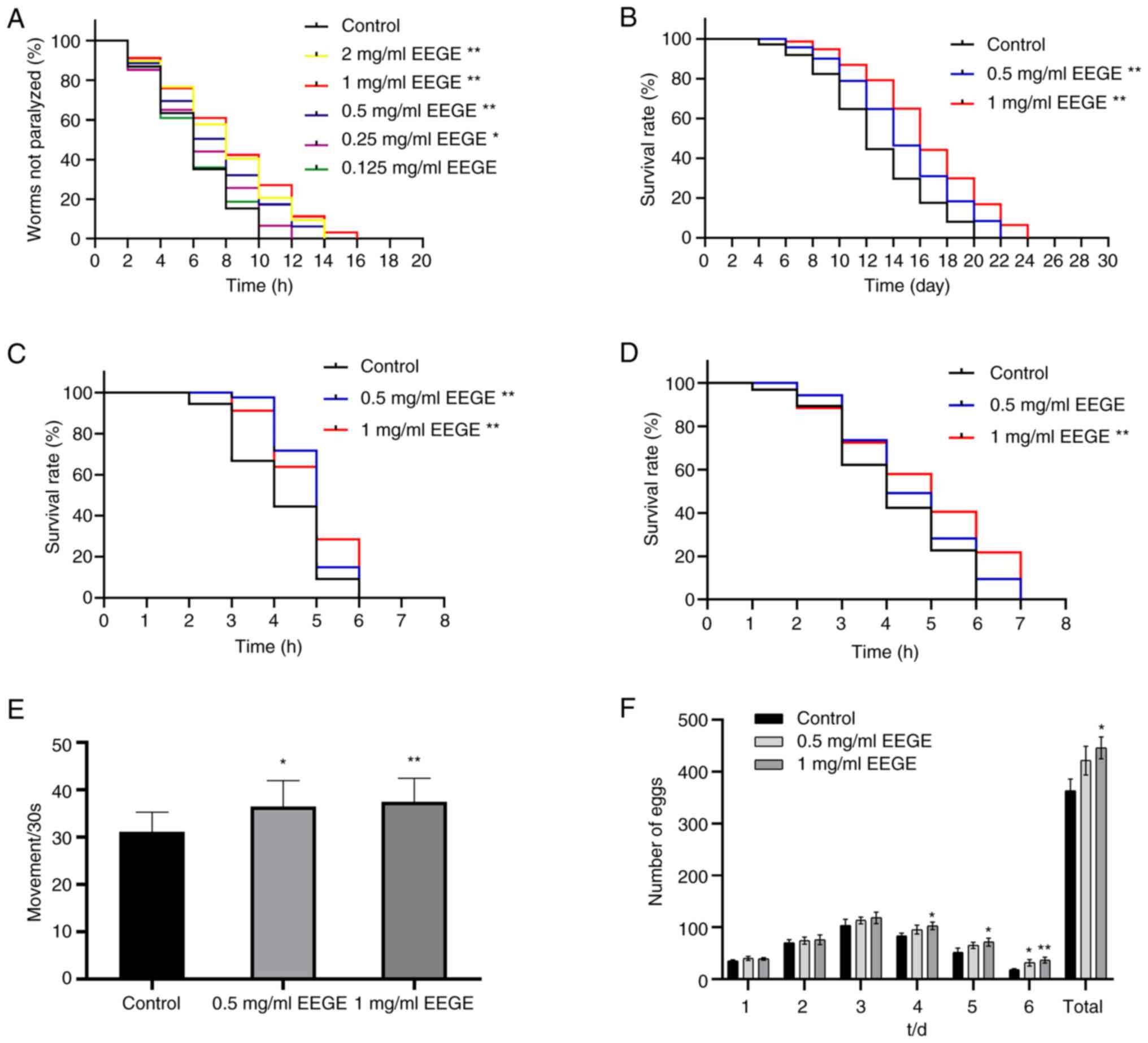
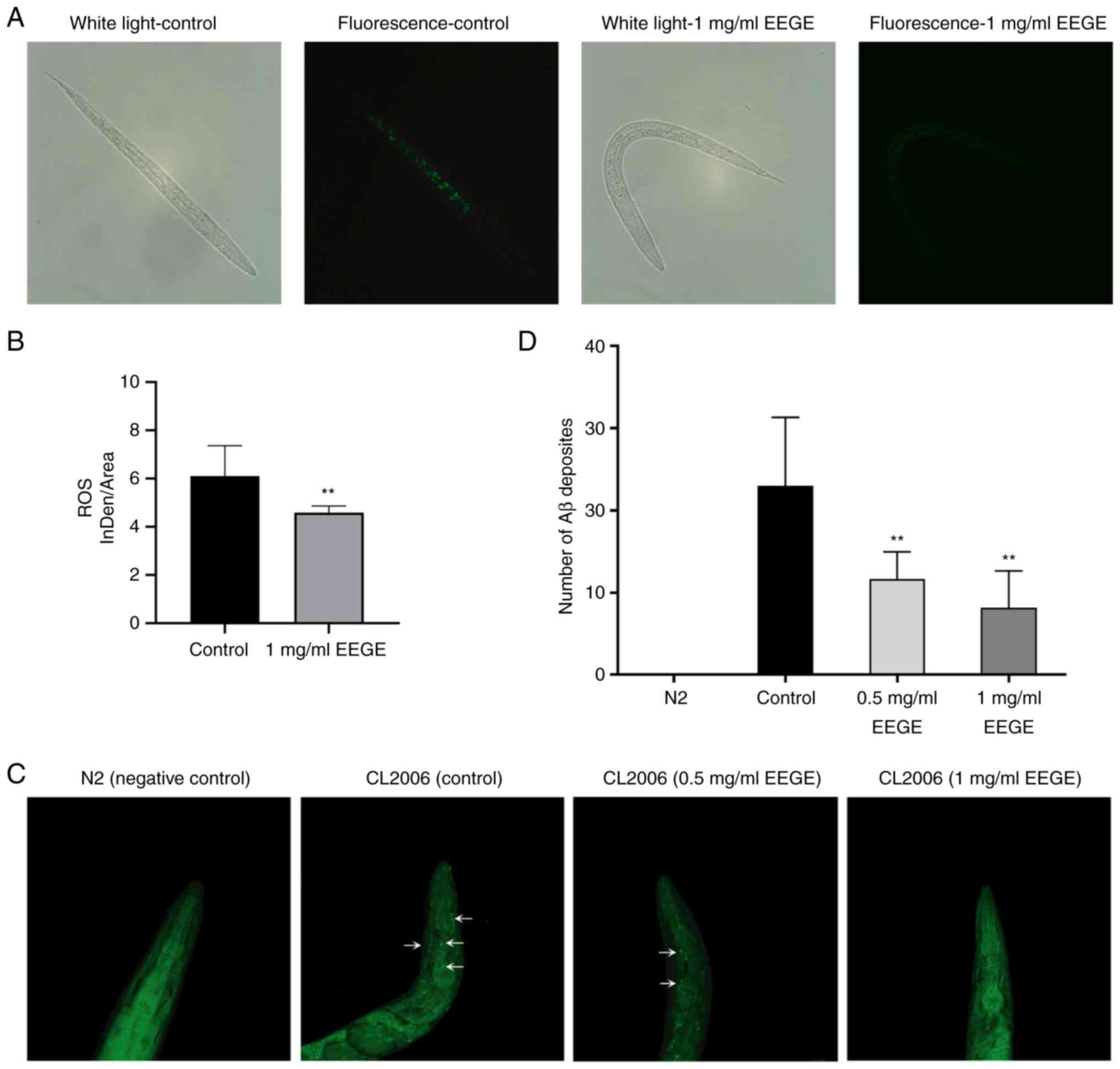
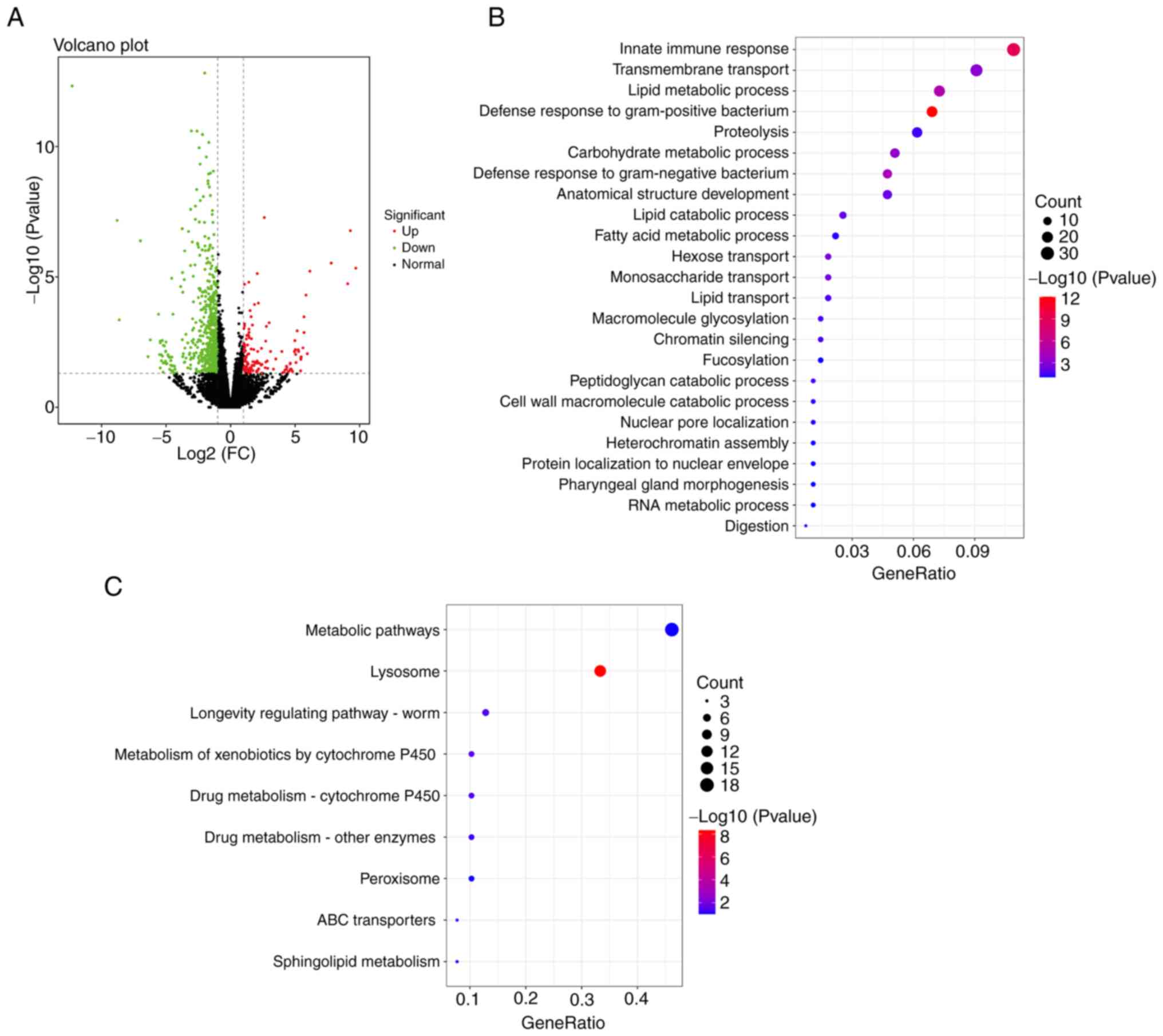
|
1
|
Lane CA, Hardy J and Schott JM:
Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. 25:59–70. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
De Strooper B and Karran E: The cellular
phase of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 164:603–615. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mohsenzadegan M and Mirshafiey A: The
immunopathogenic role of reactive oxygen species in Alzheimer
disease. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 11:203–216. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alafuzoff I, Pikkarainen M, Arzberger T,
