Liao ZX, Shang L and Wang
H: Indole-3-carbinol inhibits hepatic stellate cells proliferation
by blocking NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species/p38 MAPK pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 650:656–662. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tsai MK, Lin YL and Huang YT: Differential
inhibitory effects of salvianolic acids on activation of rat
hepatic stellate cells by platelet-derived growth factor. Planta
Med. 77:1495–1503. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang YH, Sun YC, Zuo LQ, Wang YN and Huang
Y: ASIC1a promotes high glucose and PDGF-induced hepatic stellate
cell activation by inducing autophagy through CaMKKβ/ERK signaling
pathway. Toxicol Lett. 300:1–9. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shuping You, Jun Zhao and Long Ma: Effects
of total glycosides of cistanche deserticola on the proliferation
of hepatic stellate cells induced by platelet-derived growth
factor. Chin J Pharmacol. 32:1231–1235. 2016.
|
|
5
|
Choi JH, Hwang YP, Park BH, Choi CY, Chung
YC and Jeong HG: Anthocyanins isolated from the purple-fleshed
sweet potato attenuate the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells
by blocking the PDGF receptor. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
31:212–219. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Youn MJ, Kim JK, Park SY, Kim Y, Kim SJ,
Lee JS, Chai KY, Kim HJ, Cui MX, So HS, et al: Chaga mushroom
(Inonotus obliquus) induces G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis in human
hepatoma HepG2 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 14:511–517.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duru KC, Kovaleva EG, Danilova IG and van
der Bijl P: The pharmacological potential and possible molecular
mechanisms of action of Inonotus obliquus from preclinical studies.
Phytother Res. 33:1966–1980. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kun WU, Wenming Cheng, Chunru Li, et al:
Screening and chemical constituents of anti-tumor active parts of
inonotus obliquus. J Anhui Medical University. 51:1468–1472.
2016.
|
|
9
|
Huang Y, Li X, Wang Y, Wang H, Huang C and
Li J: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic stellate cell
apoptosis through calcium-mediated JNK/P38 MAPK and
Calpain/Caspase-12 pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 394:1–12.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Foo NP, Lin SH, Lee YH, Wu MJ and Wang YJ:
α-Lipoic acid inhibits liver fibrosis through the attenuation of
ROS-triggered signaling in hepatic stellate cells activated by PDGF
and TGF-β. Toxicology. 282:39–46. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang Y, Leng TD, Inoue K, Yang T, Liu M,
Horgen FD, Fleig A, Li J and Xiong ZG: TRPM7 channels play a role
in high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and neuronal
cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 293:14393–14406. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Wang YH, Yang F, Li XF, Tian YY,
Ni MM, Zuo LQ, Meng XM and Huang Y: Effect of Acid-sensing ion
Channel 1a on the process of liver fibrosis under hyperglycemia.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 468:758–765. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li J, Li X, Xu W, Wang S, Hu Z, Zhang Q,
Deng X, Wang J, Zhang J and Guo C: Antifibrotic effects of luteolin
on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by targeting
AKT/mTOR/p70S6K and TGFβ/Smad signalling pathways. Liver Int.
35:1222–1233. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tsai TH, Shih SC, Ho TC, Ma HI, Liu MY,
Chen SL and Tsao YP: Pigment epithelium-derived factor 34-mer
peptide prevents liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell
activation through down-regulation of the PDGF receptor. PLoS One.
9(e95443)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yujie Zhang, Yutao Hong and Lei Jie:
Effects of melatonin on proliferation of HSC-T6 cells induced by
PDGF-BB and its mechanism. J Anhui Med University. 53:12–17.
2018.
|
|
16
|
You SP, Zhao J, Ma L, Tudimat M, Zhang SL
and Liu T: Preventive effects of phenylethanol glycosides from
Cistanche tubulosa on bovine serum albumin-induced hepatic fibrosis
in rats. Daru. 23(52)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expres-sion data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta DeltaC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mazumder AG, Kumari S and Singh D:
Anticonvulsant action of a selective phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
inhibitor LY294002 in pentylenetetrazole-mediated convulsions in
zebrafish. Epilepsy Res. 157(106207)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cole GW Jr, Alleva AM, Zuo JT, Sehgal SS,
Yeow WS, Schrump DS and Nguyen DM: Suppression of pro-metastasis
phenotypes expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma by the PI3K
inhibitor LY294002 or the MEK inhibitor UO126. Anticancer Res.
26:809–821. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Hepatic
stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Semin Liver Dis. 21:437–452. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Gao J, Zhang D, Zhang J, Ma J and
Jiang H: New insights into the antifibrotic effects of sorafenib on
hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 53:132–144.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Balandaykin ME and Zmitrovich IV: Review
on chaga medicinal mushroom, inonotus obliquus (Higher
Basidiomycetes): Realm of medicinal applications and approaches on
estimating its resource potential. Int J Med Mushrooms. 17:95–104.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Glamočlija J, Ćirić A, Nikolić M,
Fernandes Â, Barros L, Calhelha RC, Ferreira IC, Soković M and van
Griensven LJ: Chemical characterization and biological activity of
Chaga (Inonotus obliquus), a medicinal ‘mushroom’. J
Ethnopharmacol. 162:323–332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang GJ, Huang YJ, Chen DH and Lin YL:
Ganoderma lucidum extract attenuates the proliferation of
hepatic stellate cells by blocking the PDGF receptor. Phytother
Res. 23:833–839. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jiang M, Wu YL, Li X, Zhang Y, Xia KL, Cui
BW, Lian LH and Nan JX: Oligomeric proanthocyanidin derived from
grape seeds inhibited NF-κB signaling in activated HSC: Involvement
of JNK/ERK MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.
93:674–680. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kao YH, Chen PH, Wu TY, Lin YC, Tsai MS,
Lee PH, Tai TS, Chang HR and Sun CK: Lipopolysaccharides induce
Smad2 phosphorylation through PI3K/Akt and MAPK cascades in HSC-T6
hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 184:37–46. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fang L, Zhan S, Huang C, Cheng X, Lv X, Si
H and Li J: TRPM7 channel regulates PDGF-BB-induced proliferation
of hepatic stellate cells via PI3K and ERK pathways. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 27:713–725. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
He W, Shi F, Zhou ZW, Li B, Zhang K, Zhang
X, Ouyang C, Zhou SF and Zhu X: A bioinformatic and mechanistic
study elicits the antifibrotic effect of ursolic acid through the
attenuation of oxidative stress with the involvement of ERK,
PI3K/Akt, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in human hepatic stellate
cells and rat liver. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:3989–4104.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li Jinxing, Zhu Xianli and Li Yu: Rats
with diffuse brain injury block the ERK pathway and down-regulate
the expression of MMP-9 mRNA in brain tissue. Chin J Clin
Neurosurg. 11:288–291. 2006.
|
|
31
|
You Linlin, Dai Lili, et al: Inhibitory
effect of Danshensu on hepatic stellate cells stimulated by
PDGF-BB. J Third Military Med University. 33:1610–1614. 2011.
|
|
32
|
Xu DD, Li XF, Li YH, Liu YH, Huang C, Meng
XM and Li J: TIPE2 attenuates liver fibrosis by reversing the
activated hepatic stellate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
498:199–206. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|