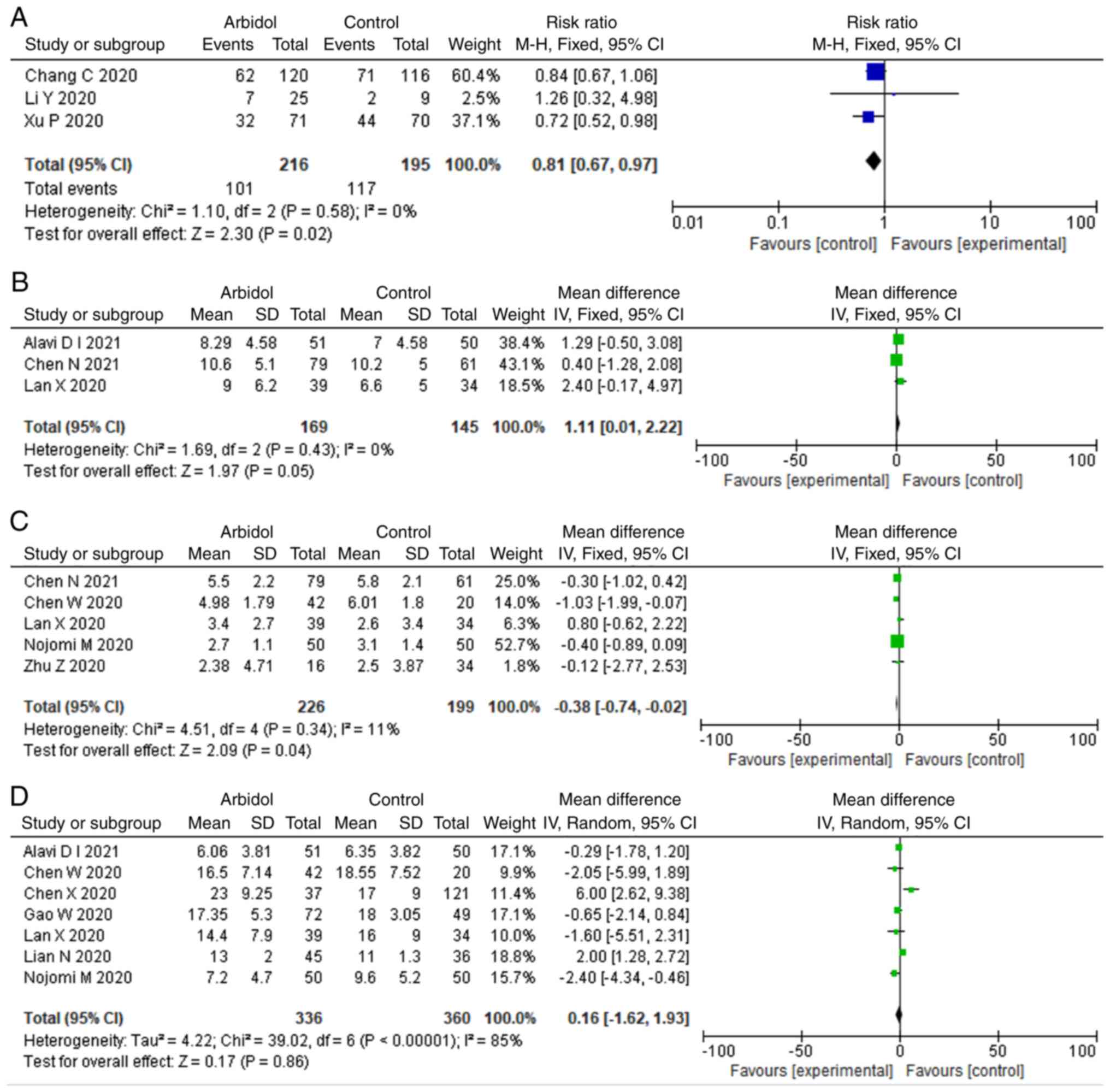
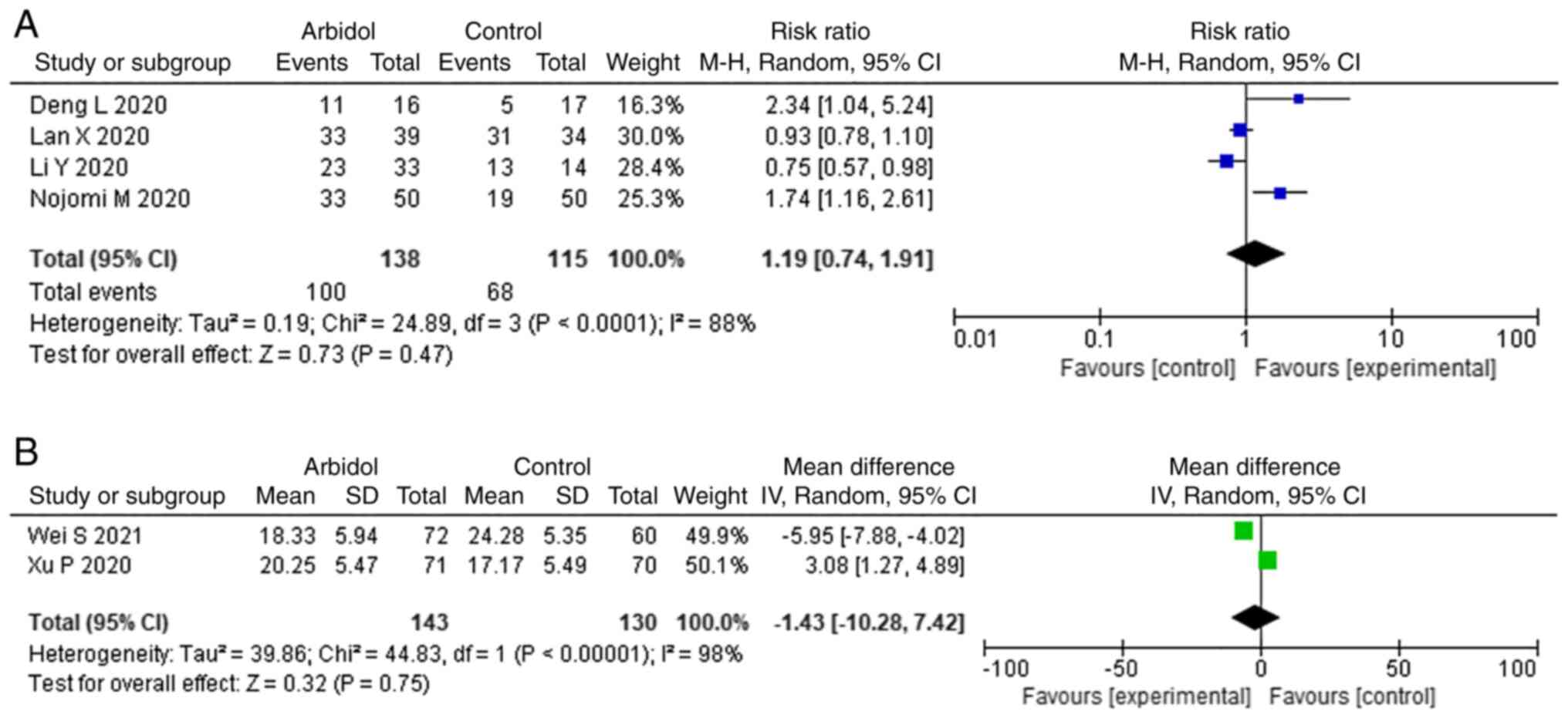
|
1
|
Welte T and Köhnlein T: Global and local
epidemiology of community-acquired pneumonia: The experience of the
CAPNETZ network. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 30:127–135.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhu YG, Tang XD, Lu YT, Zhang J and Qu JM:
Contemporary situation of community-acquired pneumonia in China: A
systematic review. J Transl Int Med. 6:26–31. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jain S, Self WH, Wunderink RG, Fakhran S,
Balk R, Bramley AM, Reed C, Grijalva CG, Anderson EJ, Courtney DM,
et al: Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among
U.S. Adults. N Engl J Med. 373:415–427. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shi T, Arnott A, Semogas I, Falsey AR,
Openshaw P, Wedzicha JA, Campbell H, Nair H and Investigators R:
The etiological role of common respiratory viruses in acute
respiratory infections in older adults: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 222:S563–S569. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Armentano GM and Carneiro-Ramos MS: Effect
of COVID-19 on cardiorenal axis: Known or unknown universe? Braz J
Med Biol Res. 55(e11932)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Blaising J, Polyak SJ and Pécheur EI:
Arbidol as a broad-spectrum antiviral: An update. Antiviral Res.
107:84–94. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ul'yanovskii NV, Kosyakov DS, Sypalov SA,
Varsegov IS, Shavrina IS and Lebedev AT: Antiviral drug Umifenovir
(Arbidol) in municipal wastewater during the COVID-19 pandemic:
Estimated levels and transformation. Sci Total Environ.
805(150380)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
McKee DL, Sternberg A, Stange U, Laufer S
and Naujokat C: Candidate drugs against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19.
Pharmacol Res. 157(104859)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kadam RU and Wilson IA: Structural basis
of influenza virus fusion inhibition by the antiviral drug Arbidol.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:206–214. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vankadari N: Arbidol: A potential
antiviral drug for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 by blocking
trimerization of the spike glycoprotein. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
56(105998)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
National Health Commission of the People's
Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment plan for COVID-19 (trial
version 8 revision). Chin J Clin Infect Dis. 14:81–88. 2021.
|
|
12
|
Abdelrahman Z, Liu Q, Jiang S, Li M, Sun
Q, Zhang Y and Wang X: Evaluation of the current therapeutic
approaches for COVID-19: A systematic review and a meta-analysis.