Thal DR, Al-Sarraj S, Bell J, Bodi I, Budka H, Capetillo-Zarate E,
Ferrer I, et al: Inter-laboratory comparison of neuropathological
assessments of beta-amyloid protein: A study of the BrainNet Europe
consortium. Acta Neuropathol. 115:533–546. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Kang X, Du L, Zhang L, Huang Y,
Wang J, Wang S, Chang Y, Liu Y and Zhao Y: Tanshinone IIA loaded
chitosan nanoparticles decrease toxicity of β-amyloid peptide in a
Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease. Free Radical
BiolMed. 193:81–94. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Song X, Sun Y, Wang Z, Su Y, Wang Y and
Wang X: Exendin-4 alleviates β-Amyloid peptide toxicity via DAF-16
in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease. Front
Aging Neurosci. 14(955113)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Du F, Zhao H, Yao M, Yang Y, Jiao J and Li
C: Deer antler extracts reduce amyloid-beta toxicity in a
Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease. J
Ethnopharmacol. 285(114850)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhi D, Yang W, Yue J, Xu S, Ma W, Zhao C,
Wang X and Wang D: HSF-1 mediated combined ginsenosides
ameliorating Alzheimer's disease like symptoms in Caernorhabditis
elegans. Nutr Neurosci. 25:2136–2148. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Anand R, Gill KD and Mahdi AA:
Therapeutics of Alzheimer's disease: Past, present and future.
