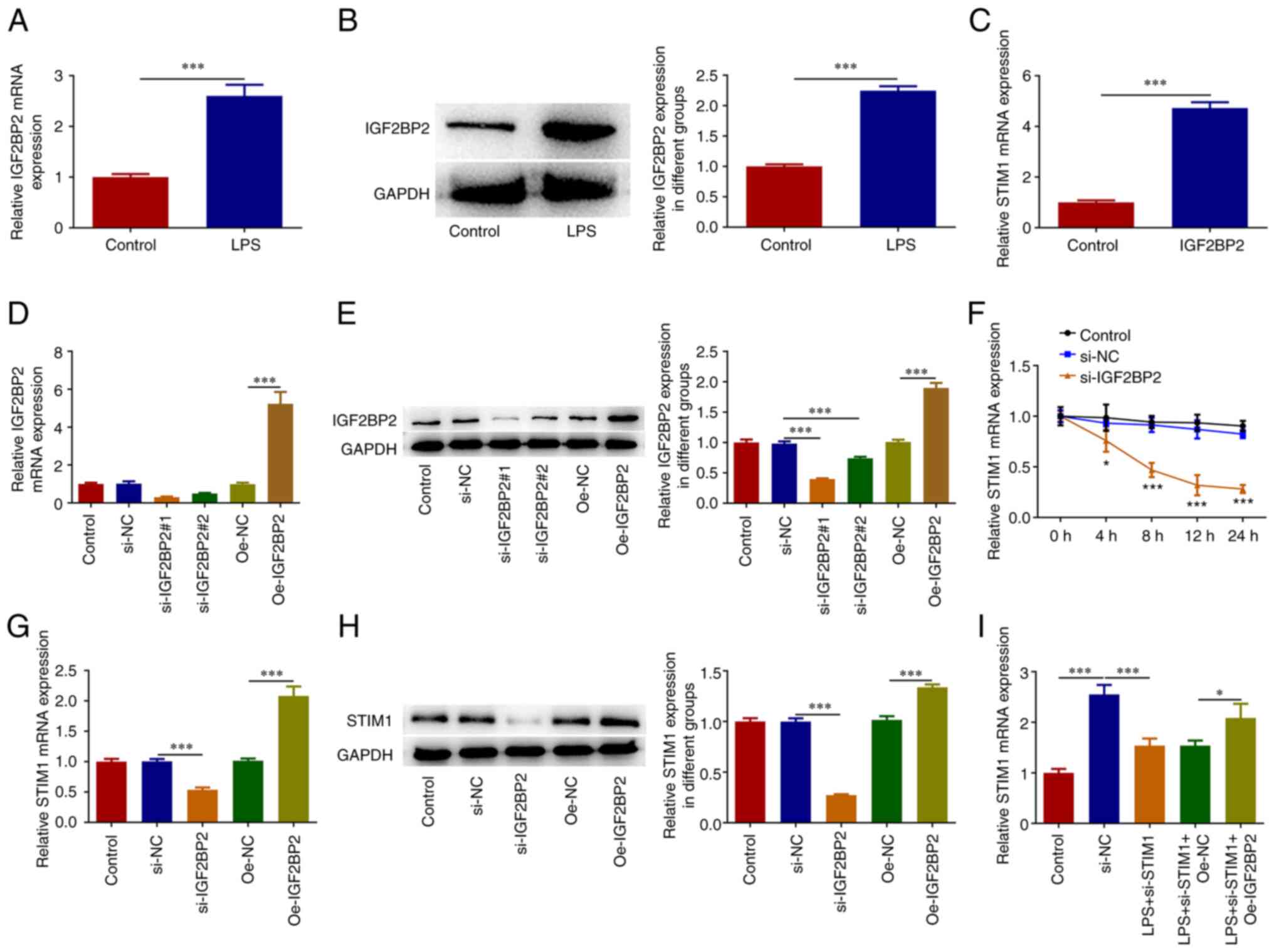
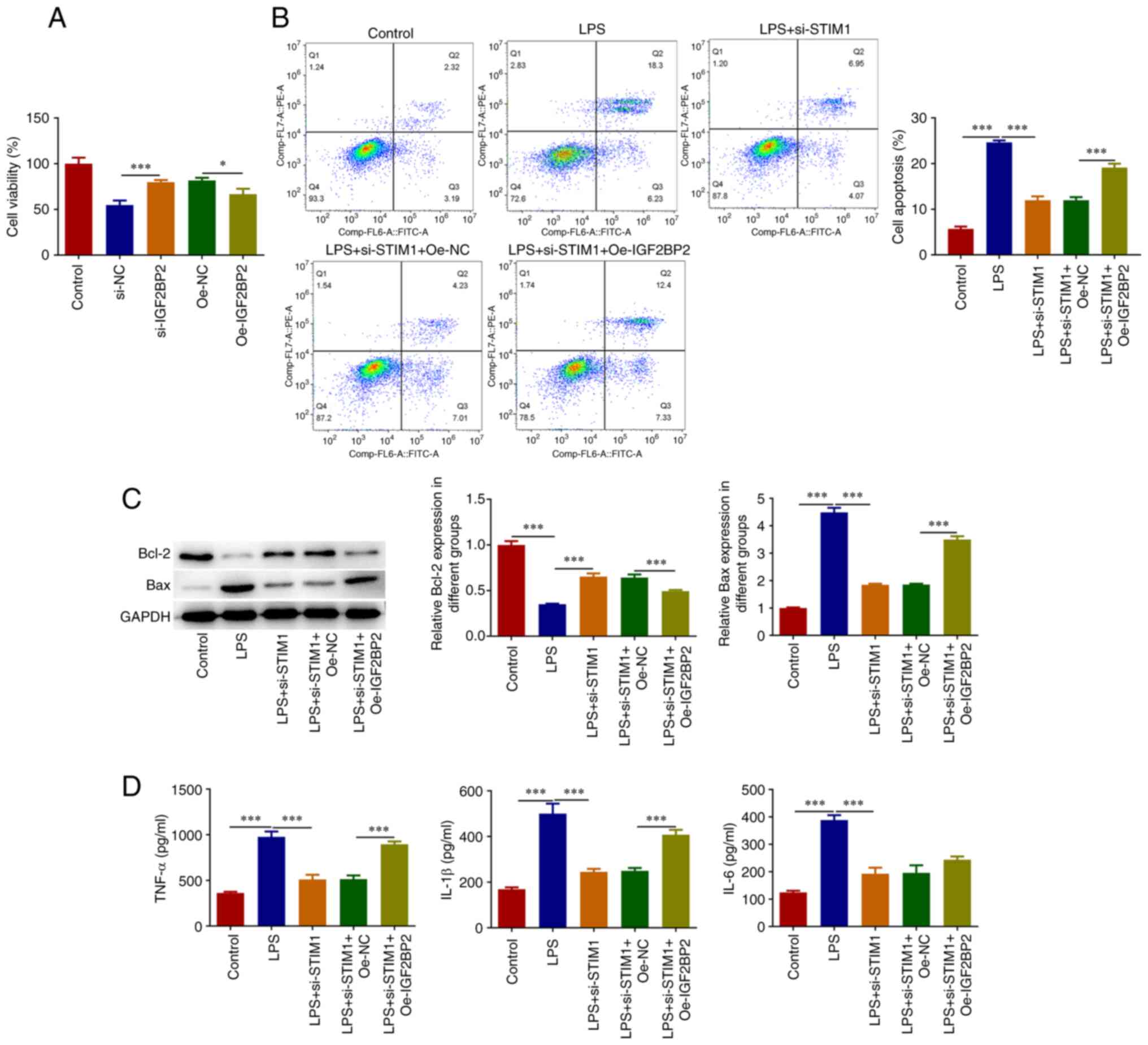
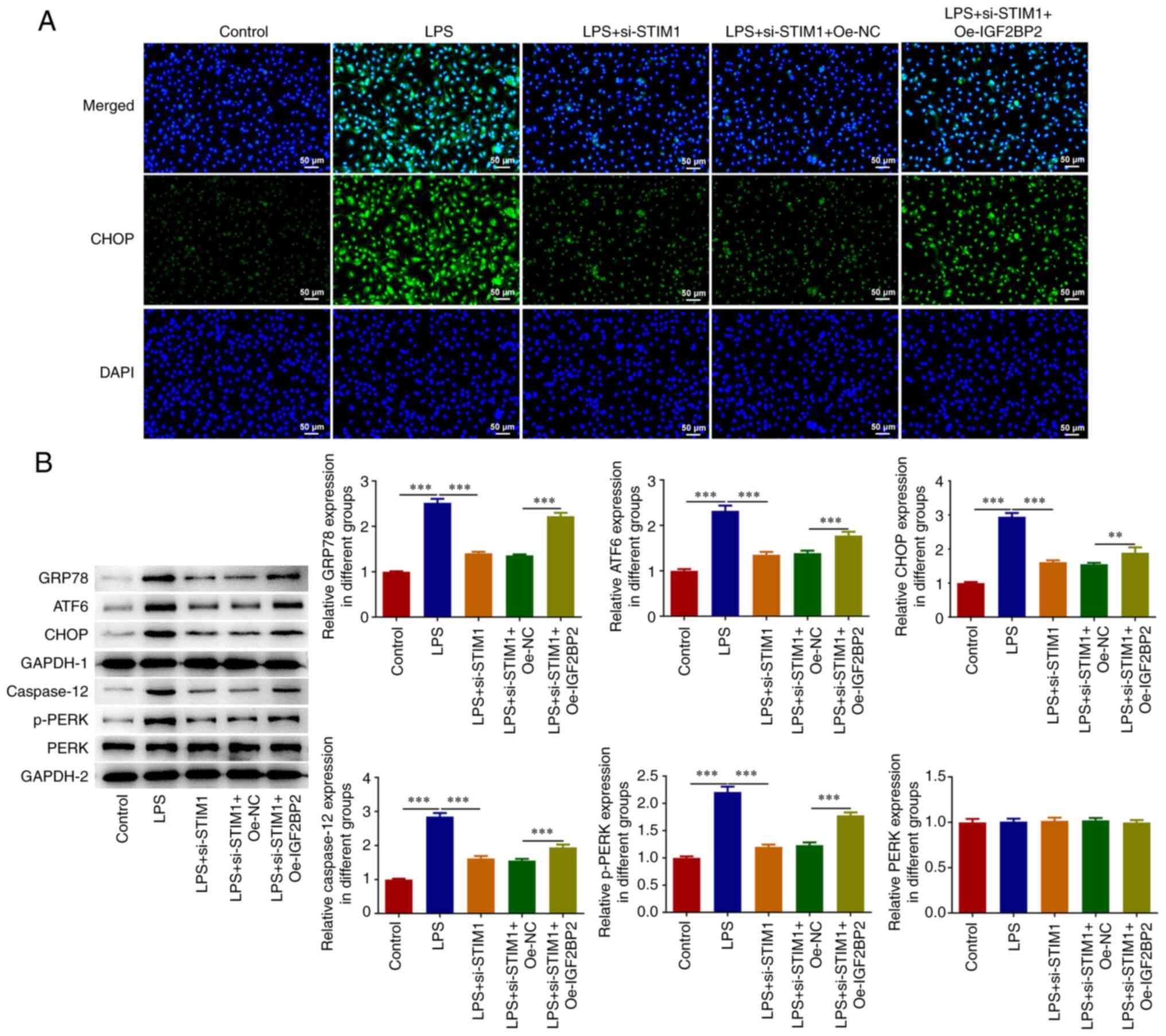
|
1
|
Bordon J, Aliberti S, Fernandez-Botran R,
Uriarte SM, Rane MJ, Duvvuri P, Peyrani P, Morlacchi LC, Blasi F
and Ramirez JA: Understanding the roles of cytokines and neutrophil
activity and neutrophil apoptosis in the protective versus
deleterious inflammatory response in pneumonia. Int J Infect Dis.
