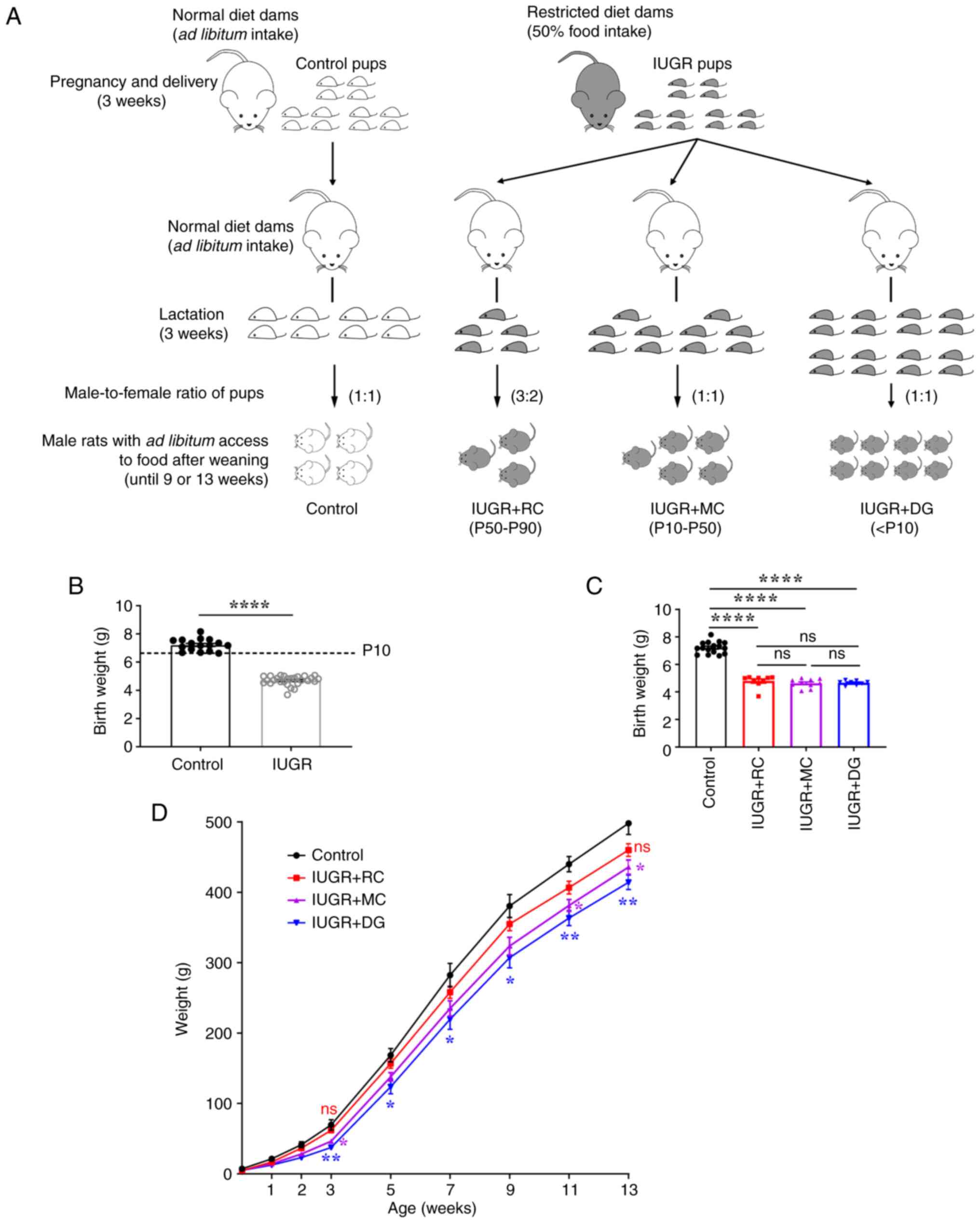
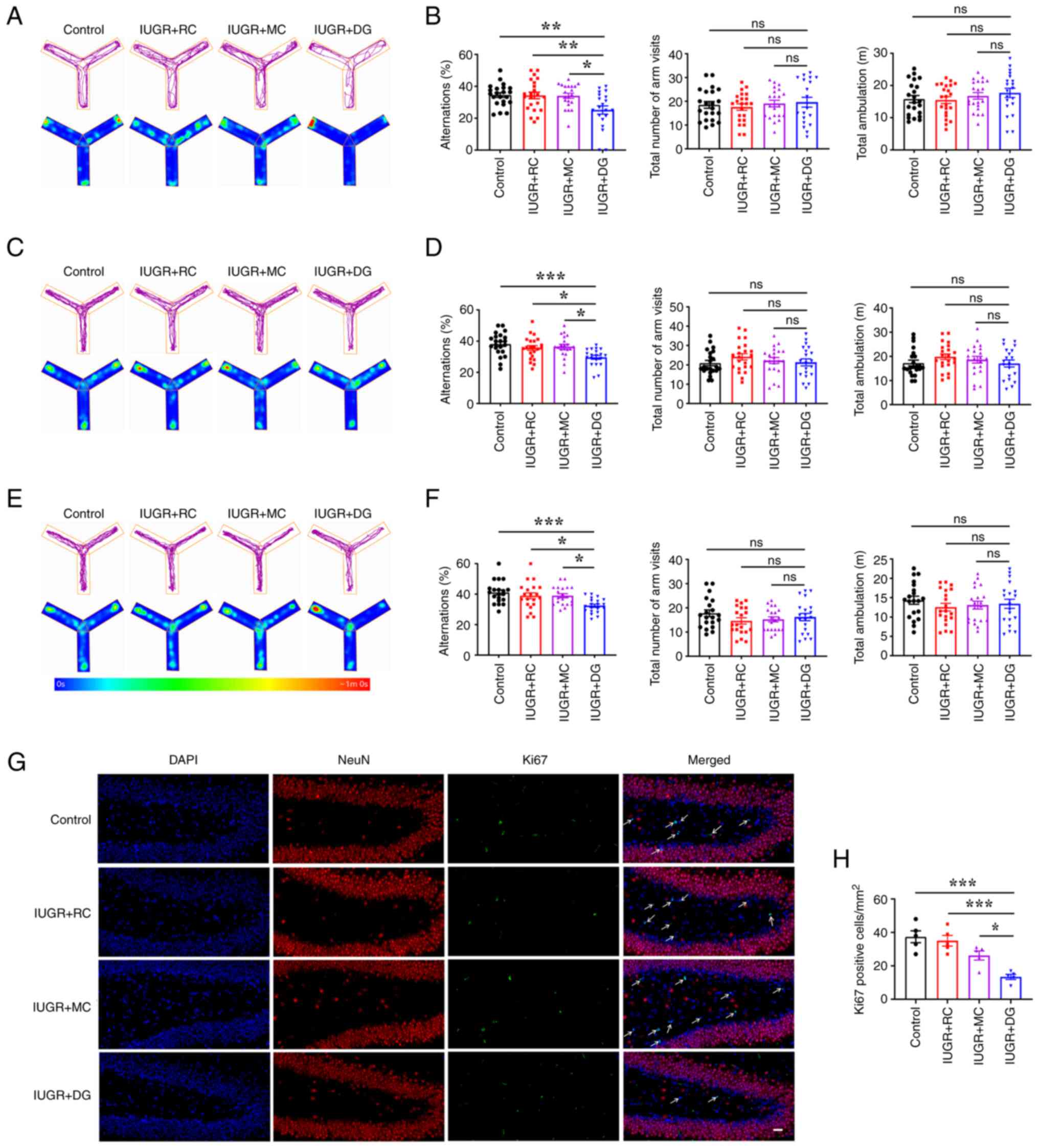
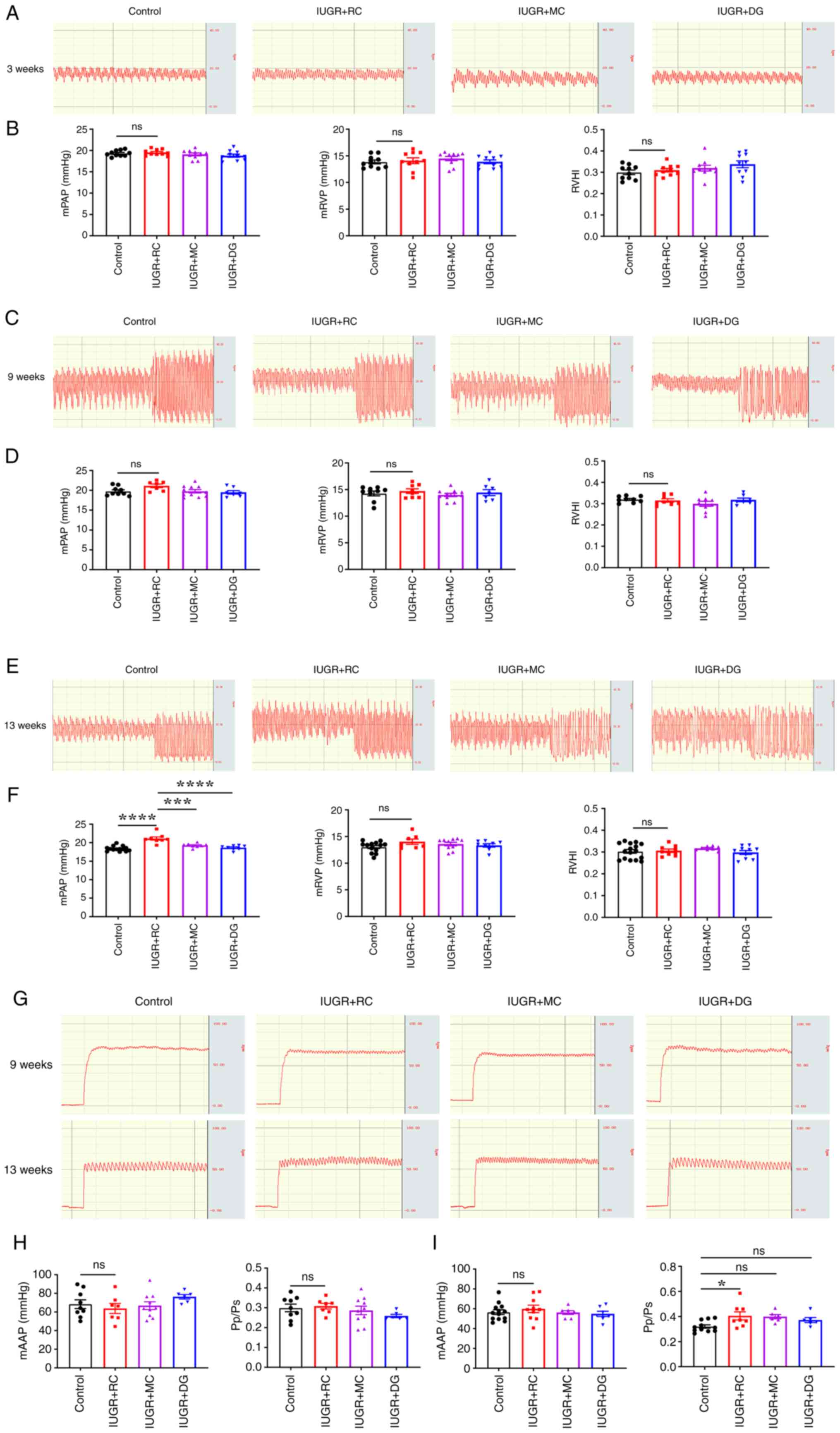
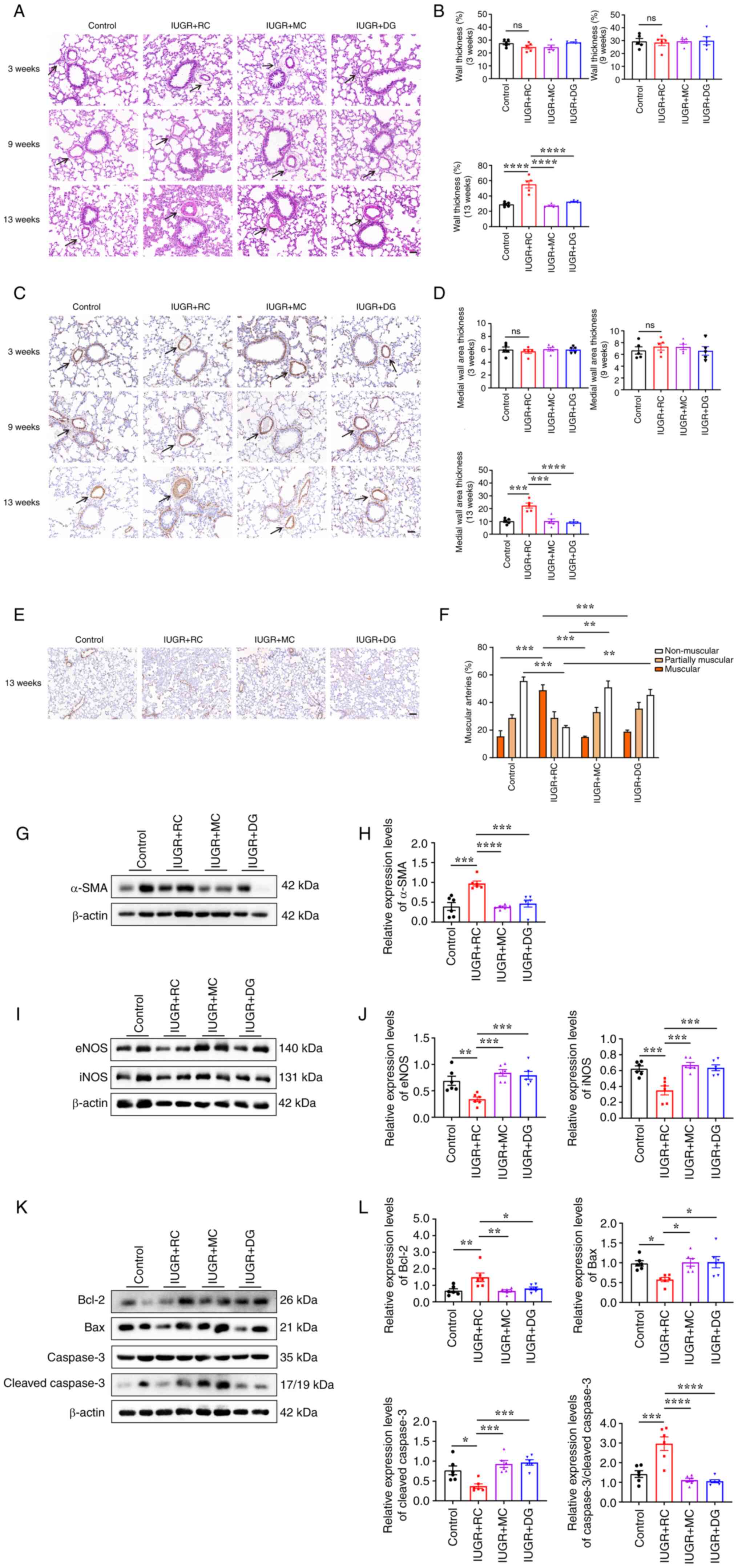
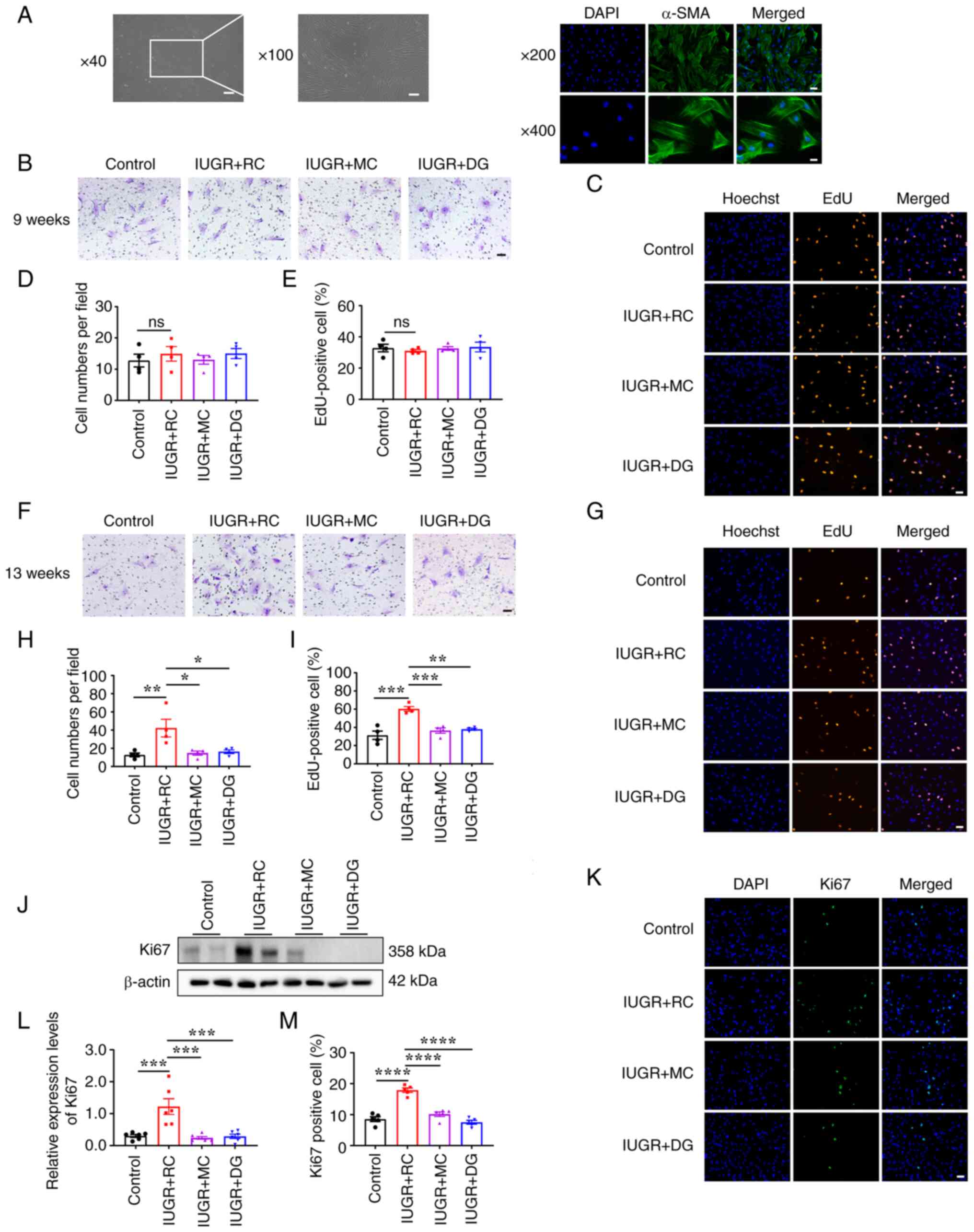
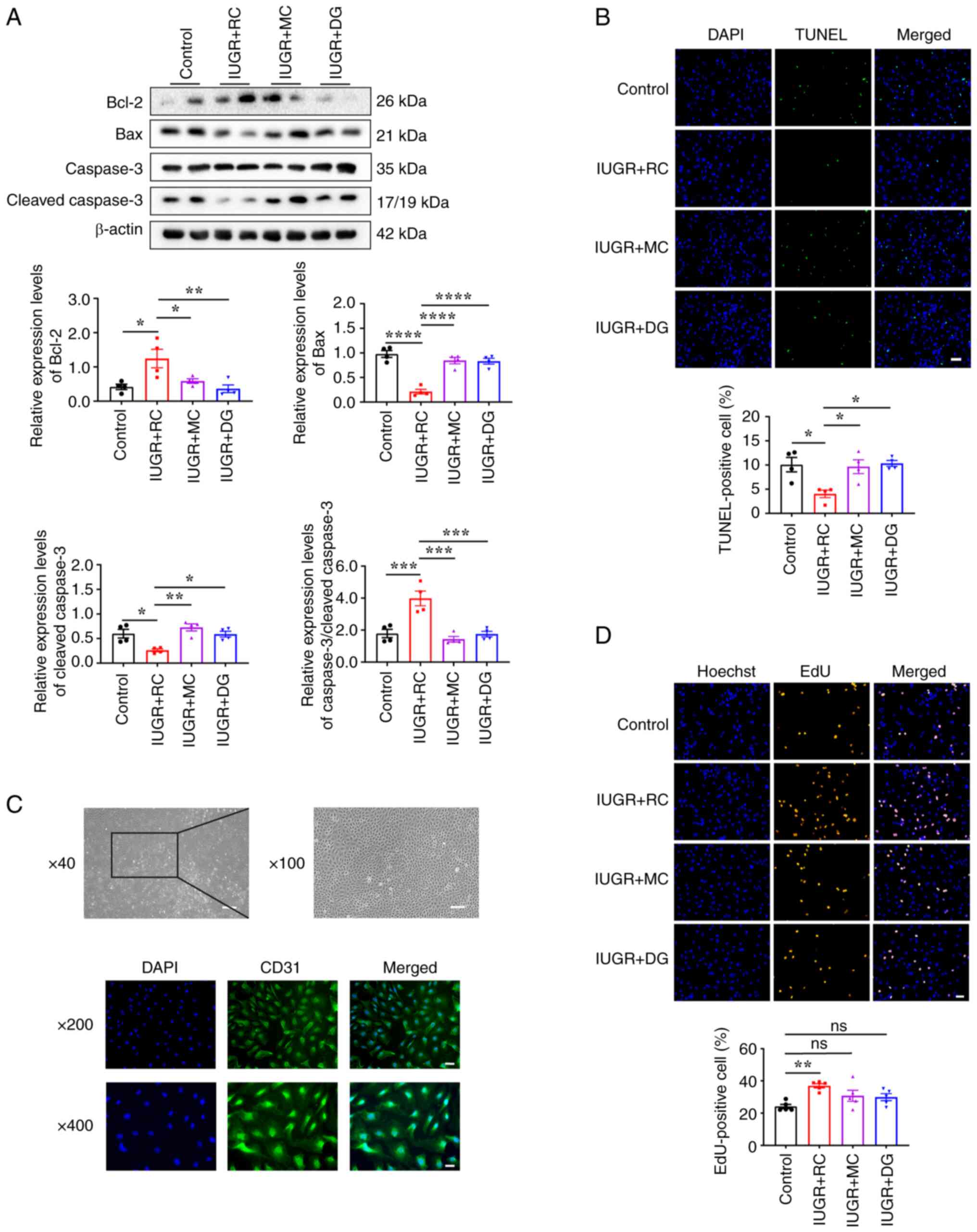
|
1
|
Kesavan K and Devaskar SU: Intrauterine
growth restriction: Postnatal monitoring and outcomes. Pediatr Clin
North Am. 66:403–423. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sharma D, Shastri S, Farahbakhsh N and