Neuropharmacology. 76 Pt A:27–50. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sangha JS, Sun X, Wally OS, Zhang K, Ji X,
Wang Z, Wang Y, Zidichouski J, Prithiviraj B and Zhang J: Liuwei
Dihuang (LWDH), a traditional Chinese medicinal formula, protects
against β-amyloid toxicity in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans.
PLoS One. 7(e43990)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li Y, Guan S, Liu C, Chen X, Zhu Y, Xie Y,
Wang J, Ji X, Li L, Li Z, et al: Neuroprotective effects of Coptis
Chinensis Franch polysaccharide on amyloid-beta (Aβ)-induced
toxicity in a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model of
Alzheimer's disease (AD). Int J Biol Macromol. 113:991–995.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ding Y, Bao X, Lao L, Ling Y, Wang Q and
Xu S: p-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol prevents memory deficits by
increasing neurotrophic factors and decreasing inflammatory factors
in a mice model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
67:1007–1019. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
He F, Duan X, Dai R, Wang W, Yang C and
Lin Q: Protective effects of ethyl acetate extraction from
Gastrodia elata blume on blood-brain barrier in focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med.
13:199–209. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang Q, Zhang C, Qu S, Dong S, Ma Q, Hao
Y, Liu Z, Wang S, Zhao H and Shi Y: Chinese herbal extracts exert
neuroprotective effect in alzheimer's disease mouse through the
dopaminergic synapse/apoptosis signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
13(817213)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Heese K: Gastrodia elata Blume (Tianma):
Hope for brain aging and dementia. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2020(8870148)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mishra M, Huang J, Lee YY, Chua DSK, Lin
X, Hu JM and Heese K: Gastrodia elata modulates amyloid precursor
protein cleavage and cognitive functions in mice. Biosci Trends.
5:129–138. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen XY, Liao DC, Sun ML, Cui XH and Wang
HB: Essential oil of acorus tatarinowii schott ameliorates
Aβ-induced toxicity in caenorhabditis elegans through an autophagy
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020(3515609)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lublin AL and Link CD: Alzheimer's disease
drug discovery: In vivo screening using Caenorhabditis elegans as a
model for β-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity. Drug Discov Today
Technol. 10:e115–e119. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dai R, Wang T, Si X, Jia Y, Wang L, Yuan
Y, Lin Q and Yang C: Vasodilatory effects and underlying mechanisms
of the ethyl acetate extracts from Gastrodia elata. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 95:564–571. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Romero-Márquez JM, Navarro-Hortal MD,
Jiménez-Trigo V, Vera-Ramírez L, Forbes-Hernández TJ, Esteban-Muñoz
A, Giampieri F, Bullón P, Battino M, Sánchez-González C and Quiles
JL: An oleuropein rich-olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf extract
reduces β-amyloid and tau proteotoxicity through regulation of
oxidative- and heat shock-stress responses in Caenorhabditis
elegans. Food Chem Toxicol. 162(112914)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Navarro-Hortal MD, Romero-Márquez JM,
Esteban-Muñoz A, Sánchez-González C, Rivas-García L, Llopis J,
Cianciosi D, Giampieri F, Sumalla-Cano S, Battino M and Quiles JL:
Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa cv. Romina) methanolic extract
attenuates Alzheimer's beta amyloid production and oxidative stress
by SKN-1/NRF and DAF-16/FOXO mediated mechanisms in C. elegans.