Front Pharmacol. 12(607408)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jomah S, Asdaq SMB and Al-Yamani MJ:
Clinical efficacy of antivirals against novel coronavirus
(COVID-19): A review. J Infect Public Health. 13:1187–1195.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PCM, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JAC, et
al: The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343(d5928)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Leneva IA, Burtseva EI, Yatsyshina SB,
Fedyakina IT, Kirillova ES, Selkova EP, Osipova E and Maleev VV:
Virus susceptibility and clinical effectiveness of anti-influenza
drugs during the 2010-2011 influenza season in Russia. Int J Infect
Dis. 43:77–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhu Z, Lu Z, Xu T, Chen C, Yang G, Zha T,
Lu J and Xue Y: Arbidol monotherapy is superior to
lopinavir/ritonavir in treating COVID-19. J Infect. 81:e21–e23.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li M, Yu T, Zhu J, Wang Y, Yang Y, Zhao K,
Yi Y and He J, Li C and He J: Comparison of the antiviral effect of
Arbidol and Chloroquine in treating COVID-19. Ann Palliat Med.
10:3307–3312. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nojomi M, Yassin Z, Keyvani H, Makiani MJ,
Roham M, Laali A, Dehghan N, Navaei M and Ranjbar M: Effect of
arbidol (Umifenovir) on COVID-19: A randomized controlled trial.
BMC Infect Dis. 20(954)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen C, Zhang YI, Huang J, Yin P, Cheng Z,
Wu J, Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen BO, Lu M, et al: Favipiravir versus
Arbidol for COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. medRxiv
2020.03.17.20037432.
|
|
21
|
Wang ZL, Yang B, Li Q, Wen L and Zhang R:
Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in
Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis. 71:769–777. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Darazam IA, Shokouhi S, Mardani M,
Pourhoseingholi MA, Rabiei MM, Hatami F, Shabani M, Moradi O,
Gharehbagh FJ, Irvani SSN, et al: Umifenovir in hospitalized
moderate to severe COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial.
Int Immunopharmacol. 99(107969)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen W, Yao M, Fang Z, Lv X, Deng M and Wu
Z: A study on clinical effect of Arbidol combined with adjuvant
therapy on COVID-19. J Med Virol. 92:2702–2708. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jie X, Hongmei Y, Ping F, Kuikui Z, Bohan
Y and Rui M: Beneficial effect of Arbidol in the management of
COVID-19 infection. Aging (Albany NY). 13:9253–9264.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao W, Chen S, Wang K, Chen R, Guo Q, Lu
J, Wu X, He Y, Yan Q, Wang S, et al: Clinical features and efficacy
of antiviral drug, Arbidol in 220 nonemergency COVID-19 patients
from East-West-Lake Shelter Hospital in Wuhan: A retrospective case
series. Virol J. 17(162)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen N, Wang X, Zhang S, Lin R and Jiang
Y: Efficacy analysis of Arbidol treatment in patients with 2019
novel coronavirus pneumonia: A retrospective cohort study. Ann
Palliat Med. 10:10626–10632. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Deng L, Li C, Zeng Q, Liu X, Li X, Zhang
H, Hong Z and Xia J: Arbidol combined with LPV/r versus LPV/r alone
against corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective cohort study. J
Infect. 81:e1–e5. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu P, Huang J, Fan Z, Huang W, Qi M, Lin
X, Song W and Yi L: Arbidol/IFN-α2b therapy for patients with
corona virus disease 2019: A retrospective multicenter cohort
study. Microbes Infect. 22:200–205. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wei S, Xu S and Pan YH: Efficacy of
arbidol in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study. World J Clin
Cases. 9:7350–7357. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lian N, Xie H, Lin S, Huang J, Zhao J and
Lin Q: Umifenovir treatment is not associated with improved
outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A retrospective
study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 26:917–921. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu MY, Wang S, Yao WF, Wu HZ, Meng SN and
Wei MJ: Pharmacokinetic properties and bioequivalence of two
formulations of arbidol: An open-label, single-dose,
randomized-sequence, two-period crossover study in healthy Chinese
male volunteers. Clin Ther. 31:784–792. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Xie Z, Lin W, Cai W, Wen C, Guan Y,
Mo X, Wang J, Wang Y, Peng P, et al: Efficacy and safety of
lopinavir/ritonavir or arbidol in adult patients with mild/moderate
COVID-19: An exploratory randomized controlled trial. Med (N Y).