Sharma P: Intrauterine growth restriction-part 1. J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 29:3977–3987. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bernstein PS and Divon MY: Etiologies of
fetal growth restriction. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 40:723–729.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rosenberg A: The IUGR newborn. Semin
Perinatol. 32:219–224. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chernausek SD: Update: Consequences of
abnormal fetal growth. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:689–695.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Longo S, Bollani L, Decembrino L, Di
Comite A, Angelini M and Stronati M: Short-term and long-term
sequelae in intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR). J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 26:222–225. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tomi M, Zhao Y, Thamotharan S, Shin BC and
Devaskar SU: Early life nutrient restriction impairs blood-brain
metabolic profile and neurobehavior predisposing to Alzheimer's
disease with aging. Brain Res. 1495:61–75. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
An J, Wang J, Guo L, Xiao Y, Lu W, Li L,
Chen L, Wang X and Dong Z: The impact of gut microbiome on
metabolic disorders during catch-up growth in
small-for-gestational-age. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12(630526)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lee PA, Chernausek SD, Hokken-Koelega AC
and Czernichow P: International Small for Gestational Age Advisory
Board. International small for gestational age advisory board
consensus development conference statement: Management of short
children born small for gestational age, April 24-October 1, 2001.
Pediatrics. 111:1253–1261. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ong KK: Catch-up growth in small for
gestational age babies: Good or bad? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes
Obes. 14:30–34. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Eriksson JG, Forsén T, Tuomilehto J,
Winter PD, Osmond C and Barker DJ: Catch-up growth in childhood and
death from coronary heart disease: Longitudinal study. BMJ.
318:427–431. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Berends LM, Fernandez-Twinn DS,
Martin-Gronert MS, Cripps RL and Ozanne SE: Catch-up growth
following intra-uterine growth-restriction programmes an
insulin-resistant phenotype in adipose tissue. Int J Obes (Lond).
