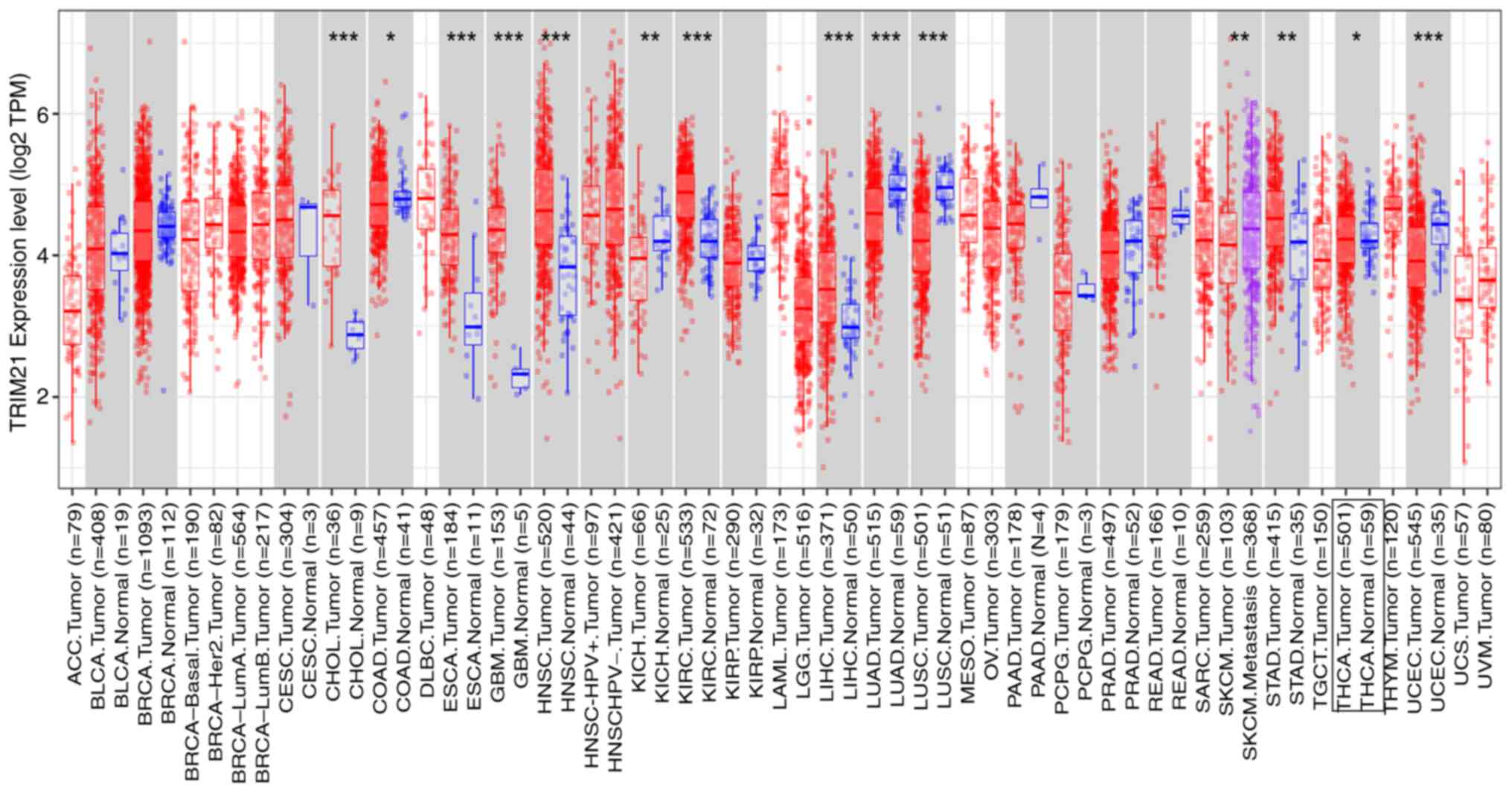
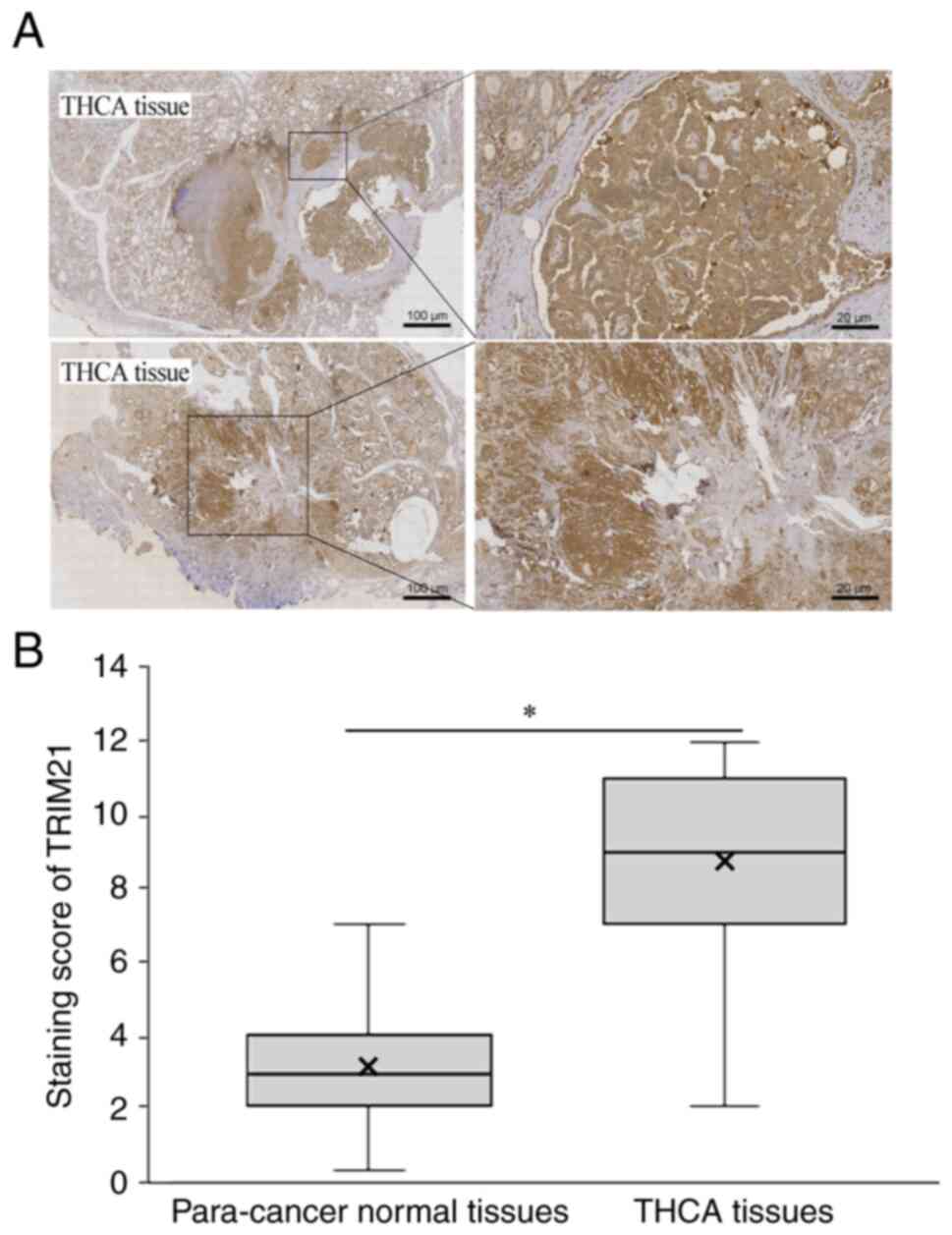
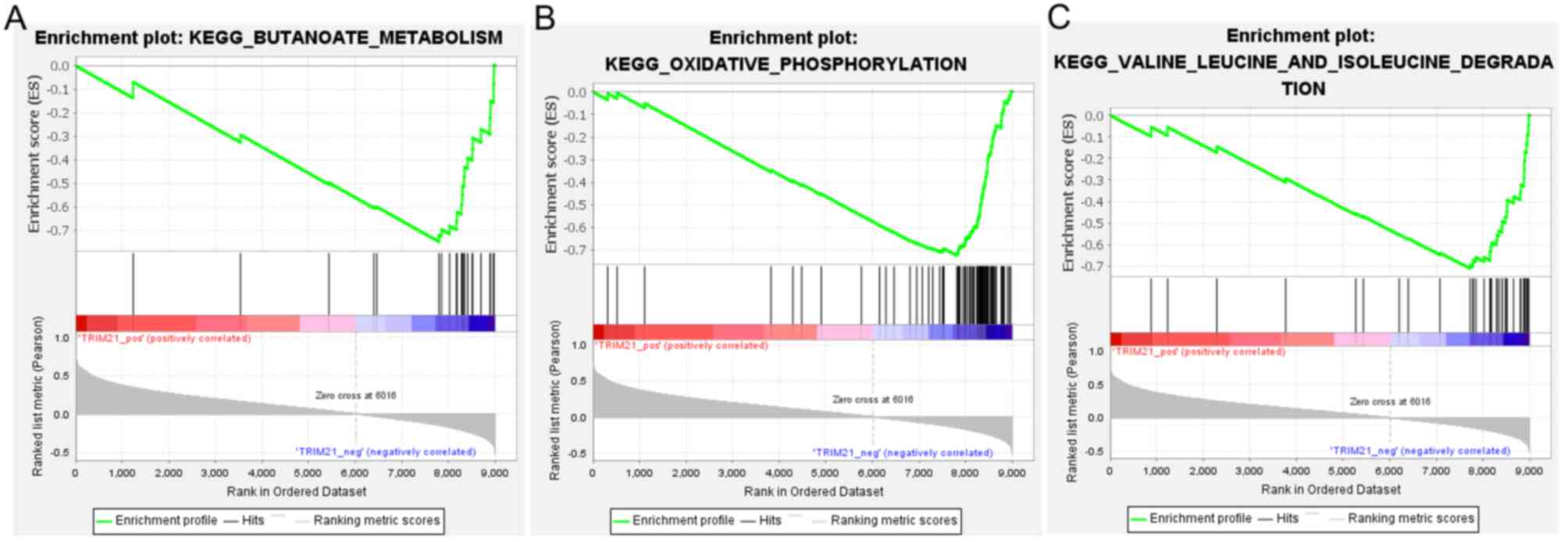
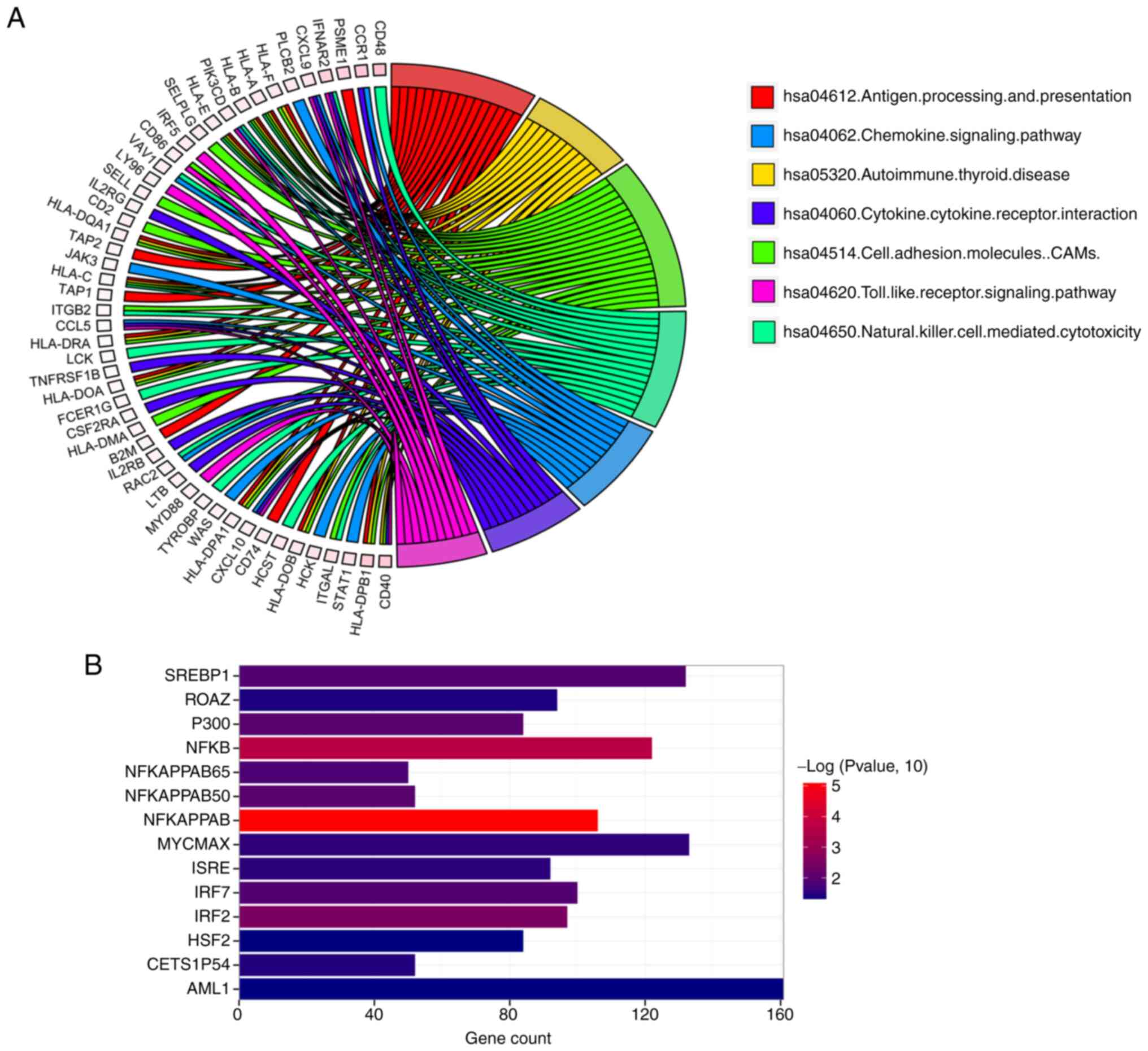
|
1
|
Du L, Zhao Z, Zheng R, Li H, Zhang S, Li
R, Wei W and He J: Epidemiology of thyroid cancer: Incidence and
mortality in China, 2015. Front Oncol. 10(1702)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Takami H, Ito Y, Okamoto T and Yoshida A:
Therapeutic strategy for differentiated thyroid carcinoma in Japan
based on a newly established guideline managed by Japanese society
of thyroid surgeons and Japanese association of endocrine surgeons.
World J Surg. 35:111–121. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM family proteins: Roles
in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci.
42:297–311. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vunjak M and Versteeg GA: TRIM proteins.
Curr Biol. 29:R42–R44. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Valletti A, Marzano F, Pesole G, Sbisa E
and Tullo A: Targeting chemoresistant tumors: Could TRIM
proteins-p53 axis be a possible answer? Int J Mol Sci.
20(1776)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alomari M: TRIM21-A potential novel
therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Res.
