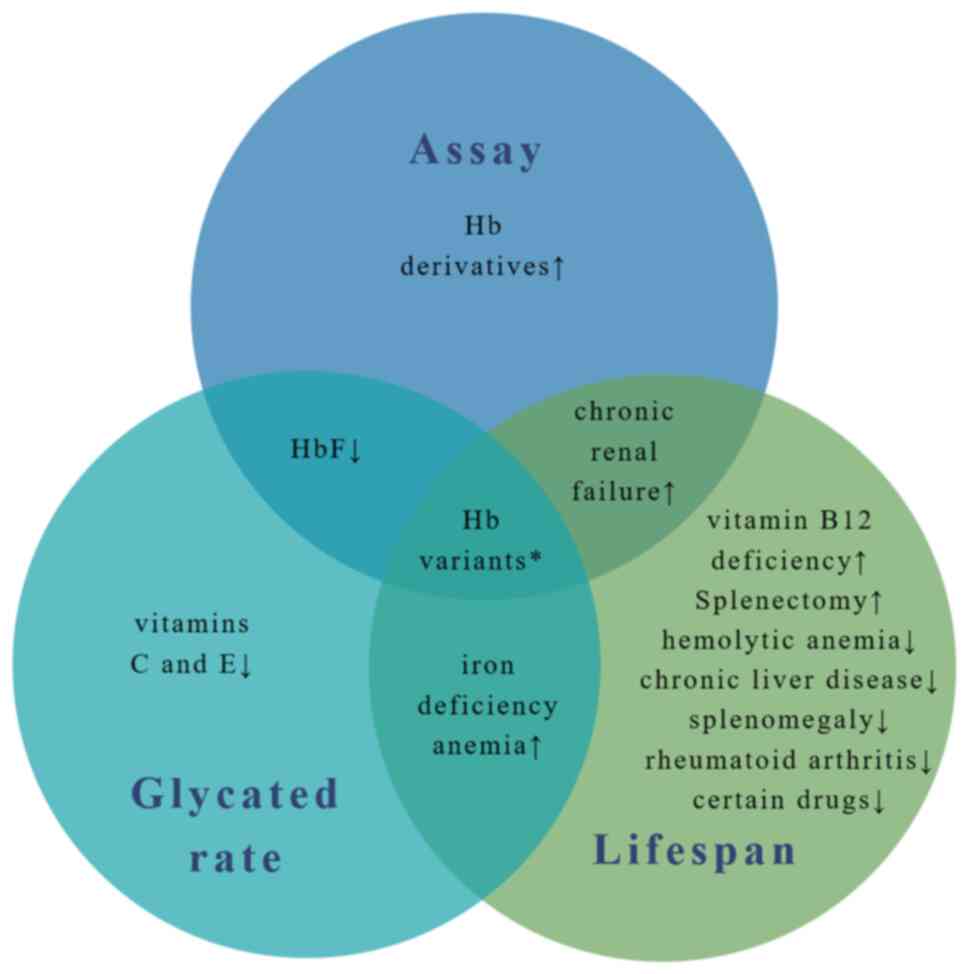
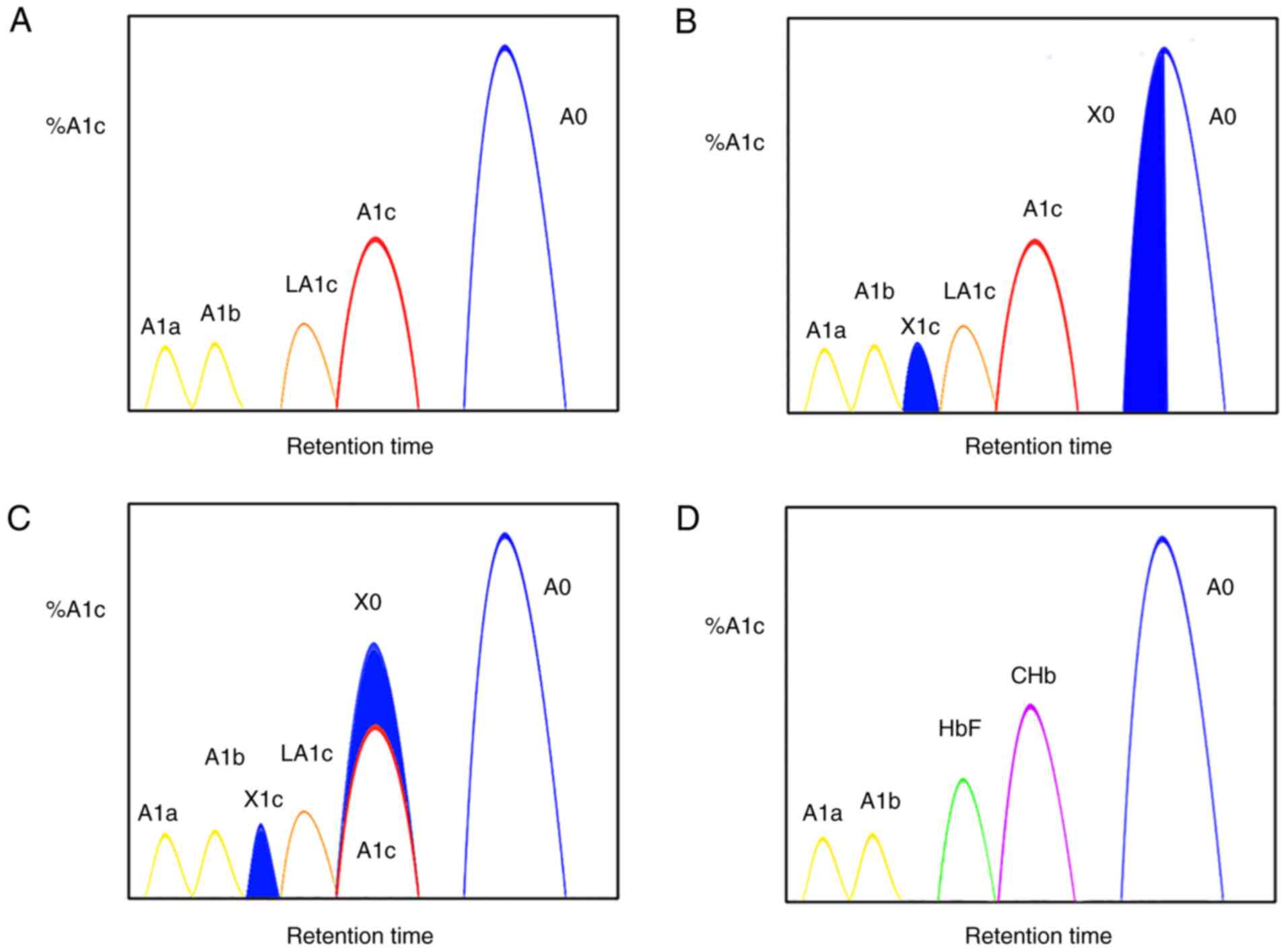
|
1
|
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration.
Sarwar N, Gao P, Seshasai SR, Gobin R, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio
E, Ingelsson E, Lawlor DA, Selvin E, et al: Diabetes mellitus,
fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease:
A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet.
375:2215–2222. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial
Research Group. Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford
O, Davis M, Rand L and Siebert C: The effect of intensive treatment
of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term
complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med.
329:977–986. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Intensive blood-glucose control with
sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and
risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33).
UK prospective diabetes study (UKPDS) group. Lancet. 352:837–853.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
American Diabetes Association. 2.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care
in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 44 (Suppl 1):S15–S33.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Weykamp C, John WG, Mosca A, Hoshino T,
Little R, Jeppsson JO, Goodall I, Miedema K, Myers G, Reinauer H,
et al: The IFCC reference measurement system for HbA1c: A 6-year
progress report. Clin Chem. 54:240–248. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bunn HF: Evaluation of glycosylated
hemoglobin diabetic patients. Diabetes. 30:613–617. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mossine VV and Mawhinney TP:
1-Amino-1-deoxy-D-fructose (‘fructosamine’) and its derivatives.
Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 64:291–402. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shapiro R, McManus MJ, Zalut C and Bunn
HF: Sites of nonenzymatic glycosylation of human hemoglobin A. J
Biol Chem. 255:3120–3127. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harris NS, Weaver KD, Beal SG and Winter
WE: The interaction between Hb A1C and selected genetic factors in
the African American population in the USA. J Appl Lab Med.