37:1051–1057. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ong KK, Ahmed ML, Emmett PM, Preece MA and
Dunger DB: Association between postnatal catch-up growth and
obesity in childhood: Prospective cohort study. BMJ. 320:967–971.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yan L, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Xu S, Ullah R, Luo
X, Xu X, Ma X, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al: Postnatal delayed growth
impacts cognition but rescues programmed impaired pulmonary
vascular development in an IUGR rat model. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc
Dis. 29:1418–1428. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rueda-Clausen CF, Morton JS and Davidge
ST: Effects of hypoxia-induced intrauterine growth restriction on
cardiopulmonary structure and function during adulthood. Cardiovasc
Res. 81:713–722. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kuo AH, Li C, Huber HF, Schwab M,
Nathanielsz PW and Clarke GD: Maternal nutrient restriction during
pregnancy and lactation leads to impaired right ventricular
function in young adult baboons. J Physiol. 595:4245–4260.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mericq V, Martinez-Aguayo A, Uauy R,
Iñiguez G, Van der Steen M and Hokken-Koelega A: Long-term
metabolic risk among children born premature or small for
gestational age. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:50–62. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kelishadi R, Haghdoost AA, Jamshidi F,
Aliramezany M and Moosazadeh M: Low birthweight or rapid catch-up
growth: Which is more associated with cardiovascular disease and
its risk factors in later life? A systematic review and
cryptanalysis. Paediatr Int Child Health. 35:110–123.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z, Luo X, Lv Y, Yan L, Xu S, Wang Y,
Zhong Y, Hang C, Jyotsnav J, Lai D, et al: Intrauterine growth
restriction programs intergenerational transmission of pulmonary
arterial hypertension and endothelial dysfunction via sperm
epigenetic modifications. Hypertension. 74:1160–1171.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Luo X, Hang C, Zhang Z, Le K, Ying Y, Lv
Y, Yan L, Huang Y, Ye L, Xu X, et al: PVECs-derived exosomal
microRNAs regulate PASMCs via FoxM1 signaling in IUGR-induced
pulmonary hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc.
11(e027177)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lv Y, Tang LL, Wei JK, Xu XF, Gu W, Fu LC,
Zhang LY and Du LZ: Decreased Kv1.5 expression in intrauterine
growth retardation rats with exaggerated pulmonary hypertension. Am
J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 305:L856–L865. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dabral S, Tian X, Kojonazarov B, Savai R,
Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N, Florio M, Sun J, Jonigk D, Maegel L, et
al: Notch1 signalling regulates endothelial proliferation and
apoptosis in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J.
48:1137–1149. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Courboulin A, Barrier M, Perreault T,
Bonnet P, Tremblay VL, Paulin R, Tremblay E, Lambert C, Jacob MH,
Bonnet SN, et al: Plumbagin reverses proliferation and resistance
to apoptosis in experimental PAH. Eur Respir J. 40:618–629.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Jimenez-Chillaron JC and Patti ME: To
catch up or not to catch up: Is this the question? Lessons from
animal models. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 14:23–29.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
National Research Council: Committee for
the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals:
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition.
National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2011.
|
|
26
|
Xu XF, Lv Y, Gu WZ, Tang LL, Wei JK, Zhang
LY and Du LZ: Epigenetics of hypoxic pulmonary arterial
hypertension following intrauterine growth retardation rat:
Epigenetics in PAH following IUGR. Respir Res.
14(20)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Barrow PC, Barbellion S and Stadler J:
Preclinical evaluation of juvenile toxicity. Methods Mol Biol.
691:17–35. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shokouhi G, Kosari-Nasab M and Salari AA:
Silymarin sex-dependently improves cognitive functions and alters
TNF-α, BDNF, and glutamate in the hippocampus of mice with mild
traumatic brain injury. Life Sci. 257(118049)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Olofinnade AT, Adeyeba A, Onaolapo AY and
Onaolapo OJ: An assessment of the effects of
azodicarbonamide-containing diet on neurobehaviour, brain
antioxidant status and membrane lipid peroxidation status in rats.
Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 20:49–57. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sadiki FZ, Idrissi ME, Cioanca O, Trifan
A, Hancianu M, Hritcu L and Postu PA: Tetraclinis articulata
essential oil mitigates cognitive deficits and brain oxidative
stress in an Alzheimer's disease amyloidosis model. Phytomedicine.
