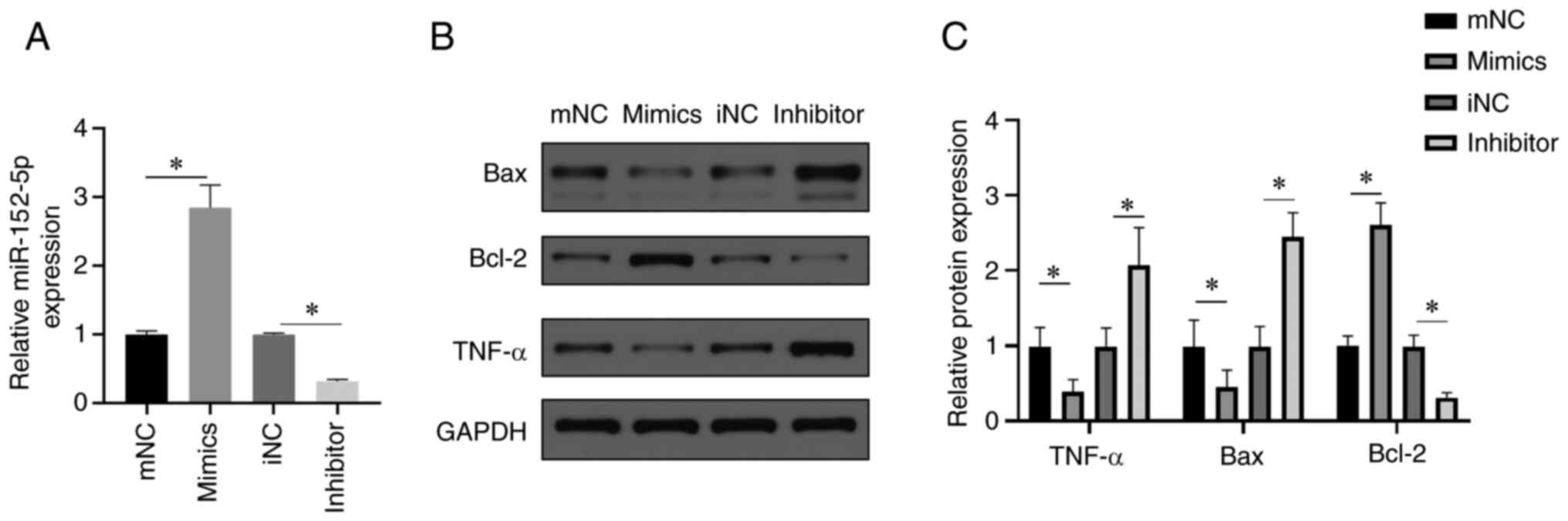
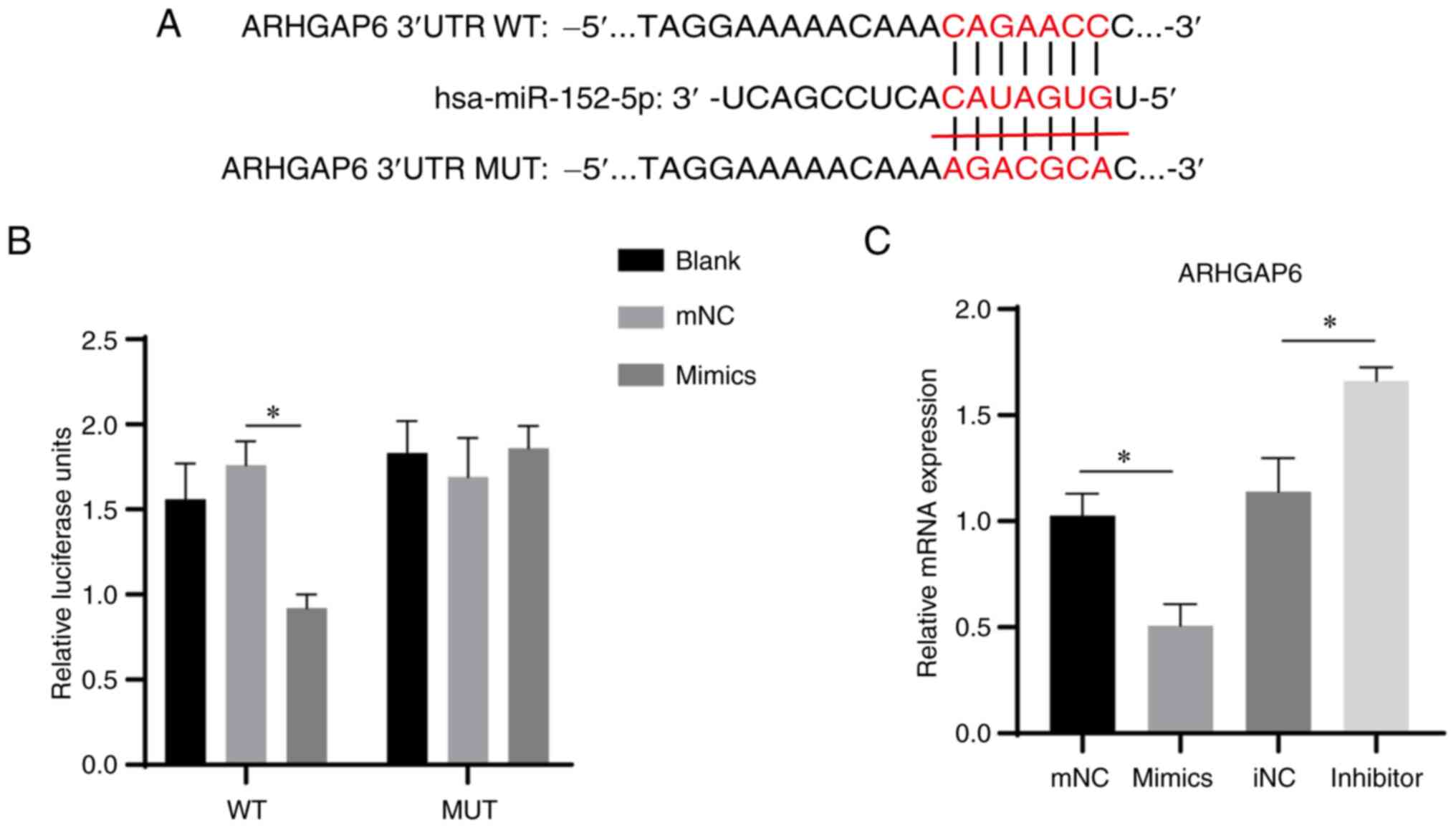
|
1
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A,
Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR,
Cheng S, Das SR, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019
update: A report from the American heart association. Circulation.
139:e56–e528. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bennett S, Ravindran R, Duckett S, Cubukcu
A, Jones H and Kwok CS: Acute coronary syndrome secondary to
cardiac infiltration and coronary occlusion of chronic lymphocytic
leukemia-a case report. J Cardiol Cases. 23:257–260.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fath AR, Aglan A, Varkoly KS, Eldaly AS,
Beladi RN, Forlemu A, Mihyawi N, Solsi A, Israr S and Lucas AR:
Distinct coagulopathy with myocardial injury and pulmonary embolism
in COVID-19. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep.
9(23247096211019559)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Shao C, Cheng S, Zhu Y and Liang
B: Effect of Guanxin V in animal model of acute myocardial
infarction. BMC Complement Med Ther. 21(72)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Galiuto L, DeMaria AN and Iliceto S:
Microvascular damage during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion:
Pathophysiology, clinical implications and potential therapeutic
approach evaluated by myocardial contrast echocardiography. Ital
Heart J. 1:108–116. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li M, Tang X, Liu X, Cui X, Lian M, Zhao
M, Peng H and Han X: Targeted miR-21 loaded liposomes for acute
myocardial infarction. J Mater Chem B. 8:10384–10391.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Peacock WF, Baumann BM, Rivers EJ, Davis
TE, Handy B, Jones CW, Hollander JE, Limkakeng AT, Mehrotra A, Than
M, et al: Using sex-specific cutoffs for high-sensitivity cardiac
troponin T to diagnose acute myocardial infarction. Acad Emerg Med.