Food Chem. 372(131272)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Romero-Márquez JM, Navarro-Hortal MD,
Jiménez-Trigo V, Muñoz-Ollero P, Forbes-Hernández TY, Esteban-Muñoz
A, Giampieri F, Noya ID, Bullón P, Vera-Ramírez L, et al: An
olive-derived extract 20% Rich in hydroxytyrosol prevents β-amyloid
aggregation and oxidative stress, two features of Alzheimer
disease, via SKN-1/NRF2 and HSP-16.2 in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Antioxidants (Basel). 11(629)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Qadir A, Aqil M, Ali A, Ahmad FJ, Ahmad S,
Arif M and Khan N: GC-MS analysis of the methanolic extracts of
Smilax China and Salix alba and their antioxidant activity. Turk J
Chem. 44:352–363. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala
A, Yang M and Rice-Evans C: Antioxidant activity applying an
improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol
Med. 26:1231–1237. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
DanQing L, YuJie G, ChengPeng Z, HongZhi
D, Yi H, BiSheng H and Yan C: N-butanol extract of Hedyotis diffusa
protects transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans from Aβ-induced
toxicity. Phytother Res. 35:1048–1061. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Meng F, Li J, Rao Y, Wang W and Fu Y:
Gengnianchun extends the lifespan of caenorhabditis elegans via the
Insulin/IGF-1 signalling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018(4740739)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dilberger B, Baumanns S, Schmitt F,
Schmiedl T, Hardt M, Wenzel U and Eckert GP: Mitochondrial
oxidative stress impairs energy metabolism and reduces stress
resistance and longevity of C. elegans. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(6840540)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhi D, Wang D, Yang W, Duan Z, Zhu S, Dong
J, Wang N, Wang N, Fei D, Zhang Z, et al: Dianxianning improved
amyloid β-induced pathological characteristics partially through
DAF-2/DAF-16 insulin like pathway in transgenic C. elegans. Sci
Rep. 7(11408)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Yi K and Zhao Y: Fucoidan inhibits
amyloid-β-induced toxicity in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans by
reducing the accumulation of amyloid-β and decreasing the
production of reactive oxygen species. Food Funct. 9:552–560.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ito K and Murphy D: Application of ggplot2
to pharmacometric graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
2(e79)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Markesbery WR: Oxidative stress hypothesis
in Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 23:134–147.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chiang PK, Lam MA and Luo Y: The many
faces of amyloid beta in Alzheimer's disease. Curr Mol Med.
8:580–584. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Huang GB, Zhao T, Muna SS, Jin HM, Park
JL, Jo KS, Lee BH, Chae SW, Kim SY, Park SH, et al: Therapeutic
potential of Gastrodia elata Blume for the treatment of Alzheimer's
disease. Neural Regen Res. 8:1061–1070. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Link CD: Expression of human beta-amyloid
peptide in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 92:9368–9372. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fay DS, Fluet A, Johnson CJ and Link CD:
In vivo aggregation of beta-amyloid peptide variants. J Neurochem.
71:1616–1625. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhu S, Li H, Dong J, Yang W, Liu T, Wang
Y, Wang X, Wang M and Zhi D: Rose essential oil delayed Alzheimer's
disease-like symptoms by SKN-1 pathway in C. elegans. J Agric Food
Chem. 65:8855–8865. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Pagano G, Rengo G, Pasqualetti G,
Femminella GD, Monzani F, Ferrara N and Tagliati M: Cholinesterase
inhibitors for Parkinson's disease: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 86:767–773.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Li H, Jin S, Lu Y, Peng Y, Zhao L
and Wang X: Cannabidiol protects against Alzheimer's disease in C.