6:167–179. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Weykamp C: HbA1c: A review of analytical
and clinical aspects. Ann Lab Med. 33:393–400. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ang SH, Thevarajah M, Alias Y and Khor SM:
Current aspects in hemoglobin A1c detection: A review. Clin Chim
Acta. 439:202–211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rhea JM and Molinaro R: Pathology
consultation on HbA(1c) methods and interferences. Am J Clin
Pathol. 141:5–16. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jaisson S, Leroy N, Meurice J, Guillard E
and Gillery P: First evaluation of Capillarys 2 Flex
Piercing® (Sebia) as a new analyzer for HbA1c assay by
capillary electrophoresis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:1769–1775.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Teodoro-Morrison T, Janssen MJ, Mols J,
Hendrickx BH, Velmans MH, Lotz J, Lackner K, Lennartz L, Armbruster
D, Maine G and Yip PM: Evaluation of a next generation direct whole
blood enzymatic assay for hemoglobin A1c on the ARCHITECT c8000
chemistry system. Clin Chem Lab Med. 53:125–132. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Little RR, Rohlfing CL, Hanson S, Connolly
S, Higgins T, Weykamp CW, D'Costa M, Luzzi V, Owen WE and Roberts
WL: Effects of hemoglobin (Hb) E and HbD traits on measurements of
glycated Hb (HbA1c) by 23 methods. Clin Chem. 54:1277–1282.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yun YM, Ji M, Ko DH, Chun S, Kwon GC, Lee
K, Song SH, Seong MW, Park SS and Song J: Hb variants in Korea:
Effect on HbA1c using five routine methods. Clin Chem Lab Med.
55:1234–1242. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xu A, Chen W, Xia Y, Zhou Y and Ji L:
Effects of common hemoglobin variants on HbA1c measurements in
China: Results for α- and β-globin variants measured by six
methods. Clin Chem Lab Med. 56:1353–1361. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rohlfing CL, Connolly SM, England JD,
Hanson SE, Moellering CM, Bachelder JR and Little RR: The effect of
elevated fetal hemoglobin on hemoglobin A1c results: Five common
hemoglobin A1c methods compared with the IFCC reference method. Am
J Clin Pathol. 129:811–814. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chachou A, Randoux C, Millart H, Chanard J
and Gillery P: Influence of in vivo hemoglobin carbamylation on
HbA1c measurements by various methods. Clin Chem Lab Med.
38:321–326. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Weykamp C, Kemna E, Leppink S and
Siebelder C: Glycation rate of haemoglobins S, C, D, E, J and G,
and analytical interference on the measurement of HbA1c with
affinity chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 53:e207–e210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Coban E, Ozdogan M and Timuragaoglu A:
Effect of iron deficiency anemia on the levels of hemoglobin A1c in
nondiabetic patients. Acta Haematol. 112:126–128. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Koga M, Morita S, Saito H, Mukai M and
Kasayama S: Association of erythrocyte indices with glycated
haemoglobin in pre-menopausal women. Diabet Med. 24:843–847.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Son JI, Rhee SY, Woo JT, Hwang JK, Chin
SO, Chon S, Oh S, Kim SW and Kim YS: Hemoglobin a1c may be an
inadequate diagnostic tool for diabetes mellitus in anemic
subjects. Diabetes Metab J. 37:343–348. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Thom CS, Dickson CF, Gell DA and Weiss MJ:
Hemoglobin variants: Biochemical properties and clinical
correlates. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
3(a011858)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dessi M, Pieri M, Pignalosa S, Martino FG
and Zenobi R: Performances of capillary electrophoresis and HPLC
methods in HbA1c determination: Diagnostic accuracy in HbS and
HbD-Iran variants' presence. J Clin Lab Anal. 29:57–60.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Suo M, Wen D, Wang W, Zhang D, Xu S, Wang
X and Hu T: False measurement of glycated hemoglobin in patients
without hemoglobin A. Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20180128)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nathan DM, Kuenen J, Borg R, Zheng H,
Schoenfeld D and Heine RJ: A1c-Derived Average Glucose Study Group.
Translating the A1C assay into estimated average glucose values.