17:e76–83. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hespanhol V and Barbara C: Pneumonia
mortality, comorbidities matter? Pulmonology. 26:123–129.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bartoletti M, Azap O, Barac A, Bussini L,
Ergonul O, Krause R, Paño-Pardo JR, Power NR, Sibani M, Szabo BG,
et al: ESCMID COVID-19 living guidelines: Drug treatment and
clinical management. Clin Microbiol Infect. 28:222–238.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman MS,
Menendez R, Chalmers JD, Wunderink RG and van der Poll T:
Pneumonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7(25)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Prina E, Ranzani OT and Torres A:
Community-acquired pneumonia. Lancet. 386:1097–1108.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khan MM, Yang WL and Wang P: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in sepsis. Shock. 44:294–304. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu Q, Korner H, Wu H and Wei W:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in autoimmune diseases. Immunobiology.
225(151881)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cao X and Wan H and Wan H: Urolithin A
induces protective autophagy to alleviate inflammation, oxidative
stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress in pediatric pneumonia.
Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 50:147–153. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xue Y, Zhou S, Xie W, Meng M, Ma N, Zhang
H, Wang Y, Chang G and Shen X: STIM1-Orai1 interaction exacerbates
LPS-induced inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in bovine
hepatocytes through store-operated calcium entry. Genes (Basel).
13(874)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Feng YF, Liu XT, Li YC, Zhu HM, Sun
MR, Li P, Liu B and Yang H: Songorine promotes cardiac
mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2 induction during sepsis. Redox
Biol. 38(101771)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pan S, Zhao X, Shao C, Fu B, Huang Y,
Zhang N, Dou X, Zhang Z, Qiu Y, Wang R, et al: STIM1 promotes
angiogenesis by reducing exosomal miR-145 in breast cancer
MDA-MB-231 cells. Cell Death Dis. 12(38)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Garrud TAC and Jaggar JH: STIMulating
blood pressure. Elife. 11(e77978)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bolotina VM: Orai1, STIM1, and iPLA2beta
determine arterial vasoconstriction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:1066–1067. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li H, Jiang Z, Liu X and Yang Z: Higher
plasma level of STIM1, OPG are correlated with stent restenosis
after PCI. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:21089–21097. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu X, Huang H, Zong Y and Zhang L:
SRY-related high-mobility group box 9 (SOX9) alleviates cigarette
smoke extract (CSE)-induced inflammatory injury in human bronchial
epithelial cells by suppressing stromal interaction molecule 1
(STIM1) expression. Inflamm Res. 71:565–576. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu CC, Miao Y, Chen RL, Zhang YQ, Wu H,
Yang SM and Shang LQ: STIM1 mediates IAV-induced inflammation of
lung epithelial cells by regulating NLRP3 and inflammasome
activation via targeting miR-223. Life Sci.
266(118845)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Meng M, Huo R, Ma N, Chang G and Shen X:
beta-carotene alleviates LPS-induced inflammation through
regulating STIM1/ORAI1 expression in bovine mammary epithelial
cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 113(109377)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu X, Shen HR, Zhang JR and Li XL: The
role of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding proteins in
female reproductive pathophysiology. Reprod Biol Endocrinol.
20(89)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Yuan X and Ding N: IGF2BP2
knockdown inhibits LPS-induced pyroptosis in BEAS-2B cells by
targeting caspase 4, a crucial molecule of the non-canonical
pyroptosis pathway. Exp Ther Med. 21(593)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Paz I, Kosti I, Ares M Jr, Cline M and
Mandel-Gutfreund Y: RBPmap: A web server for mapping binding sites
of RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:W361–W367.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen W, Xu S, Xiang L, Zhang Y, Wang C,
Fan T, Huang W and Lu Z: The silencing of SAAL1 suppresses
pneumonia progression via modulating the NLR signaling pathway. Ann
Transl Med. 10(1128)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fei S, Cao L and Pan L: microRNA-3941
targets IGF2 to control LPS-induced acute pneumonia in A549 cells.