1:105–113. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lan X, Shao C, Zeng X, Wu Z and Xu Y:
Lopinavir-ritonavir alone or combined with arbidol in the treatment
of 73 hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A pilot retrospective
study. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 59:378–385. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen X, Zhu B, Hong W, Zeng J, He X, Chen
J, Zheng H, Qiu S, Deng Y, Chan JCN, et al: Associations of
clinical characteristics and treatment regimens with the duration
of viral RNA shedding in patients with COVID-19. Int J Infect Dis.
98:252–260. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang JN, Wang WJ, Peng B, Peng W, Zhang
YS, Wang YL, Wan Y, Chang J, Mao L, Miao XP, et al: Potential of
arbidol for post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 transmission: A
preliminary report of a retrospective cohort study. Curr Med Sci.
40:480–485. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang C, Ke C, Yue D, Li W, Hu Z, Liu W, Hu
S, Wang S and Liu J: Effectiveness of Arbidol for COVID-19
prevention in health professionals. Front Public Health.
8(249)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jeon S, Ko M, Lee J, Choi I, Byun SY, Park
S, Shum D and Kim S: Identification of antiviral drug candidates
against SARS-CoV-2 from FDA-approved drugs. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 64:e00819–e00820. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Weston S, Coleman CM, Haupt R, Logue J,
Matthews K, Li Y, Reyes HM, Weiss SR and Frieman MB: Broad
anti-coronavirus activity of food and drug administration-approved
drugs against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and SARS-CoV in vivo. J Virol.
94:e01218–e01220. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Angus DC, Derde L, Al-Beidh F, Annane D,
Arabi Y, Beane A, van Bentum-Puijk W, Berry L, Bhimani Z, Bonten M,
et al: Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in
patients with severe COVID-19: The REMAP-CAP COVID-19
corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
324:1317–1329. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Şimşek-Yavuz S and Çelikyurt FI: An update
of anti-viral treatment of COVID-19. Turk J Med Sci. 51:3372–3390.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Cao R, Zhang H, Liu J, Xu M, Hu H,
Li Y, Zhao L, Li W, Sun X, et al: The anti-influenza virus drug,
arbidol is an efficient inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Cell
Discov. 6(28)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Boriskin YS, Leneva IA, Pécheur EI and
Polyak SJ: Arbidol: A broad-spectrum antiviral compound that blocks
viral fusion. Curr Med Chem. 15:997–1005. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Behzadi MA and Leyva-Grado VH: Overview of
current therapeutics and novel candidates against influenza,
respiratory syncytial virus, and middle east respiratory syndrome
coronavirus infections. Front Microbiol. 10(1327)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Q, Zhou YH and Yang ZQ: The cytokine
storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory
therapy. Cell Mol Immunol. 13:3–10. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang M, Wu T, Zuo Z, You Y, Yang X, Pan L,
Hu Y, Luo X, Jiang L, Xia Z and Deng M: Evaluation of current
medical approaches for COVID-19: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ Support Palliat Care. 11:45–52. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang Y, Ding Y, Yang C, Li R, Du Q, Hao Y,
Li Z, Jiang H, Zhao J, Chen Q, et al: Inhibition of the infectivity
and inflammatory response of influenza virus by Arbidol
hydrochloride in vitro and in vivo (mice and ferret). Biomed
Pharmacother. 91:393–401. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li H, Liu R, Zhang R, Zhang S, Wei Y,
Zhang L, Zhou H and Yang C: Protective effect of arbidol against
pulmonary fibrosis and sepsis in mice. Front Pharmacol.
11(607075)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Silin DS, Lyubomska OV, Ershov FI, Frolov
VM and Kutsyna GA: Synthetic and natural immunomodulators acting as
interferon inducers. Curr Pharm Des. 15:1238–1247. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Song Y, Zhang M, Yin L, Wang K, Zhou Y,
Zhou M and Lu Y: COVID-19 treatment: Close to a cure? A rapid
review of pharmacotherapies for the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2).
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 56(106080)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Pang J, Wang MX, Ang IYH, Tan SHX, Lewis
RF, Chen JIP, Gutierrez RA, Gwee SXW, Chua PEY, Yang Q, et al:
Potential rapid diagnostics, vaccine and therapeutics for 2019
novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): A systematic review. J Clin Med.
9(623)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Guo YZ, Xu KJ, Li YT, Fu JD, Xu M, Yu L,
Sheng JF and Zhu B: Safety of protease inhibitors and Arbidol for
SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Zhejiang Province, China. J Zhejiang Univ
Sci B. 21:948–954. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Jiang S, Wang R, Li L, Hong D, Ru R, Rao
Y, Miao J, Chen N, Wu X, Ye Z, et al: Liver injury in critically
Ill and non-critically Ill COVID-19 patients: A multicenter,
retrospective, observational study. Front Med (Lausanne).
7(347)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|