56:57–63. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Abdulbasit A, Stephen Michael F, Shukurat
Onaopemipo A, Abdulmusawwir AO, Aminu I, Nnaemeka Tobechukwu A,
Wahab Imam A, Oluwaseun Aremu A, Folajimi O, Bilikis Aderonke A, et
al: Glucocorticoid receptor activation selectively influence
performance of Wistar rats in Y-maze. Pathophysiology. 25:41–50.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu YP, Zhu JJ, Cheng F, Jiang KW, Gu WZ,
Shen Z, Wu YD, Liang L and Du LZ: Ghrelin ameliorates
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via phospho-GSK3 β/β-catenin
signaling in neonatal rats. J Mol Endocrinol. 47:33–43.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Luo F, Wang X, Luo X, Li B, Zhu D, Sun H
and Tang Y: Invasive hemodynamic assessment for the right
ventricular system and hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial
hypertension in mice. J Vis Exp. 24:2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Shi W, Zhang Q, Feng W, Wang J,
Zhai C, Yan X and Li M: Inhibition of Siah2 ubiquitin ligase
ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling
through inactivation of YAP. Life Sci. 242(117159)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jones R, Jacobson M and Steudel W:
alpha-smooth-muscle actin and microvascular precursor smooth-muscle
cells in pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
20:582–594. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang S, Yue Y, Feng K, Huang X, Li H, Hou
J, Yang S, Huang S, Liang M, Chen G and Wu Z: Conditioned medium
from M2b macrophages modulates the proliferation, migration, and
apoptosis of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by deregulating
the PI3K/Akt/FoxO3a pathway. PeerJ. 8(e9110)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nie X, Dai Y, Tan J, Chen Y, Qin G, Mao W,
Zou J, Chang Y, Wang Q and Chen J: α-Solanine reverses pulmonary
vascular remodeling and vascular angiogenesis in experimental
pulmonary artery hypertension. J Hypertens. 35:2419–2435.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ye L, Wang X, Cai C, Zeng S, Bai J, Guo K,
Fang M, Hu J, Liu H, Zhu L, et al: FGF21 promotes functional
recovery after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats by
activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via FGFR1/β-kloth. Exp
Neurol. 317:34–50. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Prado EL and Dewey KG: Nutrition and brain
development in early life. Nutr Rev. 72:267–284. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Bond Allison M, Ming G-l and Song H: Adult
mammalian neural stem cells and neurogenesis: Five decades later.
Cell Stem Cell. 17:385–395. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhao C, Deng W and Gage FH: Mechanisms and
functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell. 132:645–660.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Scholzen T and Gerdes J: The Ki-67
protein: From the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol.
182:311–322. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wojtowicz JM and Kee N: BrdU assay for
neurogenesis in rodents. Nat Protoc. 1:1399–1405. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bateson P, Gluckman P and Hanson M: The
biology of developmental plasticity and the predictive adaptive
response hypothesis. J Physiol. 592:2357–2368. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Amruta N, Kandikattu HK and Intapad S:
Cardiovascular dysfunction in intrauterine growth restriction. Curr
Hypertens Rep. 24:693–708. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gortner L: Intrauterine growth restriction
and risk for arterial hypertension: A causal relationship? J
Perinat Med. 35:361–365. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Leunissen RWJ, Kerkhof GF, Stijnen T and
Hokken-Koelega ACS: Effect of birth size and catch-up growth on
adult blood pressure and carotid intima-media thickness. Horm Res
Paediatr. 77:394–401. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Teichert-Kuliszewska K, Tsoporis JN,
Desjardins JF, Yin J, Wang L, Kuebler WM and Parker TG: Absence of
the calcium-binding protein, S100A1, confers pulmonary hypertension
in mice associated with endothelial dysfunction and apoptosis.
Cardiovasc Res. 105:8–19. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Perrella MA, Edell ES, Krowka MJ, Cortese
DA and Burnett JC Jr: Endothelium-derived relaxing factor in
pulmonary and renal circulations during hypoxia. Am J Physiol.
263:R45–R50. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Dinh-Xuan AT: Endothelial modulation of
pulmonary vascular tone. Eur Respir J. 5:757–762. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Smith AP, Demoncheaux EA and Higenbottam
TW: Nitric oxide gas decreases endothelin-1 mRNA in cultured
pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Nitric Oxide. 6:153–159.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Thompson AAR and Lawrie A: Targeting
vascular remodeling to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Trends Mol Med. 23:31–45. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ruopp NF and Cockrill BA: Diagnosis and
treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: A review. JAMA.
327:1379–1391. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Budhiraja R, Tuder RM and Hassoun PM:
Endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. Circulation.
109:159–165. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|