Mol Med Rep. 17:4019–4026. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shi J, Wang H, Liu J, Zhang Y, Luo J, Li
Y, Yang C and Jiang J: Ganoderic acid B attenuates LPS-induced lung
injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 88(106990)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu H, Xu J, Gong G, Zhang Y and Wu S:
CircARL8B contributes to the development of breast cancer via
regulating miR-653-5p/HMGA2 axis. Biochem Genet. 59:1648–1665.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang R, Liu H, Bai C, Wang Y, Zhang X, Guo
R, Wu S, Wang J, Leung E, Chang H, et al: Chemical composition and
pharmacological mechanism of Qingfei Paidu Decoction and Ma Xing
Shi Gan Decoction against Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): In
silico and experimental study. Pharmacol Res.
157(104820)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gao P, Wang J, Jiang M, Li Z, Xu D, Jing J
and Yihepaer and Hu T: LncRNA SNHG16 is downregulated in Pneumonia
and Downregulates miR-210 to promote LPS-induced lung cell
apoptosis. Mol Biotechnol. 65:446–452. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Zhu Y, Gao G and Zhou Z:
Knockdown XIST alleviates LPS-induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and
inflammation injury via targeting miR-370-3p/TLR4 in acute
pneumonia. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:348–358. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang YF, Wang H, Song N, Jiang YH, Zhang
J, Meng XW, Feng XM, Liu H, Peng K and Ji FH: Dexmedetomidine
Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Myocardial inflammation and
apoptosis through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
Signaling. J Inflamm Res. 14:1217–1233. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Keestra-Gounder AM, Byndloss MX, Seyffert
N, Young BM, Chavez-Arroyo A, Tsai AY, Cevallos SA, Winter MG, Pham
OH, Tiffany CR, et al: NOD1 and NOD2 signalling links ER stress
with inflammation. Nature. 532:394–397. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang X, Yuan J, Wang H, Gan N, Zhang Q,
Liu B, Wang J, Shu Z, Rao L, Gou X, et al: Progranulin decreases
susceptibility to streptococcus pneumoniae in influenza and
protects against lethal coinfection. J Immunol. 203:2171–2182.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang QL, Yang L, Peng Y, Gao M, Yang MS,
Xing W and Xiao XZ: Ginsenoside Rg1 regulates SIRT1 to ameliorate
sepsis-induced lung inflammation and injury via inhibiting
endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Mediators Inflamm.
2019(6453296)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wu JP, Li XZ, Wang Y, Ma L, Yao TW, Zhang
YY and Long F: Effects of electroacupuncture and intracerebral
injection of VEGF on Caspase12, Caspase3, and GRP78 genes in rats
with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao
Yi Xue Ban. 50:34–39. 2019.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Parker NJ, Begley CG, Smith PJ and Fox RM:
Molecular cloning of a novel human gene (D11S4896E) at chromosomal
region 11p15.5. Genomics. 37:253–256. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Song X, Liu Y, Dong L and Wang Y:
Stromal-Interacting Molecule 1 (Stim1)/Orai1 modulates endothelial
permeability in ventilator-induced lung injury. Med Sci Monit.
24:9413–9423. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fan H, Huang H, Hu L, Zhu W, Yu Y, Lou J,
Hu L and Chen F: The activation of STIM1 mediates S-phase arrest
and cell death in paraquat induced acute lung intoxication. Toxicol
Lett. 292:123–135. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang JN, Wang F, Ke J, Li Z, Xu CH, Yang
Q, Chen X, He XY, He Y, Suo XG, et al: Inhibition of METTL3
attenuates renal injury and inflammation by alleviating TAB3 m6A
modifications via IGF2BP2-dependent mechanisms. Sci Transl Med.
14(eabk2709)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhou L, Li H, Cai H, Liu W, Pan E, Yu D
and He S: Upregulation of IGF2BP2 promotes oral squamous cell
carcinoma progression that is related to cell proliferation,
metastasis and tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Front Oncol.
12(809589)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|