Diabetes Care. 31:1473–1478. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Franco RS: Measurement of red cell
lifespan and aging. Transfus Med Hemother. 39:302–307.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Goldstein DE, Little RR, Lorenz RA, Malone
JI, Nathan D, Peterson CM and Sacks DB: Tests of glycemia in
diabetes. Diabetes Care. 27:1761–1773. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Piel FB, Howes RE, Patil AP, Nyangiri OA,
Gething PW, Bhatt S, Williams TN, Weatherall DJ and Hay SI: The
distribution of haemoglobin C and its prevalence in newborns in
Africa. Sci Rep. 3(1671)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ouzzif Z, El Maataoui A, Oukhedda N,
Messaoudi N, Mikdam M, Abdellatifi M and Doghmi K: Hemoglobinosis C
in Morocco : A report of 111 cas. Tunis Med. 95:229–233.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kato GJ, Piel FB, Reid CD, Gaston MH,
Ohene-Frempong K, Krishnamurti L, Smith WR, Panepinto JA,
Weatherall DJ, Costa FF and Vichinsky EP: Sickle cell disease. Nat
Rev Dis Primers. 4(18010)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Piel FB, Steinberg MH and Rees DC: Sickle
cell disease. N Engl J Med. 376:1561–1573. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lacy ME, Wellenius GA, Sumner AE, Correa
A, Carnethon MR, Liem RI, Wilson JG, Sacks DB, Jacobs DR Jr, Carson
AP, et al: Association of sickle cell trait with hemoglobin A1c in
African Americans. JAMA. 317:507–515. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Qiu CC, Kasten-Jolly J and Abraham EC:
Human red cell acetyltransferase. Life Sci. 42:2739–2748.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen D, Crimmins DL, Hsu FF, Lindberg FP
and Scott MG: Hemoglobin Raleigh as the cause of a falsely
increased hemoglobin A1C in an automated ion-exchange HPLC method.
Clin Chem. 44:1296–1301. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koga M, Inada S, Shimizu S, Hatazaki M,
Umayahara Y and Nishihara E: Aldimine formation reaction, the first
step of the maillard early-phase reaction, might be enhanced in
variant Hemoglobin, Hb Himeji. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 45:643–649.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bissé E, Schauber C, Zorn N, Epting T,
Eigel A, Van Dorsselaer A, Wieland H, Kister J and Kiger L:
Hemoglobin Görwihl [alpha2beta(2)5(A2)Pro->Ala], an
electrophoretically silent variant with impaired glycation. Clin
Chem. 49:137–143. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nakanishi T, Miyazaki A, Kishikawa M,
Shimizu A, Aoki K and Kikuchi M: Hb Sagami [beta
139(H17)Asn->Thr]: A new hemoglobin variant not detected by
isoelectrofocusing and propan-2-ol test, was detected by
electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom.
33:565–569. 1998.
|
|
40
|
Kabytaev K, Connolly S, Rohlfing CL, Sacks
DB, Stoyanov AV and Little RR: Higher degree of glycation of
hemoglobin S compared to hemoglobin A measured by mass
spectrometry: Potential impact on HbA1c testing. Clin Chim Acta.
458:40–43. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Watanabe T, Kato K, Yamada D, Midorikawa
S, Sato W, Shiga M, Otsuka Y, Miura M, Harano K and Harano T: A
nondiabetic case of hemoglobin variant (Hb Niigata) with
inappropriately high and low HbA1c titers detected by different
methods. Clin Chem. 44:1562–1564. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shah SC, Malone JI, Boissel JP and Kasper
TJ: Hemoglobin South Florida. New variant with normal
electrophoretic pattern mistaken for glycosylated hemoglobin.
Diabetes. 35:1073–1076. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Langdown JV, Williamson D, Beresford CH,
Gibb I, Taylor R and Deacon-Smith R: A new beta chain variant, Hb
Tyne [beta 5(A2)Pro->Ser]. Hemoglobin. 18:333–336.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Joly P, Garcia C, Lacan P, Couprie N and
Francina A: Two new hemoglobin variants: Hb Aix-Les-Bains
[β5(A2)Pro→Leu; HBB:c.17 C>T] and Hb Dubai [α122(H5)His→Leu
(α2); HBA2:c.368 A>T]. Hemoglobin. 35:147–151. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Karsegard J, Wicky J, Mensi N, Caulfield A
and Philippe J: Spurious glycohemoglobin values associated with
hydroxyurea treatment. Diabetes Care. 20:1211–1212. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bry L, Chen PC and Sacks DB: Effects of
hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays
for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 47:153–163. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stim J, Shaykh M, Anwar F, Ansari A,
Arruda JA and Dunea G: Factors determining hemoglobin carbamylation
in renal failure. Kidney Int. 48:1605–1610. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jaisson S, Leroy N, Guillard E, Desmons A
and Gillery P: Analytical performances of the D-100TM hemoglobin
testing system (Bio-Rad) for HbA1c assay. Clin Chem Lab Med.
