Spandidos Publications style
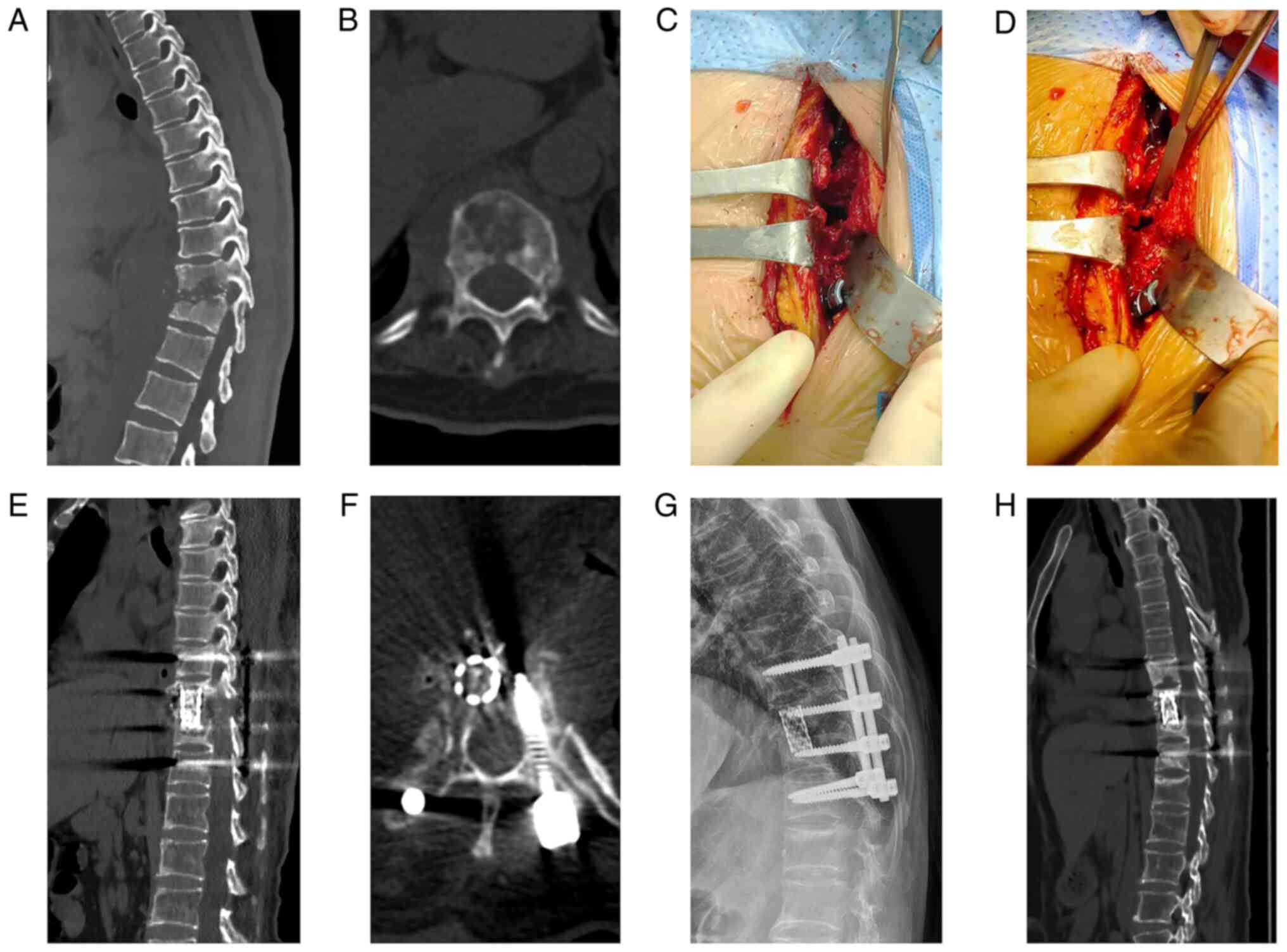
Zeng H, Liao S, Liang Y, Moro A, Chen G and Qin H: Wiltse transforaminal thoracic interbody fusion approach for the treatment of single‑segment thoracic spinal tuberculosis in elderly patients with osteoporosis: A retrospective study of 20 cases. Exp Ther Med 25: 135, 2023.
APA
Zeng, H., Liao, S., Liang, Y., Moro, A., Chen, G., & Qin, H. (2023). Wiltse transforaminal thoracic interbody fusion approach for the treatment of single‑segment thoracic spinal tuberculosis in elderly patients with osteoporosis: A retrospective study of 20 cases. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 25, 135. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2023.11834
MLA
Zeng, H., Liao, S., Liang, Y., Moro, A., Chen, G., Qin, H."Wiltse transforaminal thoracic interbody fusion approach for the treatment of single‑segment thoracic spinal tuberculosis in elderly patients with osteoporosis: A retrospective study of 20 cases". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 25.3 (2023): 135.
Chicago
Zeng, H., Liao, S., Liang, Y., Moro, A., Chen, G., Qin, H."Wiltse transforaminal thoracic interbody fusion approach for the treatment of single‑segment thoracic spinal tuberculosis in elderly patients with osteoporosis: A retrospective study of 20 cases". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 25, no. 3 (2023): 135. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2023.11834