28:463–466. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Joyce DP, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM:
Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast
cancer. Int J Cancer. 139:1443–1448. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Li X, Wu X, Wang Z, Zhang C, Cao G
and Yan T: Expression profiling of exosomal miRNAs derived from the
peripheral blood of kidney recipients with DGF using
high-throughput sequencing. Biomed Res Int.
2019(1759697)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chen G, Wang M, Ruan Z, Zhu L and Tang C:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-143-3p suppresses
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating autophagy.
Life Sci. 280(119742)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Long R, Gao L, Li Y, Li G, Qin P, Wei Z,
Li D, Qian C, Li J and Yang G: M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry
miR-1271-5p to alleviate cardiac injury in acute myocardial
infarction through down-regulating SOX6. Mol Immunol. 136:26–35.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aonuma T, Moukette B, Kawaguchi S,
Barupala NP, Sepulveda MN, Corr C, Tang Y, Liangpunsakul S, Payne
RM, Willis MS and Kim IM: Cardiomyocyte microRNA-150 confers
cardiac protection and directly represses proapoptotic small
proline-rich protein 1A. JCI Insight. 6(e150405)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
El Fatimy R, Boulaassafre S, Bouchmaa N,
El Khayari A, Vergely C, Malka G and Rochette L: The emerging role
of miRNA-132/212 cluster in neurologic and cardiovascular diseases:
Neuroprotective role in cells with prolonged longevity. Mech Ageing
Dev. 199(111566)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Eulalio A, Mano M, Dal Ferro M, Zentilin
L, Sinagra G, Zacchigna S and Giacca M: Functional screening
identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature.
492:376–381. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Henning RJ: Cardiovascular exosomes and
MicroRNAs in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 14:195–212. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Tian L and Sun Q: Diagnostic and
prognostic value of circulating miRNA-499 and miRNA-22 in acute
myocardial infarction. J Clin Lab Anal. 34:2410–2417.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guo M, Li R, Yang L, Zhu Q, Han M, Chen Z,
Ruan F, Yuan Y, Liu Z, Huang B, et al: Evaluation of exosomal
miRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for acute myocardial
infarction using next-generation sequencing. Ann Transl Med.
9(219)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
You W, Zhang X, Ji M, Yu Y, Chen C, Xiong
Y, Liu Y, Sun Y, Tan C, Zhang H, et al: MiR-152-5p as a microRNA
passenger strand special functions in human gastric cancer cells.
Int J Biol Sci. 14:644–653. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Huang F, Liu Y, Liu S and Tan G:
Exosomal miR-152-5p and miR-3681-5p function as potential
biomarkers for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Clinics
(Sao Paulo). 77(100038)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pacary E, Tixier E, Coulet F, Roussel S,
Petit E and Bernaudin M: Crosstalk between HIF-1 and ROCK pathways
in neuronal differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, neurospheres
and in PC12 neurite outgrowth. Mol Cell Neurosci. 35:409–423.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou H, Sun Y, Zhang L, Kang W, Li N and
Li Y: The RhoA/ROCK pathway mediates high glucose-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis via oxidative stress, JNK, and p38MAPK
pathways. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 34(e3022)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Huang L, Li Q, Wen R, Yu Z, Li N, Ma L and
Feng W: Rho-kinase inhibitor prevents acute injury against
transient focal cerebral ischemia by enhancing the expression and
function of GABA receptors in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 797:134–142.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang T, Fang F, Chen Y, Ma J, Xiao Z, Zou
S, Zheng N, Yan D, Liao S, Chen S, et al: Elevated plasma
interleukin-37 playing an important role in acute coronary syndrome
through suppression of ROCK activation. Oncotarget. 8:9686–9695.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Okamoto R, Li Y, Noma K, Hiroi Y, Liu PY,
Taniguchi M, Ito M and Liao JK: FHL2 prevents cardiac hypertrophy
in mice with cardiac-specific deletion of ROCK2. FASEB J.