elegans via ROS scavenging activity of its phenolic hydroxyl
groups. Eur J Pharmacol. 919(174829)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Song E, Chung H, Shim E, Jeong JK, Han BK,
Choi HJ and Hwang J: Gastrodia elata blume extract modulates
antioxidant activity and ultraviolet a-irradiated skin aging in
human dermal fibroblast cells. J Med Food. 19:1057–1064.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu Y, Lu YY, Huang L, Shi L, Zheng ZY,
Chen JN, Qu Y, Xiao HT, Luo HR and Wu GS: Para-Hydroxybenzyl
alcohol delays the progression of neurodegenerative diseases in
models of caenorhabditis elegans through activating multiple
cellular protective pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(8986287)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xin L, Yamujala R, Wang Y, Wang H, Wu WH,
Lawton MA, Long C and Di R: Acetylcholineestarase-inhibiting
alkaloids from Lycoris radiata delay paralysis of amyloid
beta-expressing transgenic C. elegans CL4176. PLoS One.
8(e63874)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Takahashi A, Watanabe T, Fujita T,
Hasegawa T, Saito M and Suganuma M: Green tea aroma fraction
reduces β-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity in Caenorhabditis
elegans transfected with human β-amyloid minigene. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 78:1206–1211. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang J, Huang XB, Wan QL, Ding AJ, Yang
ZL, Qiu MH, Sun HY, Qi SH and Luo HR: Otophylloside B protects
against Aβ toxicity in caenorhabditis elegans models of Alzheimer's
disease. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 7:207–214. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pandey S, Phulara SC, Mishra SK, Bajpai R,
Kumar A, Niranjan A, Lehri A, Upreti DK and Chauhan PS: Betula
utilis extract prolongs life expectancy, protects against amyloid-β
toxicity and reduces Alpha Synuclien in Caenorhabditis elegans via
DAF-16 and SKN-1. Comp Biochem Physiol Toxicol Pharmacol.
228(108647)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yin JA, Gao G, Liu XJ, Hao ZQ, Li K, Kang
XL, Li H, Shan YH, Hu WL, Li HP and Cai SQ: Genetic variation in
glia-neuron signalling modulates ageing rate. Nature. 551:198–203.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yue Y, Shen P, Chang AL, Qi W, Kim KH, Kim
D and Park Y: trans-Trismethoxy resveratrol decreased fat
accumulation dependent on fat-6 and fat-7 in Caenorhabditis
elegans. Food Funct. 10:4966–4974. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jia W, Su Q, Cheng Q, Peng Q, Qiao A, Luo
X, Zhang J and Wang Y: Neuroprotective effects of palmatine via the
enhancement of antioxidant defense and small heat shock protein
expression in Aβ-transgenic caenorhabditis elegans. Oxid Med Cell
Longe. 2021(9966223)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mendler M, Riedinger C, Schlotterer A,
Volk N, Fleming T, Herzig S, Nawroth PP and Morcos M: Reduction in
ins-7 gene expression in non-neuronal cells of high glucose exposed
Caenorhabditis elegans protects from reactive metabolites,
preserves neuronal structure and head motility, and prolongs
lifespan. J Diabetes Complications. 31:304–310. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Murphy CT, McCarroll SA, Bargmann CI,
Fraser A, Kamath RS, Ahringer J, Li H and Kenyon C: Genes that act
downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis
elegans. Nature. 424:277–283. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lin C, Zhang X, Zhuang C, Lin Y, Cao Y and
Chen Y: Healthspan improvements in caenorhabditis elegans with
traditional chinese herbal tea. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020(4057841)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang ZZ, Yu YT, Lin HR, Liao DC, Cui XH
and Wang HB: Lonicera japonica extends lifespan and healthspan in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Free Radic Biol Med. 129:310–322.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Brunet A: Aging and the control of the
insulin-FOXO signaling pathway. Med Sci (Paris). 28:316–320.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
54
|
Liu T, Hua Z, Han P, Zhao Y, Zhou J, Jin
Y, Li X, Huang L and Yuan Y: Mycorrhizosphere bacteria, rahnella
sp. HPDA25, promotes the growth of armillaria gallica and its
parasitic host gastrodia elata. Front Microbiol.
13(842893)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hu Y, Li C and Shen W: Gastrodin
alleviates memory deficits and reduces neuropathology in a mouse
model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathology. 34:370–377.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|