165(105443)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sun W, Wang Y, Li D, Wu Y, Ji Q and Sun T:
Tripartite motif containing 14: An oncogene in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 521:360–367. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou Z, Liu Y, Ma M and Chang L: Knockdown
of TRIM44 inhibits the proliferation and invasion in papillary
thyroid cancer cells through suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:98–103. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Zhang B, Shi T and Qin H: miR-182
promotes tumor growth and increases chemoresistance of human
anaplastic thyroid cancer by targeting tripartite motif 8.
OncoTargets Ther. 10:1115–1122. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Oke V and Wahren-Herlenius M: The
immunobiology of Ro52 (TRIM21) in autoimmunity: A critical review.
J Autoimmun. 39:77–82. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Simoes Eugénio M, Faurez F, Kara-Ali GH,
Lagarrigue M, Uhart P, Bonnet MC, Gallais I, Com E, Pineau C,
Samson M, et al: TRIM21, a new component of the TRAIL-induced
endogenous necrosome complex. Front Mol Biosci.
8(645134)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Sheng H, Sun J and Cao C:
TRIM21 suppresses invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
promoting beta-catenin ubiquitylation and degradation. Nan Fang Yi
Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 42:55–62. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Chen X, Li Z, Yong H, Wang W, Wang D, Chu
S, Li M, Hou P, Zheng J and Bai J: Trim21-mediated HIF-1alpha
degradation attenuates aerobic glycolysis to inhibit renal cancer
tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 508:115–126.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhao Z, Wang Y, Yun D, Huang Q, Meng D, Li
Q, Zhang P, Wang C, Chen H and Lu D: TRIM21 overexpression promotes
tumor progression by regulating cell proliferation, cell migration
and cell senescence in human glioma. Am J Cancer Res. 10:114–130.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ping M, Wang S, Guo Y and Jia J: TRIM21
improves apatinib treatment in gastric cancer through suppressing
EZH1 stability. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 586:177–184.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chuang CY, Chien YC, Lin CW, Chou CH, Chen
SC, Liu CL, Bai LY, Yang SF and Yu YL: TRIM21 polymorphisms are
associated with susceptibility and clinical status of oral squamous
cell carcinoma patients. Int J Med Sci. 18:2997–3003.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6(pl1)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shim SR, Kim SJ, Lee J and Rucker G:
Network meta-analysis: Application and practice using R software.
Epidemiol Health. 41(e2019013)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bible KC, Kebebew E, Brierley J, Brito JP,
Cabanillas ME, Clark TJ Jr, Di Cristofano A, Foote R, Giordano T,
Kasperbauer J, et al: 2021 American thyroid association guidelines
for management of patients with anaplastic thyroid cancer. Thyroid.
31:337–386. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Guha A, Ahuja D, Das Mandal S, Parasar B,
Deyasi K, Roy D, Sharma V, Willard B, Ghosh A and Ray PS: .
Integrated regulation of HuR by translation repression and protein
degradation determines pulsatile expression of p53 under DNA
damage. iScience. 15:342–359. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhou G, Wu H, Lin J, Lin R, Feng B and Liu
Z: TRIM21 is decreased in Colitis-associated cancer and negatively
regulates epithelial carcinogenesis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 27:458–468.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sabile A, Meyer AM, Wirbelauer C, Hess D,
Kogel U, Scheffner M and Krek W: Regulation of p27 degradation and
S-phase progression by Ro52 RING finger protein. Mol Cell Biol.
26:5994–6004. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao X, Xu F, Zhang HT, Chen M, Huang W,
Zhang Q, Zeng Q and Liu L: PKCα-GSK3β-NF-κB signaling pathway and
the possible involvement of TRIM21 in TRAIL-induced apoptosis.
Biochem Cell Biol. 94:256–264. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang J, Fang L, Zhu X, Qiao Y, Yu M, Wang
L, Chen Y, Yin W and Hua ZC: Ro52/SSA sensitizes cells to death
receptor-induced apoptosis by down-regulating c-FLIP(L). Cell Biol
Int. 36:463–468. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|