27:1439–1449. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Amin F, Ahmed A, Feroz A, Khaki PSS, Khan
MS, Tabrez S, Zaidi SK, Abdulaal WH, Shamsi A, Khan W and Bano B:
An update on the association of protein kinases with cardiovascular
diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 25:174–183. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Prakash SK, Paylor R, Jenna S,
Lamarche-Vane N, Armstrong DL, Xu B, Mancini MA and Zoghbi HY:
Functional analysis of ARHGAP6, a novel GTPase-activating protein
for RhoA. Hum Mol Genet. 9:477–488. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chang DL, Wei W, Yu ZP and Qin CK:
miR-152-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of liver
cancer cells by up-regulating FOXO expression. Pharmazie.
72:338–343. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zong DD, Liu XM, Li JH, Long YJ, Ouyang RY
and Chen Y: LncRNA-CCAT1/miR-152-5p is involved in CSE-induced
inflammation in HBE cells via regulating ERK signaling pathway. Res
Sq, 2021.
|
|
30
|
Duisters RF, Tijsen AJ, Schroen B,
Leenders JJ, Lentink V, van der Made I, Herias V, van Leeuwen RE,
Schellings MW, Barenbrug P, et al: miR-133 and miR-30 regulate
connective tissue growth factor: Implications for a role of
microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circ Res. 104:170–178,
6p. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen Y, Zhao Y, Chen W, Xie L, Zhao ZA,
Yang J, Chen Y, Lei W and Shen Z: MicroRNA-133 overexpression
promotes the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells on
acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther.
8(268)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Frangogiannis NG: Cardiac fibrosis.
Cardiovasc Res. 117:1450–1488. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cheng C, Xu DL, Liu XB, Bi SJ and Zhang J:
MicroRNA-145-5p inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in
H9c2 cardiomyocytes by targeting ROCK1. Exp Ther Med.
22(796)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yin Y, Lv L and Wang W: Expression of
miRNA-214 in the sera of elderly patients with acute myocardial
infarction and its effect on cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Exp Ther Med.
17:4657–4662. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kurose H: Cardiac fibrosis and
fibroblasts. Cells. 10(1716)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Komatsu M, Ichikawa H, Chiwaki F, Sakamoto
H, Komatsuzaki R, Asaumi M, Tsunoyama K, Fukagawa T, Matsushita H,
Boku N, et al: ARHGAP-RhoA signaling provokes homotypic
adhesion-triggered cell death of metastasized diffuse-type gastric
cancer. Oncogene. 41:4779–4794. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Decker S, Yuan ZA, Denbesten PK,
Aragon MA, Jordan-Sciutto K, Abrams WR, Huh J, McDonald C, Chen E,
et al: Effects of sodium fluoride on the actin cytoskeleton of
murine ameloblasts. Arch Oral Biol. 50:681–688. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Loirand G: Rho kinases in health and
disease: From basic science to translational research. Pharmacol
Rev. 67:1074–1095. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and
functions. Small GTPases. 5(e29846)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Streets AJ, Prosseda PP and Ong AC:
Polycystin-1 regulates ARHGAP35-dependent centrosomal RhoA
activation and ROCK signaling. JCI Insight.
5(e135385)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rao VP and Epstein DL: Rho GTPase/Rho
kinase inhibition as a novel target for the treatment of glaucoma.
BioDrugs. 21:167–177. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sharifi M, Nazarinia D, Ramezani F, Azizi
Y, Naderi N and Aboutaleb N: Necroptosis and RhoA/ROCK pathways:
Molecular targets of Nesfatin-1 in cardioprotection against
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat model. Mol Biol
Rep. 48:2507–2518. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|