53:1473–1479. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Weykamp CW, Miedema K, de Haan T and
Doelman CJ: Carbamylated hemoglobin interference in glycohemoglobin
assays. Clin Chem. 45:438–440. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Little RR, Rohlfing CL, Tennill AL, Hanson
SE, Connolly S, Higgins T, Wiedmeyer CE, Weykamp CW, Krause R and
Roberts W: Measurement of Hba(1C) in patients with chronic renal
failure. Clin Chim Acta. 418:73–76. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Dolscheid-Pommerich RC, Kirchner S, Weigel
C, Eichhorn L, Conrad R, Stoffel-Wagner B and Zur B: Impact of
carbamylation on three different methods, HPLC, capillary
electrophoresis and TINIA of measuring HbA1c levels in patients
with kidney disease. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 108:15–22.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ng JM, Cooke M, Bhandari S, Atkin SL and
Kilpatrick ES: The effect of iron and erythropoietin treatment on
the A1C of patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
Diabetes Care. 33:2310–2313. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kilpatrick ES and Atkin SL: Using
haemoglobin A(1c) to diagnose type 2 diabetes or to identify people
at high risk of diabetes. BMJ. 348(g2867)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bridges KR, Schmidt GJ, Jensen M, Cerami A
and Bunn HF: The acetylation of hemoglobin by aspirin. In vitro and
in vivo. J Clin Invest. 56:201–207. 1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Unnikrishnan R, Anjana RM and Mohan V:
Drugs affecting HbA1c levels. Indian J Endocrinol Metab.
16:528–531. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Camargo JL, Stifft J and Gross JL: The
effect of aspirin and vitamins C and E on HbA1c assays. Clin Chim
Acta. 372:206–209. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Weykamp CW, Penders TJ, Siebelder CW,
Muskiet FA and van der Slik W: Interference of carbamylated and
acetylated hemoglobins in assays of glycohemoglobin by HPLC,
electrophoresis, affinity chromatography, and enzyme immunoassay.
Clin Chem. 39:138–142. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Davie SJ, Gould BJ and Yudkin JS: Effect
of vitamin C on glycosylation of proteins. Diabetes. 41:167–173.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Xu R, Zhang S, Tao A, Chen G and Zhang M:
Influence of vitamin E supplementation on glycaemic control: A
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. PLoS One.
9(e95008)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Jain SK and Palmer M: The effect of oxygen
radicals metabolites and vitamin E on glycosylation of proteins.
Free Radic Biol Med. 22:593–596. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ceriello A, Giugliano D, Quatraro A,
Donzella C, Dipalo G and Lefebvre PJ: Vitamin E reduction of
protein glycosylation in diabetes. New prospect for prevention of
diabetic complications? Diabetes Care. 14:68–72. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Shoff SM, Mares-Perlman JA, Cruickshanks
KJ, Klein R, Klein BE and Ritter LL: Glycosylated hemoglobin
concentrations and vitamin E, vitamin C, and beta-carotene intake
in diabetic and nondiabetic older adults. Am J Clin Nutr.
58:412–416. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Weykamp CW, Penders TJ, Baadenhuijsen H,
Muskiet FA, Martina W and van der Slik W: Vitamin C and
glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 41:713–716. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Shah AD, Fox RK and Rushakoff RJ: Falsely
decreased HbA1c in a type 2 diabetic patient treated with dapsone.
Endocr Pract. 20:e229–e232. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Basavaraj GS, Gupta RD, Patel B, Jebasingh
F, George AA, Peter D, George L, Paul TV and Thomas N: Erroneous
reduction of HbA1c levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
on dapsone treatment for Hansen's disease-a single-center
retrospective cohort study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol.
88:519–522. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Mitchell K and Mukhopadhyay B:
Drug-Induced Falsely Low A1C: Report of a case series from a
diabetes clinic. Clin Diabetes. 36:80–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Diop ME, Bastard JP, Meunier N, Thévenet
S, Maachi M, Capeau J, Pialoux G and Vigouroux C: Inappropriately
low glycated hemoglobin values and hemolysis in HIV-infected
patients. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 22:1242–1247. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Robertson M: Artificially low HbA1c
associated with treatment with ribavirin. BMJ.
336(505)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Gram-Hansen P, Eriksen J, Mourits-Andersen
T and Olesen L: Glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in iron- and
vitamin B12 deficiency. J Intern Med. 227:133–136. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kim C, Bullard KM, Herman WH and Beckles
GL: Association between iron deficiency and A1C Levels among adults
without diabetes in the National Health and Nutrition Examination
Survey, 1999-2006. Diabetes Care. 33:780–785. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Attard SM, Herring AH, Wang H, Howard AG,
Thompson AL, Adair LS, Mayer-Davis EJ and Gordon-Larsen P:
Implications of iron deficiency/anemia on the classification of
diabetes using HbA1c. Nutr Diabetes. 5(e166)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Cavagnolli G, Pimentel AL, Freitas PA,
Gross JL and Camargo JL: Factors affecting A1C in non-diabetic
individuals: Review and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 445:107–114.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sundaram RC, Selvaraj N, Vijayan G, Bobby
Z, Hamide A and Rattina Dasse N: Increased plasma malondialdehyde
and fructosamine in iron deficiency anemia: Effect of treatment.
Biomed Pharmacother. 61:682–685. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Guo W, Zhou Q, Jia Y and Xu J: Increased
levels of glycated hemoglobin A1c and iron deficiency Anemia: A
review. Med Sci Monit. 25:8371–8378. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Willekens FL, Roerdinkholder-Stoelwinder
B, Groenen-Döpp YA, Bos HJ, Bosman GJ, van den Bos AG, Verkleij AJ
and Were JM: Hemoglobin loss from erythrocytes in vivo results from
spleen-facilitated vesiculation. Blood. 101:747–751.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Schnedl WJ, Wallner SJ, Piswanger C,
Krause R and Lipp RW: Glycated hemoglobin and liver disease in
diabetes mellitus. Wien Med Wochenschr. 155:411–415.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Bernstein RM, Freedman DB, Liyanage SP and
Dandona P: Glycosylated haemoglobin in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 41:604–606. 1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Pani LN, Korenda L, Meigs JB, Driver C,
Chamany S, Fox CS, Sullivan L, D'Agostino RB and Nathan DM: Effect
of aging on A1C levels in individuals without diabetes: Evidence
from the Framingham Offspring Study and the National Health and
Nutrition Examination Survey 2001-2004. Diabetes Care.
31:1991–1996. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ziemer DC, Kolm P, Weintraub WS, Vaccarino
V, Rhee MK, Twombly JG, Narayan KM, Koch DD and Phillips LS:
Glucose-independent, black-white differences in hemoglobin A1c
levels: A cross-sectional analysis of 2 studies. Ann Intern Med.
152:770–777. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Herman WH, Ma Y, Uwaifo G, Haffner S, Kahn
SE, Horton ES, Lachin JM, Montez MG, Brenneman T and Barrett-Connor
E: Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. Differences in A1C
by race and ethnicity among patients with impaired glucose
tolerance in the diabetes prevention program. Diabetes Care.
30:2453–2457. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Bergenstal RM, Gal RL, Connor CG,
Gubitosi-Klug R, Kruger D, Olson BA, Willi SM, Aleppo G, Weinstock
RS, Wood J, et al: Racial differences in the relationship of
glucose concentrations and hemoglobin A1c Levels. Ann Intern Med.
167:95–102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Selvin E, Steffes MW, Zhu H, Matsushita K,
Wagenknecht L, Pankow J, Coresh J and Brancati FL: Glycated
hemoglobin, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in nondiabetic
adults. N Engl J Med. 362:800–811. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Nakatani R, Murata T, Usui T, Moriyoshi K,
Komeda T, Masuda Y, Kakita-Kobayashi M, Tagami T, Imashuku S, Kono
S, et al: Importance of the average glucose level and estimated
glycated hemoglobin in a diabetic patient with hereditary hemolytic
Anemia and liver cirrhosis. Intern Med. 57:537–543. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda
B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA,
Ogurtsova K, et al: Global and regional diabetes prevalence
estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from
the International diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th)
edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 157(107843)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
American Diabetes Association. Standards
of medical care in diabetes-2013. Diabetes Care. 36 (Suppl
1):S11–S66. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Bergman M, Abdul-Ghani M, DeFronzo RA,
Manco M, Sesti G, Fiorentino TV, Ceriello A, Rhee M, Phillips LS,
Chung S, et al: Review of methods for detecting glycemic disorders.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 165(108233)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Campbell L, Pepper T and Shipman K: HbA1c:
A review of non-glycaemic variables. J Clin Pathol. 72:12–19.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Xu A, Sun J, Li J, Chen W, Zheng R, Han Z
and Ji L: Hb I: A α-globin chain variant causing unexpected
HbA1c results. J Clin Lab Anal.
33(e22671)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|